Paper reading: Realtime Multi-person 2D Pose estimation using Part Affinity Fields(1)
本论文有提供代码https://github.com/CMU-Perceptual-Computing-Lab/caffe_rtpose ,可运行。
以下为本人对文章的理解,如果有错误欢迎讨论,如转载请标明出处。
1。 Introduction
Pose estimation 的挑战:
1〉图像中不知道多少人,在什么位置,什么尺度
2〉人与人之间因接触,遮挡而变得复杂
3〉实时性的要求,图像中人越多,计算复杂度越大。
A common approach: person detection + pose estimation for each person (top->down)
问题: 1〉if person detector fails-> no recovery (人离得近的时候person detector很容易检测不到)
2〉计算时间和人数有关,人越多越耗时。
bottom up approaches 不存在以上两个问题。
但bottom up不直接受益于global information -〉关键是利用来自other body parts and other people的contextual cues(上下文线索)。
本文使用bottom up 的方法,but utilizes global contextual information in the detection of parts and their association。
本文提出Part Affinity Fields (PAFs), a set of 2D vector fields。每个2D vector field 会encode 一个limb(肢)的位置和方向。
这些fields(包含parts的连接和方向) 和 confidence maps for parts (关节的置信map)一起通过sequential prediction framework来jointly学习和预测。
confidence maps for parts和Part Affinity Fields 都是2D spatial grids, 可以表达unstructured, multimodal uncertainty hat arises due to occlusion and contact,而且可以用卷积分析。
-------
下面这句话,不太理解:
As the confidence maps and affinity fields encode global context in their prediction, they allow an efficient algorithm that uses greedy association over a minimum spanning tree without significant loss in the quality of pose estimates.
------
3.method
3.1. Confidence Maps for Part Detection
每一个body part (j)算一个confidence map。所以有多少个part(关节),就有多少个相对应part的confidence map。
图像区域中每个点都有一个confidence值,构成confidence map。
confidence map中每点的值与真值位置的距离有关,离得越近confidence 越高。
用高斯分布来描述,confidence峰值就是真值位置。
假设k个人,图像中每个人都有预测位置的confidence map,将k个人的confidence map的集合合成为一个confidence map时,取该点各个人的confidence的最大值。
这个看一下Figure2b应该就可以理解这个最大的意思,有点像取交集的感觉。
文章里说这里用max而不用average是为了:及时多个peak点离得很近,精度仍然不受影响。如图3a。
在test阶段,在预测的confidence maps上进行非极大值抑制来获得body part candidates.
--
[ps: 非极大值抑制,简称为NMS算法。是一种获取局部最大值的有效方法。非极大值抑制NMS在目标检测,定位等领域是一种被广泛使用的方法。对于目标具体位置定位过程,不管是使用sw(sliding Window)还是ss(selective search)方法,都会产生好多的候选区域。NMS,简单的说,对于有相交的就选取其中置信度最高的一个作为最后结果,对于没相交的就直接保留下来,作为最后结果。]
3.2. Part Affinity Fields for Part Association
有了body parts, 那么在不知道几个人的情况下怎么把这些body parts 组合成full-body pose (哪些parts是同一个人的)?
思路1(最终未使用):
任意两body parts之间是否相连接需要一个置信度(是否同一个人)的measurement.
那么,可以在两body parts之间连线的中间取n个点,计算它们的confidence map来作为measurement.
在limb(肢)上n个点的confidence maps中取最大的值合成limb(肢)c的confidence map-Sc。
使用midpoint 表达可能会因为多人重叠产生空间上的ambuigity(模能两可),如图4b是n=1的情况。
这种方法的局限是在于只使用了location信息,而忽略了limb的orientation信息。
为解决以上问题,提出了part affinity field.
思路2:part affinity field (本paper的核心贡献)
好处:location 和orientation信息都使用了。
每一种limb(肢)在关联的两个body part之间都有一个affinity field ,其中的每一个pixel都有一个2D vector描述方向。
affinity field map的维度是w*h*2 (因为vector是二维的)。
若某个点有多人重叠,则将k个人的vector求和,再除以人数。
在test时,confidence score的计算方法:
计算预测的PAF(vector)与candidate limb 方向的alignment (方向是否一致,用点积计算)。
3.3. Multi-Person Parsing using PAFs
这部分讲在得到了confidence map 和 part affinity fields后如何进行推理分析,也就是所谓的bottom-up算法。
先定义一些表达:
假设通过对confidence map进行极大值抑制,得到多个body part,每个body part 有多个detection candidate。 (图像中有多人,所以会有多个detection candidate)。
假设![]() 是第j个body part 的第m 个detection candidate的location.
是第j个body part 的第m 个detection candidate的location.
下面的z表示连接关系,目的是找到最优的可能连接方式。
找到两两body part 之间最优连接的问题:
就变成了a maximum weight bipartite graph matching 的问题,如图4a。
----
关于maximum weight bipartite graph matching problem:
可参考http://www.csie.ntnu.edu.tw/~u91029/Matching.html 来理解概念,具体求解的方法有很多,本paper使用Hungarian algorithm是链接中的匈牙利演算法。
[另外,paper 上的Refer:D. B. West et al. Introduction to graph theory, volume 2. Prentice hall Upper Saddle River, 2001. 4]
----
所以,变成graph问题后,可以这样理解:
graph的nodes就是body part detection candidates,
graph的edges就是所有可能的body part之间的connections,
每个edge上的weight就是公式7计算出来的part affinity aggregate.
A matching in a bipartite graph is a subset of the edges chosen in such a way that no two edges share an node.
就是找到权值最大的edge连接方式。
下面是数学表达式。
本paper使用Hungarian algorithm来获得最大匹配。
找到multiple persons的full body pose的问题就变成:
在K-partite graph 中求maximum weight cliques partition,如图5a。
(其实paper最终并没有做整个graph的 优化,而是作了简化。下面其实是为了解释简化是有道理的。)
-----
ps: 在英文的表达中,maximal clique和maximum 完全不同的。
团clique(clique)是一个无向图(undirected graph )的子图,该子图中任意两个顶点之间均存在一条边。
极大团maximal clique是一个团,该团不能被更大的团所包含,换句话说,再也不存在一个点与该团中的任意顶点之间存在一条边。
团的大小size是指一个团中包含的顶点数,size=k的团,称为k-团。
最大团maximum clique是指一个图中size最大的maximal clique。
求解上述的maximum weight cliques partition:This problem is NP hard [39] and many relaxations exist.
---
ps:关于NP hard可参考http://blog.csdn.net/bitcarmanlee/article/details/51935400
用通俗的话来解释,NP问题就是其解的正确性很容易被检验出来,这里的很容易检验指的是存在一个多项式算法。
----
本文中为优化增加了两个relaxation :
1.选择最少的edges形成tree skeleton(骨骼)of human pose,而不使用整个的graph
2.把cliques partition problem 分解成一系列的bipartite matching subproblems,然后独立地分析adjacent tree nodes之间的匹配。
然后paper中论述了为什么采用minimal greedy的算法(取每一小步的最优组成最终的最优)也包含着global inference over multiple person,大致意思是因为CNN本身有比较广泛的感受野,所以global的信息也在里面了。
(这里我的理解比较肤浅,其实就将求整体graph最优,简化为了求两两part连接最优。只要单独算出来的每个limb是最优的,组合在一起就是最优的。)
在这两个条件下,优化问题就简化成:
所以,通过公式(8)-(10)我们可以顺序获得每个limb(肢)的正确的correct candidates.
然后把share 同一part的limb集合在一起就得到了full-body pose。
3.4. Joint Learning Part Detection and Association with Sequential Prediction
loss方程:计算预测和理想值之间的L2 loss。(2个branch都是这么计算)
这里,loss方程有一个空间上的加权weight spatially,是因为有些数据集并没有完全标记所有的人,用其提供的mask说明有些区域可能包含unlabeled的人。
W是binary mask。在没标记的位置W为0。
下面是在第t个stage时的loss方程。
最终的目标函数是将各个stage的loss求和。
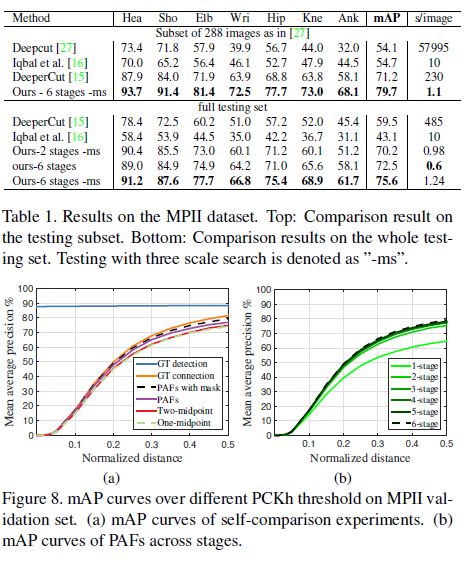
4. Result
在2个数据集上测试:1〉MPII 2〉MSCOCO2016
对尺度比较小的人检测效果不如其他算法。
It is the noteworthy that our method has won, but has lower accuracy than the top-down methods on people of smaller scales (APM). The reason is that our method has
to deal with a much larger scale range spanned by all people in the image in one shot. In contrast, top-down methods rescale the patch of each detected area to preferable size independently and thus suffer less from small people.