【AutoAgument for OD】《Learning Data Augmentation Strategies for Object Detection》
文章目录
- 1 Background and Motivation
- 2 Related Work
- 3 Advantages / Contributions
- 4 Method
- 5 Experiments
-
- 5.1 Learning a data augmentation policy
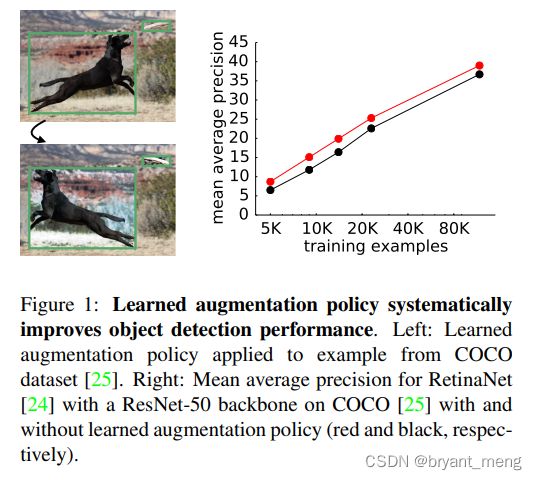
- 5.2 Learned augmentation policy systematically improves object detection
- 5.3 Exploiting learned augmentation policies achieves state-of-the-art object detection
- 5.4 Learned augmentation policies transfer to other detection datasets
- 5.5 Learned augmentation policies mimic the performance of larger annotated datasets
- 5.6 Learned data augmentation improves model regularization
- 6 Conclusion(own)
1 Background and Motivation
【AutoAugment】《AutoAugment:Learning Augmentation Policies from Data》(同作者的前期工作)
AutoAugment for 分类,本文 AutoAugment for 目标检测
基于分类的 data augmentation 被研究的很多,DA 的 potential has not been thoroughly investigated for object detection
Thus, we investigate how learned, specialized data augmentation policies improve generalization performance for detection models.
基于分类任务的 autoaugment
- learning a generator that can create data from scratch
- learning a set of transformations as applied to already existing training set samples
作者的 transformations 包含
- the whole image without affecting the bounding box locations(增广目标外的区域)
- transformations that affect the whole image while changing the bounding box locations bounding box locations(同时增广目标内外区域)
- applied to objects within the bounding boxes(仅增广目标)
2 Related Work
- MNIST 流行 elastic distortions which effect scale, translation, and rotation
- ImageNe 流行 Random cropping and image mirroring
- 目标检测流行 image mirror and multi-scale training
- randomly erase or add noise to patches of images for improved accuracy robustness or both
- learns an occlusion pattern for each object to create adversarial examples
- cut-and-paste
- learning data augmentation strategies
3 Advantages / Contributions
针对目标检测任务,提出了基于 learning 的 DA 方法
跨数据集跨目标检测器验证了其性能不错(generalize across datasets, dataset sizes, backbone architectures),能到 SOTA(小目标和 mAP75 提升最明显)
4 Method
Object detection introduces an additional complication of maintaining consistency between a bounding box location and a distorted image.

22 operations for search space
- Color operations
Equalize, Contrast, Brightness 等 - Geometric operations
Rotate, ShearX, TranslationY 等 - Bounding box operations
BBox Only Equalize, BBox Only Rotate, BBox Only FlipLR 等
搜索空间复杂度
( 22 × L × M ) N × K = ( 22 × 6 × 6 ) 2 × 5 ≈ 9.6 × 1 0 28 (22 \times L \times M)^{N \times K} = (22 \times 6 \times \ 6)^{2 \times 5} \approx 9.6 \times 10^{28} (22×L×M)N×K=(22×6× 6)2×5≈9.6×1028
其中 M M M 表示增广方法 range of magnitudes 的 uniformly-spaced values, L L L 表示增广方法 probability 的 uniformly-spaced values,也即离散化表示不同增广方法的 magnitudes 和被选中的 probability,压缩搜索空间(更省空间的方法参考 【Randaugment】《Randaugment:Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space》,同步了不同方法之间的 magnitudes)
K = 5 K=5 K=5 sub-policies,auto 出 5 个 sub-policies 增广组合进行随机增广
N = 2 N=2 N=2 images transformations, each sub-policy consists of 2 operations
each operation consists of 3 predictions corresponding to the selected image transformation, probability of application and magnitude of the transformation.
auto 时候,the reward signal for the controller is the mAP
具体使用
5 Experiments
Datasets
5.1 Learning a data augmentation policy
the most commonly used operation in good policies is Rotate,Equalize and BBox Only TranslateY.
5.2 Learned augmentation policy systematically improves object detection
only searched using 5K COCO training examples
看看结果
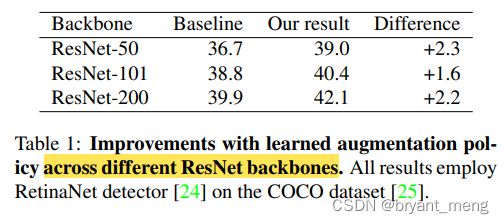
不同 backbone 均有提升

注意最后一行表格是策略累加
5.3 Exploiting learned augmentation policies achieves state-of-the-art object detection

anchor 的 aspect ratios from {1/2, 1, 2} to {1/5, 1/4, 1/3, 1/2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
These experiments additionally show that the augmentation policy transfers well across a different backbone architecture, detection algorithm, image sizes (i.e. 640 → 1280 pixels), and training procedure (training from scratch → using ImageNet pre-training) .
5.4 Learned augmentation policies transfer to other detection datasets

sub COCO 上 auto 出增广策略,VOC 上测试,提升很多

especially well on detecting smaller objects
5.5 Learned augmentation policies mimic the performance of larger annotated datasets

do relatively better on the harder task of AP75 (average precision IoU=0.75)
which is consistent with the gains observed with small objects.
5.6 Learned data augmentation improves model regularization

loss 更高,可以进一步优化,以防过拟合

L2 norm 稀疏,不容易过拟合
6 Conclusion(own)
bbox only augmentation
代码https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/blob/b24729de804fdb751b06467d3dce0637fa652060/models/official/detection/utils/autoaugment_utils.py
# Copyright 2018 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""AutoAugment util file."""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import inspect
import math
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
from tensorflow.contrib import image as contrib_image
from tensorflow.contrib import training as contrib_training
# This signifies the max integer that the controller RNN could predict for the
# augmentation scheme.
_MAX_LEVEL = 10.
# Represents an invalid bounding box that is used for checking for padding
# lists of bounding box coordinates for a few augmentation operations
_INVALID_BOX = [[-1.0, -1.0, -1.0, -1.0]]
def policy_v0():
"""Autoaugment policy that was used in AutoAugment Detection Paper."""
# Each tuple is an augmentation operation of the form
# (operation, probability, magnitude). Each element in policy is a
# sub-policy that will be applied sequentially on the image.
policy = [
[('TranslateX_BBox', 0.6, 4), ('Equalize', 0.8, 10)],
[('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.2, 2), ('Cutout', 0.8, 8)],
[('Sharpness', 0.0, 8), ('ShearX_BBox', 0.4, 0)],
[('ShearY_BBox', 1.0, 2), ('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.6, 6)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 0.6, 10), ('Color', 1.0, 6)],
]
return policy
def policy_v1():
"""Autoaugment policy that was used in AutoAugment Detection Paper."""
# Each tuple is an augmentation operation of the form
# (operation, probability, magnitude). Each element in policy is a
# sub-policy that will be applied sequentially on the image.
policy = [
[('TranslateX_BBox', 0.6, 4), ('Equalize', 0.8, 10)],
[('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.2, 2), ('Cutout', 0.8, 8)],
[('Sharpness', 0.0, 8), ('ShearX_BBox', 0.4, 0)],
[('ShearY_BBox', 1.0, 2), ('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.6, 6)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 0.6, 10), ('Color', 1.0, 6)],
[('Color', 0.0, 0), ('ShearX_Only_BBoxes', 0.8, 4)],
[('ShearY_Only_BBoxes', 0.8, 2), ('Flip_Only_BBoxes', 0.0, 10)],
[('Equalize', 0.6, 10), ('TranslateX_BBox', 0.2, 2)],
[('Color', 1.0, 10), ('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.4, 6)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 0.8, 10), ('Contrast', 0.0, 10)],
[('Cutout', 0.2, 2), ('Brightness', 0.8, 10)],
[('Color', 1.0, 6), ('Equalize', 1.0, 2)],
[('Cutout_Only_BBoxes', 0.4, 6), ('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.8, 2)],
[('Color', 0.2, 8), ('Rotate_BBox', 0.8, 10)],
[('Sharpness', 0.4, 4), ('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.0, 4)],
[('Sharpness', 1.0, 4), ('SolarizeAdd', 0.4, 4)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 1.0, 8), ('Sharpness', 0.2, 8)],
[('ShearY_BBox', 0.6, 10), ('Equalize_Only_BBoxes', 0.6, 8)],
[('ShearX_BBox', 0.2, 6), ('TranslateY_Only_BBoxes', 0.2, 10)],
[('SolarizeAdd', 0.6, 8), ('Brightness', 0.8, 10)],
]
return policy
def policy_vtest():
"""Autoaugment test policy for debugging."""
# Each tuple is an augmentation operation of the form
# (operation, probability, magnitude). Each element in policy is a
# sub-policy that will be applied sequentially on the image.
policy = [
[('TranslateX_BBox', 1.0, 4), ('Equalize', 1.0, 10)],
]
return policy
def policy_v2():
"""Additional policy that performs well on object detection."""
# Each tuple is an augmentation operation of the form
# (operation, probability, magnitude). Each element in policy is a
# sub-policy that will be applied sequentially on the image.
policy = [
[('Color', 0.0, 6), ('Cutout', 0.6, 8), ('Sharpness', 0.4, 8)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 0.4, 8), ('Sharpness', 0.4, 2),
('Rotate_BBox', 0.8, 10)],
[('TranslateY_BBox', 1.0, 8), ('AutoContrast', 0.8, 2)],
[('AutoContrast', 0.4, 6), ('ShearX_BBox', 0.8, 8),
('Brightness', 0.0, 10)],
[('SolarizeAdd', 0.2, 6), ('Contrast', 0.0, 10),
('AutoContrast', 0.6, 0)],
[('Cutout', 0.2, 0), ('Solarize', 0.8, 8), ('Color', 1.0, 4)],
[('TranslateY_BBox', 0.0, 4), ('Equalize', 0.6, 8),
('Solarize', 0.0, 10)],
[('TranslateY_BBox', 0.2, 2), ('ShearY_BBox', 0.8, 8),
('Rotate_BBox', 0.8, 8)],
[('Cutout', 0.8, 8), ('Brightness', 0.8, 8), ('Cutout', 0.2, 2)],
[('Color', 0.8, 4), ('TranslateY_BBox', 1.0, 6), ('Rotate_BBox', 0.6, 6)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 0.6, 10), ('BBox_Cutout', 1.0, 4), ('Cutout', 0.2, 8)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 0.0, 0), ('Equalize', 0.6, 6), ('ShearY_BBox', 0.6, 8)],
[('Brightness', 0.8, 8), ('AutoContrast', 0.4, 2),
('Brightness', 0.2, 2)],
[('TranslateY_BBox', 0.4, 8), ('Solarize', 0.4, 6),
('SolarizeAdd', 0.2, 10)],
[('Contrast', 1.0, 10), ('SolarizeAdd', 0.2, 8), ('Equalize', 0.2, 4)],
]
return policy
def policy_v3():
""""Additional policy that performs well on object detection."""
# Each tuple is an augmentation operation of the form
# (operation, probability, magnitude). Each element in policy is a
# sub-policy that will be applied sequentially on the image.
policy = [
[('Posterize', 0.8, 2), ('TranslateX_BBox', 1.0, 8)],
[('BBox_Cutout', 0.2, 10), ('Sharpness', 1.0, 8)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 0.6, 8), ('Rotate_BBox', 0.8, 10)],
[('Equalize', 0.8, 10), ('AutoContrast', 0.2, 10)],
[('SolarizeAdd', 0.2, 2), ('TranslateY_BBox', 0.2, 8)],
[('Sharpness', 0.0, 2), ('Color', 0.4, 8)],
[('Equalize', 1.0, 8), ('TranslateY_BBox', 1.0, 8)],
[('Posterize', 0.6, 2), ('Rotate_BBox', 0.0, 10)],
[('AutoContrast', 0.6, 0), ('Rotate_BBox', 1.0, 6)],
[('Equalize', 0.0, 4), ('Cutout', 0.8, 10)],
[('Brightness', 1.0, 2), ('TranslateY_BBox', 1.0, 6)],
[('Contrast', 0.0, 2), ('ShearY_BBox', 0.8, 0)],
[('AutoContrast', 0.8, 10), ('Contrast', 0.2, 10)],
[('Rotate_BBox', 1.0, 10), ('Cutout', 1.0, 10)],
[('SolarizeAdd', 0.8, 6), ('Equalize', 0.8, 8)],
]
return policy
def blend(image1, image2, factor):
"""Blend image1 and image2 using 'factor'.
Factor can be above 0.0. A value of 0.0 means only image1 is used.
A value of 1.0 means only image2 is used. A value between 0.0 and
1.0 means we linearly interpolate the pixel values between the two
images. A value greater than 1.0 "extrapolates" the difference
between the two pixel values, and we clip the results to values
between 0 and 255.
Args:
image1: An image Tensor of type uint8.
image2: An image Tensor of type uint8.
factor: A floating point value above 0.0.
Returns:
A blended image Tensor of type uint8.
"""
if factor == 0.0:
return tf.convert_to_tensor(image1)
if factor == 1.0:
return tf.convert_to_tensor(image2)
image1 = tf.to_float(image1)
image2 = tf.to_float(image2)
difference = image2 - image1
scaled = factor * difference
# Do addition in float.
temp = tf.to_float(image1) + scaled
# Interpolate
if factor > 0.0 and factor < 1.0:
# Interpolation means we always stay within 0 and 255.
return tf.cast(temp, tf.uint8)
# Extrapolate:
#
# We need to clip and then cast.
return tf.cast(tf.clip_by_value(temp, 0.0, 255.0), tf.uint8)
def cutout(image, pad_size, replace=0):
"""Apply cutout (https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552) to image.
This operation applies a (2*pad_size x 2*pad_size) mask of zeros to
a random location within `img`. The pixel values filled in will be of the
value `replace`. The located where the mask will be applied is randomly
chosen uniformly over the whole image.
Args:
image: An image Tensor of type uint8.
pad_size: Specifies how big the zero mask that will be generated is that
is applied to the image. The mask will be of size
(2*pad_size x 2*pad_size).
replace: What pixel value to fill in the image in the area that has
the cutout mask applied to it.
Returns:
An image Tensor that is of type uint8.
"""
image_height = tf.shape(image)[0]
image_width = tf.shape(image)[1]
# Sample the center location in the image where the zero mask will be applied.
cutout_center_height = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[], minval=0, maxval=image_height,
dtype=tf.int32)
cutout_center_width = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[], minval=0, maxval=image_width,
dtype=tf.int32)
lower_pad = tf.maximum(0, cutout_center_height - pad_size)
upper_pad = tf.maximum(0, image_height - cutout_center_height - pad_size)
left_pad = tf.maximum(0, cutout_center_width - pad_size)
right_pad = tf.maximum(0, image_width - cutout_center_width - pad_size)
cutout_shape = [image_height - (lower_pad + upper_pad),
image_width - (left_pad + right_pad)]
padding_dims = [[lower_pad, upper_pad], [left_pad, right_pad]]
mask = tf.pad(
tf.zeros(cutout_shape, dtype=image.dtype),
padding_dims, constant_values=1)
mask = tf.expand_dims(mask, -1)
mask = tf.tile(mask, [1, 1, 3])
image = tf.where(
tf.equal(mask, 0),
tf.ones_like(image, dtype=image.dtype) * replace,
image)
return image
def solarize(image, threshold=128):
# For each pixel in the image, select the pixel
# if the value is less than the threshold.
# Otherwise, subtract 255 from the pixel.
return tf.where(image < threshold, image, 255 - image)
def solarize_add(image, addition=0, threshold=128):
# For each pixel in the image less than threshold
# we add 'addition' amount to it and then clip the
# pixel value to be between 0 and 255. The value
# of 'addition' is between -128 and 128.
added_image = tf.cast(image, tf.int64) + addition
added_image = tf.cast(tf.clip_by_value(added_image, 0, 255), tf.uint8)
return tf.where(image < threshold, added_image, image)
def color(image, factor):
"""Equivalent of PIL Color."""
degenerate = tf.image.grayscale_to_rgb(tf.image.rgb_to_grayscale(image))
return blend(degenerate, image, factor)
def contrast(image, factor):
"""Equivalent of PIL Contrast."""
degenerate = tf.image.rgb_to_grayscale(image)
# Cast before calling tf.histogram.
degenerate = tf.cast(degenerate, tf.int32)
# Compute the grayscale histogram, then compute the mean pixel value,
# and create a constant image size of that value. Use that as the
# blending degenerate target of the original image.
hist = tf.histogram_fixed_width(degenerate, [0, 255], nbins=256)
mean = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(hist, tf.float32)) / 256.0
degenerate = tf.ones_like(degenerate, dtype=tf.float32) * mean
degenerate = tf.clip_by_value(degenerate, 0.0, 255.0)
degenerate = tf.image.grayscale_to_rgb(tf.cast(degenerate, tf.uint8))
return blend(degenerate, image, factor)
def brightness(image, factor):
"""Equivalent of PIL Brightness."""
degenerate = tf.zeros_like(image)
return blend(degenerate, image, factor)
def posterize(image, bits):
"""Equivalent of PIL Posterize."""
shift = 8 - bits
return tf.bitwise.left_shift(tf.bitwise.right_shift(image, shift), shift)
def rotate(image, degrees, replace):
"""Rotates the image by degrees either clockwise or counterclockwise.
Args:
image: An image Tensor of type uint8.
degrees: Float, a scalar angle in degrees to rotate all images by. If
degrees is positive the image will be rotated clockwise otherwise it will
be rotated counterclockwise.
replace: A one or three value 1D tensor to fill empty pixels caused by
the rotate operation.
Returns:
The rotated version of image.
"""
# Convert from degrees to radians.
degrees_to_radians = math.pi / 180.0
radians = degrees * degrees_to_radians
# In practice, we should randomize the rotation degrees by flipping
# it negatively half the time, but that's done on 'degrees' outside
# of the function.
image = contrib_image.rotate(wrap(image), radians)
return unwrap(image, replace)
def random_shift_bbox(image, bbox, pixel_scaling, replace,
new_min_bbox_coords=None):
"""Move the bbox and the image content to a slightly new random location.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bbox: 1D Tensor that has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
of type float that represents the normalized coordinates between 0 and 1.
The potential values for the new min corner of the bbox will be between
[old_min - pixel_scaling * bbox_height/2,
old_min - pixel_scaling * bbox_height/2].
pixel_scaling: A float between 0 and 1 that specifies the pixel range
that the new bbox location will be sampled from.
replace: A one or three value 1D tensor to fill empty pixels.
new_min_bbox_coords: If not None, then this is a tuple that specifies the
(min_y, min_x) coordinates of the new bbox. Normally this is randomly
specified, but this allows it to be manually set. The coordinates are
the absolute coordinates between 0 and image height/width and are int32.
Returns:
The new image that will have the shifted bbox location in it along with
the new bbox that contains the new coordinates.
"""
# Obtains image height and width and create helper clip functions.
image_height = tf.to_float(tf.shape(image)[0])
image_width = tf.to_float(tf.shape(image)[1])
def clip_y(val):
return tf.clip_by_value(val, 0, tf.to_int32(image_height) - 1)
def clip_x(val):
return tf.clip_by_value(val, 0, tf.to_int32(image_width) - 1)
# Convert bbox to pixel coordinates.
min_y = tf.to_int32(image_height * bbox[0])
min_x = tf.to_int32(image_width * bbox[1])
max_y = clip_y(tf.to_int32(image_height * bbox[2]))
max_x = clip_x(tf.to_int32(image_width * bbox[3]))
bbox_height, bbox_width = (max_y - min_y + 1, max_x - min_x + 1)
image_height = tf.to_int32(image_height)
image_width = tf.to_int32(image_width)
# Select the new min/max bbox ranges that are used for sampling the
# new min x/y coordinates of the shifted bbox.
minval_y = clip_y(
min_y - tf.to_int32(pixel_scaling * tf.to_float(bbox_height) / 2.0))
maxval_y = clip_y(
min_y + tf.to_int32(pixel_scaling * tf.to_float(bbox_height) / 2.0))
minval_x = clip_x(
min_x - tf.to_int32(pixel_scaling * tf.to_float(bbox_width) / 2.0))
maxval_x = clip_x(
min_x + tf.to_int32(pixel_scaling * tf.to_float(bbox_width) / 2.0))
# Sample and calculate the new unclipped min/max coordinates of the new bbox.
if new_min_bbox_coords is None:
unclipped_new_min_y = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[], minval=minval_y, maxval=maxval_y,
dtype=tf.int32)
unclipped_new_min_x = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[], minval=minval_x, maxval=maxval_x,
dtype=tf.int32)
else:
unclipped_new_min_y, unclipped_new_min_x = (
clip_y(new_min_bbox_coords[0]), clip_x(new_min_bbox_coords[1]))
unclipped_new_max_y = unclipped_new_min_y + bbox_height - 1
unclipped_new_max_x = unclipped_new_min_x + bbox_width - 1
# Determine if any of the new bbox was shifted outside the current image.
# This is used for determining if any of the original bbox content should be
# discarded.
new_min_y, new_min_x, new_max_y, new_max_x = (
clip_y(unclipped_new_min_y), clip_x(unclipped_new_min_x),
clip_y(unclipped_new_max_y), clip_x(unclipped_new_max_x))
shifted_min_y = (new_min_y - unclipped_new_min_y) + min_y
shifted_max_y = max_y - (unclipped_new_max_y - new_max_y)
shifted_min_x = (new_min_x - unclipped_new_min_x) + min_x
shifted_max_x = max_x - (unclipped_new_max_x - new_max_x)
# Create the new bbox tensor by converting pixel integer values to floats.
new_bbox = tf.stack([
tf.to_float(new_min_y) / tf.to_float(image_height),
tf.to_float(new_min_x) / tf.to_float(image_width),
tf.to_float(new_max_y) / tf.to_float(image_height),
tf.to_float(new_max_x) / tf.to_float(image_width)])
# Copy the contents in the bbox and fill the old bbox location
# with gray (128).
bbox_content = image[shifted_min_y:shifted_max_y + 1,
shifted_min_x:shifted_max_x + 1, :]
def mask_and_add_image(
min_y_, min_x_, max_y_, max_x_, mask, content_tensor, image_):
"""Applies mask to bbox region in image then adds content_tensor to it."""
mask = tf.pad(mask,
[[min_y_, (image_height - 1) - max_y_],
[min_x_, (image_width - 1) - max_x_],
[0, 0]], constant_values=1)
content_tensor = tf.pad(content_tensor,
[[min_y_, (image_height - 1) - max_y_],
[min_x_, (image_width - 1) - max_x_],
[0, 0]], constant_values=0)
return image_ * mask + content_tensor
# Zero out original bbox location.
mask = tf.zeros_like(image)[min_y:max_y+1, min_x:max_x+1, :]
grey_tensor = tf.zeros_like(mask) + replace[0]
image = mask_and_add_image(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x, mask,
grey_tensor, image)
# Fill in bbox content to new bbox location.
mask = tf.zeros_like(bbox_content)
image = mask_and_add_image(new_min_y, new_min_x, new_max_y, new_max_x, mask,
bbox_content, image)
return image, new_bbox
def _clip_bbox(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x):
"""Clip bounding box coordinates between 0 and 1.
Args:
min_y: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
min_x: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
max_y: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
max_x: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
Returns:
Clipped coordinate values between 0 and 1.
"""
min_y = tf.clip_by_value(min_y, 0.0, 1.0)
min_x = tf.clip_by_value(min_x, 0.0, 1.0)
max_y = tf.clip_by_value(max_y, 0.0, 1.0)
max_x = tf.clip_by_value(max_x, 0.0, 1.0)
return min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x
def _check_bbox_area(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x, delta=0.05):
"""Adjusts bbox coordinates to make sure the area is > 0.
Args:
min_y: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
min_x: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
max_y: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
max_x: Normalized bbox coordinate of type float between 0 and 1.
delta: Float, this is used to create a gap of size 2 * delta between
bbox min/max coordinates that are the same on the boundary.
This prevents the bbox from having an area of zero.
Returns:
Tuple of new bbox coordinates between 0 and 1 that will now have a
guaranteed area > 0.
"""
height = max_y - min_y
width = max_x - min_x
def _adjust_bbox_boundaries(min_coord, max_coord):
# Make sure max is never 0 and min is never 1.
max_coord = tf.maximum(max_coord, 0.0 + delta)
min_coord = tf.minimum(min_coord, 1.0 - delta)
return min_coord, max_coord
min_y, max_y = tf.cond(tf.equal(height, 0.0),
lambda: _adjust_bbox_boundaries(min_y, max_y),
lambda: (min_y, max_y))
min_x, max_x = tf.cond(tf.equal(width, 0.0),
lambda: _adjust_bbox_boundaries(min_x, max_x),
lambda: (min_x, max_x))
return min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x
def _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob):
"""Reduce the probability of the bbox-only operation.
Probability is reduced so that we do not distort the content of too many
bounding boxes that are close to each other. The value of 3.0 was a chosen
hyper parameter when designing the autoaugment algorithm that we found
empirically to work well.
Args:
prob: Float that is the probability of applying the bbox-only operation.
Returns:
Reduced probability.
"""
return prob / 3.0
def _apply_bbox_augmentation(image, bbox, augmentation_func, *args):
"""Applies augmentation_func to the subsection of image indicated by bbox.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bbox: 1D Tensor that has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
of type float that represents the normalized coordinates between 0 and 1.
augmentation_func: Augmentation function that will be applied to the
subsection of image.
*args: Additional parameters that will be passed into augmentation_func
when it is called.
Returns:
A modified version of image, where the bbox location in the image will
have `ugmentation_func applied to it.
"""
image_height = tf.to_float(tf.shape(image)[0])
image_width = tf.to_float(tf.shape(image)[1])
min_y = tf.to_int32(image_height * bbox[0])
min_x = tf.to_int32(image_width * bbox[1])
max_y = tf.to_int32(image_height * bbox[2])
max_x = tf.to_int32(image_width * bbox[3])
image_height = tf.to_int32(image_height)
image_width = tf.to_int32(image_width)
# Clip to be sure the max values do not fall out of range.
max_y = tf.minimum(max_y, image_height - 1)
max_x = tf.minimum(max_x, image_width - 1)
# Get the sub-tensor that is the image within the bounding box region.
bbox_content = image[min_y:max_y + 1, min_x:max_x + 1, :]
# Apply the augmentation function to the bbox portion of the image.
augmented_bbox_content = augmentation_func(bbox_content, *args)
# Pad the augmented_bbox_content and the mask to match the shape of original
# image.
augmented_bbox_content = tf.pad(augmented_bbox_content,
[[min_y, (image_height - 1) - max_y],
[min_x, (image_width - 1) - max_x],
[0, 0]])
# Create a mask that will be used to zero out a part of the original image.
mask_tensor = tf.zeros_like(bbox_content)
mask_tensor = tf.pad(mask_tensor,
[[min_y, (image_height - 1) - max_y],
[min_x, (image_width - 1) - max_x],
[0, 0]],
constant_values=1)
# Replace the old bbox content with the new augmented content.
image = image * mask_tensor + augmented_bbox_content
return image
def _concat_bbox(bbox, bboxes):
"""Helper function that concates bbox to bboxes along the first dimension."""
# Note if all elements in bboxes are -1 (_INVALID_BOX), then this means
# we discard bboxes and start the bboxes Tensor with the current bbox.
bboxes_sum_check = tf.reduce_sum(bboxes)
bbox = tf.expand_dims(bbox, 0)
# This check will be true when it is an _INVALID_BOX
bboxes = tf.cond(tf.equal(bboxes_sum_check, -4.0),
lambda: bbox,
lambda: tf.concat([bboxes, bbox], 0))
return bboxes
def _apply_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(image, bbox, new_bboxes, prob,
augmentation_func, func_changes_bbox,
*args):
"""Applies _apply_bbox_augmentation with probability prob.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bbox: 1D Tensor that has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
of type float that represents the normalized coordinates between 0 and 1.
new_bboxes: 2D Tensor that is a list of the bboxes in the image after they
have been altered by aug_func. These will only be changed when
func_changes_bbox is set to true. Each bbox has 4 elements
(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x) of type float that are the normalized
bbox coordinates between 0 and 1.
prob: Float that is the probability of applying _apply_bbox_augmentation.
augmentation_func: Augmentation function that will be applied to the
subsection of image.
func_changes_bbox: Boolean. Does augmentation_func return bbox in addition
to image.
*args: Additional parameters that will be passed into augmentation_func
when it is called.
Returns:
A tuple. Fist element is a modified version of image, where the bbox
location in the image will have augmentation_func applied to it if it is
chosen to be called with probability `prob`. The second element is a
Tensor of Tensors of length 4 that will contain the altered bbox after
applying augmentation_func.
"""
should_apply_op = tf.cast(
tf.floor(tf.random_uniform([], dtype=tf.float32) + prob), tf.bool)
if func_changes_bbox:
augmented_image, bbox = tf.cond(
should_apply_op,
lambda: augmentation_func(image, bbox, *args),
lambda: (image, bbox))
else:
augmented_image = tf.cond(
should_apply_op,
lambda: _apply_bbox_augmentation(image, bbox, augmentation_func, *args),
lambda: image)
new_bboxes = _concat_bbox(bbox, new_bboxes)
return augmented_image, new_bboxes
def _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation(image, bboxes, prob, aug_func,
func_changes_bbox, *args):
"""Applies aug_func to the image for each bbox in bboxes.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bboxes: 2D Tensor that is a list of the bboxes in the image. Each bbox
has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x) of type float.
prob: Float that is the probability of applying aug_func to a specific
bounding box within the image.
aug_func: Augmentation function that will be applied to the
subsections of image indicated by the bbox values in bboxes.
func_changes_bbox: Boolean. Does augmentation_func return bbox in addition
to image.
*args: Additional parameters that will be passed into augmentation_func
when it is called.
Returns:
A modified version of image, where each bbox location in the image will
have augmentation_func applied to it if it is chosen to be called with
probability prob independently across all bboxes. Also the final
bboxes are returned that will be unchanged if func_changes_bbox is set to
false and if true, the new altered ones will be returned.
"""
# Will keep track of the new altered bboxes after aug_func is repeatedly
# applied. The -1 values are a dummy value and this first Tensor will be
# removed upon appending the first real bbox.
new_bboxes = tf.constant(_INVALID_BOX)
# If the bboxes are empty, then just give it _INVALID_BOX. The result
# will be thrown away.
bboxes = tf.cond(tf.equal(tf.size(bboxes), 0),
lambda: tf.constant(_INVALID_BOX),
lambda: bboxes)
bboxes = tf.ensure_shape(bboxes, (None, 4))
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
# pylint:disable=line-too-long
wrapped_aug_func = lambda _image, bbox, _new_bboxes: _apply_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
_image, bbox, _new_bboxes, prob, aug_func, func_changes_bbox, *args)
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
# pylint:enable=line-too-long
# Setup the while_loop.
num_bboxes = tf.shape(bboxes)[0] # We loop until we go over all bboxes.
idx = tf.constant(0) # Counter for the while loop.
# Conditional function when to end the loop once we go over all bboxes
# images_and_bboxes contain (_image, _new_bboxes)
cond = lambda _idx, _images_and_bboxes: tf.less(_idx, num_bboxes)
# Shuffle the bboxes so that the augmentation order is not deterministic if
# we are not changing the bboxes with aug_func.
if not func_changes_bbox:
loop_bboxes = tf.random.shuffle(bboxes)
else:
loop_bboxes = bboxes
# Main function of while_loop where we repeatedly apply augmentation on the
# bboxes in the image.
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
body = lambda _idx, _images_and_bboxes: [
_idx + 1, wrapped_aug_func(_images_and_bboxes[0],
loop_bboxes[_idx],
_images_and_bboxes[1])]
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
_, (image, new_bboxes) = tf.while_loop(
cond, body, [idx, (image, new_bboxes)],
shape_invariants=[idx.get_shape(),
(image.get_shape(), tf.TensorShape([None, 4]))])
# Either return the altered bboxes or the original ones depending on if
# we altered them in anyway.
if func_changes_bbox:
final_bboxes = new_bboxes
else:
final_bboxes = bboxes
return image, final_bboxes
def _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(image, bboxes, prob, aug_func,
func_changes_bbox, *args):
"""Checks to be sure num bboxes > 0 before calling inner function."""
num_bboxes = tf.shape(bboxes)[0]
image, bboxes = tf.cond(
tf.equal(num_bboxes, 0),
lambda: (image, bboxes),
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
lambda: _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation(
image, bboxes, prob, aug_func, func_changes_bbox, *args))
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
return image, bboxes
def rotate_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob, degrees, replace):
"""Apply rotate to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, rotate, func_changes_bbox, degrees, replace)
def shear_x_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob, level, replace):
"""Apply shear_x to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, shear_x, func_changes_bbox, level, replace)
def shear_y_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob, level, replace):
"""Apply shear_y to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, shear_y, func_changes_bbox, level, replace)
def translate_x_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob, pixels, replace):
"""Apply translate_x to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, translate_x, func_changes_bbox, pixels, replace)
def translate_y_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob, pixels, replace):
"""Apply translate_y to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, translate_y, func_changes_bbox, pixels, replace)
def flip_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob):
"""Apply flip_lr to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, tf.image.flip_left_right, func_changes_bbox)
def solarize_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob, threshold):
"""Apply solarize to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, solarize, func_changes_bbox, threshold)
def equalize_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob):
"""Apply equalize to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, equalize, func_changes_bbox)
def cutout_only_bboxes(image, bboxes, prob, pad_size, replace):
"""Apply cutout to each bbox in the image with probability prob."""
func_changes_bbox = False
prob = _scale_bbox_only_op_probability(prob)
return _apply_multi_bbox_augmentation_wrapper(
image, bboxes, prob, cutout, func_changes_bbox, pad_size, replace)
def _rotate_bbox(bbox, image_height, image_width, degrees):
"""Rotates the bbox coordinated by degrees.
Args:
bbox: 1D Tensor that has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
of type float that represents the normalized coordinates between 0 and 1.
image_height: Int, height of the image.
image_width: Int, height of the image.
degrees: Float, a scalar angle in degrees to rotate all images by. If
degrees is positive the image will be rotated clockwise otherwise it will
be rotated counterclockwise.
Returns:
A tensor of the same shape as bbox, but now with the rotated coordinates.
"""
image_height, image_width = (
tf.to_float(image_height), tf.to_float(image_width))
# Convert from degrees to radians.
degrees_to_radians = math.pi / 180.0
radians = degrees * degrees_to_radians
# Translate the bbox to the center of the image and turn the normalized 0-1
# coordinates to absolute pixel locations.
# Y coordinates are made negative as the y axis of images goes down with
# increasing pixel values, so we negate to make sure x axis and y axis points
# are in the traditionally positive direction.
min_y = -tf.to_int32(image_height * (bbox[0] - 0.5))
min_x = tf.to_int32(image_width * (bbox[1] - 0.5))
max_y = -tf.to_int32(image_height * (bbox[2] - 0.5))
max_x = tf.to_int32(image_width * (bbox[3] - 0.5))
coordinates = tf.stack(
[[min_y, min_x], [min_y, max_x], [max_y, min_x], [max_y, max_x]])
coordinates = tf.cast(coordinates, tf.float32)
# Rotate the coordinates according to the rotation matrix clockwise if
# radians is positive, else negative
rotation_matrix = tf.stack(
[[tf.cos(radians), tf.sin(radians)],
[-tf.sin(radians), tf.cos(radians)]])
new_coords = tf.cast(
tf.matmul(rotation_matrix, tf.transpose(coordinates)), tf.int32)
# Find min/max values and convert them back to normalized 0-1 floats.
min_y = -(tf.to_float(tf.reduce_max(new_coords[0, :])) / image_height - 0.5)
min_x = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_min(new_coords[1, :])) / image_width + 0.5
max_y = -(tf.to_float(tf.reduce_min(new_coords[0, :])) / image_height - 0.5)
max_x = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_max(new_coords[1, :])) / image_width + 0.5
# Clip the bboxes to be sure the fall between [0, 1].
min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x = _clip_bbox(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x = _check_bbox_area(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
return tf.stack([min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x])
def rotate_with_bboxes(image, bboxes, degrees, replace):
"""Equivalent of PIL Rotate that rotates the image and bbox.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bboxes: 2D Tensor that is a list of the bboxes in the image. Each bbox
has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x) of type float.
degrees: Float, a scalar angle in degrees to rotate all images by. If
degrees is positive the image will be rotated clockwise otherwise it will
be rotated counterclockwise.
replace: A one or three value 1D tensor to fill empty pixels.
Returns:
A tuple containing a 3D uint8 Tensor that will be the result of rotating
image by degrees. The second element of the tuple is bboxes, where now
the coordinates will be shifted to reflect the rotated image.
"""
# Rotate the image.
image = rotate(image, degrees, replace)
# Convert bbox coordinates to pixel values.
image_height = tf.shape(image)[0]
image_width = tf.shape(image)[1]
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
wrapped_rotate_bbox = lambda bbox: _rotate_bbox(
bbox, image_height, image_width, degrees)
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
bboxes = tf.map_fn(wrapped_rotate_bbox, bboxes)
return image, bboxes
def translate_x(image, pixels, replace):
"""Equivalent of PIL Translate in X dimension."""
image = contrib_image.translate(wrap(image), [-pixels, 0])
return unwrap(image, replace)
def translate_y(image, pixels, replace):
"""Equivalent of PIL Translate in Y dimension."""
image = contrib_image.translate(wrap(image), [0, -pixels])
return unwrap(image, replace)
def _shift_bbox(bbox, image_height, image_width, pixels, shift_horizontal):
"""Shifts the bbox coordinates by pixels.
Args:
bbox: 1D Tensor that has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
of type float that represents the normalized coordinates between 0 and 1.
image_height: Int, height of the image.
image_width: Int, width of the image.
pixels: An int. How many pixels to shift the bbox.
shift_horizontal: Boolean. If true then shift in X dimension else shift in
Y dimension.
Returns:
A tensor of the same shape as bbox, but now with the shifted coordinates.
"""
pixels = tf.to_int32(pixels)
# Convert bbox to integer pixel locations.
min_y = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_height) * bbox[0])
min_x = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_width) * bbox[1])
max_y = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_height) * bbox[2])
max_x = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_width) * bbox[3])
if shift_horizontal:
min_x = tf.maximum(0, min_x - pixels)
max_x = tf.minimum(image_width, max_x - pixels)
else:
min_y = tf.maximum(0, min_y - pixels)
max_y = tf.minimum(image_height, max_y - pixels)
# Convert bbox back to floats.
min_y = tf.to_float(min_y) / tf.to_float(image_height)
min_x = tf.to_float(min_x) / tf.to_float(image_width)
max_y = tf.to_float(max_y) / tf.to_float(image_height)
max_x = tf.to_float(max_x) / tf.to_float(image_width)
# Clip the bboxes to be sure the fall between [0, 1].
min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x = _clip_bbox(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x = _check_bbox_area(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
return tf.stack([min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x])
def translate_bbox(image, bboxes, pixels, replace, shift_horizontal):
"""Equivalent of PIL Translate in X/Y dimension that shifts image and bbox.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bboxes: 2D Tensor that is a list of the bboxes in the image. Each bbox
has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x) of type float with values
between [0, 1].
pixels: An int. How many pixels to shift the image and bboxes
replace: A one or three value 1D tensor to fill empty pixels.
shift_horizontal: Boolean. If true then shift in X dimension else shift in
Y dimension.
Returns:
A tuple containing a 3D uint8 Tensor that will be the result of translating
image by pixels. The second element of the tuple is bboxes, where now
the coordinates will be shifted to reflect the shifted image.
"""
if shift_horizontal:
image = translate_x(image, pixels, replace)
else:
image = translate_y(image, pixels, replace)
# Convert bbox coordinates to pixel values.
image_height = tf.shape(image)[0]
image_width = tf.shape(image)[1]
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
wrapped_shift_bbox = lambda bbox: _shift_bbox(
bbox, image_height, image_width, pixels, shift_horizontal)
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
bboxes = tf.map_fn(wrapped_shift_bbox, bboxes)
return image, bboxes
def shear_x(image, level, replace):
"""Equivalent of PIL Shearing in X dimension."""
# Shear parallel to x axis is a projective transform
# with a matrix form of:
# [1 level
# 0 1].
image = contrib_image.transform(
wrap(image), [1., level, 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.])
return unwrap(image, replace)
def shear_y(image, level, replace):
"""Equivalent of PIL Shearing in Y dimension."""
# Shear parallel to y axis is a projective transform
# with a matrix form of:
# [1 0
# level 1].
image = contrib_image.transform(
wrap(image), [1., 0., 0., level, 1., 0., 0., 0.])
return unwrap(image, replace)
def _shear_bbox(bbox, image_height, image_width, level, shear_horizontal):
"""Shifts the bbox according to how the image was sheared.
Args:
bbox: 1D Tensor that has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
of type float that represents the normalized coordinates between 0 and 1.
image_height: Int, height of the image.
image_width: Int, height of the image.
level: Float. How much to shear the image.
shear_horizontal: If true then shear in X dimension else shear in
the Y dimension.
Returns:
A tensor of the same shape as bbox, but now with the shifted coordinates.
"""
image_height, image_width = (
tf.to_float(image_height), tf.to_float(image_width))
# Change bbox coordinates to be pixels.
min_y = tf.to_int32(image_height * bbox[0])
min_x = tf.to_int32(image_width * bbox[1])
max_y = tf.to_int32(image_height * bbox[2])
max_x = tf.to_int32(image_width * bbox[3])
coordinates = tf.stack(
[[min_y, min_x], [min_y, max_x], [max_y, min_x], [max_y, max_x]])
coordinates = tf.cast(coordinates, tf.float32)
# Shear the coordinates according to the translation matrix.
if shear_horizontal:
translation_matrix = tf.stack(
[[1, 0], [-level, 1]])
else:
translation_matrix = tf.stack(
[[1, -level], [0, 1]])
translation_matrix = tf.cast(translation_matrix, tf.float32)
new_coords = tf.cast(
tf.matmul(translation_matrix, tf.transpose(coordinates)), tf.int32)
# Find min/max values and convert them back to floats.
min_y = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_min(new_coords[0, :])) / image_height
min_x = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_min(new_coords[1, :])) / image_width
max_y = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_max(new_coords[0, :])) / image_height
max_x = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_max(new_coords[1, :])) / image_width
# Clip the bboxes to be sure the fall between [0, 1].
min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x = _clip_bbox(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x = _check_bbox_area(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
return tf.stack([min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x])
def shear_with_bboxes(image, bboxes, level, replace, shear_horizontal):
"""Applies Shear Transformation to the image and shifts the bboxes.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bboxes: 2D Tensor that is a list of the bboxes in the image. Each bbox
has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x) of type float with values
between [0, 1].
level: Float. How much to shear the image. This value will be between
-0.3 to 0.3.
replace: A one or three value 1D tensor to fill empty pixels.
shear_horizontal: Boolean. If true then shear in X dimension else shear in
the Y dimension.
Returns:
A tuple containing a 3D uint8 Tensor that will be the result of shearing
image by level. The second element of the tuple is bboxes, where now
the coordinates will be shifted to reflect the sheared image.
"""
if shear_horizontal:
image = shear_x(image, level, replace)
else:
image = shear_y(image, level, replace)
# Convert bbox coordinates to pixel values.
image_height = tf.shape(image)[0]
image_width = tf.shape(image)[1]
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
wrapped_shear_bbox = lambda bbox: _shear_bbox(
bbox, image_height, image_width, level, shear_horizontal)
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
bboxes = tf.map_fn(wrapped_shear_bbox, bboxes)
return image, bboxes
def autocontrast(image):
"""Implements Autocontrast function from PIL using TF ops.
Args:
image: A 3D uint8 tensor.
Returns:
The image after it has had autocontrast applied to it and will be of type
uint8.
"""
def scale_channel(image):
"""Scale the 2D image using the autocontrast rule."""
# A possibly cheaper version can be done using cumsum/unique_with_counts
# over the histogram values, rather than iterating over the entire image.
# to compute mins and maxes.
lo = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_min(image))
hi = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_max(image))
# Scale the image, making the lowest value 0 and the highest value 255.
def scale_values(im):
scale = 255.0 / (hi - lo)
offset = -lo * scale
im = tf.to_float(im) * scale + offset
im = tf.clip_by_value(im, 0.0, 255.0)
return tf.cast(im, tf.uint8)
result = tf.cond(hi > lo, lambda: scale_values(image), lambda: image)
return result
# Assumes RGB for now. Scales each channel independently
# and then stacks the result.
s1 = scale_channel(image[:, :, 0])
s2 = scale_channel(image[:, :, 1])
s3 = scale_channel(image[:, :, 2])
image = tf.stack([s1, s2, s3], 2)
return image
def sharpness(image, factor):
"""Implements Sharpness function from PIL using TF ops."""
orig_image = image
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32)
# Make image 4D for conv operation.
image = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
# SMOOTH PIL Kernel.
kernel = tf.constant(
[[1, 1, 1], [1, 5, 1], [1, 1, 1]], dtype=tf.float32,
shape=[3, 3, 1, 1]) / 13.
# Tile across channel dimension.
kernel = tf.tile(kernel, [1, 1, 3, 1])
strides = [1, 1, 1, 1]
degenerate = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(
image, kernel, strides, padding='VALID', rate=[1, 1])
degenerate = tf.clip_by_value(degenerate, 0.0, 255.0)
degenerate = tf.squeeze(tf.cast(degenerate, tf.uint8), [0])
# For the borders of the resulting image, fill in the values of the
# original image.
mask = tf.ones_like(degenerate)
padded_mask = tf.pad(mask, [[1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]])
padded_degenerate = tf.pad(degenerate, [[1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]])
result = tf.where(tf.equal(padded_mask, 1), padded_degenerate, orig_image)
# Blend the final result.
return blend(result, orig_image, factor)
def equalize(image):
"""Implements Equalize function from PIL using TF ops."""
def scale_channel(im, c):
"""Scale the data in the channel to implement equalize."""
im = tf.cast(im[:, :, c], tf.int32)
# Compute the histogram of the image channel.
histo = tf.histogram_fixed_width(im, [0, 255], nbins=256)
# For the purposes of computing the step, filter out the nonzeros.
nonzero = tf.where(tf.not_equal(histo, 0))
nonzero_histo = tf.reshape(tf.gather(histo, nonzero), [-1])
step = (tf.reduce_sum(nonzero_histo) - nonzero_histo[-1]) // 255
def build_lut(histo, step):
# Compute the cumulative sum, shifting by step // 2
# and then normalization by step.
lut = (tf.cumsum(histo) + (step // 2)) // step
# Shift lut, prepending with 0.
lut = tf.concat([[0], lut[:-1]], 0)
# Clip the counts to be in range. This is done
# in the C code for image.point.
return tf.clip_by_value(lut, 0, 255)
# If step is zero, return the original image. Otherwise, build
# lut from the full histogram and step and then index from it.
result = tf.cond(tf.equal(step, 0),
lambda: im,
lambda: tf.gather(build_lut(histo, step), im))
return tf.cast(result, tf.uint8)
# Assumes RGB for now. Scales each channel independently
# and then stacks the result.
s1 = scale_channel(image, 0)
s2 = scale_channel(image, 1)
s3 = scale_channel(image, 2)
image = tf.stack([s1, s2, s3], 2)
return image
def wrap(image):
"""Returns 'image' with an extra channel set to all 1s."""
shape = tf.shape(image)
extended_channel = tf.ones([shape[0], shape[1], 1], image.dtype)
extended = tf.concat([image, extended_channel], 2)
return extended
def unwrap(image, replace):
"""Unwraps an image produced by wrap.
Where there is a 0 in the last channel for every spatial position,
the rest of the three channels in that spatial dimension are grayed
(set to 128). Operations like translate and shear on a wrapped
Tensor will leave 0s in empty locations. Some transformations look
at the intensity of values to do preprocessing, and we want these
empty pixels to assume the 'average' value, rather than pure black.
Args:
image: A 3D Image Tensor with 4 channels.
replace: A one or three value 1D tensor to fill empty pixels.
Returns:
image: A 3D image Tensor with 3 channels.
"""
image_shape = tf.shape(image)
# Flatten the spatial dimensions.
flattened_image = tf.reshape(image, [-1, image_shape[2]])
# Find all pixels where the last channel is zero.
alpha_channel = flattened_image[:, 3]
replace = tf.concat([replace, tf.ones([1], image.dtype)], 0)
# Where they are zero, fill them in with 'replace'.
flattened_image = tf.where(
tf.equal(alpha_channel, 0),
tf.ones_like(flattened_image, dtype=image.dtype) * replace,
flattened_image)
image = tf.reshape(flattened_image, image_shape)
image = tf.slice(image, [0, 0, 0], [image_shape[0], image_shape[1], 3])
return image
def _cutout_inside_bbox(image, bbox, pad_fraction):
"""Generates cutout mask and the mean pixel value of the bbox.
First a location is randomly chosen within the image as the center where the
cutout mask will be applied. Note this can be towards the boundaries of the
image, so the full cutout mask may not be applied.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bbox: 1D Tensor that has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)
of type float that represents the normalized coordinates between 0 and 1.
pad_fraction: Float that specifies how large the cutout mask should be in
in reference to the size of the original bbox. If pad_fraction is 0.25,
then the cutout mask will be of shape
(0.25 * bbox height, 0.25 * bbox width).
Returns:
A tuple. Fist element is a tensor of the same shape as image where each
element is either a 1 or 0 that is used to determine where the image
will have cutout applied. The second element is the mean of the pixels
in the image where the bbox is located.
"""
image_height = tf.shape(image)[0]
image_width = tf.shape(image)[1]
# Transform from shape [1, 4] to [4].
bbox = tf.squeeze(bbox)
min_y = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_height) * bbox[0])
min_x = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_width) * bbox[1])
max_y = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_height) * bbox[2])
max_x = tf.to_int32(tf.to_float(image_width) * bbox[3])
# Calculate the mean pixel values in the bounding box, which will be used
# to fill the cutout region.
mean = tf.reduce_mean(image[min_y:max_y + 1, min_x:max_x + 1],
reduction_indices=[0, 1])
# Cutout mask will be size pad_size_heigh * 2 by pad_size_width * 2 if the
# region lies entirely within the bbox.
box_height = max_y - min_y + 1
box_width = max_x - min_x + 1
pad_size_height = tf.to_int32(pad_fraction * (box_height / 2))
pad_size_width = tf.to_int32(pad_fraction * (box_width / 2))
# Sample the center location in the image where the zero mask will be applied.
cutout_center_height = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[], minval=min_y, maxval=max_y+1,
dtype=tf.int32)
cutout_center_width = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[], minval=min_x, maxval=max_x+1,
dtype=tf.int32)
lower_pad = tf.maximum(
0, cutout_center_height - pad_size_height)
upper_pad = tf.maximum(
0, image_height - cutout_center_height - pad_size_height)
left_pad = tf.maximum(
0, cutout_center_width - pad_size_width)
right_pad = tf.maximum(
0, image_width - cutout_center_width - pad_size_width)
cutout_shape = [image_height - (lower_pad + upper_pad),
image_width - (left_pad + right_pad)]
padding_dims = [[lower_pad, upper_pad], [left_pad, right_pad]]
mask = tf.pad(
tf.zeros(cutout_shape, dtype=image.dtype),
padding_dims, constant_values=1)
mask = tf.expand_dims(mask, 2)
mask = tf.tile(mask, [1, 1, 3])
return mask, mean
def bbox_cutout(image, bboxes, pad_fraction, replace_with_mean):
"""Applies cutout to the image according to bbox information.
This is a cutout variant that using bbox information to make more informed
decisions on where to place the cutout mask.
Args:
image: 3D uint8 Tensor.
bboxes: 2D Tensor that is a list of the bboxes in the image. Each bbox
has 4 elements (min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x) of type float with values
between [0, 1].
pad_fraction: Float that specifies how large the cutout mask should be in
in reference to the size of the original bbox. If pad_fraction is 0.25,
then the cutout mask will be of shape
(0.25 * bbox height, 0.25 * bbox width).
replace_with_mean: Boolean that specified what value should be filled in
where the cutout mask is applied. Since the incoming image will be of
uint8 and will not have had any mean normalization applied, by default
we set the value to be 128. If replace_with_mean is True then we find
the mean pixel values across the channel dimension and use those to fill
in where the cutout mask is applied.
Returns:
A tuple. First element is a tensor of the same shape as image that has
cutout applied to it. Second element is the bboxes that were passed in
that will be unchanged.
"""
def apply_bbox_cutout(image, bboxes, pad_fraction):
"""Applies cutout to a single bounding box within image."""
# Choose a single bounding box to apply cutout to.
random_index = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[], maxval=tf.shape(bboxes)[0], dtype=tf.int32)
# Select the corresponding bbox and apply cutout.
chosen_bbox = tf.gather(bboxes, random_index)
mask, mean = _cutout_inside_bbox(image, chosen_bbox, pad_fraction)
# When applying cutout we either set the pixel value to 128 or to the mean
# value inside the bbox.
replace = mean if replace_with_mean else 128
# Apply the cutout mask to the image. Where the mask is 0 we fill it with
# `replace`.
image = tf.where(
tf.equal(mask, 0),
tf.cast(tf.ones_like(image, dtype=image.dtype) * replace,
dtype=image.dtype),
image)
return image
# Check to see if there are boxes, if so then apply boxcutout.
image = tf.cond(tf.equal(tf.size(bboxes), 0), lambda: image,
lambda: apply_bbox_cutout(image, bboxes, pad_fraction))
return image, bboxes
NAME_TO_FUNC = {
'AutoContrast': autocontrast,
'Equalize': equalize,
'Posterize': posterize,
'Solarize': solarize,
'SolarizeAdd': solarize_add,
'Color': color,
'Contrast': contrast,
'Brightness': brightness,
'Sharpness': sharpness,
'Cutout': cutout,
'BBox_Cutout': bbox_cutout,
'Rotate_BBox': rotate_with_bboxes,
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
'TranslateX_BBox': lambda image, bboxes, pixels, replace: translate_bbox(
image, bboxes, pixels, replace, shift_horizontal=True),
'TranslateY_BBox': lambda image, bboxes, pixels, replace: translate_bbox(
image, bboxes, pixels, replace, shift_horizontal=False),
'ShearX_BBox': lambda image, bboxes, level, replace: shear_with_bboxes(
image, bboxes, level, replace, shear_horizontal=True),
'ShearY_BBox': lambda image, bboxes, level, replace: shear_with_bboxes(
image, bboxes, level, replace, shear_horizontal=False),
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
'Rotate_Only_BBoxes': rotate_only_bboxes,
'ShearX_Only_BBoxes': shear_x_only_bboxes,
'ShearY_Only_BBoxes': shear_y_only_bboxes,
'TranslateX_Only_BBoxes': translate_x_only_bboxes,
'TranslateY_Only_BBoxes': translate_y_only_bboxes,
'Flip_Only_BBoxes': flip_only_bboxes,
'Solarize_Only_BBoxes': solarize_only_bboxes,
'Equalize_Only_BBoxes': equalize_only_bboxes,
'Cutout_Only_BBoxes': cutout_only_bboxes,
}
def _randomly_negate_tensor(tensor):
"""With 50% prob turn the tensor negative."""
should_flip = tf.cast(tf.floor(tf.random_uniform([]) + 0.5), tf.bool)
final_tensor = tf.cond(should_flip, lambda: tensor, lambda: -tensor)
return final_tensor
def _rotate_level_to_arg(level):
level = (level/_MAX_LEVEL) * 30.
level = _randomly_negate_tensor(level)
return (level,)
def _shrink_level_to_arg(level):
"""Converts level to ratio by which we shrink the image content."""
if level == 0:
return (1.0,) # if level is zero, do not shrink the image
# Maximum shrinking ratio is 2.9.
level = 2. / (_MAX_LEVEL / level) + 0.9
return (level,)
def _enhance_level_to_arg(level):
return ((level/_MAX_LEVEL) * 1.8 + 0.1,)
def _shear_level_to_arg(level):
level = (level/_MAX_LEVEL) * 0.3
# Flip level to negative with 50% chance.
level = _randomly_negate_tensor(level)
return (level,)
def _translate_level_to_arg(level, translate_const):
level = (level/_MAX_LEVEL) * float(translate_const)
# Flip level to negative with 50% chance.
level = _randomly_negate_tensor(level)
return (level,)
def _bbox_cutout_level_to_arg(level, hparams):
cutout_pad_fraction = (level/_MAX_LEVEL) * hparams.cutout_max_pad_fraction
return (cutout_pad_fraction,
hparams.cutout_bbox_replace_with_mean)
def level_to_arg(hparams):
return {
'AutoContrast': lambda level: (),
'Equalize': lambda level: (),
'Posterize': lambda level: (int((level/_MAX_LEVEL) * 4),),
'Solarize': lambda level: (int((level/_MAX_LEVEL) * 256),),
'SolarizeAdd': lambda level: (int((level/_MAX_LEVEL) * 110),),
'Color': _enhance_level_to_arg,
'Contrast': _enhance_level_to_arg,
'Brightness': _enhance_level_to_arg,
'Sharpness': _enhance_level_to_arg,
'Cutout': lambda level: (int((level/_MAX_LEVEL) * hparams.cutout_const),),
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
'BBox_Cutout': lambda level: _bbox_cutout_level_to_arg(
level, hparams),
'TranslateX_BBox': lambda level: _translate_level_to_arg(
level, hparams.translate_const),
'TranslateY_BBox': lambda level: _translate_level_to_arg(
level, hparams.translate_const),
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
'ShearX_BBox': _shear_level_to_arg,
'ShearY_BBox': _shear_level_to_arg,
'Rotate_BBox': _rotate_level_to_arg,
'Rotate_Only_BBoxes': _rotate_level_to_arg,
'ShearX_Only_BBoxes': _shear_level_to_arg,
'ShearY_Only_BBoxes': _shear_level_to_arg,
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
'TranslateX_Only_BBoxes': lambda level: _translate_level_to_arg(
level, hparams.translate_bbox_const),
'TranslateY_Only_BBoxes': lambda level: _translate_level_to_arg(
level, hparams.translate_bbox_const),
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
'Flip_Only_BBoxes': lambda level: (),
'Solarize_Only_BBoxes': lambda level: (int((level/_MAX_LEVEL) * 256),),
'Equalize_Only_BBoxes': lambda level: (),
# pylint:disable=g-long-lambda
'Cutout_Only_BBoxes': lambda level: (
int((level/_MAX_LEVEL) * hparams.cutout_bbox_const),),
# pylint:enable=g-long-lambda
}
def bbox_wrapper(func):
"""Adds a bboxes function argument to func and returns unchanged bboxes."""
def wrapper(images, bboxes, *args, **kwargs):
return (func(images, *args, **kwargs), bboxes)
return wrapper
def _parse_policy_info(name, prob, level, replace_value, augmentation_hparams):
"""Return the function that corresponds to `name` and update `level` param."""
func = NAME_TO_FUNC[name]
args = level_to_arg(augmentation_hparams)[name](level)
# Check to see if prob is passed into function. This is used for operations
# where we alter bboxes independently.
# pytype:disable=wrong-arg-types
if 'prob' in inspect.getargspec(func)[0]:
args = tuple([prob] + list(args))
# pytype:enable=wrong-arg-types
# Add in replace arg if it is required for the function that is being called.
if 'replace' in inspect.getargspec(func)[0]:
# Make sure replace is the final argument
assert 'replace' == inspect.getargspec(func)[0][-1]
args = tuple(list(args) + [replace_value])
# Add bboxes as the second positional argument for the function if it does
# not already exist.
if 'bboxes' not in inspect.getargspec(func)[0]:
func = bbox_wrapper(func)
return (func, prob, args)
def _apply_func_with_prob(func, image, args, prob, bboxes):
"""Apply `func` to image w/ `args` as input with probability `prob`."""
assert isinstance(args, tuple)
assert 'bboxes' == inspect.getargspec(func)[0][1]
# If prob is a function argument, then this randomness is being handled
# inside the function, so make sure it is always called.
if 'prob' in inspect.getargspec(func)[0]:
prob = 1.0
# Apply the function with probability `prob`.
should_apply_op = tf.cast(
tf.floor(tf.random_uniform([], dtype=tf.float32) + prob), tf.bool)
augmented_image, augmented_bboxes = tf.cond(
should_apply_op,
lambda: func(image, bboxes, *args),
lambda: (image, bboxes))
return augmented_image, augmented_bboxes
def select_and_apply_random_policy(policies, image, bboxes):
"""Select a random policy from `policies` and apply it to `image`."""
policy_to_select = tf.random_uniform([], maxval=len(policies), dtype=tf.int32)
# Note that using tf.case instead of tf.conds would result in significantly
# larger graphs and would even break export for some larger policies.
for (i, policy) in enumerate(policies):
image, bboxes = tf.cond(
tf.equal(i, policy_to_select),
lambda selected_policy=policy: selected_policy(image, bboxes),
lambda: (image, bboxes))
return (image, bboxes)
def build_and_apply_nas_policy(policies, image, bboxes,
augmentation_hparams):
"""Build a policy from the given policies passed in and apply to image.
Args:
policies: list of lists of tuples in the form `(func, prob, level)`, `func`
is a string name of the augmentation function, `prob` is the probability
of applying the `func` operation, `level` is the input argument for
`func`.
image: tf.Tensor that the resulting policy will be applied to.
bboxes:
augmentation_hparams: Hparams associated with the NAS learned policy.
Returns:
A version of image that now has data augmentation applied to it based on
the `policies` pass into the function. Additionally, returns bboxes if
a value for them is passed in that is not None
"""
replace_value = [128, 128, 128]
# func is the string name of the augmentation function, prob is the
# probability of applying the operation and level is the parameter associated
# with the tf op.
# tf_policies are functions that take in an image and return an augmented
# image.
tf_policies = []
for policy in policies:
tf_policy = []
# Link string name to the correct python function and make sure the correct
# argument is passed into that function.
for policy_info in policy:
policy_info = list(policy_info) + [replace_value, augmentation_hparams]
tf_policy.append(_parse_policy_info(*policy_info))
# Now build the tf policy that will apply the augmentation procedue
# on image.
def make_final_policy(tf_policy_):
def final_policy(image_, bboxes_):
for func, prob, args in tf_policy_:
image_, bboxes_ = _apply_func_with_prob(
func, image_, args, prob, bboxes_)
return image_, bboxes_
return final_policy
tf_policies.append(make_final_policy(tf_policy))
augmented_images, augmented_bboxes = select_and_apply_random_policy(
tf_policies, image, bboxes)
# If no bounding boxes were specified, then just return the images.
return (augmented_images, augmented_bboxes)
# TODO(barretzoph): Add in ArXiv link once paper is out.
def distort_image_with_autoaugment(image, bboxes, augmentation_name):
"""Applies the AutoAugment policy to `image` and `bboxes`.
Args:
image: `Tensor` of shape [height, width, 3] representing an image.
bboxes: `Tensor` of shape [N, 4] representing ground truth boxes that are
normalized between [0, 1].
augmentation_name: The name of the AutoAugment policy to use. The available
options are `v0`, `v1`, `v2`, `v3` and `test`. `v0` is the policy used for
all of the results in the paper and was found to achieve the best results
on the COCO dataset. `v1`, `v2` and `v3` are additional good policies
found on the COCO dataset that have slight variation in what operations
were used during the search procedure along with how many operations are
applied in parallel to a single image (2 vs 3).
Returns:
A tuple containing the augmented versions of `image` and `bboxes`.
"""
available_policies = {'v0': policy_v0, 'v1': policy_v1, 'v2': policy_v2,
'v3': policy_v3, 'test': policy_vtest}
if augmentation_name not in available_policies:
raise ValueError('Invalid augmentation_name: {}'.format(augmentation_name))
policy = available_policies[augmentation_name]()
# Hparams that will be used for AutoAugment.
augmentation_hparams = contrib_training.HParams(
cutout_max_pad_fraction=0.75,
cutout_bbox_replace_with_mean=False,
cutout_const=100,
translate_const=250,
cutout_bbox_const=50,
translate_bbox_const=120)
return build_and_apply_nas_policy(policy, image, bboxes, augmentation_hparams)