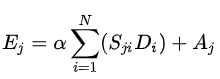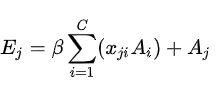DANet网络结构代码
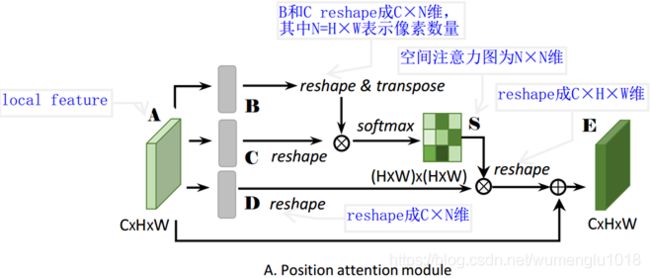
α表示尺度系数,初始化为0,并逐渐地学习分配到更大的权重。每个位置的结果特征E,是所有位置和原始位置的加权和。因此它具有全局上下文视图,并能根据空间注意力图有选择地聚合上下文。
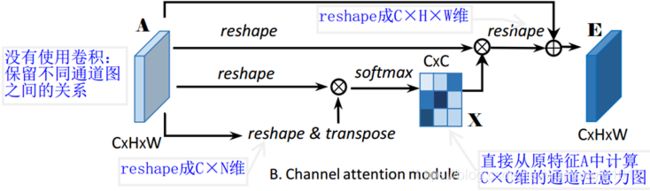
β表示尺度系数,初始化为0,并逐渐地学习分配到更大的权重。每个通道的结果特征E,是所有通道特征和原始特征的加权和。实现了对特征图之间的长程语义依赖关系建模,有助于提高特征的辨别性。
import numpy as np
import torch
import math
from torch.nn import Module, Sequential, Conv2d, ReLU,AdaptiveMaxPool2d, AdaptiveAvgPool2d, \
NLLLoss, BCELoss, CrossEntropyLoss, AvgPool2d, MaxPool2d, Parameter, Linear, Sigmoid, Softmax, Dropout, Embedding
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
torch_ver = torch.__version__[:3]
__all__ = ['PAM_Module', 'CAM_Module']
class PAM_Module(Module):
""" Position attention module"""
#Ref from SAGAN
def __init__(self, in_dim):
super(PAM_Module, self).__init__()
self.chanel_in = in_dim
# 先经过3个卷积层生成3个新特征图B C D (尺寸不变)
self.query_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1)
self.key_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1)
self.value_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim, kernel_size=1)
self.gamma = Parameter(torch.zeros(1)) # α尺度系数初始化为0,并逐渐地学习分配到更大的权重
self.softmax = Softmax(dim=-1) # 对每一行进行softmax
def forward(self, x):
"""
inputs :
x : input feature maps( B × C × H × W)
returns :
out : attention value + input feature
attention: B × (H×W) × (H×W)
"""
m_batchsize, C, height, width = x.size()
# B -> (N,C,HW) -> (N,HW,C)
proj_query = self.query_conv(x).view(m_batchsize, -1, width*height).permute(0, 2, 1)
# C -> (N,C,HW)
proj_key = self.key_conv(x).view(m_batchsize, -1, width*height)
# BC,空间注意图 -> (N,HW,HW)
energy = torch.bmm(proj_query, proj_key)
# S = softmax(BC) -> (N,HW,HW)
attention = self.softmax(energy)
# D -> (N,C,HW)
proj_value = self.value_conv(x).view(m_batchsize, -1, width*height)
# DS -> (N,C,HW)
out = torch.bmm(proj_value, attention.permute(0, 2, 1)) # torch.bmm表示批次矩阵乘法
# output -> (N,C,H,W)
out = out.view(m_batchsize, C, height, width)
out = self.gamma*out + x
return out
class CAM_Module(Module):
""" Channel attention module"""
def __init__(self, in_dim):
super(CAM_Module, self).__init__()
self.chanel_in = in_dim
self.gamma = Parameter(torch.zeros(1)) # β尺度系数初始化为0,并逐渐地学习分配到更大的权重
self.softmax = Softmax(dim=-1) # 对每一行进行softmax
def forward(self,x):
"""
inputs :
x : input feature maps( B × C × H × W)
returns :
out : attention value + input feature
attention: B × C × C
"""
m_batchsize, C, height, width = x.size()
# A -> (N,C,HW)
proj_query = x.view(m_batchsize, C, -1)
# A -> (N,HW,C)
proj_key = x.view(m_batchsize, C, -1).permute(0, 2, 1)
# 矩阵乘积,通道注意图:X -> (N,C,C)
energy = torch.bmm(proj_query, proj_key)
# 这里实现了softmax用最后一维的最大值减去了原始数据,获得了一个不是太大的值
# 沿着最后一维的C选择最大值,keepdim保证输出和输入形状一致,除了指定的dim维度大小为1
# expand_as表示以复制的形式扩展到energy的尺寸
energy_new = torch.max(energy, -1, keepdim=True)[0].expand_as(energy)-energy
attention = self.softmax(energy_new)
# A -> (N,C,HW)
proj_value = x.view(m_batchsize, C, -1)
# XA -> (N,C,HW)
out = torch.bmm(attention, proj_value)
# output -> (N,C,H,W)
out = out.view(m_batchsize, C, height, width)
out = self.gamma*out + x
return out
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
module = CAM_Module()
in_data = torch.randint(0, 255, (2, 3, 7, 7), dtype=torch.float32)
print(module(in_data).size())
'''融合代码如下 :
class DANetHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, norm_layer):
super(DANetHead, self).__init__()
inter_channels = in_channels // 4 # in_channels=2018,通道数缩减为512
self.conv5a = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, inter_channels, 3, padding=1, bias=False), norm_layer(inter_channels), nn.ReLU())
self.conv5c = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, inter_channels, 3, padding=1, bias=False), norm_layer(inter_channels), nn.ReLU())
self.sa = PAM_Module(inter_channels) # 空间注意力模块
self.sc = CAM_Module(inter_channels) # 通道注意力模块
self.conv51 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, inter_channels, 3, padding=1, bias=False), norm_layer(inter_channels), nn.ReLU())
self.conv52 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inter_channels, inter_channels, 3, padding=1, bias=False), norm_layer(inter_channels), nn.ReLU())
# nn.Dropout2d(p,inplace):p表示将元素置0的概率;inplace若设置为True,会在原地执行操作。
self.conv6 = nn.Sequential(nn.Dropout2d(0.1, False), nn.Conv2d(512, out_channels, 1)) # 输出通道数为类别的数目
self.conv7 = nn.Sequential(nn.Dropout2d(0.1, False), nn.Conv2d(512, out_channels, 1))
self.conv8 = nn.Sequential(nn.Dropout2d(0.1, False), nn.Conv2d(512, out_channels, 1))
def forward(self, x):
# 经过一个1×1卷积降维后,再送入空间注意力模块
feat1 = self.conv5a(x)
sa_feat = self.sa(feat1)
# 先经过一个卷积后,再使用有dropout的1×1卷积输出指定的通道数
sa_conv = self.conv51(sa_feat)
sa_output = self.conv6(sa_conv)
# 经过一个1×1卷积降维后,再送入通道注意力模块
feat2 = self.conv5c(x)
sc_feat = self.sc(feat2)
# 先经过一个卷积后,再使用有dropout的1×1卷积输出指定的通道数
sc_conv = self.conv52(sc_feat)
sc_output = self.conv7(sc_conv)
feat_sum = sa_conv+sc_conv # 两个注意力模块结果相加
sasc_output = self.conv8(feat_sum) # 最后再送入1个有dropout的1×1卷积中
output = [sasc_output]
output.append(sa_output)
output.append(sc_output)
return tuple(output) # 输出模块融合后的结果,以及两个模块各自的结果