Pytorch深度学习(五):加载数据集以及mini-batch的使用
Pytorch深度学习(五):加载数据集以及mini-batch的使用
- 参考B站课程:《PyTorch深度学习实践》完结合集
- 传送门:《PyTorch深度学习实践》完结合集
一、预备知识
- Dataset是一个抽象函数,不能直接实例化,所以我们要创建一个自己类,继承Dataset
继承Dataset后我们必须实现三个函数:
init()是初始化函数,之后我们可以提供数据集路径进行数据的加载
getitem()帮助我们通过索引找到某个样本
len()帮助我们返回数据集大小
class DiabetesDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filepath):
xy = np.loadtxt(filepath, delimiter=',', dtype=np.float32)
self.len = xy.shape[0]
self.xdata = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, :-1])
self.ydata = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, [-1]])
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.xdata[index], self.ydata[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
- 用DataLoader为数据进行分组,batch_size是一个组中有多少个样本,shuffle表示要不要对样本进行随机排列。一般来说,训练集我们随机排列,测试集不需要。num_workers表示我们可以用多少进程并行的运算,由于我的版本原因(cuda不好使),只能选择num_workers=0,一般可以写num_workers=2,进行并行运算算提高速度。
dataset = DiabetesDataset('diabetes.csv.gz')
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
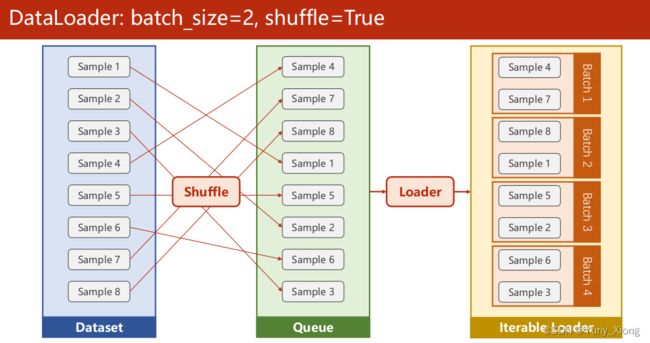
示意图中选择了batch_size=2,于是取每两组样本为mini-batch。而在程序中,我们选取了batch_size=32,于是取每32个样本为一个mini-batch,最后mini-batch根据具体的样本总数决定其包含的样本数量。
二、程序实现
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class DiabetesDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filepath):
xy = np.loadtxt(filepath, delimiter=',', dtype=np.float32)
self.len = xy.shape[0]
self.xdata = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, :-1])
self.ydata = torch.from_numpy(xy[:, [-1]])
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.xdata[index], self.ydata[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
dataset = DiabetesDataset('diabetes.csv.gz')
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
xtest = dataset.xdata
ytest = dataset.ydata
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(8,6)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(6,4)
self.linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(4,1)
self.sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear1(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear2(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.linear3(x))
return x
model = Model()
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
costlist = []
acclist = []
# 若使用的是非linux系统,则以下循环部分需要封装
for epoch in range(10000):
l = 0
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
# 1. Prepare data
inputs, labels = data
# 2. Forward
ypred = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(ypred, labels)
l += loss.item()
#print(epoch, i, loss.item())
# 3. Backward
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
# 4. Updata
optimizer.step()
costlist.append(l / len(inputs))
# 每迭代1000次测试一次精确度
if epoch % 1000 == 999:
ypredtest = model(xtest)
ypredlabel = torch.where(ypredtest>0.5, torch.tensor([1]), torch.tensor([0]))
acc = torch.eq(ypredlabel, ytest).sum().item() / ytest.size(0)
acclist.append(acc)
print('the accuracy of testdataset:', acc)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(range(10000), costlist)
plt.title('error of mini-batch')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])*1000 , acclist)
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.title('the accuracy of test dataset')
plt.show()
- 输出结果
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8234519104084321
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8313570487483531
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.855072463768116
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8629776021080369
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8669301712779973
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8682476943346509
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8722002635046113
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8748353096179183
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8761528326745718
the accuracy of testdataset: 0.8774703557312253
- 输出图片
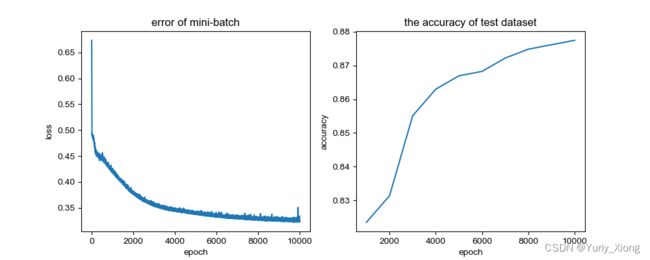
由于我的计算机的性能的限制,且mini-batch的使用对于计算力的耗费更大,所以我们只计算了10000步,更长的步数需要花的时间更多,预计迭代步数突破10w后,会得到一个准确率更高的好结果。