【目标检测算法】YOLO-V5网络框架与代码分析
文章目录
- 一 YOLOv5网络架构与组件
-
- 1.1 Focus模块
- 1.2 CSPNet模块
- 1.3 SPP (Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
- 1.4 PANet(Path-Aggregation Network)
- 二 YOLOv5代码
-
- 2.1 激活函数及代码
- 2.2 网络组件代码
-
- 池化自动扩充
- 标准卷积:conv+BN+Silu
- Bottleneck模块
- CSP模块
- SPP模块 空间金字塔池化
- Focus模块
- 2.3 数据集创建相关代码
-
- letterbox代码
- 数据增强
- 2.4 general代码
-
- AP值计算
- loss计算
以YOLOv5s为例进行分析。
一 YOLOv5网络架构与组件
YOLOv5 包括:(代码中并没有划分出颈部)
- Input:Mosaic数据增强
- Backbone:Focus, BottleneckCSP, SPP
- Head:PANet + Detect (YOLOv3/v4 Head)
利用Netron可以实现网络结构的在线审视。
同时注意,需要利用Yolov5代码中models/export.py将四种模型的pt文件转换成对应的onnx文件后,再使用netron工具查看。
参考:网络可视化工具netron详细安装流程
这里只截取一部分:

新版的yolo里好像没有export文件,不过粘贴复制旧版的export也可以使用:
import argparse
import sys
import time
sys.path.append('./') # to run '$ python *.py' files in subdirectories
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import models
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.activations import Hardswish, SiLU
from utils.general import set_logging, check_img_size
from utils.torch_utils import select_device
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='./yolov5n.pt', help='weights path') # from yolov5/models/
parser.add_argument('--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640, 640], help='image size') # height, width
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=1, help='batch size')
parser.add_argument('--dynamic', action='store_true', help='dynamic ONNX axes')
parser.add_argument('--grid', action='store_true', help='export Detect() layer grid')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cpu', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.img_size *= 2 if len(opt.img_size) == 1 else 1 # expand
print(opt)
set_logging()
t = time.time()
# Load PyTorch model
device = select_device(opt.device)
model = attempt_load(opt.weights) # load FP32 model
# model = attempt_load(opt.weights, map_location=device) # load FP32 model
labels = model.names
# Checks
gs = int(max(model.stride)) # grid size (max stride)
opt.img_size = [check_img_size(x, gs) for x in opt.img_size] # verify img_size are gs-multiples
# Input
img = torch.zeros(opt.batch_size, 3, *opt.img_size).to(device) # image size(1,3,320,192) iDetection
# Update model
for k, m in model.named_modules():
m._non_persistent_buffers_set = set() # pytorch 1.6.0 compatibility
if isinstance(m, models.common.Conv): # assign export-friendly activations
if isinstance(m.act, nn.Hardswish):
m.act = Hardswish()
elif isinstance(m.act, nn.SiLU):
m.act = SiLU()
# elif isinstance(m, models.yolo.Detect):
# m.forward = m.forward_export # assign forward (optional)
model.model[-1].export = not opt.grid # set Detect() layer grid export
y = model(img) # dry run
# TorchScript export
try:
print('\nStarting TorchScript export with torch %s...' % torch.__version__)
f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.torchscript.pt') # filename
ts = torch.jit.trace(model, img)
ts.save(f)
print('TorchScript export success, saved as %s' % f)
except Exception as e:
print('TorchScript export failure: %s' % e)
# ONNX export
try:
import onnx
print('\nStarting ONNX export with onnx %s...' % onnx.__version__)
f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.onnx') # filename
torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=12, input_names=['images'],
output_names=['classes', 'boxes'] if y is None else ['output'],
dynamic_axes={'images': {0: 'batch', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'}, # size(1,3,640,640)
'output': {0: 'batch', 2: 'y', 3: 'x'}} if opt.dynamic else None)
# Checks
onnx_model = onnx.load(f) # load onnx model
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model) # check onnx model
# print(onnx.helper.printable_graph(onnx_model.graph)) # print a human readable model
print('ONNX export success, saved as %s' % f)
except Exception as e:
print('ONNX export failure: %s' % e)
# CoreML export
try:
import coremltools as ct
print('\nStarting CoreML export with coremltools %s...' % ct.__version__)
# convert model from torchscript and apply pixel scaling as per detect.py
model = ct.convert(ts, inputs=[ct.ImageType(name='image', shape=img.shape, scale=1 / 255.0, bias=[0, 0, 0])])
f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.mlmodel') # filename
model.save(f)
print('CoreML export success, saved as %s' % f)
except Exception as e:
print('CoreML export failure: %s' % e)
# Finish
print('\nExport complete (%.2fs). Visualize with https://github.com/lutzroeder/netron.' % (time.time() - t))
1.1 Focus模块
Focus模块是为减少FLOPS和提高速度而设计的,而不是提高mAP。

在YOLOv5中,作者希望减少Conv2d计算的成本,并实际使用张量重塑来减少空间(分辨率)和增加深度(通道数量)。
输入转换:[h, w, c] -> [h//2, w//2, c*4]。(长和宽变为原来的一半,通道数变为原来的四倍,把宽度w和高度h的信息整合到c空间中)
以Yolov5s的结构为例,原始640* 640* 3的图像输入Focus结构,采用切片操作,先变成320* 320* 12的特征图,再经过一次32个卷积核的卷积操作,最终变成320* 320* 32的特征图。而yolov5m的Focus结构中的卷积操作使用了48个卷积核,因此Focus结构后的特征图变成 320* 320*48。yolov5l,yolov5x也是同样的原理。
1.2 CSPNet模块
作用:增强CNN的学习能力、减少推理计算的问题、降低内存成本。
1.3 SPP (Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
在CSP之上添加SPP块,通过不同池化核大小的最大池化进行特征提取,显著增加了感受野 (receptive field),提取出最重要的上下文特征 (context features),并且几乎不会降低网络运行速度。
值得注意的是:虽然使用了不同大小的池化核,但池化前后每条分支的高宽一致,因为stride=1,padding=kerner/2。
1.4 PANet(Path-Aggregation Network)

特征金字塔(FPN)的特征图大小有不同的尺度,对不同尺度做融合。红色虚线箭头表示在FPN算法中,因为要走自底向上的过程,浅层的特征传递到顶层要经过几十甚至一百多个网络层,显然经过这么多层的传递,浅层特征信息丢失会比较厉害。绿色虚线箭头为添加的一个Bottom-up path augmentation,本身这个结构不到10层,这样浅层特征经过底下原来FPN的lateral connection连接到P2再从P2沿着bottom-up path augmentation传递到顶层,经过的层数就不到10层,能较好地保留浅层特征信息。
二 YOLOv5代码
2.1 激活函数及代码
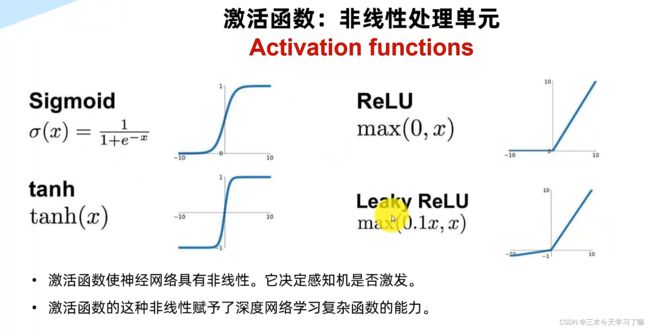

swish(x)=x⋅sigmoid(βx)
β是个常数或者可训练的参数,当β=1时,我们也称作SiLU激活函数。
代码在utils中的activations
class SiLU(nn.Module):
@staticmethod
def forward(x):
return x * torch. Sigmoid(x)
class Mish(nn.Module):
@staticmethod
def forward(x):
return x * F.softplus(x).tanh()
内存节约代码:
class MemoryEfficientSwish(nn.Module):
class F(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x):
# save_for_backward函数可以将对象保存起来,用于后续的backward函数
ctx.save_for_backward(x) # 会保留此input的全部信息, 并提供避免in-place操作导致的input在backward被修改的情况.
return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
x = ctx.saved_tensors[0] # #ctx.saved_tensors会返回forward函数内存储的对象
sx = torch.sigmoid(x)
return grad_output * (sx * (1 + x * (1 - sx)))
2.2 网络组件代码
models–>common
下图来自:深入浅出Yolo系列之Yolov5核心基础知识完整讲解

池化自动扩充
# 为same卷积或same池化自动扩充
def autopad(k, p=None): # kernel, padding
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
(n - K + 2p)/ s == n,且s = 1,则 p = k // 2。
标准卷积:conv+BN+Silu
图中所画为CBL,我下载的是V5.0版本,为CBS,这部分不用纠结看代码就行。
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x): # 网络的执行顺序是根据 forward 函数来决定的
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x))) # 先卷积在BatchNormalization最后Silu
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
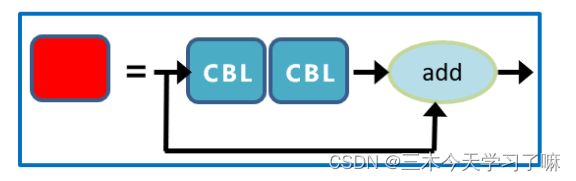
Bottleneck模块
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
# 根据self.add的值确定是否有shortcut
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
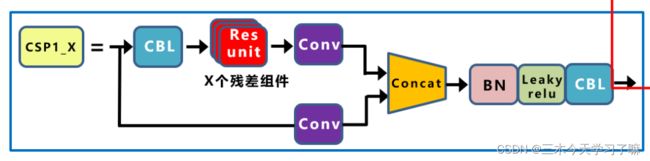
CSP模块
class BottleneckCSP(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = nn.Conv2d(c1, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv3 = nn.Conv2d(c_, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv4 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * c_) # applied to cat(cv2, cv3)
self.act = nn.SiLU()
# *操作符可以把一个list拆开成一个个独立的元素
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
y1 = self.cv3(self.m(self.cv1(x)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv4(self.act(self.bn(torch.cat((y1, y2), 1))))
SPP模块 空间金字塔池化
class SPP(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) layer https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.4729
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * (len(k) + 1), c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1))
Focus模块
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act)
# self.contract = Contract(gain=2)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat((x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]), 1))
# return self.conv(self. Contract(x))
2.3 数据集创建相关代码
letterbox代码
utils–>augmentations
图像缩放: 保持图片的宽高比例,剩下的部分采用灰色填充。
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
"""
缩放(resize)到输入大小img_size的时候,如果没有设置上采样的话,则只进行下采样
因为上采样图片会让图片模糊,对训练不友好影响性能。
"""
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle # 获取最小的矩形填充
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, 32), np.mod(dh, 32) # wh padding
# 如果scaleFill=True,则不进行填充,直接resize成img_size, 任由图片进行拉伸和压缩
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
# 计算上下左右填充大小
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
# 进行填充
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
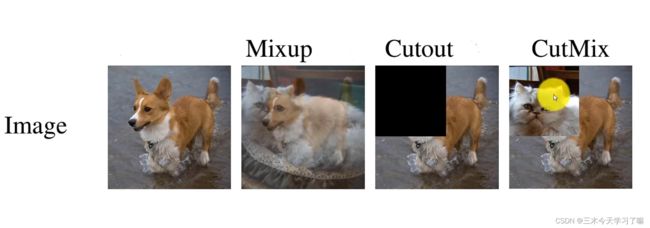
数据增强
def load_mosaic(self, index):
# YOLOv5 4-mosaic loader. Loads 1 image + 3 random images into a 4-image mosaic
labels4, segments4 = [], []
s = self.img_size
yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border) # mosaic center x, y
indices = [index] + random.choices(self.indices, k=3) # 3 additional image indices
random.shuffle(indices)
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image
# load_image加载图片并根据设定的输入大小与图片原大小的比例ratio进行resize
img, _, (h, w) = self.load_image(index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels
labels, segments = self.labels[index].copy(), self.segments[index].copy()
if labels.size:
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], w, h, padw, padh) # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
segments = [xyn2xy(x, w, h, padw, padh) for x in segments]
labels4.append(labels)
segments4.extend(segments)
# Concat/clip labels
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
for x in (labels4[:, 1:], *segments4):
np.clip(x, 0, 2 * s, out=x) # clip when using random_perspective()
# img4, labels4 = replicate(img4, labels4) # replicate
# Augment
img4, labels4, segments4 = copy_paste(img4, labels4, segments4, p=self.hyp['copy_paste'])
img4, labels4 = random_perspective(img4,
labels4,
segments4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
2.4 general代码
AP值计算
utils–>metrics
def ap_per_class(tp, conf, pred_cls, target_cls, plot=False, save_dir='.', names=(), eps=1e-16):
""" Compute the average precision, given the recall and precision curves.
# Arguments
tp: True positives (nparray, nx1 or nx10).
conf: Objectness value from 0-1 (nparray).
pred_cls: Predicted object classes (nparray).
target_cls: True object classes (nparray).
plot: Plot precision-recall curve at [email protected]
save_dir: Plot save directory
# Returns
The average precision as computed in py-faster-rcnn.
"""
# Sort by objectness
i = np.argsort(-conf)
tp, conf, pred_cls = tp[i], conf[i], pred_cls[i]
# Find unique classes
unique_classes, nt = np.unique(target_cls, return_counts=True)
nc = unique_classes.shape[0] # number of classes, number of detections
# Create Precision-Recall curve and compute AP for each class
px, py = np.linspace(0, 1, 1000), [] # for plotting
ap, p, r = np.zeros((nc, tp.shape[1])), np.zeros((nc, 1000)), np.zeros((nc, 1000))
for ci, c in enumerate(unique_classes):
i = pred_cls == c
n_l = nt[ci] # number of labels
n_p = i.sum() # number of predictions
if n_p == 0 or n_l == 0:
continue
# Accumulate FPs and TPs
fpc = (1 - tp[i]).cumsum(0)
tpc = tp[i].cumsum(0)
# Recall
recall = tpc / (n_l + eps) # recall curve
r[ci] = np.interp(-px, -conf[i], recall[:, 0], left=0) # negative x, xp because xp decreases
# Precision
precision = tpc / (tpc + fpc) # precision curve
p[ci] = np.interp(-px, -conf[i], precision[:, 0], left=1) # p at pr_score
# AP from recall-precision curve
for j in range(tp.shape[1]):
ap[ci, j], mpre, mrec = compute_ap(recall[:, j], precision[:, j])
if plot and j == 0:
py.append(np.interp(px, mrec, mpre)) # precision at [email protected]
# Compute F1 (harmonic mean of precision and recall)
f1 = 2 * p * r / (p + r + eps)
names = [v for k, v in names.items() if k in unique_classes] # list: only classes that have data
names = dict(enumerate(names)) # to dict
if plot:
plot_pr_curve(px, py, ap, Path(save_dir) / 'PR_curve.png', names)
plot_mc_curve(px, f1, Path(save_dir) / 'F1_curve.png', names, ylabel='F1')
plot_mc_curve(px, p, Path(save_dir) / 'P_curve.png', names, ylabel='Precision')
plot_mc_curve(px, r, Path(save_dir) / 'R_curve.png', names, ylabel='Recall')
i = smooth(f1.mean(0), 0.1).argmax() # max F1 index
p, r, f1 = p[:, i], r[:, i], f1[:, i]
tp = (r * nt).round() # true positives
fp = (tp / (p + eps) - tp).round() # false positives
return tp, fp, p, r, f1, ap, unique_classes.astype(int)
def compute_ap(recall, precision):
""" Compute the average precision, given the recall and precision curves
# Arguments
recall: The recall curve (list)
precision: The precision curve (list)
# Returns
Average precision, precision curve, recall curve
"""
# Append sentinel values to beginning and end
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.0], recall, [1.0]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([1.0], precision, [0.0]))
# Compute the precision envelope
mpre = np.flip(np.maximum.accumulate(np.flip(mpre)))
# Integrate area under curve
method = 'interp' # methods: 'continuous', 'interp'
if method == 'interp':
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 101) # 101-point interp (COCO)
ap = np.trapz(np.interp(x, mrec, mpre), x) # integrate
else: # 'continuous'
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0] # points where x axis (recall) changes
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1]) # area under curve
return ap, mpre, mrec
加断点调试后,ap矩阵,列是:0.5:0.05:0.95,行是20个类,元素含义为置信度。

loss计算
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, xywh=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, eps=1e-7):
# Returns Intersection over Union (IoU) of box1(1,4) to box2(n,4)
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if xywh: # transform from xywh to xyxy
(x1, y1, w1, h1), (x2, y2, w2, h2) = box1.chunk(4, 1), box2.chunk(4, 1)
w1_, h1_, w2_, h2_ = w1 / 2, h1 / 2, w2 / 2, h2 / 2
b1_x1, b1_x2, b1_y1, b1_y2 = x1 - w1_, x1 + w1_, y1 - h1_, y1 + h1_
b2_x1, b2_x2, b2_y1, b2_y2 = x2 - w2_, x2 + w2_, y2 - h2_, y2 + h2_
else: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1.chunk(4, 1)
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2.chunk(4, 1)
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
# IoU
iou = inter / union
if CIoU or DIoU or GIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared
rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 + (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center dist ** 2
if CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / (h2 + eps)) - torch.atan(w1 / (h1 + eps)), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha) # CIoU
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
return iou # IoU