sklearn学习笔记SVM 之 自定义Kernel
推荐阅读:
功能强大的Python包sklearn概述
机器学习可使用的数据集介绍
数据集的导入及缺失值处理
本次实验主要是自定义一个内核 Kernel 函数,然后使用 sklearn.datasets 自带的鸢尾花 Iris 数据集样本进行 SVM 分类。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm # sklearn自带SVM分类器
from sklearn import datasets # 导入数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
h = .02 # 网格中的步长
# 设置颜色
cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0', '#FFA0A0', '#A0A0FF'])
cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'r', 'b'])
# 自定义 Kernel 函数
def my_kernel(X, Y):
"""
We create a custom kernel:
(2 0)
k(X, Y) = X ( ) Y.T
(0 1)
"""
M = np.array( [ [2, 0], [0, 1.0] ] )
# M = np.array( [ [2, 1], [1, 1.0] ] )
return np.dot(np.dot(X, M), Y.T)
# 导入鸢尾花(Iris)数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data # 取数据集的特征向量
Y = iris.target # 取数据集的标签(鸢尾花类型)
X = X[:, 0:2] # 取前两列特征向量用作分类
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, train_size = 0.8, random_state = 6)
clf = svm.SVC(kernel = my_kernel) # 创建 SVM 分类器
clf.fit(x_train, y_train.ravel()) # 拟合数据
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min(), X[:, 0].max() # 第0列的范围
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min(), X[:, 1].max() # 第1列的范围
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)) # 生成网格采样点
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # 预测分类值
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) # 使之与输入的形状相同
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap = cm_light)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c = Y, edgecolors = 'k', cmap = cm_dark) # 样本
plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max)
plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max)
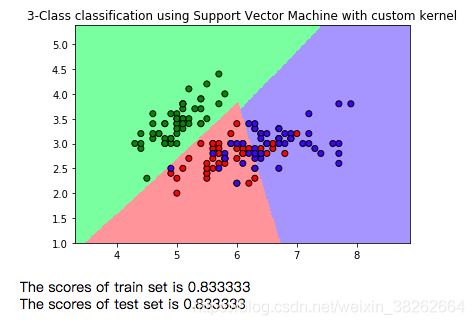
plt.title('3-Class classification using Support Vector Machine with custom kernel', fontsize = 12)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()
# 计算准确率
print("The scores of train set is %f" %(clf.score(x_train, y_train))) # 训练集准确率
print("The scores of test set is %f" %(clf.score(x_test, y_test))) # 测试集准确率基于 Anaconda + Jupyter Notebook 环境的运行结果为:
推荐阅读:
sklearn学习笔记SVM 之 鸢尾花二特征分类
sklearn学习笔记SVM 之 非线性SVM
sklearn学习笔记SVM 之 分离超平面的最大边距