RNN LSTM GRU ATT等模型 学习笔记
目录
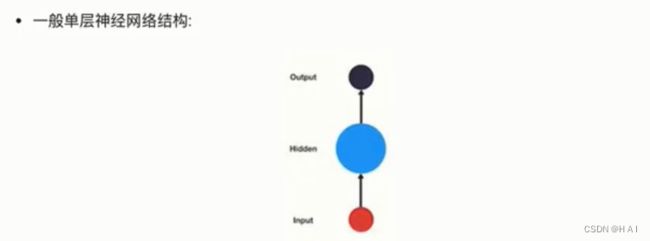
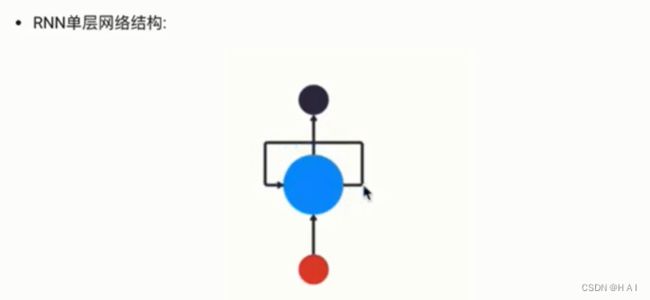
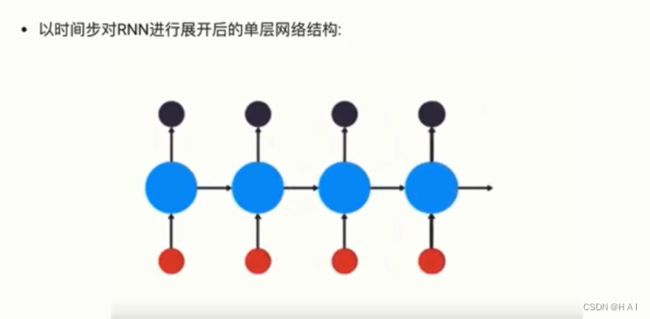
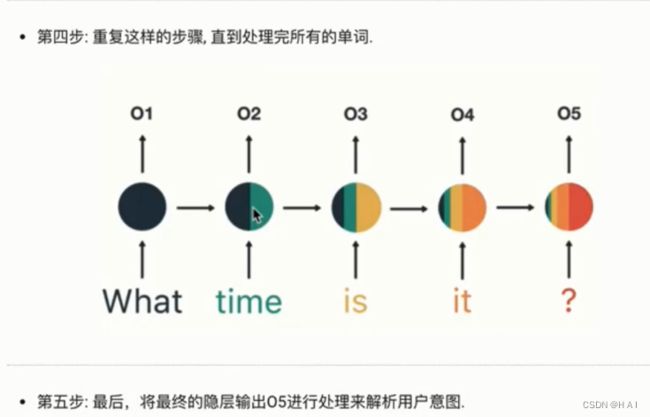
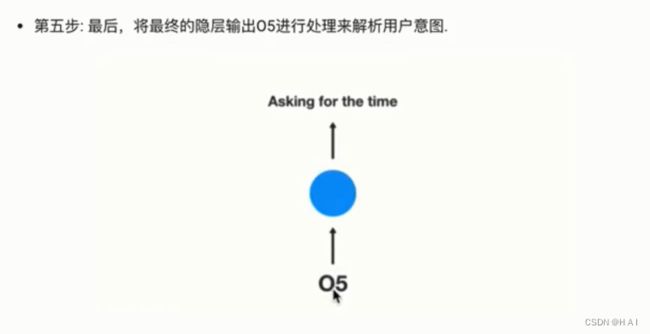
1.如何理解RNN
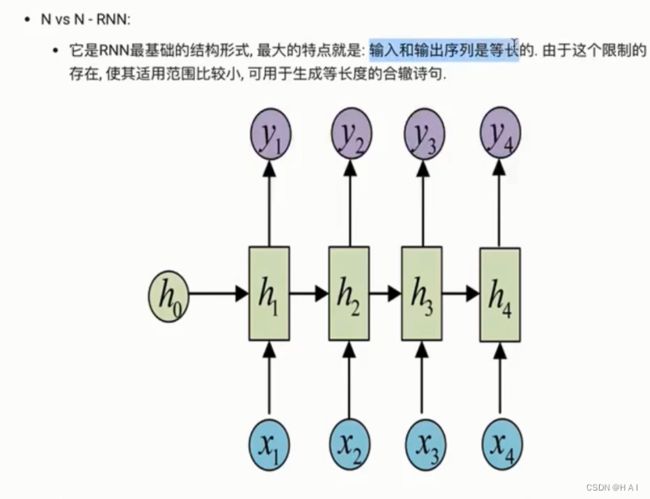
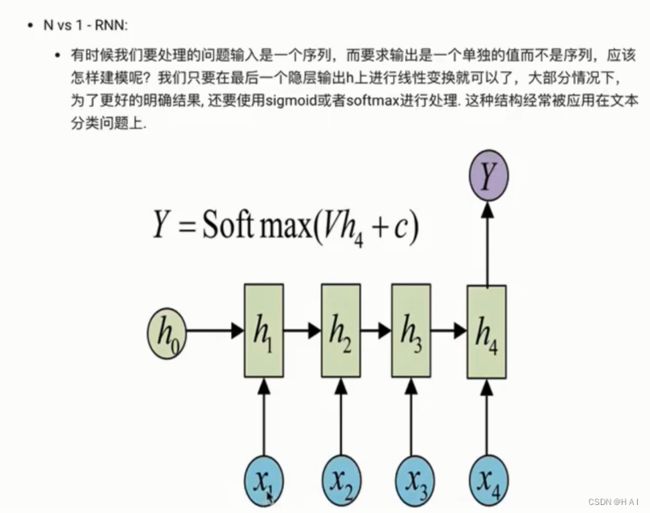
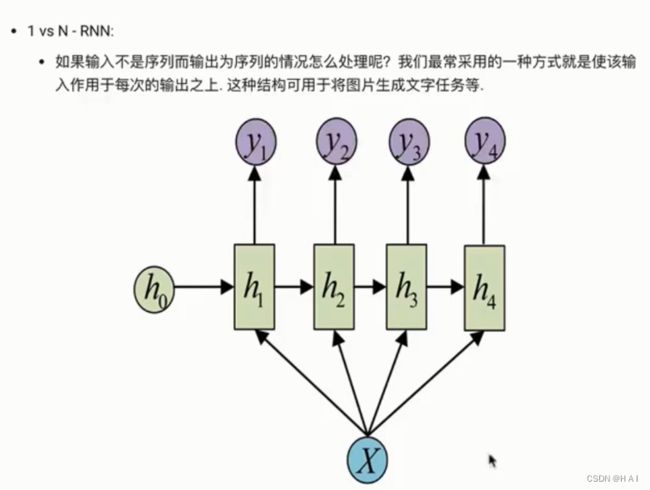
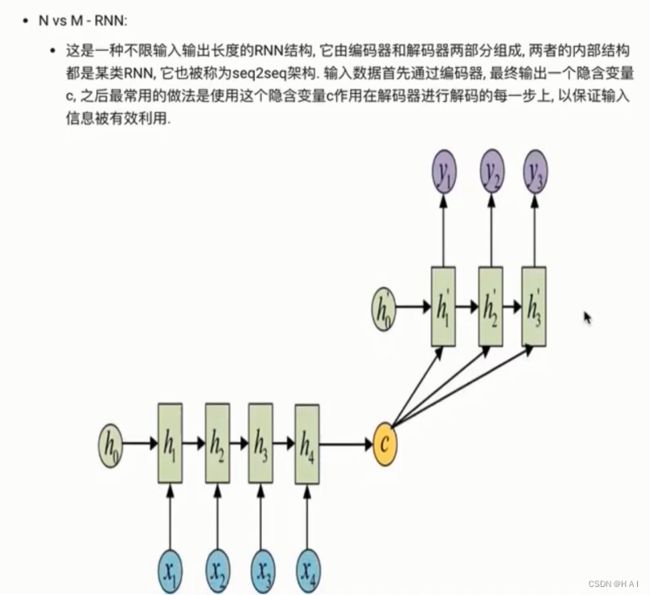
2.RNN分类
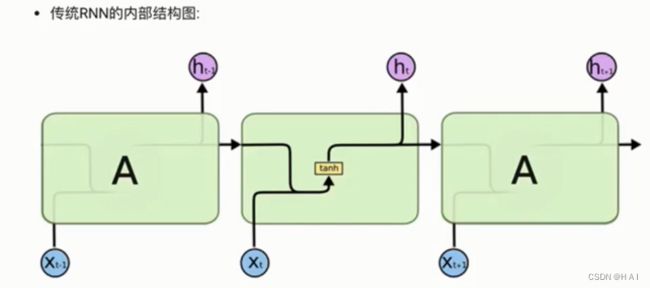
3.传统RNN模型构造
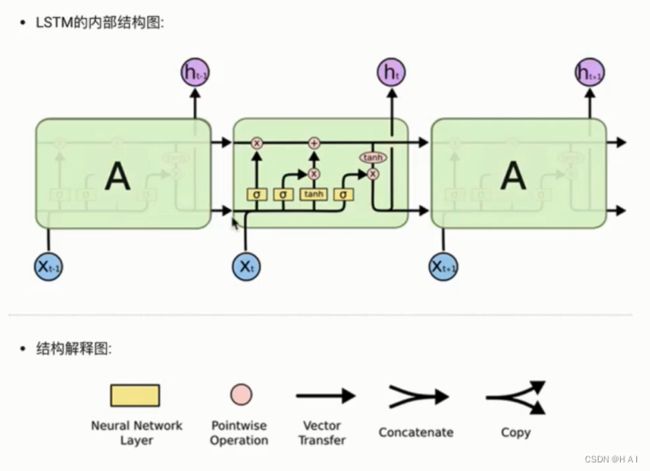
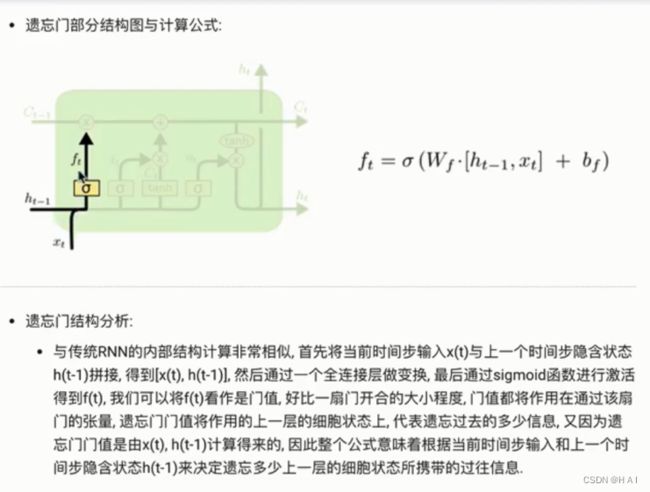
4.LSTM
5.GRU
6.注意力机制
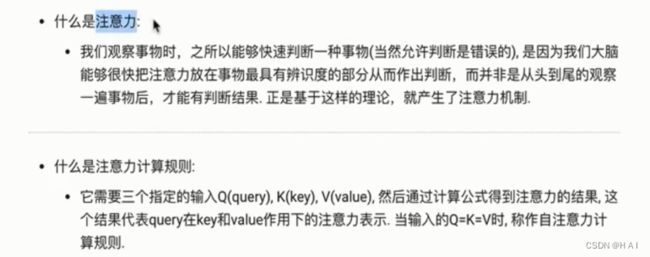
什么是注意力机制
7.RNN LSTM GRU 注意力机制 代码实现
1.如何理解RNN
2.RNN分类
3.传统RNN模型构造
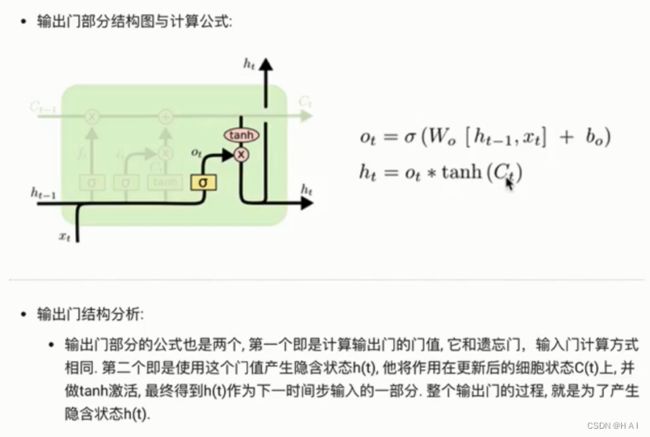
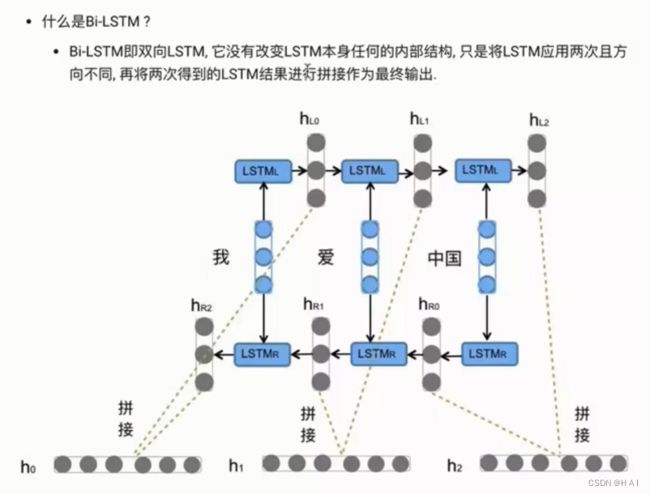
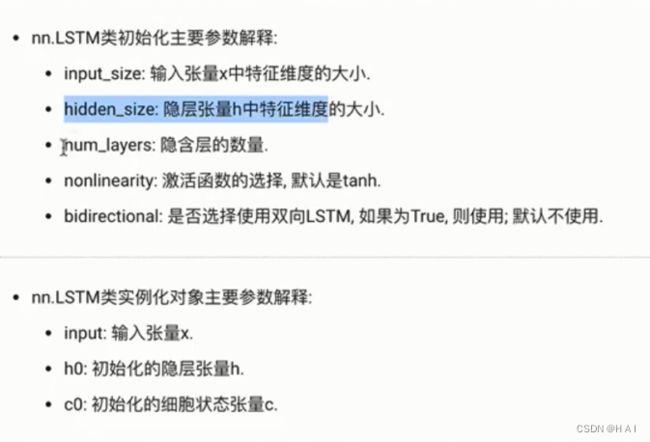
4.LSTM
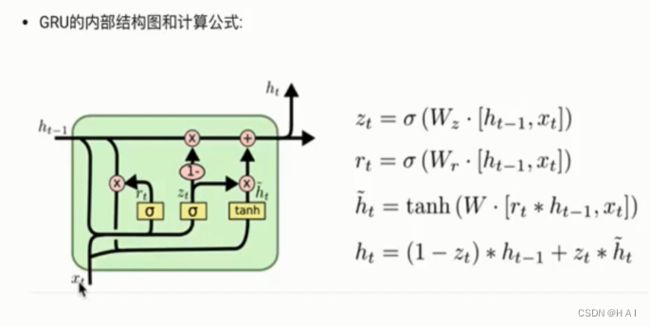
5.GRU
参数同LSTM一样
6.注意力机制
什么是注意力机制
7.RNN LSTM GRU 注意力机制 代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 参数一: 输入x的特征维度, 词嵌入的维度; 参数二: 隐藏层神经元的个数; 参数三: 隐藏层的层数
rnn = nn.RNN(5, 6, 1)
# 1: 代表当前批次的样本个数, 3: 当前样本的sequence_length, 5: 词嵌入的维度
input1 = torch.randn(1, 3, 5)
# 1: 隐藏层的层数, 3: 当前样本的sequence_length, 6: 隐藏层神经元的个数
h0 = torch.randn(1, 3, 6)
output, hn = rnn(input1, h0)
# print(output)
# print(hn)
# -----------------------------------------------
# 参数一: 输入x的特征维度, 词嵌入的维度; 参数二: 隐藏层神经元的个数; 参数三: 隐藏层的层数
lstm = nn.LSTM(5, 6, 2)
# 1: 代表当前批次的样本个数, 3: 当前样本的sequence_length, 5: 词嵌入的维度
input1 = torch.randn(1, 3, 5)
# 2: 隐藏层的层数, 3: 当前样本的sequence_length, 6: 隐藏层神经元的个数
h0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 6)
c0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 6)
output, (hn, cn) = lstm(input1, (h0, c0))
# print(output)
# print(output.shape)
# print(hn)
# print(hn.shape)
# print(cn)
# print(cn.shape)
# -----------------------------------------------
# 参数一: 输入x的特征维度, 词嵌入的维度; 参数二: 隐藏层的神经元个数; 参数三: 两个隐藏层
gru = nn.GRU(5, 6, 2)
# 1: 批次样本数量; 3: 序列的长度sequence_length; 5: 词嵌入的维度
input1 = torch.randn(1, 3, 5)
# 2: 两个隐藏层; 3: 序列的长度sequence_length; 6: 隐藏层的神经元个数
h0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 6)
output, hn = gru(input1, h0)
# print(output)
# print(output.shape)
# print(hn)
# print(hn.shape)
# ------------------------------------------------
mat1 = torch.randn(10, 3, 4)
mat2 = torch.randn(10, 4, 5)
res = torch.bmm(mat1, mat2)
# print(res.size())
# ------------------------------------------------
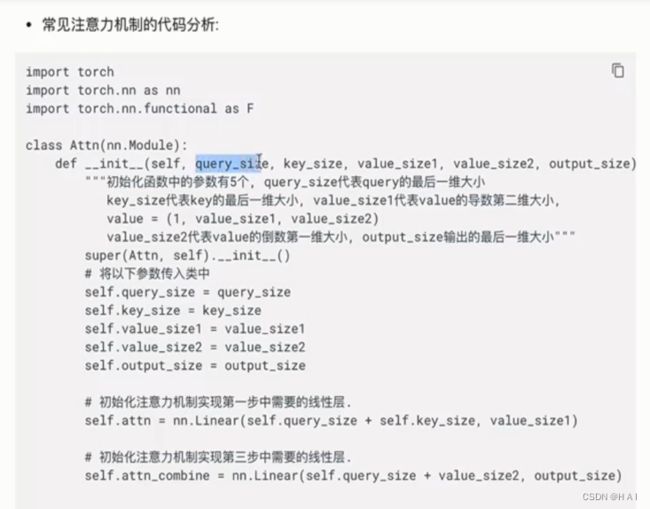
class Attn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, query_size, key_size, value_size1, value_size2, output_size):
# query_size代表的是Q的最后一个维度, key_size代表的K的最后一个维度
# V的尺寸表示(1, value_sie1, value_size2)
# output_size代表输出的最后一个维度的大小
super(Attn, self).__init__()
self.query_size = query_size
self.key_size = key_size
self.value_size1 = value_size1
self.value_size2 = value_size2
self.output_size = output_size
# 初始化注意力机制实现中第一步的线性层
self.attn = nn.Linear(self.query_size + self.key_size, self.value_size1)
# 初始化注意力机制实现制红第三步的线性层
self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.query_size + self.value_size2, self.output_size)
def forward(self, Q, K, V):
# 注意我们假定Q ,K, V都是三维张量
#第一步, 将Q, K进行纵轴的拼接,然后做一次线性变换,最后使用softmax进行处理得到注意力向量
attn_weights = F.softmax(self.attn(torch.cat((Q[0], K[0]), 1)), dim=1)
# 将注意力矩阵和V进行一次bmm运算
attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0), V)
# 再次去Q[0]进行降维,再次和上面的运算结果进行一次拼接
output = torch.cat((Q[0], attn_applied[0]), 1)
# 第三步就是将上面的输出进行一次线性变换,然后再扩展维度成3维张量
output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0)
return output, attn_weights
query_size = 32
key_size = 32
value_size1 = 32
value_size2 = 64
output_size = 64
attn = Attn(query_size, key_size, value_size1, value_size2, output_size)
Q = torch.randn(1, 1, 32)
K = torch.randn(1, 1, 32)
V = torch.randn(1, 32, 64)
output = attn(Q, K, V)
# print(output[0])
print(output[0].size())
# print(output[1])
print(output[1].size())