数据库的操作进阶
文章目录
- 1:数据库约束
-
- 1.1:约束类型
- 1.2:NULL约束
- 1.3:UNIQUE:唯一约束
- 1.4:DEFAULT:默认值约束
- 1.5:PRIMARY KEY:主键约束
- 1.6:FOREIGN KEY:外键约束
- 2:表的设计
- 3:新增
- 4:查询
-
- 4.1:聚合查询
-
-
- 聚合函数
-
- 4.2:分组查询
-
-
- HAVING
-
- 4.3:联合查询
-
-
- 4.3.1:内连接
-
- **SQL Select语句完整的执行顺序:**
-
-
- 4.3.2:外连接
- 内外连接的区别:
- 4.3.3:自连接
-
- 4.4:子查询
-
-
- 4.4.1:单行子查询
- 4.4.2:多行子查询:
-
-
- [NOT] IN关键字
-
- 4.4.3:在from子句中使用子查询:
-
- 4.5:合并查询
-
-
- union
- union all
-
1:数据库约束
1.1:约束类型
(约束就是让数据库更好的为程序员检查数据是否正确)
-
NOT NULL - 指示某列不能存储 NULL 值。
-
UNIQUE - 保证某列的每行必须有唯一的值。
-
DEFAULT - 规定没有给列赋值时的默认值。
-
PRIMARY KEY - NOT NULL 和 UNIQUE 的结合。确保某列(或两个列多个列的结合)有唯一标
识,有助于更容易更快速地找到表中的一个特定的记录。
-
FOREIGN KEY - 保证一个表中的数据匹配另一个表中的值的参照完整性。
-
CHECK - 保证列中的值符合指定的条件。对于MySQL数据库,对CHECK子句进行分析,但是忽略
CHECK子句
1.2:NULL约束
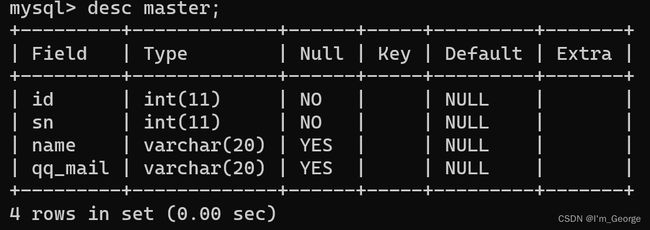
创建表时,可以指定某列不为空:
create table master(id int not null , sn int not null , name varchar(20) , qq_mail varchar(20));
1.3:UNIQUE:唯一约束
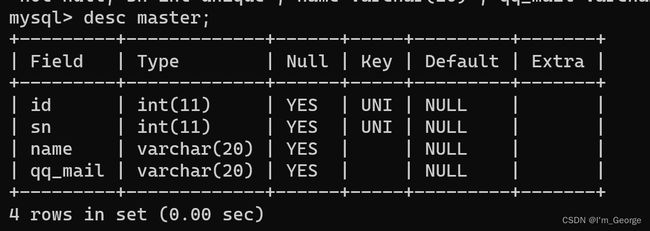
指定sn列为唯一的、不重复的:
create table master(id int unique, sn int unique , name varchar(20) , qq_mail varchar(20)); -- right
create table master(id int unique and not null, sn int unique , name varchar(20) , qq_mail varchar(20)); -- error
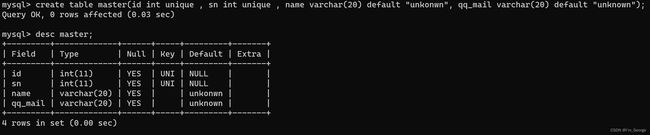
1.4:DEFAULT:默认值约束
指定插入数据时,name列为空,默认值unkown:
create table master(id int unique, sn int unique , name varchar(20) default "unknown" , qq_mail varchar(20) default "unknown");
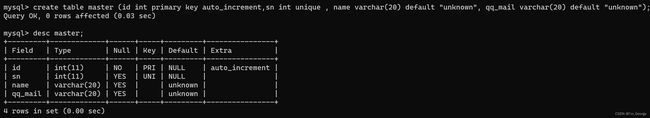
1.5:PRIMARY KEY:主键约束
(非常重要的约束,每条记录的身份标识)
(在实际的开发中,每个表都会有一个主键,主要用一个整数来表示记录的ID)
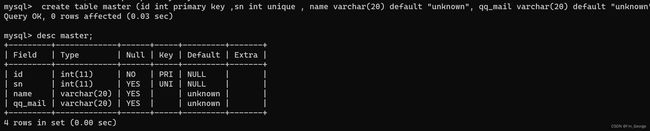
指定id列为主键:
创建表时候不可以出现多个主键,即一个表中只能有一个主键。虽然一个表中只能有一个主键,但是MySQL允许多个列放在一起共同作为一个主键(联合主键)。
create table master (id int primary key ,sn int unique , name varchar(20) default "unknown", qq_mail varchar(20) default "unknown"); -- right
create table master (id int primary key ,sn int primary key , name varchar(20) default "unknown", qq_mail varchar(20) default "unknown"); -- error
-- ERROR 1068 (42000): Multiple primary key defined
create table master (id int primary key ,sn int unique and not null , name varchar(20) default "unknown", qq_mail varchar(20) default "unknown"); -- error
对于整数类型的主键,常配搭自增长auto_increment来使用。插入数据对应字段不给值时,使用最大
值+1,即自增主键不会重复利用中间的空隙,浪费就浪费数又用不完 。
-- 主键是 NOT NULL 和 UNIQUE 的结合,可以不用 NOT NULL
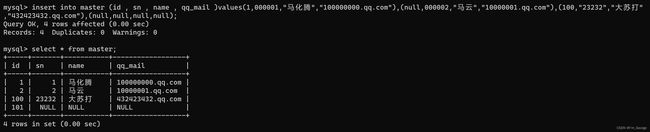
create table master (id int primary key auto_increment,sn int unique , name varchar(20) default "unknown", qq_mail varchar(20) default "unknown");
insert into master (id , sn , name , qq_mail )values(1,000001,"马化腾","100000000.qq.com"),(null,000002,"马云","10000001.qq.com"),(100,"23232","大苏打","432423432.qq.com"),(null,null,null,null);
-- 这里插入语句中的null并不是赋值为空而是使用自增主键。
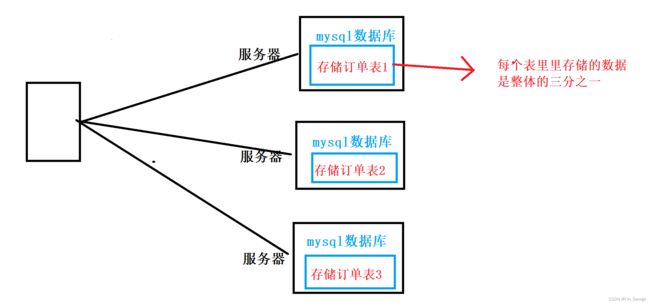
在这个场景下,如果再插入一个数据,这个数据会落在三个服务器之一,新的这个数据的主键ID如何分配,能否继续使用MySQL自带的自增主键。
涉及一个分布式系统中唯一ID生成算法,实现公式 = 时间戳 + 主机编号 + 随机因子 => 结合这三部分就可以得到一个全局唯一的ID。
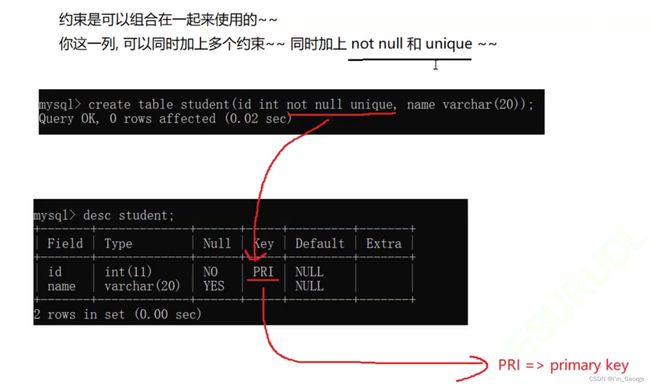
约束可以组合在一起使用,当这一列同时加上 unique 与 not null 的时候,就相当于primary key
主键在插入记录的时候,需要先搜索然后再插入,正因为unique 与 primary key 这样的列都有搜索要求
所以数据库会这样的列自动添加索引来提高搜索速度。
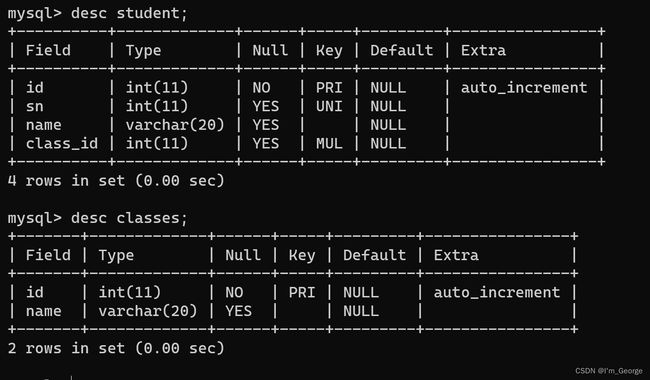
1.6:FOREIGN KEY:外键约束
外键用于关联其他表的主键或唯一键
-- 格式
foreign key (字段名) references 主表(列)
-- 班级表:
create table classes(id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
-- 学生表:
create table student (id int primary key auto_increment, sn int unique, name varchar(20),class_id int , foreign key (class_id) references classes(id));
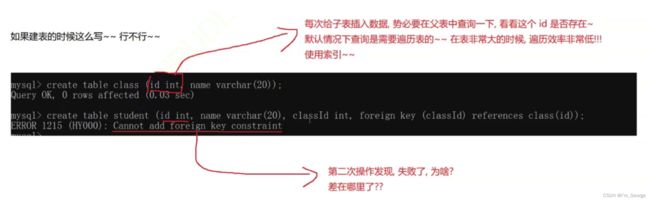
外键的约束:
外键的约束是父表对子表做了约束,但实际上反过来子表也会对父表做约束
-- 删除ID为1的class记录,会发现删除失败的
delete from classes where ID = 1;
-- 这是因为ID为1被子表给引用了,如果真的删除成功子表中的数据不就僵住了。
delete from classes where ID = 2;
-- 这个可以删除成功,因为ID为2没有被子表给引用。
要想顺利的删除,要先删除子表后删除父表
要想创建外键,就要求父表所对应的列要有primary key 或者 unique 条件限制,因为你每次给子表插入数据的时候,都要在父表中查询一下子表这个ID存不存在,默认情况下的查询是遍历表,在表中的数据非常多的时候,遍历的效率非常的低,要使用索引。
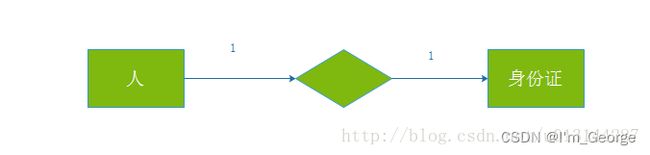
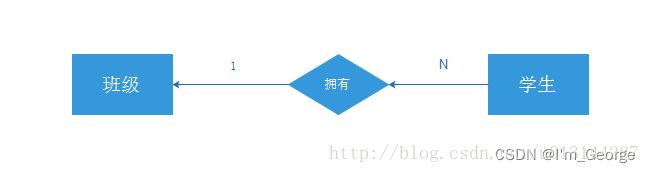
2:表的设计
一对一:
多对一:
一对多的关系:
student(ID, name, classID);
class(ID, name);
-- 这样就构成了一对多的关系
student(ID, name);
class(ID, name, studentID);
-- mysql中没有没有一个像数组这样的类型,所以不可以这样搞一对多
-- 但是想redis这样的数据库中就有像数组这样的类型,就可以这样搞
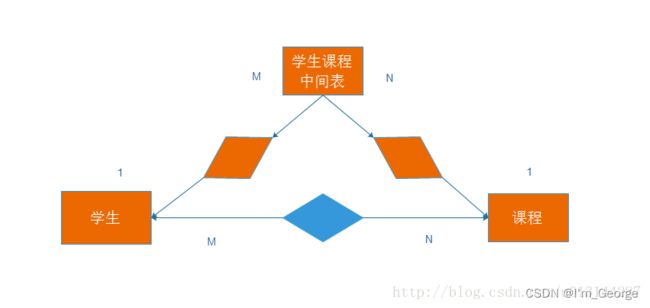
多对多:
多对多的关系,就建立一个关联表,一个学生可能有好几门课 ,一个课程可能有很多的学生,
那就弄一个学生-课程关联表,将两个变量联系起来。
3:新增
插入查询结果
INSERT INTO table_name [(column [, column ...])] SELECT ...
CREATE TABLE test_user (
id INT primary key auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(20) comment '姓名',
age INT comment '年龄',
email VARCHAR(20) comment '邮箱',
sex varchar(1) comment '性别',
mobile varchar(20) comment '手机号'
);
create table student(id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), age int );
insert into test_user(name) select name from student;
要求这里的查询结果临时表中的列数,列的类型要与待插入表一样
4:查询
4.1:聚合查询
聚合函数
(这里的每个函数都是针对每一列中每一行进行计算的,select sum(math) from exam_result ----> 执行的顺序其实显示将所有的math进行select然后在进行sum求和操作)
| count( ) | 返回查询到的数据的数量 |
|---|---|
| sum( ) | 返回查询到的数据的总和,不是数字没有意义 |
| avg( ) | 返回查询到的数据的 平均值,不是数字没有意义 |
| max( ) | 返回查询到的数据的 最大值,不是数字没有意义 |
| min( ) | 返回查询到的数据的 最小值,不是数字没有意义 |
- count( * ) / count( 1 ) 会统计表中所有的记录的条数,包括字段的类型是null的。
- count(字段) 会统计该字段中所有的记录的条数,但是不包括null的
- count(…) 注意count与()中间不可以有空格
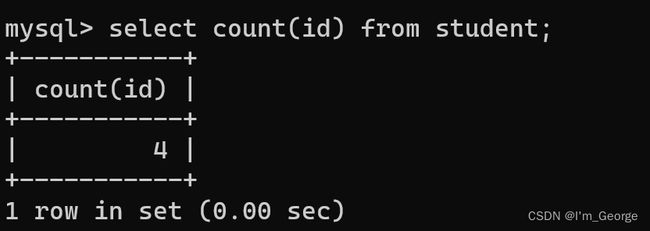
-- 统计班级共有多少同学
select count(id) from student;
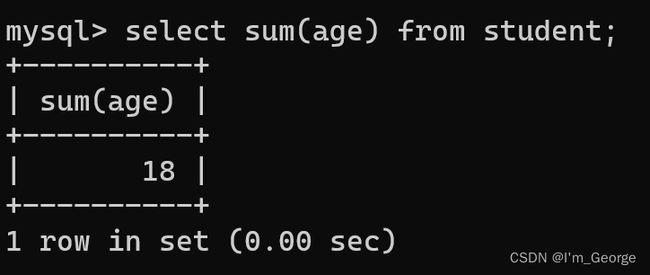
-- 统计一下年龄的总和
select sum(age) from student;
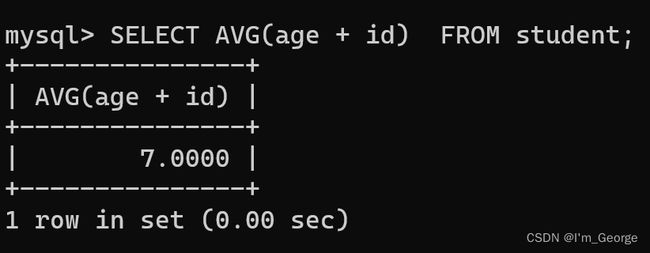
-- 统计一下id 与 age 的平均值
SELECT AVG(age + id) FROM student;
4.2:分组查询
通过group by 来进行分组查询,如果不指定group by的话就相当于是一组,把所有的行进行聚合,引入group by之后就可以针对不同的组来分别进行聚合。需要注意的是:聚合函数是分组后,对每个组进行计算的。
SELECT 中使用 GROUP BY 子句可以对指定列进行分组查询。需要满足:使用 GROUP BY 进行分组查
询时,SELECT 指定的字段必须是“分组依据字段”,其他字段若想出现在SELECT 中则必须包含在聚合函
数中。
-- 格式:
select column1, sum(column2), .. from table group by column1,column3;
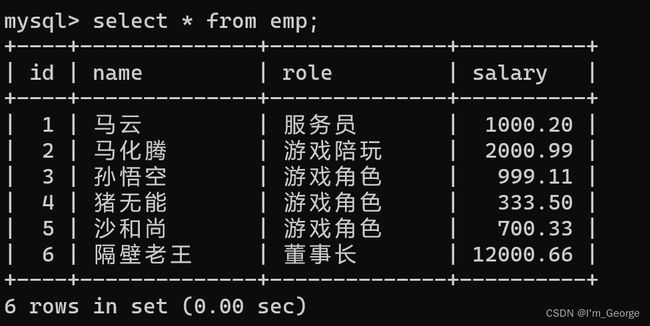
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
role varchar(20) not null,
salary numeric(11,2)
);
insert into emp(name, role, salary) values
('马云','服务员', 1000.20),
('马化腾','游戏陪玩', 2000.99),
('孙悟空','游戏角色', 999.11),
('猪无能','游戏角色', 333.5),
('沙和尚','游戏角色', 700.33),
('隔壁老王','董事长', 12000.66);
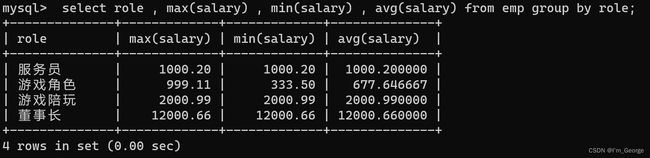
-- 查询每个角色的最高工资、最低工资和平均工资
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role;
HAVING
GROUP BY 子句进行分组以后,需要对分组结果再进行条件过滤时,不能使用 WHERE 语句,而需要用
HAVING
注意having条件过滤用在分组之后,where的条件过滤用在分组之前。
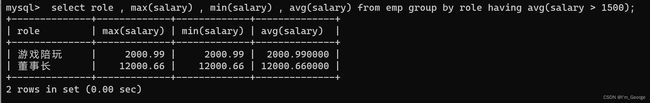
-- 显示平均工资高于1500的角色和它的平均工资
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role having avg(salary) > 1500;
-- 计算每个岗位的平均薪资但是要刨除孙悟空的数据,而且要抛出平均薪资在10w以上的岗位。
select role , avg(salary) from emp where emp.name != "孙悟空" group by role having avg(salary) > 100000;
-- 这里需要在分组前先刨除孙悟空的数据,然后在进行分组
4.3:联合查询
联合查询是非常危险的因为表膨胀的太快
4.3.1:内连接
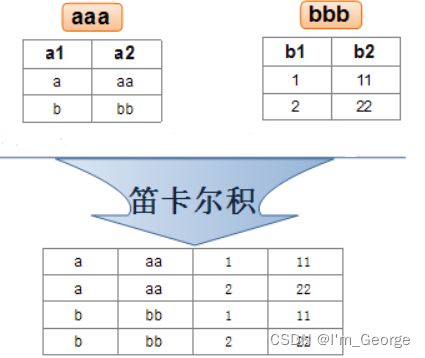
实际开发中往往数据来自不同的表,所以需要多表联合查询。多表查询是对多张表的数据取笛卡尔积:
笛卡尔积是通过排列组合而来的,会得到一张更大的表,这张表的列数是前两个表之和,行数是前两个表之积
所以有很多的数据是错误的,我们需要在后面添加连接条件(筛选有效数据的条件)
示例:
drop table if exists classes;
drop table if exists student;
drop table if exists course;
drop table if exists score;
create table classes (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), `desc` varchar(100));
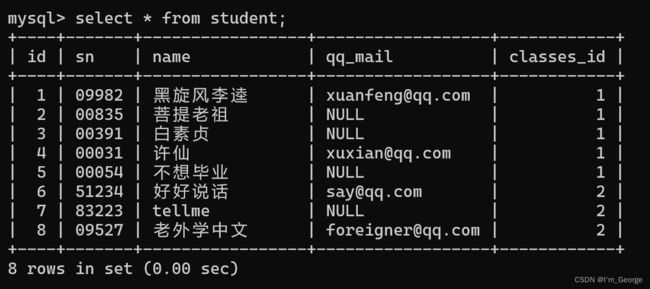
create table student (id int primary key auto_increment, sn varchar(20), name varchar(20), qq_mail varchar(20) ,
classes_id int);
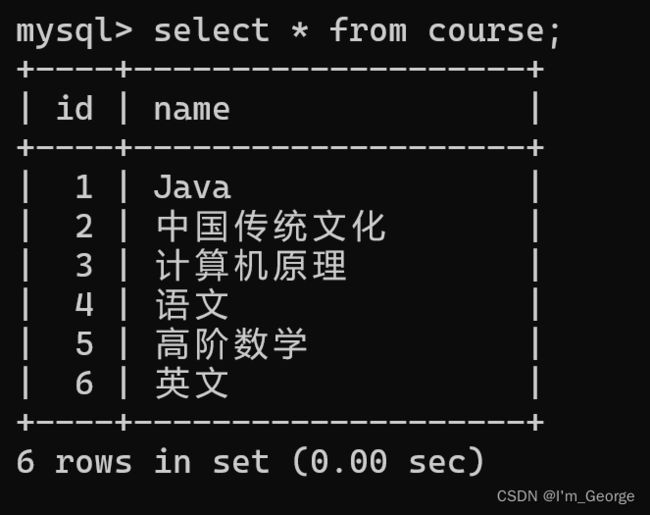
create table course(id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
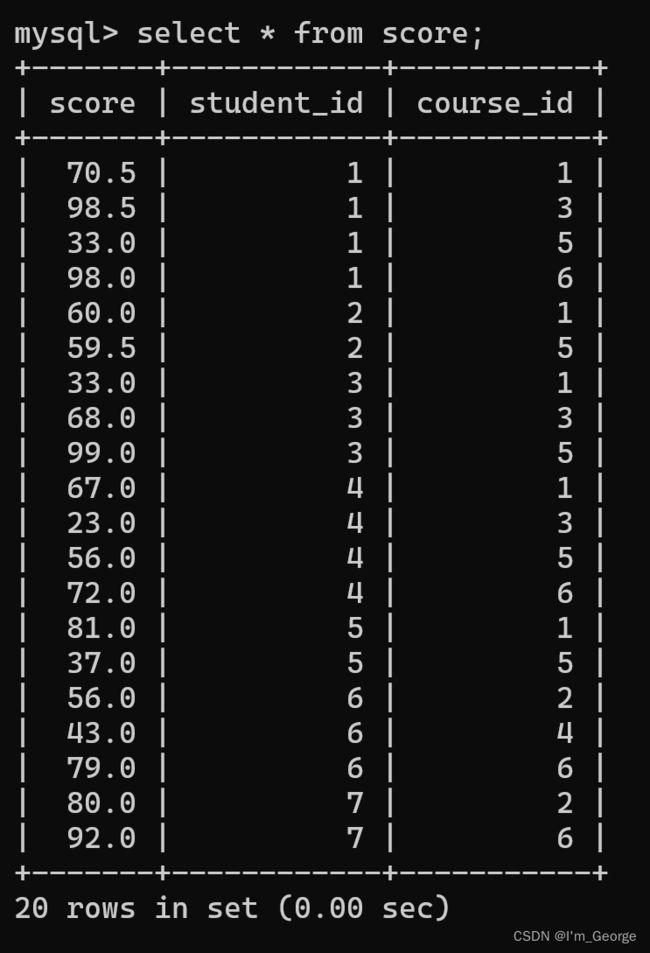
create table score(score decimal(3, 1), student_id int, course_id int);
insert into classes(name, `desc`) values
('计算机系2019级1班', '学习了计算机原理、C和Java语言、数据结构和算法'),
('中文系2019级3班','学习了中国传统文学'),
('自动化2019级5班','学习了机械自动化');
insert into student(sn, name, qq_mail, classes_id) values
('09982','黑旋风李逵','[email protected]',1),
('00835','菩提老祖',null,1),
('00391','白素贞',null,1),
('00031','许仙','[email protected]',1),
('00054','不想毕业',null,1),
('51234','好好说话','[email protected]',2),
('83223','tellme',null,2),
('09527','老外学中文','[email protected]',2);
insert into course(name) values
('Java'),('中国传统文化'),('计算机原理'),('语文'),('高阶数学'),('英文');
insert into score(score, student_id, course_id) values
-- 黑旋风李逵
(70.5, 1, 1),(98.5, 1, 3),(33, 1, 5),(98, 1, 6),
-- 菩提老祖
(60, 2, 1),(59.5, 2, 5),
-- 白素贞
(33, 3, 1),(68, 3, 3),(99, 3, 5),
-- 许仙
(67, 4, 1),(23, 4, 3),(56, 4, 5),(72, 4, 6),
-- 不想毕业
(81, 5, 1),(37, 5, 5),
-- 好好说话
(56, 6, 2),(43, 6, 4),(79, 6, 6),
-- tellme
(80, 7, 2),(92, 7, 6);
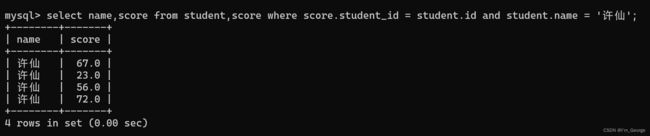
例1:
-- 查询“许仙”同学的 成绩
-- 写法1:
select name , score from student , score where student.id = score.student_id and student.name = "许仙";
-- 写法2:
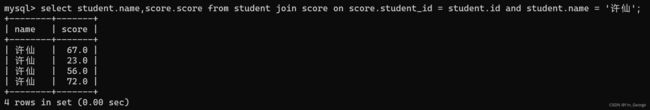
select student.name,score.score from student join score on student.id = score.student_id and student.name = "许仙";
例2:
-- 查询所有同学的成绩,及同学的个人信息:
-- 写法一:
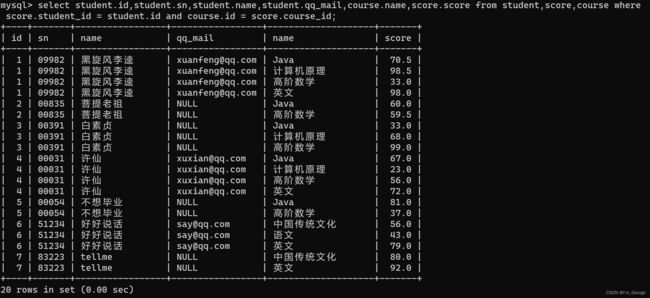
select student.id,student.sn,student.name,student.qq_mail,course.name,score.score from student,score,course where score.student_id = student.id and course.id = score.course_id;
-- 写法二:
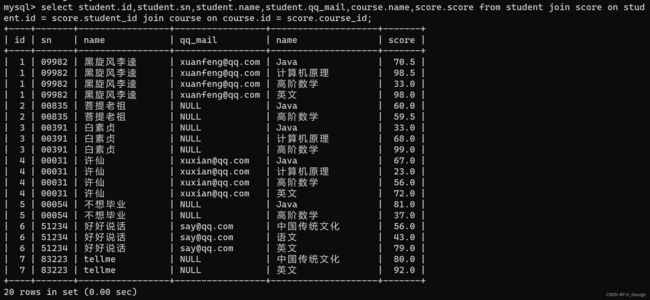
select student.id,student.sn,student.name,student.qq_mail,course.name,score.score from student join score on student.id = score.student_id join course on course.id = score.course_id; -- student join score join course
注意这里想把student,course,score这三个表给结合起来,我们用score当作中间的连接物来连接。
例三:
-- 查询所有同学的总成绩,及同学的个人信息
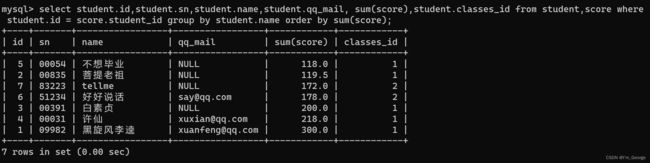
select student.id,student.sn,student.name,student.qq_mail, sum(score),student.classes_id from student,score where student.id = score.student_id group by student.name order by sum(score); -- right
-- 执行顺序:from -> student与score两个表进行联合, where -> 筛选出正确的组合方式,group by -> 进行分组 sum(score) -> 按照分的组进行score求和,-> select挑选出 你想要的列 -> order by(sum(score)) -> 根据总的分数进行排名。
select student.id,student.sn,student.name,student.qq_mail, sum(score),student.classes_id from student,score group by student.name having student.id = score.student_id order by sum(score); -- error
-- 执行顺序:from -> student与score两个表进行联合,group by student.name -> 进行分组 -> sum(score) 按照分的组进行score求和 -> having 条件执行 -> select -> order by
-- 这里sum根据分组求和完之后就变成一行了,很多数据就丢失了,后面在执行having就没法执行了。
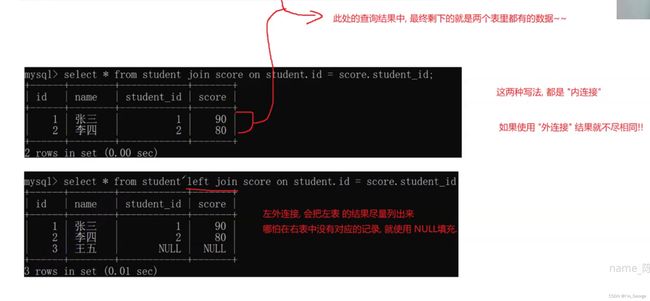
from多个表只能实现内连接,但是join on 既可以实现内连接也可以实现外连接。
SQL Select语句完整的执行顺序:
- 1、from子句组装来自不同数据源的数据; (先join在on)
- 2、where子句基于指定的条件对记录行进行筛选;
- 3、group by子句将数据划分为多个分组;
- 4、使用聚集函数进行计算;
- 5、使用having子句筛选分组;
- 6、计算所有的表达式;
- 7、select 的字段;
- 8、使用order by对结果集进行排序。
4.3.2:外连接
外连接分为左外连接和右外连接。如果联合查询,左侧的表完全显示我们就说是左外连接;右侧的表完
全显示我们就说是右外连接。
-- 格式:
-- 左外连接,表1完全显示
select 字段名 from 表名1 left join 表名2 on 连接条件;
-- 右外连接,表2完全显示
select 字段 from 表名1 right join 表名2 on 连接条件;
例1:
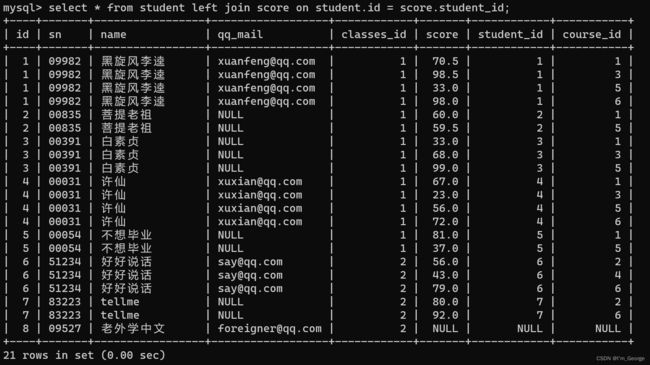
-- 查询所有同学的成绩,及同学的个人信息,如果该同学没有成绩,也需要显示
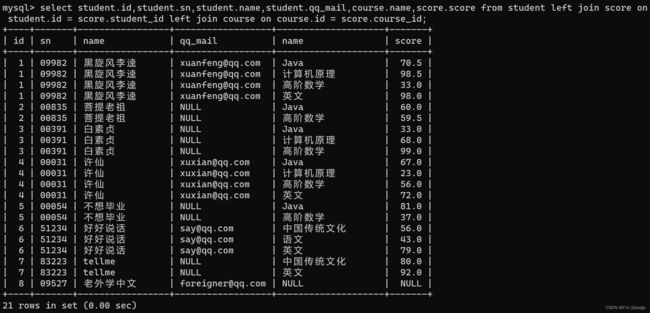
select student.id,student.sn,student.name,student.qq_mail,course.name,score.score from student left join score on student.id = score.student_id left join course on course.id = score.course_id;
例2:
select * from student left join score sco on stu.id=sco.student_id;
-- 即使不满足 stu.id = sco.student_id 也要把左侧的student的信息打印出来
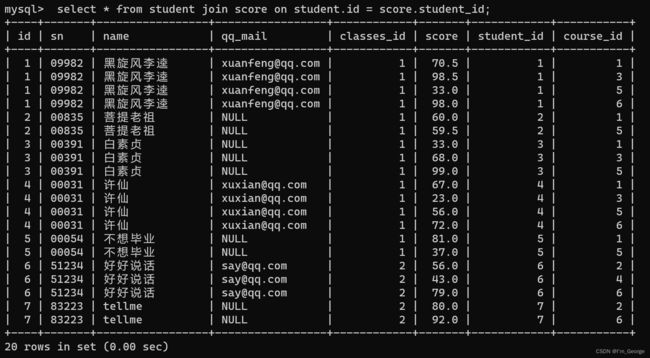
select * from student join score on student.id = score.student_id;
内外连接的区别:
基本上没啥区别
4.3.3:自连接
自连接是指在同一张表连接自身进行查询。
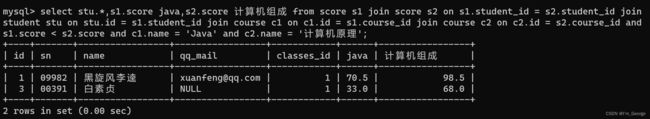
-- 显示所有“计算机原理”成绩比“Java”成绩高的成绩信息
select stu.*,s1.score java,s2.score 计算机组成 from score s1 join score s2 on s1.student_id = s2.student_id join student stu on stu.id = s1.student_id join course c1 on c1.id = s1.course_id join course c2 on c2.id = s2.course_id and s1.score < s2.score and c1.name = 'Java' and c2.name = '计算机原理';
自连接将行之间计算转化为列之间的计算,因为我们平时大部分使用列之间进行比较
4.4:子查询
(把一个查询作为另一个查询的条件)
4.4.1:单行子查询
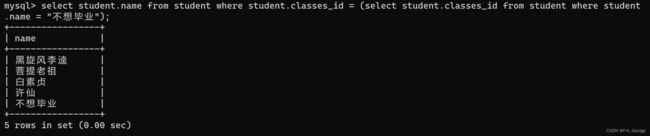
-- 查询与“不想毕业” 同学的同班同学:
select student.name from student where student.classes_id = (select student.classes_id from student where student.name = "不想毕业");
一般不建议套娃
4.4.2:多行子查询:
返回多行记录的子查询
[NOT] IN关键字
-- 查询“语文”或“英文”课程的成绩信息
-- 使用 in
select * from score where score.course_id in (select id from course where course.name = '语文' or course.name = '英文');
-- 使用not in
select * from score where score.course_id not in (select id from course where course.name != '语文' or course.name != '英文');
可以使用多列包含:
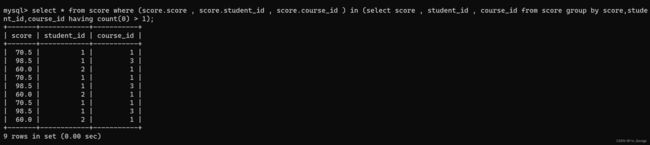
-- 插入重复的分数:score, student_id, course_id列重复
insert into score (score , student_id , course_id)values(70.5, 1, 1),(98.5, 1, 3),(60, 2, 1);
-- 查询重复的分数
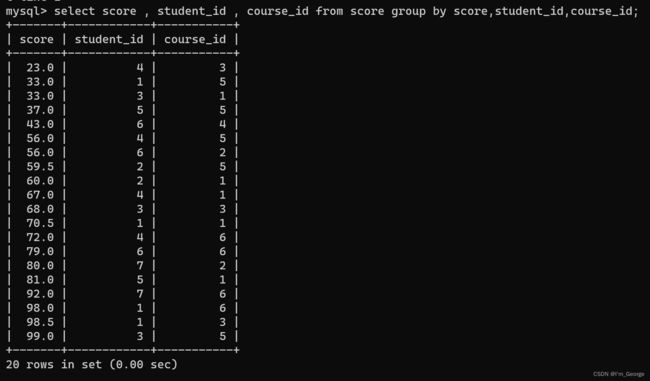
select * from score where (score.score , score.student_id , score.course_id ) in (select score , student_id , course_id from score group by score,student_id,course_id having count(0) > 1); -- (难点) 解析如下
select score , student_id , course_id from score group by score,student_id,course_id having count(0) > 1);
-- 在score里面根据score , student_id , course_id进行分组,优先级顺序是从左往右依次递减,当这条语句执行的目的是将score , student_id , course_id 都相同的记录进行合并。然后再执行count(0)语句,来计算每组有几条语句合并成了一条,再执行having语句,只有满足每组有>=1条记录合并成一组的才留下。
-->> 以上做法的目的是找到重复的语句,需要注意的是每个组里面是先执行count再执行having。
-- 最后再执行select * from score where (score.score , score.student_id , score.course_id ) in 从而找到所有的重复语句并将其打印出来。
补充:
子查询的结果是在内存中的,如果查询结果太大,内存放不下,in就用不了了,就可以使用exists代替。但是exists的可读性比较差,执行效率也大大低于in,只是使用这个解决特殊场景
单行子查询与多行子查询的不同就在于子查询语句返回的记录的条数,当返回一个数据的时候用=来接受
当返回多个数据的时候就用in 或 exists 来接收
4.4.3:在from子句中使用子查询:
子查询语句出现在from子句中。这里要用到数据查询的技巧,把一个子查询当做一个临时表使用
-- 查询所有比“中文系2019级3班”平均分高的成绩信息
-- 获取“中文系2019级3班”的平均分,将其看作临时表
select classes.name, avg(score) from student join score on student.id = score.student_id join classes on classes.id = student.classes_id where classes.name = '中文系2019级3班';
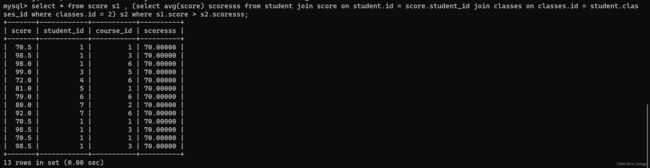
-- 查询所有比“中文系2019级3班”平均分高的成绩信息
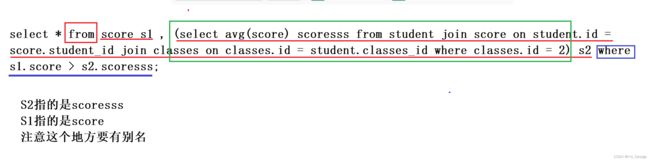
select * from score s1 , (select avg(score) scoresss from student join score on student.id = score.student_id join classes on classes.id = student.classes_id where classes.id = 2) s2 where s1.score > s2.scoresss;
4.5:合并查询
在实际应用中,为了合并多个select的执行结果,可以使用集合操作符 union,union all。使用UNION
和UNION ALL时,前后查询的结果集中,字段需要一致。
union
该操作符用于取得两个结果集的并集。当使用该操作符时,会自动去掉结果集中的重复行。
-- 查询id小于3,或者名字为“英文”的课程:
select * from course where course.name = "英文" union select * from course where course.id < 3;
-- 或者使用or来实现
select * from course where id<3 or name='英文';
直接使用or不久行了吗,为啥呀使用union?
用or只能查询来自同一个表中的数据,如果使用union查询的结果可以来自不同的表,只是查询结果的列匹配
union all
该操作符用于取得两个结果集的并集。当使用该操作符时,不会去掉结果集中的重复行。
-- 查询id小于3,或者名字为“Java”的课程
select * from course where course.name = "英文" union all select * from course where course.id < 3;
union于union all差不多,union 有去重的功能,将重复的数据仅保留一份,而union all没有去重的功能。