LWZ压缩编码原理与C++实现
LWZ编码原理
LZW算法又叫“串表压缩算法,”就是通过建立一个字符串表,用较短的代码来表示较长的字符串来实现压缩,提取原始文本文件数据中的不同字符,基于这些字符创建一个编译表,然后用编译表中的字符的索引来替代原始文本文件数据中的相应字符,减少原始数据大小。
编码流程
步骤1:将词典初始化为包含所有可能的单字符,当前前缀P初始化为空。
步骤2:当前字符C=字符流中的下一个字符。
步骤3:判断P+C是否在词典中
(1)如果“是”,则用C扩展P,即让P=P+C,返回到步骤2。
(2)如果“否”,则
输出与当前前缀P相对应的码字W;
将P+C添加到词典中;
令P=C,并返回到步骤2
解码流程
LWZ编码并不传输词典,而是在解码的过程中根据已有的编码规则动态建立词典,达到传输中编解码同步的效果。
LZW解码算法开始时,译码词典和编码词典相同,包含所有可能的前缀根。具体解码算法如下:
步骤1:在开始译码时词典包含所有可能的前缀根。
步骤2:令CW:=码字流中的第一个码字。
步骤3:输出当前缀-符串string.CW到码字流。
步骤4:先前码字PW:=当前码字CW。
步骤5:当前码字CW:=码字流的下一个码字。
步骤6:判断当前缀-符串string.CW 是否在词典中。
(1)如果”是”,则把当前缀-符串string.CW输出到字符流。
当前前缀P:=先前缀-符串string.PW。
当前字符C:=当前前缀-符串string.CW的第一个字符。
把缀-符串P+C添加到词典。
(2)如果”否”,则当前前缀P:=先前缀-符串string.PW。
当前字符C:=当前缀-符串string.CW的第一个字符。
输出缀-符串P+C到字符流,然后把它添加到词典中。
步骤7:判断码字流中是否还有码字要译。
(1)如果”是”,就返回步骤4。
(2)如果”否”,结束。
C++代码:
bitio.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __BITIO__
#define __BITIO__
#include bitio.cpp
#include LWZ_E.cpp
#include \n" , argv[0]);
fprintf(stdout, "\t: E or D reffers encode or decode\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: input file name\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: output file name\n" );
return -1;
}
if ('E' == argv[1][0]) { // do encoding
fp = fopen(argv[2], "rb");
bf = OpenBitFileOutput(argv[3]);
if (NULL != fp && NULL != bf) {
LZWEncode(fp, bf);
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileOutput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "encoding done\n");
}
}
else if ('D' == argv[1][0]) { // do decoding
bf = OpenBitFileInput(argv[2]);
fp = fopen(argv[3], "wb");
if (NULL != fp && NULL != bf) {
LZWDecode(bf, fp);
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileInput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "decoding done\n");
}
}
else { // otherwise
fprintf(stderr, "not supported operation\n");
}
return 0;
}
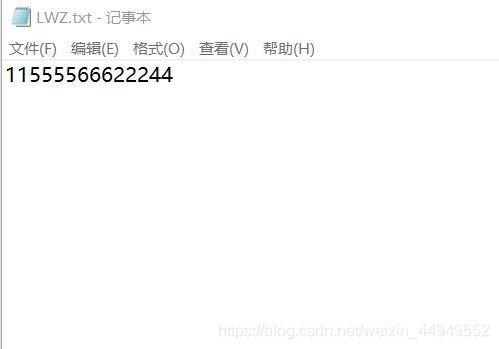
最后进行LWZ压缩编解码测试:创建如下的文本文件,输入一串字符串
进行压缩编码,得到一个二进制文件(.dat),再将这个二进制文件解码为txt文件
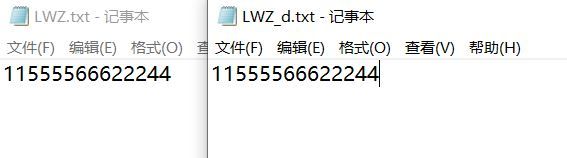
可见编解码成功。
压缩效率分析
对十种不同格式的文件进行LWZ压缩:
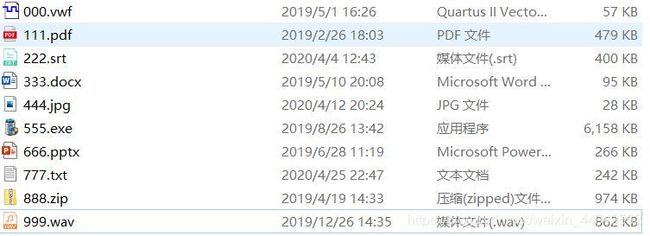
压缩完成后得到文件:
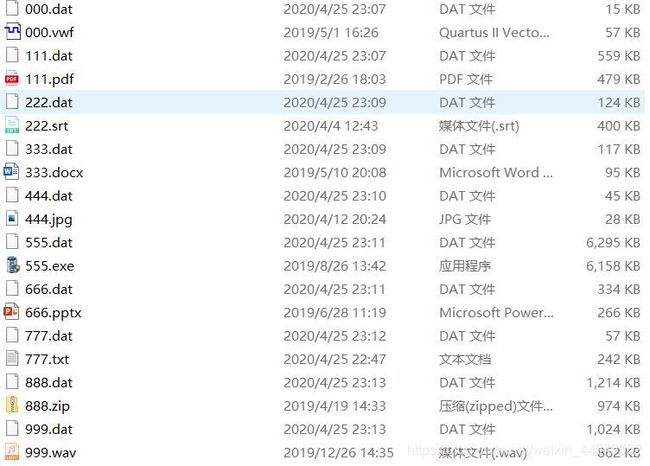
对编码效率进行分析:
| 文件类型 | 编码前文件大小 | 编码后文件大小 | 压缩比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| .vwf | 57KB | 15KB | 380% |
| 479KB | 559KB | 85.6% | |
| .srt | 400KB | 124KB | 322% |
| .docx | 95KB | 117KB | 81.1% |
| .jpg | 28KB | 45KB | 62.2% |
| .exe | 6158KB | 6259KB | 98.3% |
| .pptx | 266KB | 334KB | 67.6% |
| .txt | 242KB | 57KB | 425% |
| .zip | 974KB | 1214KB | 80.2% |
| .wav | 862KB | 1024KB | 84.2% |
从压缩效率分析来看,.txt 文件与.srt文件这样的文本类型文件得到了较大的压缩比,而其他文件,比如多媒体文件,则出现了负压缩,结果表明了LWZ压缩编码适合于文本文件这样重复内容较多的文件,而其他文件也许并不存在大量的重复数据,压缩效果并不好,在构建词典的过程中形成的词典比较庞大,导致了数据的增加。