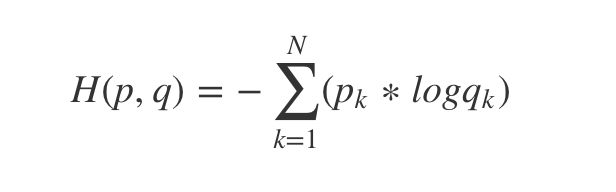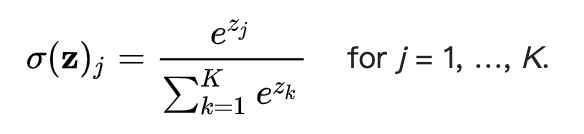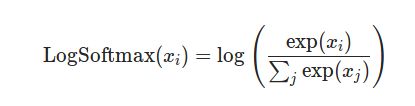pytorch中交叉熵nn.BCELoss与nn.CrossEntropyLoss的区别
参考:https://www.jb51.net/article/181634.htm
简单总结
nn.BCELoss
用于二分类问题,前面应该加一个Sigmoid函数(如下)
![]()

当S(x)=0.5,它的斜率是最大,则在x=0时取得最大斜率

nn.CrossEntropyLoss :自动在前面有Sofrmax层
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/watermelon1123/article/details/91044856,
https://blog.csdn.net/liangjiu2009/article/details/107769512(计算过程)
计算
import os
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda()
y_pred = torch.tensor([[ 5.0060, 1.3594, -0.4604, 0.3486, 0.3273, 0.7445, 0.7974, -0.6486,
-0.5508, -0.6279, 2.7097, 1.7399, 1.4096, 1.0342, 1.4090, 0.5836,
0.7386, 0.6439, 0.2210, 1.4657, -0.8205, -0.2882, -1.3240, 0.1541,
-0.2943, -1.2346, -0.3386, -0.2060, -0.6794, -0.8053, 0.0475, -1.6140,
-1.5633, -1.5470, -1.3992, -1.3593, -1.5412, -1.2203]],
device='cuda:0',)
l = torch.tensor([0], device='cuda:0')
logsoftmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
lsm_a = logsoftmax(y_pred )
# print(logsoftmax(y_pred[j]))
nll = nn.NLLLoss()
ce = nll(lsm_a, l)
print('ce::', ce)
loss = criterion(y_pred, l)
print(loss)
1、而实际计算,先整个计算过程如参考链接中所示,下面是将输出进行softmax后的结果
2、对softmax的结果进行log和取反
对公式最后变形的理解

上面图片的公式算是简化之后的,对于交叉熵的预测结果使用one-hot编码方式,例如,预测输入的东西是三类中的哪一个,标签中会只有一个是1,其他都是0,例如三类预测分别是猫、狗、兔,若这是狗想预测为狗则标签为[0,1,0],但在函数中只要写(假设是一个单通道的图片,),红色框中表示预测值中和输出标签为1相同索引位置的值,交叉熵最后和这个值相等,因为不是只有一个位置是1标签,其他都是0,累加过程中无用,
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda()
# 这个标签的1表示值是1的索引,相当于上面例子中[0,1,0]
loss = criterion(y_pred, [1])