Tensorflow 卷积神经网络 Inception-v3模型 迁移学习 花朵识别
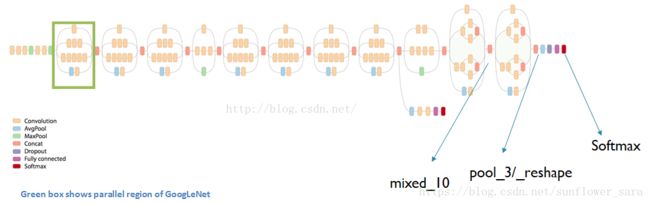
Inception-v3模型结构:
Inception-v3简介:
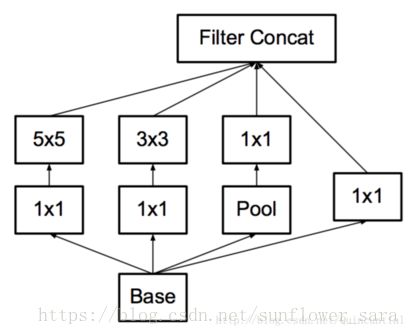
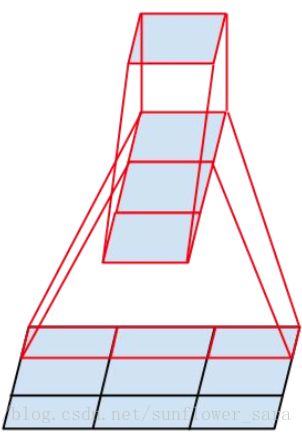
1.基于大滤波器尺寸分解卷积
在视觉网络中,预期相近激活的输出是高度相关的。因此,我们可以预期,它们的激活可以在聚合之前被减少,并且这应该会导致类似的富有表现力的局部表示。
全卷积网络 减少计算可以提高效率
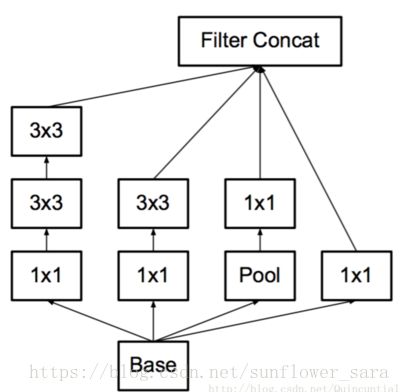
2.分解到更小的卷积
5×5换2个3×3
共享权重 减少参数数量
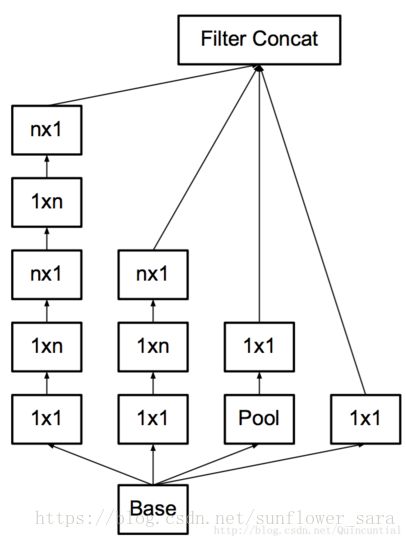
3.空间分解为不对称卷积
可以通过1×n卷积和后面接一个n×1卷积替换任何n×n卷积,并且随着n增长,计算成本节省显著增加
4 利用辅助分类器
辅助分类器起着正则化项的作用
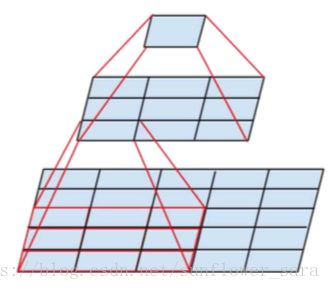
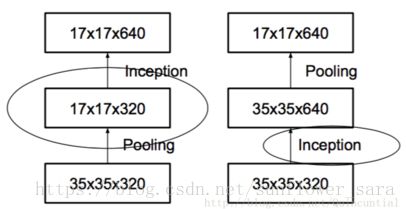
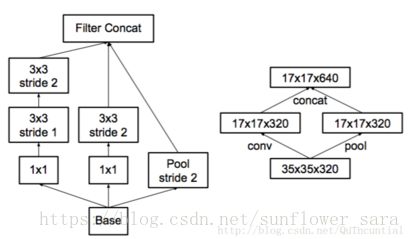
5 有效的网格尺寸减少
池化
先池化再卷积 产生瓶颈
先卷积再池化 计算效率变差
图10。缩减网格尺寸的同时扩展滤波器组的Inception模块。它不仅廉价并且避免了原则1中提出的表示瓶颈。右侧的图表示相同的解决方案,但是从网格大小而不是运算的角度来看。
7. 通过标签平滑进行模型正则化
谷歌提供的训练好的Inception-v3模型: https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/models/inception_dec_2015.zip
案例使用的数据集: http://download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz
数据集文件解压后,包含5个子文件夹,子文件夹的名称为花的名称,代表了不同的类别。平均每一种花有734张图片,图片是RGB色彩模式,大小也不相同。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Apr 24 10:11:28 2018
@author: admin
@author: tz_zs
卷积神经网络 Inception-v3模型 迁移学习
"""
import glob
import os.path
import random
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile
# inception-v3 模型瓶颈层的节点个数
BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE = 2048
# inception-v3 模型中代表瓶颈层结果的张量名称
BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME = 'pool_3/_reshape:0'
# 图像输入张量所对应的名称
JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME = 'DecodeJpeg/contents:0'
# 下载的谷歌训练好的inception-v3模型文件目录
#MODEL_DIR = '/path/to/model/google2015-inception-v3'
MODEL_DIR = 'E:/DeepLearning/Git/cnn/inception_dec_2015'
# 下载的谷歌训练好的inception-v3模型文件名
MODEL_FILE = 'tensorflow_inception_graph.pb'
# 保存训练数据通过瓶颈层后提取的特征向量
CACHE_DIR = 'tmp/bottleneck'
# 图片数据的文件夹
INPUT_DATA = 'E:/DeepLearning/Git/cnn/flower_photos'
#训练模型的保存地址
MODEL_SAVE_PATH="E:/DeepLearning/Git/cnn/model"
# 验证的数据百分比
VALIDATION_PERCENTAGE = 10
# 测试的数据百分比
TEST_PERCENTACE = 10
# 定义神经网路的设置
LEARNING_RATE = 0.01
STEPS = 200
BATCH = 100
# 这个函数把数据集分成训练,验证,测试三部分
def create_image_lists(testing_percentage, validation_percentage):
"""
这个函数把数据集分成训练,验证,测试三部分
:param testing_percentage:测试的数据百分比 10
:param validation_percentage:验证的数据百分比 10
:return:
"""
result = {}
# 获取目录下所有子目录
sub_dirs = [x[0] for x in os.walk(INPUT_DATA)]
# ['/path/to/flower_data', '/path/to/flower_data\\daisy', '/path/to/flower_data\\dandelion',
# '/path/to/flower_data\\roses', '/path/to/flower_data\\sunflowers', '/path/to/flower_data\\tulips']
# 数组中的第一个目录是当前目录,这里设置标记,不予处理
is_root_dir = True
for sub_dir in sub_dirs: # 遍历目录数组,每次处理一种
if is_root_dir:
is_root_dir = False
continue
# 获取当前目录下所有的有效图片文件
extensions = ['jpg', 'jepg', 'JPG', 'JPEG']
file_list = []
dir_name = os.path.basename(sub_dir) # 返回路径名路径的基本名称,如:daisy|dandelion|roses|sunflowers|tulips
for extension in extensions:
file_glob = os.path.join(INPUT_DATA, dir_name, '*.' + extension) # 将多个路径组合后返回
file_list.extend(glob.glob(file_glob)) # glob.glob返回所有匹配的文件路径列表,extend往列表中追加另一个列表
if not file_list: continue
# 通过目录名获取类别名称
label_name = dir_name.lower() # 返回其小写
# 初始化当前类别的训练数据集、测试数据集、验证数据集
training_images = []
testing_images = []
validation_images = []
for file_name in file_list: # 遍历此类图片的每张图片的路径
base_name = os.path.basename(file_name) # 路径的基本名称也就是图片的名称,如:102841525_bd6628ae3c.jpg
# 随机讲数据分到训练数据集、测试集和验证集
chance = np.random.randint(100)
if chance < validation_percentage:
validation_images.append(base_name)
elif chance < (testing_percentage + validation_percentage):
testing_images.append(base_name)
else:
training_images.append(base_name)
result[label_name] = {
'dir': dir_name,
'training': training_images,
'testing': testing_images,
'validation': validation_images
}
return result
# 这个函数通过类别名称、所属数据集和图片编号获取一张图片的地址
def get_image_path(image_lists, image_dir, label_name, index, category):
"""
:param image_lists:所有图片信息
:param image_dir:根目录 ( 图片特征向量根目录 CACHE_DIR | 图片原始路径根目录 INPUT_DATA )
:param label_name:类别的名称( daisy|dandelion|roses|sunflowers|tulips )
:param index:编号
:param category:所属的数据集( training|testing|validation )
:return: 一张图片的地址
"""
# 获取给定类别的图片集合
label_lists = image_lists[label_name]
# 获取这种类别的图片中,特定的数据集(base_name的一维数组)
category_list = label_lists[category]
mod_index = index % len(category_list) # 图片的编号%此数据集中图片数量
# 获取图片文件名
base_name = category_list[mod_index]
sub_dir = label_lists['dir']
# 拼接地址
full_path = os.path.join(image_dir, sub_dir, base_name)
return full_path
# 图片的特征向量的文件地址
def get_bottleneck_path(image_lists, label_name, index, category):
return get_image_path(image_lists, CACHE_DIR, label_name, index, category) + '.txt' # CACHE_DIR 特征向量的根地址
# 计算特征向量
def run_bottleneck_on_image(sess, image_data, image_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
"""
:param sess:
:param image_data:图片内容
:param image_data_tensor:
:param bottleneck_tensor:
:return:
"""
bottleneck_values = sess.run(bottleneck_tensor, {image_data_tensor: image_data})
bottleneck_values = np.squeeze(bottleneck_values)
return bottleneck_values
# 获取一张图片对应的特征向量的路径
def get_or_create_bottleneck(sess, image_lists, label_name, index, category, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
"""
:param sess:
:param image_lists:
:param label_name:类别名
:param index:图片编号
:param category:
:param jpeg_data_tensor:
:param bottleneck_tensor:
:return:
"""
label_lists = image_lists[label_name]
sub_dir = label_lists['dir']
sub_dir_path = os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, sub_dir) # 到类别的文件夹
if not os.path.exists(sub_dir_path): os.makedirs(sub_dir_path)
bottleneck_path = get_bottleneck_path(image_lists, label_name, index, category) # 获取图片特征向量的路径
if not os.path.exists(bottleneck_path): # 如果不存在
# 获取图片原始路径
image_path = get_image_path(image_lists, INPUT_DATA, label_name, index, category)
# 获取图片内容
image_data = gfile.FastGFile(image_path, 'rb').read()
# 计算图片特征向量
bottleneck_values = run_bottleneck_on_image(sess, image_data, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
# 将特征向量存储到文件
bottleneck_string = ','.join(str(x) for x in bottleneck_values)
with open(bottleneck_path, 'w') as bottleneck_file:
bottleneck_file.write(bottleneck_string)
else:
# 读取保存的特征向量文件
with open(bottleneck_path, 'r') as bottleneck_file:
bottleneck_string = bottleneck_file.read()
# 字符串转float数组
bottleneck_values = [float(x) for x in bottleneck_string.split(',')]
return bottleneck_values
# 随机获取一个batch的图片作为训练数据(特征向量,类别)
def get_random_cached_bottlenecks(sess, n_classes, image_lists, how_many, category, jpeg_data_tensor,
bottleneck_tensor):
"""
:param sess:
:param n_classes: 类别数量
:param image_lists:
:param how_many: 一个batch的数量
:param category: 所属的数据集
:param jpeg_data_tensor:
:param bottleneck_tensor:
:return: 特征向量列表,类别列表
"""
bottlenecks = []
ground_truths = []
for _ in range(how_many):
# 随机一个类别和图片编号加入当前的训练数据
label_index = random.randrange(n_classes)
label_name = list(image_lists.keys())[label_index] # 随机图片的类别名
image_index = random.randrange(65536) # 随机图片的编号
bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(sess, image_lists, label_name, image_index, category, jpeg_data_tensor,
bottleneck_tensor) # 计算此图片的特征向量
ground_truth = np.zeros(n_classes, dtype=np.float32)
ground_truth[label_index] = 1.0
bottlenecks.append(bottleneck)
ground_truths.append(ground_truth)
return bottlenecks, ground_truths
# 获取全部的测试数据
def get_test_bottlenecks(sess, image_lists, n_classes, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
bottlenecks = []
ground_truths = []
label_name_list = list(image_lists.keys()) # ['dandelion', 'daisy', 'sunflowers', 'roses', 'tulips']
for label_index, label_name in enumerate(label_name_list): # 枚举每个类别,如:0 sunflowers
category = 'testing'
for index, unused_base_name in enumerate(image_lists[label_name][category]): # 枚举此类别中的测试数据集中的每张图片
'''''
print(index, unused_base_name)
0 10386503264_e05387e1f7_m.jpg
1 1419608016_707b887337_n.jpg
2 14244410747_22691ece4a_n.jpg
...
105 9467543719_c4800becbb_m.jpg
106 9595857626_979c45e5bf_n.jpg
107 9922116524_ab4a2533fe_n.jpg
'''
bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(
sess, image_lists, label_name, index, category, jpeg_data_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
ground_truth = np.zeros(n_classes, dtype=np.float32)
ground_truth[label_index] = 1.0
bottlenecks.append(bottleneck)
ground_truths.append(ground_truth)
return bottlenecks, ground_truths
def main(_):
image_lists = create_image_lists(TEST_PERCENTACE, VALIDATION_PERCENTAGE)
n_classes = len(image_lists.keys())
# 读取模型
with gfile.FastGFile(os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, MODEL_FILE), 'rb') as f:
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
# 加载模型,返回对应名称的张量
bottleneck_tensor, jpeg_data_tensor = tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, return_elements=[BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME,
JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME])
# 输入
bottleneck_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE], name='BottleneckInputPlaceholder')
ground_truth_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes], name='GroundTruthInput')
# 全连接层
with tf.name_scope('final_training_ops'):
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE, n_classes], stddev=0.001))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n_classes]))
logits = tf.matmul(bottleneck_input, weights) + biases
final_tensor = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
# 损失
cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=ground_truth_input)
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
# 优化
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(LEARNING_RATE).minimize(cross_entropy_mean)
# 正确率
with tf.name_scope('evaluation'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(final_tensor, 1), tf.argmax(ground_truth_input, 1))
#sens_prediction = tf.equal(1-tf.argmax(final_tensor, 1), tf.argmax(ground_truth_input, 1))
#spec_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(final_tensor, 1), tf.argmax(ground_truth_input, 1))
# TP=sum(tf.argmax(final_tensor, 1), tf.argmax(ground_truth_input, 1))
evaluation_step = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
#saver=tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
# 初始化参数
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
print( sess.run(init))
for i in range(STEPS):
# 每次获取一个batch的训练数据
train_bottlenecks, train_ground_truth = get_random_cached_bottlenecks(sess, n_classes, image_lists, BATCH,
'training', jpeg_data_tensor,
bottleneck_tensor)
# 训练
sess.run(train_step,
feed_dict={bottleneck_input: train_bottlenecks, ground_truth_input: train_ground_truth})
# 验证
if i % 100 == 0 or i + 1 == STEPS:
validation_bottlenecks, validation_ground_truth = get_random_cached_bottlenecks(sess, n_classes,
image_lists, BATCH,
'validation',
jpeg_data_tensor,
bottleneck_tensor)
validation_accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict={bottleneck_input: validation_bottlenecks,
ground_truth_input: validation_ground_truth})
print('Step %d: Validation accuracy on random sampled %d examples = %.1f%%' % (
i, BATCH, validation_accuracy * 100))
# 测试
test_bottlenecks, test_ground_truth = get_test_bottlenecks(sess, image_lists, n_classes, jpeg_data_tensor,
bottleneck_tensor)
test_accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step,
feed_dict={bottleneck_input: test_bottlenecks, ground_truth_input: test_ground_truth})
print('Final test accuracy = %.1f%%' % (test_accuracy * 100))
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()