MATLAB 图像分割
7.1点检测
代码:
- tofloat函数:
function [out,revertclass] = tofloat(in) % tofloat将输入转换为浮点型,使用fft2将会导致标定的问题。 % revertclass将输出类型转化为和输入相同的类型 % 如果输入的图像不是single类型,tofloat将会将其转换为single类型 % % implement:将所有图像类型以及操作存储起来(cell),通过函数句柄,将 % 非double和single的函数进行转化,将其转化为single类型的函数(im2single) % % revertclass 通过im2xx将其转化为输入的类型 identity = @(x) x; tosingle = @im2single; table = {'uint8', tosingle, @im2uint8 'uint16',tosingle,@im2uint16 'int16',tosingle,@im2uint16 'logical',tosingle,@logical 'double',identity,identity 'single',identity,identity}; classIndex = find(strcmp(class(in),table(:,1))); % class(in) return the type of the input image, then compare with % the first column in the table(cell). if isempty(classIndex) error('Unsupported input image class'); end % determine whether to find out = table{classIndex,2}(in); revertclass=table{classIndex,3};实验代码:
7.2检测指定方向的线
代码:
clc
clear
f=imread('Fig1004(a).tif')
subplot(321);imshow(f)
w=[2 -1 -1;-1 2 -1;-1 -1 2];
g=imfilter(tofloat(f),w);
subplot(322);imshow(g,[])
gtop=g(1:120,1:120);%Top,left section.
gtop=pixeldup(gtop,4);%Enlarge by pixel duplication.
subplot(323);imshow(gtop,[])
gbot =g(end - 119:end, end-119:end);
gbot=pixeldup(gbot,4);
subplot(324);imshow(gbot,[])
g=abs(g);
subplot(325);imshow(g,[])
T=max(g(:));
g=g>=T;
subplot(326);imshow(g)
7.3使用Sobel边缘检测器
代码:
f = imread("Fig1006(a).tif"); % 图像大小:486×486
subplot(3,2,1),imshow(f),title('(a)原始图像');
[gv, t] = edge(f,'sobel','vertical');
subplot(3,2,2),imshow(gv),title('(b)Sobel模板处理后结果');
gv = edge(f, 'sobel', 0.15, 'vertical');
subplot(3,2,3),imshow(gv),title('(c)使用指定阈值的结果');
gboth = edge(f, 'sobel', 0.15);
subplot(3,2,4),imshow(gboth),title('(d)指点阈值确定垂直边缘和水平边缘的结果');
w45 = [-2 -1 0;-1 0 1; 0 1 2];
g45 = imfilter(double(f), w45, 'replicate');
T = 0.3 * max(abs(g45(:)));
g45 = g45 >= T;
subplot(3,2,5),imshow(g45),title('(e)-45°方向边缘');
f45= [0 1 2;-1 0 1;-2 -1 0];
h45= imfilter(double(f), f45,'replicate');
T = 0.3 * max(abs(h45(:)));
h45 = h45 >= T;
subplot(3,2,6),imshow(h45),title('(f)+45°方向边缘');
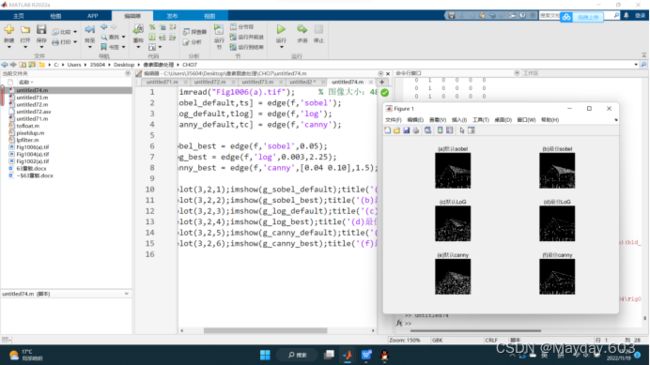
7.4Sobel、LoG和Canny边缘检测器的比较
代码:
f = imread("Fig1006(a).tif"); % 图像大小:486×486
[g_sobel_default,ts] = edge(f,'sobel');
[g_log_default,tlog] = edge(f,'log');
[g_canny_default,tc] = edge(f,'canny');
g_sobel_best = edge(f,'sobel',0.05);
g_log_best = edge(f,'log',0.003,2.25);
g_canny_best = edge(f,'canny',[0.04 0.10],1.5);
subplot(3,2,1);imshow(g_sobel_default);title('(a)默认sobel');
subplot(3,2,2);imshow(g_sobel_best);title('(b)最佳sobel');
subplot(3,2,3);imshow(g_log_default);title('(c)默认LoG');
subplot(3,2,4);imshow(g_log_best);title('(d)最佳LoG');
subplot(3,2,5);imshow(g_canny_default);title('(e)默认canny');
subplot(3,2,6);imshow(g_canny_best);title('(f)最佳canny');
7.5霍夫变换的说明
代码:
f=zeros(101,101);
f(1,1) =1;f(101,1) = 1;f(1,101) = 1;
f(101,101)=1;f(51,51)=1;
subplot(221),imshow(f)
H=hough(f);
subplot(222),imshow(H,[])
[H,theta,rho]=hough(f);
subplot(223),imshow(H,[],'XData',theta,'YData',rho,'InitialMagnification','fit')
axis on,axis normal
xlabel('\theta'),ylabel('\rho')
7.6使用霍夫变换做检测和连接
代码:
f=g_canny_best
[H,theta,rho]=hough(f,'ThetaResolution',0.2);
imshow(H,[],'XData',theta,'YData',rho,'InitialMagnification','fit')
axis on,axis normal
xlabel('\theta'),ylabel('\rho')
peaks=houghpeaks(H,5);
hold on
plot(theta(peaks(:,2)),rho(peaks(:,1)), ...
'LineStyle','none','marker','s','color','w')
lines=houghlines(f,theta,rho,peaks);
figure,imshow(f),hold on
for k=1:length(lines)
xy=[lines(k).point1;lines(k).point2];
plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),'LineWidth',4,'Color',[.8 .8 .8]);
end
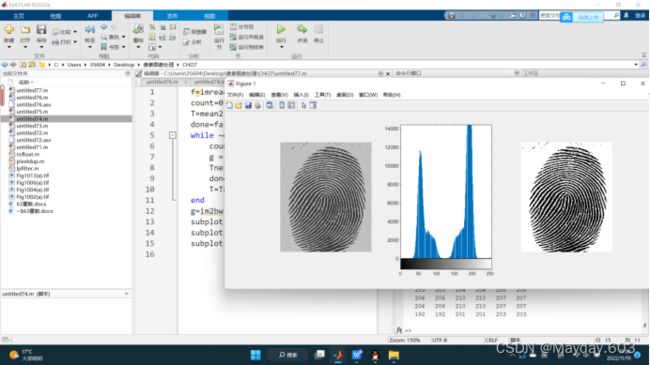
7.7计算全局阈值
代码:
f=imread('Fig1013(a).tif')
count=0;
T=mean2(f);
done=false;
while ~done
count=count+1;
g = f> T;
Tnext=0.5*(mean(f(g))+mean(f(~g)));
done=abs(T-Tnext)<0.5;
T=Tnext;
end
g=im2bw(f,T/255);
subplot(131),imshow(f)
subplot(132),imhist(f)
subplot(133),imshow(g)
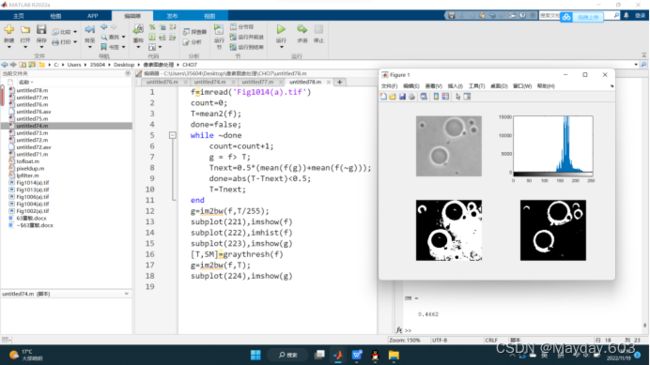
7.8使用Otsu方法和基本全局阈值处理方法分割图像的比较
代码:
f=imread('Fig1014(a).tif')
count=0;
T=mean2(f);
done=false;
while ~done
count=count+1;
g = f> T;
Tnext=0.5*(mean(f(g))+mean(f(~g)));
done=abs(T-Tnext)<0.5;
T=Tnext;
end
g=im2bw(f,T/255);
subplot(221),imshow(f)
subplot(222),imhist(f)
subplot(223),imshow(g)
[T,SM]=graythresh(f)
g=im2bw(f,T);
subplot(224),imshow(g)
7.9使用基于梯度的边缘信息改进全局阈值处理
otsuthresh函数:
function [T,SM]=otsuthresh(h)
h=h/sum(h);
h=h(:);
i=(1:numel(h))';
P1=cumsum(h);
m=cumsum(i.*h);
mG=m(end);
sigSquared=((mG*P1-m).^2)./(P1.*(1-P1)+eps);
maxSigsq=max(sigSquared);
T=mean(find(sigSquared==maxSigsq));
T=(T-1)/(numel(h)-1);
SM=maxSigsq / (sum(((i-mG).^2).*h)+eps);
代码:
f = tofloat(imread("Fig1016(a).tif"));
subplot(231),imshow(f),title('原图像');
subplot(232),imhist(f),title('原图像直方图');
sx = fspecial('sobel');
sy = sx';
gx = imfilter(f,sx,'replicate');
gy = imfilter(f,sy,'replicate');
grad = sqrt(gx.*gx+gy.*gy);
grad = grad/max(grad(:));
h =imhist(grad);
Q = percentile2i(h,0.999);
markerImage = grad>Q;
subplot(233),imshow(markerImage),title('以99.9%进行阈值处理后的梯度幅值图像');
fp = f.*markerImage;
subplot(234),imshow(fp),title('原图像与梯度幅值乘积的图像');
hp = imhist(fp);
hp(1) = 0;
subplot(235),bar(hp),title('原图像与梯度幅值乘积的直方图');
T = otsuthresh(hp);
T*(numel(hp)-1)
g = im2bw(f,T);
subplot(236),imshow(g),title('改进边缘后的图像')
-
7.10使用拉普拉斯算子边缘信息来改进全局阈值处理
代码:
f = tofloat(imread("Fig1017(a).tif"));
subplot(231),imshow(f),title('原始图像');
subplot(232),imhist(f),title('原始图像的直方图');
hf = imhist(f);
[Tf SMf] = graythresh(f);
gf = im2bw(f,Tf);
subplot(233),imshow(gf),title('对原始图像进行分割的图像');
w= [-1 -1 -1;-1 8 -1;-1 -1 -1];
lap = abs(imfilter(f,w,'replicate'));
lap = lap/max(lap(:));
h = imhist(lap);
Q = percentile2i(h,0.995);
markerImage = lap >Q;
fp = f.*markerImage;
subplot(234),imshow(fp),title('标记图像与原图像的乘积');
hp = imhist(fp);
hp(1) =0;
subplot(235),bar(hp)
T = otsuthresh(hp);
g = im2bw(f,T);a
subplot(236),imshow(g),title('修改边缘后的阈值处理图像')
7.11全局和局部阈值处理的比较
localmean函数:
function mean=localmean(f,nhood)
if nargin==1
nhood=ones(3)/9;
else
nhood=nhood/sum(nhood(:));
end
mean=imfilter(tofloat(f),nhood,'replicate');
end
代码:
f = tofloat(imread("Fig1018(a).tif"));
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(f);title('(a) 酵母细胞的图像');
[TGlobal] = graythresh(f);
gGlobal = im2bw(f, TGlobal);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(gGlobal);title('(b)用 Otsus 方法分割的图像');
g = localthresh(f, ones(3), 30, 1.5, 'global');
SIG = stdfilt(f, ones(3));
subplot(2,2,3), imshow(SIG, [ ]) ;title('(c) 局部标准差图像');
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(g);title('(d) 用局部阈值处理分割的图像 ');
-
7.12使用移动平均的图像阈值处理
localthresh函数:
function g=localthresh(f,nhood,a,b,meantype)
f=tofloat(f);
SIG=stdfilt(f,nhood);
if nargin==5 && strcmp(meantype,'global')
MEAN=mean2(f);
else
MEAN=localmean(f,nhood);
end
g=(f>a*SIG) & (f>b*MEAN);
end
代码:
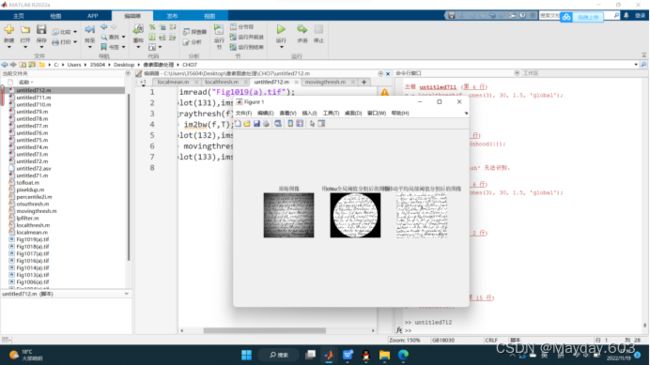
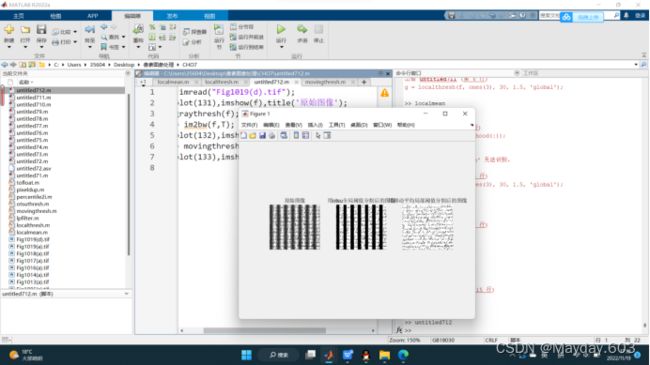
f = imread("Fig1019(d).tif");
subplot(131),imshow(f),title('原始图像');
T =graythresh(f);
g1 = im2bw(f,T);
subplot(132),imshow(g1),title('用otsu全局阈值分割后的图像');
g2 = movingthresh(f,20,0.5);
subplot(133),imshow(g2),title('用移动平均局部阈值分割后的图像');
7.13用区域生长检测焊接空隙
regiongrow函数:
function [g,NR,SI,TI]=regiongrow(f,S,T)
f=tofloat(f);
if numel(S)==1
SI=f==S;
S1=S;
else
SI=bwmorph(3,'shrink',Inf);
S1=f(SI);
end
TI=false(size(f));
for K=1:length(S1)
seedvalue=S1(K);
S=abs(f-seedvalue)<=T;
TI=TI|S;
end
[g,NR]=bwlabel(imreconstruct(SI,TI));
代码:
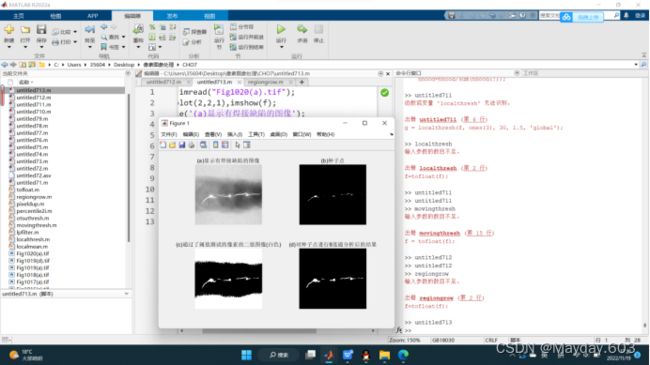
f = imread("Fig1020(a).tif");
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(f);
title('(a)显示有焊接缺陷的图像');
%函数regiongrow返回的NR为是不同区域的数目,参数SI是一副含有种子点的图像
%TI是包含在经过连通前通过阈值测试的像素
[g,NR,SI,TI]=regiongrow(f,1,0.26);%种子的像素值为255,65为阈值
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(SI);
title('(b)种子点');
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(TI);
title('(c)通过了阈值测试的像素的二值图像(白色)');
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(g);
title('(d)对种子点进行8连通分析后的结果');
7.14使用区域分离和聚合的图像分割
splitmerge函数:
function g=splitmerge(f,mindim,fun)%f是待分割的原图,mindim是定义分解中所允许的最小的块,必须是2的正整数次幂
Q=2^nextpow2(max(size(f)));
[M,N]=size(f);
f=padarray(f,[Q-M,Q-N],'post');%:填充图像或填充数组。f是输入图像,输出是填充后的图像,先将图像填充到2的幂次以使后面的分解可行
%然后是填充的行数和列数,post:表示在每一维的最后一个元素后填充,B = padarray(A,padsize,padval,direction)
%不含padval就用0填充,Q代表填充后图像的大小。
S=qtdecomp(f,@split_test,mindim,fun);%S传给split_test,qtdecomp divides a square image into four
% equal-sized square blocks, and then tests each block to see if it
% meets some criterion of homogeneity. If a block meets the criterion,
% it is not divided any further. If it does not meet the criterion,
% it is subdivided again into four blocks, and the test criterion is
% applied to those blocks. This process is repeated iteratively until
% each block meets the criterion. The result can have blocks of several
% different sizes.S是包含四叉树结构的稀疏矩阵,存储的值是块的大小及坐标,以稀疏矩阵形式存储
Lmax=full(max(S(:)));%将以稀疏矩阵存储形式存储的矩阵变换成以普通矩阵(full matrix)形式存储,full,sparse只是存储形式的不同
g=zeros(size(f));
MARKER=zeros(size(f));
for k=1:Lmax
[vals,r,c]=qtgetblk(f,S,k);%vals是一个数组,包含f的四叉树分解中大小为k*k的块的值,是一个k*k*个数的矩阵,
%个数是指S中有多少个这样大小的块,f是被四叉树分的原图像,r,c是对应的左上角块的坐标如2*2块,代表的是左上角开始块的坐标
if ~isempty(vals)
for I=1:length(r)
xlow=r(I);
ylow=c(I);
xhigh=xlow+k-1;
yhigh=ylow+k-1;
region=f(xlow:xhigh,ylow:yhigh);%找到对应的区域
flag=feval(fun,region);%evaluates the function handle, fhandle,using arguments x1 through xn.执行函数fun,region是参数
if flag%如果返回的是1,则进行标记
g(xlow:xhigh,ylow:yhigh)=1;%然后将对应的区域置1
MARKER(xlow,ylow)=1;%MARKER矩阵对应的左上角坐标置1
end
end
end
end
g=bwlabel(imreconstruct(MARKER,g));%imreconstruct默认2D图像8连通,这个函数就是起合的作用
g=g(1:M,1:N);%返回原图像的大小
代码:
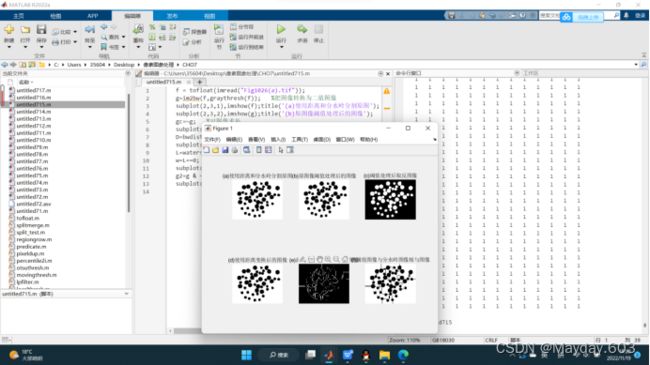
f = imread("Fig1023(a).tif");
subplot(231),imshow(f),title('原始图像');
g32 = splitmerge(f,32,@predicate) %使用最小块为32进行分割
subplot(232),imshow(g32),title('使用最小块为32进行分割图像');
g16 = splitmerge(f,16,@predicate) %使用最小块为16进行分割
subplot(233),imshow(g16),title('使用最小块为16进行分割图像');
g8= splitmerge(f,8,@predicate) %使用最小块为8进行分割
subplot(234),imshow(g8),title('使用最小块为8进行分割图像');
g4 = splitmerge(f,4,@predicate) %使用最小块为4进行分割
subplot(235),imshow(g4),title('使用最小块为4进行分割图像');
g2 = splitmerge(f,2,@predicate) %使用最小块为2进行分割
subplot(236),imshow(g2),title('使用最小块为2进行分割图像');
7.15使用距离和分水岭变换分割二值图像
代码:
f = tofloat(imread("Fig1026(a).tif"));
g=im2bw(f,graythresh(f)); %把图像转换为二值图像
subplot(2,3,1),imshow(f);title('(a)使用距离和分水岭分割原图');
subplot(2,3,2),imshow(g);title('(b)原图像阈值处理后的图像');
gc=~g; %对图像求补
subplot(2,3,3),imshow(gc),title('(c)阈值处理后取反图像');
D=bwdist(gc); %计算其距离变换
subplot(2,3,4),imshow(D),title('(d)使用距离变换后的图像');
L=watershed(-D); %计算负距离变换的分水岭变换
w=L==0; %L 的零值即分水岭的脊线像素
subplot(2,3,5),imshow(w),title('(e)距离变换后的负分水岭图像');
g2=g & ~w; %原始二值图像和图像 w 的 “补” 的逻辑 “与” 操作可完成分割
subplot(2,3,6),imshow(g2),title('(f)阈值图像与分水岭图像相与图像');
7.16使用梯度和分水岭变换分割灰度图像
代码:
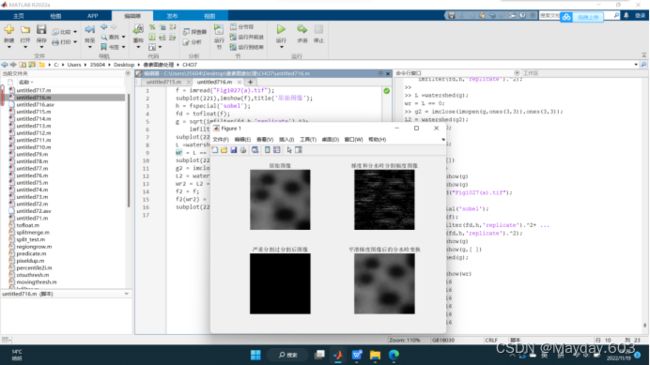
f = imread("Fig1027(a).tif");
subplot(221),imshow(f),title('原始图像');
h = fspecial('sobel');
fd = tofloat(f);
g = sqrt(imfilter(fd,h,'replicate').^2+ ...
imfilter(fd,h,'replicate').^2);
subplot(222),imshow(g,[]),title('梯度和分水岭分割幅度图像');
L =watershed(g);
wr = L == 0;
subplot(223),imshow(wr),title('严重分割过分割后图像');
g2 = imclose(imopen(g,ones(3,3)),ones(3,3));
L2 = watershed(g2);
wr2 = L2 == 0;
f2 = f;
f2(wr2) = 255;
subplot(224),imshow(f2),title('平滑梯度图像后的分水岭变换');
7.17标记符控制的分水岭分割示例
代码:
f = imread("Fig1028(a).tif");
subplot(241),imshow(f),title('原始图像');
h = fspecial('sobel');
fd = tofloat(f);
g = sqrt(imfilter(fd,h,'replicate').^2+imfilter(fd,h,'replicate').^2);
L =watershed(g);
wr = L == 0;
subplot(242),imshow(wr),title('梯度幅度图像进行分水岭变换图像');
rm = imregionalmin(g); %计算图像中所有的局部小区域的位置
subplot(243),imshow(rm),title('梯度幅值的局部小区域图像');
im = imextendedmin(f,2); %用于计算比临近点更暗的图像中“低点”的集合
fim = f;
fim(im) = 175;
subplot(244),imshow(f,[]),title('内部标记符图像');
Lim = watershed(bwdist(im));
em = Lim == 0;
subplot(245),imshow(em,[]),title('外部标记符图像');
g2 = imimposemin(g,im|em); %用来修改一幅图像,使得其只在指定的位置处取得局部最小值
subplot(246),imshow(g2),title('修改后的梯度幅值图像');
L2 = watershed(g2);
f2 = f;
f2(L2 == 0) = 255;
subplot(247),imshow(f2),title('最后的分割图像');