DPCM编码实现
DPCM编码实现
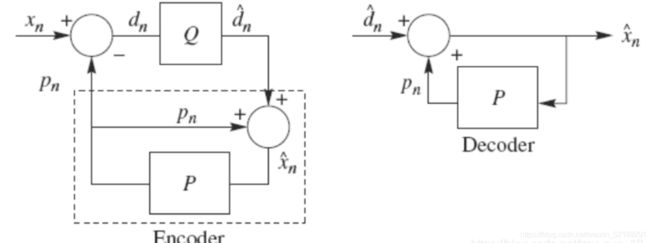
1.实验原理
工具:c语言
原理
2.实验内容
实验步骤
1.缓冲区分配
2.当位置1置0的实现
代码实现
1、向左进行DPCM
void DPCMLeft(int Width,int Height,void *yBuff,void *recBuff,void *errBuff)//DPCM向左预测
{
unsigned char *yB=NULL;
yB = (unsigned char *)yBuff;
unsigned char *recB=NULL;
recB = (unsigned char *)recBuff;
unsigned char *errB=NULL;
errB = (unsigned char *)errBuff;
int P1,P2;//P1为当前值与预测值的误差,P2为量化后的误差
unsigned char P3;//P3为反量化后的误差
for(int i=0;i<Height;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<Width;j++)
{
if(j == 0)//向左进行预测时,图像最左边一列的像素值直接输出,无需进行差分预测
{
*(recB+j+i*Width)=*(yB+j+i*Width);//当前值即为重建值,作为下一个像素的参考值
*(errB+j+i*Width)=0;//误差为0
}
else//当不是最左边一列的像素时,进行DPCM
{
P1=*(yB+j+i*Width)-*(recB+(j-1)+i*Width);//求当前值与参考值的差值
if(P1%2==0)//对差值进行8bit均匀量化,并进行+128的偏移以输出
P2=P1/2+128;
else
P2=(P1-1)/2+128;
*(errB+j+i*Width)=unsigned char(P2);//将误差写入errB缓存区域
P3=unsigned char(P2*2);//对量化后的误差反量化
*(recB+j+i*Width)=*(recB+(j-1)+i*Width)+P3;
//将参考值与反量化得到的误差相加,作为当前像素的重建值,即下一个像素的参考值
}
}
}
}
2、向上进行DPCM
void DPCMUp(int Width,int Height,void *yBuff,void *recBuff,void *errBuff)//DPCM向上预测
{
unsigned char *yB=NULL;
yB = (unsigned char *)yBuff;
unsigned char *recB=NULL;
recB = (unsigned char *)recBuff;
unsigned char *errB=NULL;
errB = (unsigned char *)errBuff;
int P1,P2;//P1为当前值与预测值的误差,P2为量化后的误差
unsigned char P3;//P3为反量化后的误差
for(int i=0;i<Height;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<Width;j++)
{
if(i == 0)//向上进行预测时,图像最上边一列的像素值直接输出,无需进行差分预测
{
*(recB+j+i*Width)=*(yB+j+i*Width);//当前值即为重建值,作为下一个像素的参考值
*(errB+j+i*Width)=0;//误差为0
}
else//当不是最上边一列的像素时,进行DPCM
{
P1=*(yB+j+i*Width)-*(recB+j+(i-1)*Width);//求当前值与参考值的差值
if(P1%2==0)//对差值进行8bit均匀量化,并进行+128的偏移以输出
P2=P1/2+128;
else
P2=(P1-1)/2+128;
*(errB+j+i*Width)=unsigned char(P2);//将误差写入errB缓存区域
P3=unsigned char(P2*2);//对量化后的误差反量化
*(recB+j+i*Width)=*(recB+j+(i-1)*Width)+P3;
//将参考值与反量化得到的误差相加,作为当前像素的重建值,即下一个像素的参考值
}
}
}
}
PSNR计算
int simplest_yuv420_psnr(void *yBuff1,void *yBuff2, int w, int h, int num)//计算Y分量的PSNR
{
unsigned char *yB1=NULL;
yB1 = (unsigned char *)yBuff1;
unsigned char *yB2=NULL;
yB2 = (unsigned char *)yBuff2;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
double mse_sum = 0, mse = 0, psnr = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < h ; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < w; k++)
{
mse_sum += pow((double)(*(yB1+k+j*w) - *(yB2+k+j*w)), 2);//取每个差值的平方,并进行累加
}
}
mse = mse_sum / (w * h); //根据公式计算mse
psnr = 10 * log10(255.0 * 255.0 / mse); //根据公式计算psnr
printf("%5.3f\n", psnr);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4、主函数
#include 实验结果
向左预测:
向上预测:
3.总结
1.由图看到:向左预测量化后的误差图像的边缘灰度值较为统一,而向上预测量化后的误差图像边缘灰度有明显的反白
2.理论上,量化比特数的影响:随着量化比特数的减小,压缩效率应该越来越高,但同时PSNR的值应该越来越小,表明重建出的图像质量应该越来越差。
3.经过DPCM+熵编码的PSNR值比只经过熵编码的PSNR值小,表明经过DPCM预测编码后重建出的图像质量比原始图像的质量差。但是图像大小比直接使用熵编码减小的更多。
参考文章链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_52189060/article/details/116081574?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/zsy_cuc_18?spm=1010.2135.3001.5343