11月份Aidlux智慧交通AI安全实战--(目标检测+安全算法)
智慧安防实战训练营链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xgOCqBRGnl9QasViLUozMw
1.1 AI对抗攻击算法介绍
对抗攻击(adversarial attack)是AI安全方向的重要分支,其核心逻辑是在数据中增加一些微小扰动,在人类视觉系统无法察觉的情况下,使得算法模型对这些数据产生误判。其中被增加扰动的数据也称为对抗样本。
我们该怎么去理解对抗样本呢?总的来说,我把它当作生成噪声的艺术,其攻击价值的底层依托是算法模型的过拟合问题。
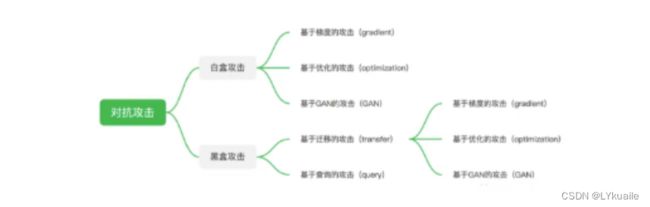
1.2 常用AI对抗攻击算法划分
上面我们了解了对抗攻击对AI项目带来的安全风险,接下来我们再了解一下目前主流对抗攻击算法的总体分支与逻辑:
其中,当算法模型参数和训练数据等信息被攻击者所掌握,并且攻击者在此基础上进行的针对性攻击称为白盒攻击。白盒攻击主要分为基于梯度的攻击,基于优化的攻击以及基于GAN的攻击。
而在对算法模型的结构和参数一无所知,甚至相关训练数据也一无所知的情况下,进行攻击的过程称为黑盒攻击。黑盒攻击主要分为基于迁移的攻击和基于查询的攻击两大类。基于迁移的攻击逻辑由白盒攻击延伸而来,一般会有一个白盒模型作为替身模型(surrogate)进行攻击,而生成的对抗样本一般也会对其他模型有一定的迁移攻击性。基于查询的攻击其主要是通过查询黑盒模型的输出信息,对黑盒模型进行直接的攻击,但完成整个攻击流程往往需要大量的查询,容易被模型所有者检测到异常。
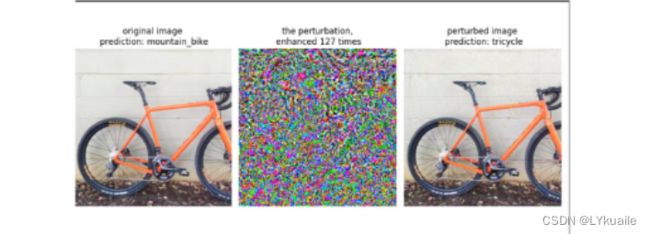
1.3 对抗攻击效果验证
我们可以看到经过攻击后,模型将山地自行车错判成三轮车
将敞篷车错判成小巴士,
将出租车错判成美洲驼。
2.1 对抗防御流程
既然对抗攻击的效果如此强,并且会引发重大安全风险,那么我们就必须进行对抗防御。本次训练营带着大家尝试白盒防御的实验,本次白盒防御算法选用刚才讲到过的GCM防御模块。
看看是攻击者的剑厉害,还是防御者的盾更厉害 !
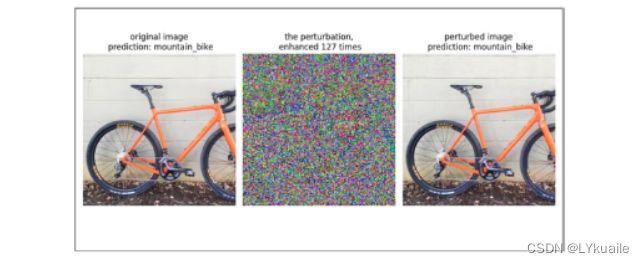
2.2 对抗效果验证
我们可以看到,模型并未受到对抗攻击的影响,还是输出了正确的结果。将使用防御模块后生成的对抗扰动与未使用防御模块的对抗扰动进行对比,我们可以发现,防御模块确实起到了应有的防御作用。
3.1训练营作业
使用车辆检测结果+对抗样本生成+对抗防御策略,完成AI安全风险预警的业务功能。
3.2 项目主要流程:
项目对抗攻击检测+喵提醒效果验证
代码流程:
YOLOv5车辆检测-->目标车辆特征提取-->对抗攻击检测模型-->喵提醒
3.3 代码实现:
# aidlux相关
from cvs import *
import aidlite_gpu
from utils_2 import detect_postprocess, preprocess_img, draw_detect_res, extract_detect_res
import os
import torch
import requests
import time
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.models import mobilenet_v2,resnet18
from advertorch.utils import predict_from_logits
from advertorch.utils import NormalizeByChannelMeanStd
from robust_layer import GradientConcealment, ResizedPaddingLayer
from timm.models import create_model
from advertorch.attacks import LinfPGDAttack
from advertorch_examples.utils import ImageNetClassNameLookup
from advertorch_examples.utils import bhwc2bchw
from advertorch_examples.utils import bchw2bhwc
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# AidLite初始化:调用AidLite进行AI模型的加载与推理,需导入aidlite
aidlite = aidlite_gpu.aidlite()
# Aidlite模型路径
model_path = '/home/Lesson5_code/Lesson5_code/yolov5_code/models/yolov5_car_best-fp16.tflite'
# 定义输入输出shape
in_shape = [1 * 640 * 640 * 3 * 4]
out_shape = [1 * 25200 * 6 * 4]
# 加载Aidlite检测模型:支持tflite, tnn, mnn, ms, nb格式的模型加载
aidlite.ANNModel(model_path, in_shape, out_shape, 4, 0)
# 读取图片进行推理
# 设置测试集路径
source = "/home/Lesson5_code/Lesson5_code/adv_code/test_images"
images_list = os.listdir(source)
print(images_list)
frame_id = 0
# 读取数据集
for image_name in images_list:
frame_id += 1
print("frame_id:", frame_id)
image_path = os.path.join(source, image_name)
frame = cvs.imread(image_path)
# 预处理
img = preprocess_img(frame, target_shape=(640, 640), div_num=255, means=None, stds=None)
# 数据转换:因为setTensor_Fp32()需要的是float32类型的数据,所以送入的input的数据需为float32,大多数的开发者都会忘记将图像的数据类型转换为float32
aidlite.setInput_Float32(img, 640, 640)
# 模型推理API
aidlite.invoke()
# 读取返回的结果
pred = aidlite.getOutput_Float32(0)
# 数据维度转换
pred = pred.reshape(1, 25200, 6)[0]
# 模型推理后处理
pred = detect_postprocess(pred, frame.shape, [640, 640, 3], conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45)
# 绘制推理结果
res_img = draw_detect_res(frame, pred)
cvs.imshow(res_img)
# 测试结果展示停顿
time.sleep(5)
#图片裁剪,提取车辆目标区域
cut_img = extract_detect_res(frame, pred, image_name)
cvs.imshow(cut_img)
### 读取图片
def get_image():
img_path = os.path.join("/home/Lesson5_code/Lesson5_code/adv_code/adv_results", "vid_5_26780.jpg_0.png")
img_url = "https://farm1.static.flickr.com/230/524562325_fb0a11d1e1.jpg"
def _load_image():
from skimage.io import imread
return imread(img_path) / 255.
if os.path.exists(img_path):
return _load_image()
else:
import urllib
urllib.request.urlretrieve(img_url, img_path)
return _load_image()
def tensor2npimg(tensor):
return bchw2bhwc(tensor[0].cpu().numpy())
normalize = NormalizeByChannelMeanStd(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
np_img = get_image()
img = torch.tensor(bhwc2bchw(np_img))[None, :, :, :].float().to(device)
imagenet_label2classname = ImageNetClassNameLookup()
### 常规模型加载
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, l=290):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.l = l
self.gcm = GradientConcealment()
#model = resnet18(pretrained=True)
model = mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True)
# pth_path = "/Users/rocky/Desktop/训练营/model/mobilenet_v2-b0353104.pth"
# print(f'Loading pth from {pth_path}')
# state_dict = torch.load(pth_path, map_location='cpu')
# is_strict = False
# if 'model' in state_dict.keys():
# model.load_state_dict(state_dict['model'], strict=is_strict)
# else:
# model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=is_strict)
normalize = NormalizeByChannelMeanStd(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
self.model = nn.Sequential(normalize, model)
def load_params(self):
pass
def forward(self, x):
#x = self.gcm(x)
#x = ResizedPaddingLayer(self.l)(x)
out = self.model(x)
return out
### 对抗攻击监测模型
class Detect_Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=2):
super(Detect_Model, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
#model = create_model('mobilenetv3_large_075', pretrained=False, num_classes=num_classes)
model = create_model('resnet50', pretrained=False, num_classes=num_classes)
# self.multi_PreProcess = multi_PreProcess()
pth_path = os.path.join("/home/Lesson5_code/Lesson5_code/model", 'track2_resnet50_ANT_best_albation1_64_checkpoint.pth')
state_dict = torch.load(pth_path, map_location='cpu')
is_strict = False
if 'model' in state_dict.keys():
model.load_state_dict(state_dict['model'], strict=is_strict)
else:
model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=is_strict)
normalize = NormalizeByChannelMeanStd(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# self.model = nn.Sequential(normalize, self.multi_PreProcess, model)
self.model = nn.Sequential(normalize, model)
def load_params(self):
pass
def forward(self, x):
# x = x[:,:,32:193,32:193]
# x = F.interpolate(x, size=(224,224), mode="bilinear", align_corners=True)
# x = self.multi_PreProcess.forward(x)
out = self.model(x)
if self.num_classes == 2:
out = out.softmax(1)
#return out[:,1:]
return out[:,1:]
model = Model().eval().to(device)
detect_model = Detect_Model().eval().to(device)
### 对抗攻击监测
detect_pred = detect_model(img)
print(detect_pred)
if detect_pred > 0.5:
id = 'tj90mrH'
# 填写喵提醒中,发送的消息,这里放上前面提到的图片外链
text = "出现对抗攻击风险!!"
ts = str(time.time()) # 时间戳
type = 'json' # 返回内容格式
request_url = "http://miaotixing.com/trigger?"
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.67 Safari/537.36 Edg/87.0.664.47'}
result = requests.post(request_url + "id=" + id + "&text=" + text + "&ts=" + ts + "&type=" + type,
headers=headers)
print(text)
print(result)
else:
pred = imagenet_label2classname(predict_from_logits(model(img)))
print(pred)
3.4 效果验证