莫烦-pytorch
pytorch 莫烦
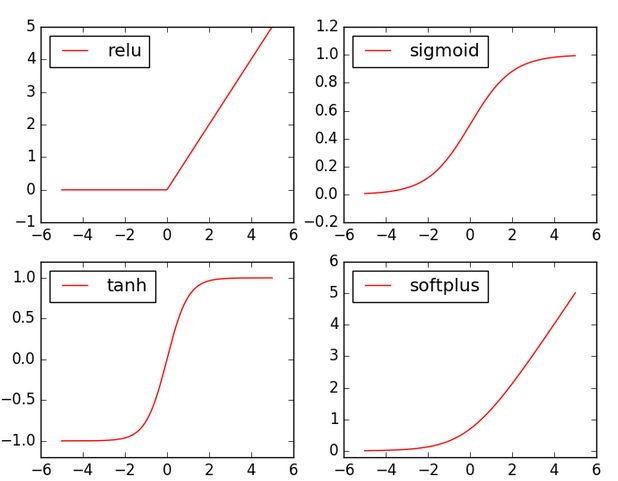
激励函数
Y = AF(Wx)
这里的AF()就是激励函数,其实就是另外一个非线性函数。比如relu,sigmoid,tanh
回归
- 建立神经网络
class Net(torch.nn.Module): # 继承 torch 的 Module
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__() # 继承 __init__ 功能
# 定义每层用什么样的形式
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # 隐藏层线性输出
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # 输出层线性输出
def forward(self, x): # 这同时也是 Module 中的 forward 功能
# 正向传播输入值, 神经网络分析出输出值
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # 激励函数(隐藏层的线性值)
x = self.predict(x) # 输出值
return x
- 训练网络
# optimizer 是训练的工具,有四个常用的optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2) # 传入 net 的所有参数, 学习率
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # 预测值和真实值的误差计算公式 (均方差)
for t in range(100):
prediction = net(x) # 喂给 net 训练数据 x, 输出预测值
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # 计算两者的误差
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空上一步的残余更新参数值
loss.backward() # 误差反向传播, 计算参数更新值
optimizer.step() # 将参数更新值施加到 net 的 parameters 上
分类
- 建立神经网络
def forward(self, x):
# 正向传播输入值, 神经网络分析出输出值
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # 激励函数(隐藏层的线性值)
x = self.out(x) # 输出值, 但是这个不是预测值, 预测值还需要再另外计算
return x
- 训练网络
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
快速搭建
搭建神经网络不止class net()这种方法,有一个快速的方法torch.nn.Sequential()
net = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
Sequential方法直接认定的就是relu()这种激励函数,而对于自己手写的net来说,可以在forward()方法中指定激励函数,就会更加灵活一些。
保存与提取
- 保存
torch.save(net1, 'net.pkl') # 保存整个网络
torch.save(net1.state_dict(), 'net_params.pkl') # 只保存网络中的参数 (速度快, 占内存少)
- 提取
def restore_net():
# restore entire net1 to net2
net2 = torch.load('net.pkl')
prediction = net2(x)
- 提取网络参数
网络参数:能独立地反映网络特性的参数
提取所有网路参数
net3.load_state_dict(torch.load('net_params.pkl'))
prediction = net3(x)
批训练
DataLoader
# 先转换成 torch 能识别的 Dataset
torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(data_tensor=x, target_tensor=y)
# 把 dataset 放入 DataLoader
loader = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=torch_dataset, # torch TensorDataset format
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, # mini batch size.,就是每次取多少数据
shuffle=True, # 要不要打乱数据 (打乱比较好)
num_workers=2, # 多线程来读数据
)
优化器
要让神经网络聪明起来!!!!
- SGD
- Momentum
- AdaGrad
- RMSProp
- Adam
- SGD
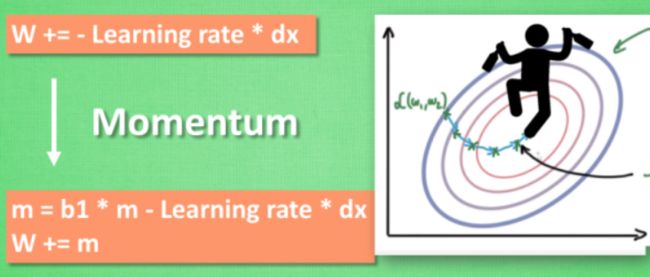
- Momentum
所以我们把这个人从平地上放到了一个斜坡上, 只要他往下坡的方向走一点点, 由于向下的惯性, 他不自觉地就一直往下走, 走的弯路也变少了. 这就是 Momentum 参数更新.
- AdaGrad
而是给他一双不好走路的鞋子, 使得他一摇晃着走路就脚疼, 鞋子成为了走弯路的阻力, 逼着他往前直着走
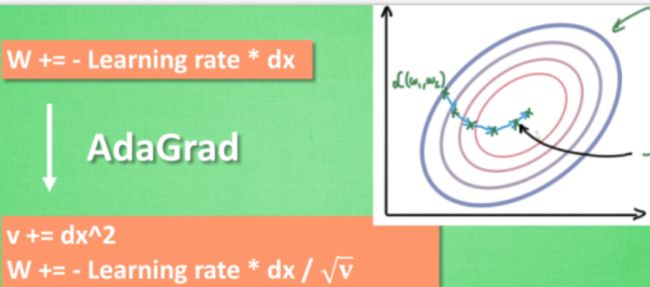
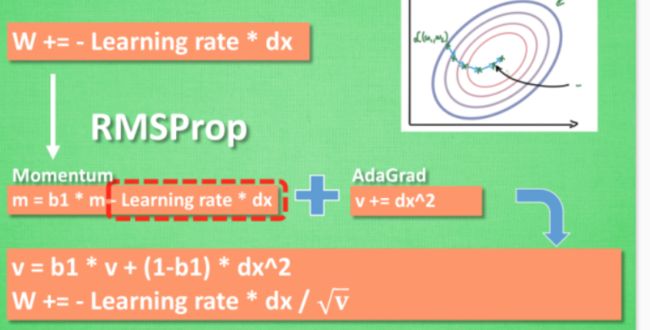
- RMSProp
是momentum和adagrad的集合体,同时具备两者的优势。但是RMSProp并没有包含momentum的一部分,所以在Adam中又进一步改进
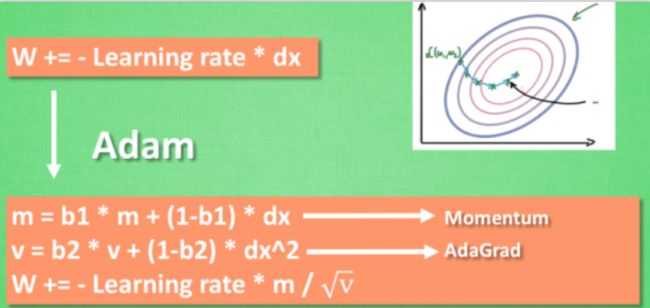
- Adam
对于Adam来说,能快好的达到目标,快速收敛到最好的地方
Optimizer
- SGD
- Momentum
- RMSProp
- Adam
net_SGD = Net()
net_Momentum = Net()
net_RMSprop = Net()
net_Adam = Net()
# different optimizers
opt_SGD = torch.optim.SGD(net_SGD.parameters(), lr=LR)
opt_Momentum = torch.optim.SGD(net_Momentum.parameters(), lr=LR, momentum=0.8)
opt_RMSprop = torch.optim.RMSprop(net_RMSprop.parameters(), lr=LR, alpha=0.9)
opt_Adam = torch.optim.Adam(net_Adam.parameters(), lr=LR, betas=(0.9, 0.99))
在实验中,对各个优化器还是都应该试一试,看看哪个更好
CNN
-
- 从下到上的顺序, 首先是输入的图片(image), 经过一层卷积层 (convolution), 然后在用池化(pooling)方式处理卷积的信息, 这里使用的是 max pooling 的方式.
- 然后在经过一次同样的处理, 把得到的第二次处理的信息传入两层全连接的神经层 (fully connected),这也是一般的两层神经网络层,最后在接上一个分类器(classifier)进行分类预测. 这仅仅是对卷积神经网络在图片处理上一次简单的介绍.
-
- 卷积层(Convolutional Layer) - 主要作用是提取特征
- 池化层(Max Pooling Layer) - 主要作用是下采样(downsampling),却不会损坏识别结果
- 全连接层(Fully Connected Layer) - 主要作用是分类预测
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1, # input height
out_channels=16, # n_filters
kernel_size=5, # filter size
stride=1, # filter movement/step
padding=2, # 如果想要 con2d 出来的图片长宽没有变化, padding=(kernel_size-1)/2 当 stride=1
), # output shape (16, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2), # 在 2x2 空间里向下采样, output shape (16, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (16, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32, 14, 14)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(2), # output shape (32, 7, 7)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10) # fully connected layer, output 10 classes
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # 展平多维的卷积图成 (batch_size, 32 * 7 * 7)
output = self.out(x)
return output
这个 CNN 整体流程是 卷积(Conv2d) -> 激励函数(ReLU) -> 池化, 向下采样 (MaxPooling) -> 再来一遍 -> 展平多维的卷积成的特征图 -> 接入全连接层 (Linear) -> 输出
RNN
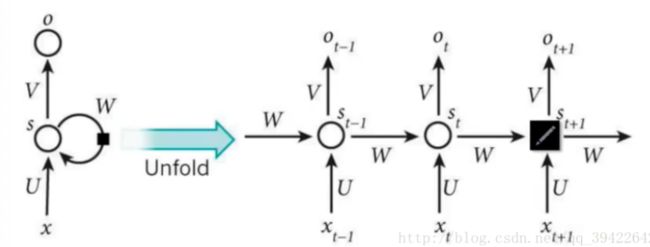
RNN是在有顺序的数据上进行学习的,在反向传递得到误差的时候,每一步都会乘以自己的一个参数W,若W是小于1,则误差传递到初始时间的时候会接近0,即梯度消失;反之,则是梯度爆炸!hong!然后LSTM是为了解决这个问题而提出来的
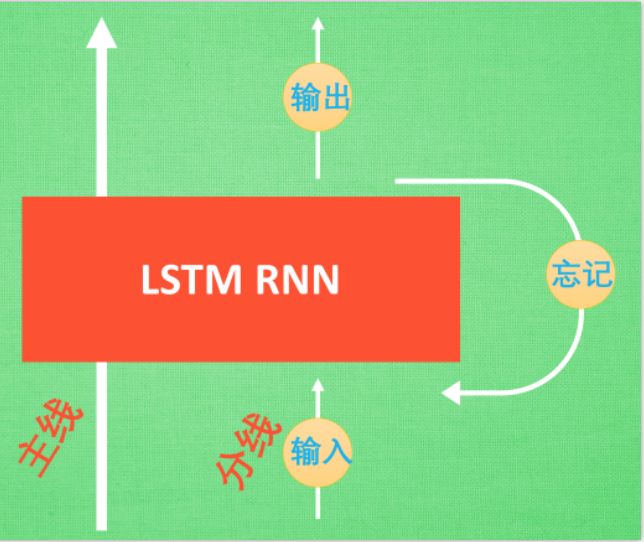
LSTM循环神经网络
-
主线:就是主线剧情
-
分线,即是原本的RNN体系。
1. 输入:重要程度 写入主线剧情 进行分析.
2.忘记: 如果此时的分线剧情更改了我们对之前剧情的想法, 那么忘记控制就会将之前的某些主线剧情忘记, 按比例替换成现在的新剧情
3.输出:基于目前的主线剧情和分线剧情判断要输出的到底是什么
RNN分类问题
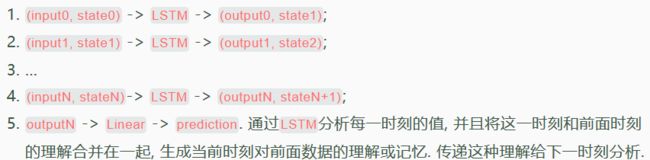
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM( # LSTM 效果要比 nn.RNN() 好多了
input_size=28, # 图片每行的数据像素点
hidden_size=64, # rnn hidden unit
num_layers=1, # 有几层 RNN layers
batch_first=True, # input & output 会是以 batch size 为第一维度的特征集 e.g. (batch, time_step, input_size)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(64, 10) # 输出层
def forward(self, x):
# x shape (batch, time_step, input_size)
# r_out shape (batch, time_step, output_size)
# h_n shape (n_layers, batch, hidden_size) LSTM 有两个 hidden states, h_n 是分线, h_c 是主线
# h_c shape (n_layers, batch, hidden_size)
r_out, (h_n, h_c) = self.rnn(x, None) # None 表示 hidden state 会用全0的 state
# 选取最后一个时间点的 r_out 输出
# 这里 r_out[:, -1, :] 的值也是 h_n 的值
out = self.out(r_out[:, -1, :])
return out
RNN回归问题
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.RNN( # 这回一个普通的 RNN 就能胜任
input_size=1,
hidden_size=32, # rnn hidden unit
num_layers=1, # 有几层 RNN layers
batch_first=True, # input & output 会是以 batch size 为第一维度的特征集 e.g. (batch, time_step, input_size)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32, 1)
def forward(self, x, h_state): # 因为 hidden state 是连续的, 所以我们要一直传递这一个 state
# x (batch, time_step, input_size)
# h_state (n_layers, batch, hidden_size)
# r_out (batch, time_step, output_size)
r_out, h_state = self.rnn(x, h_state) # h_state 也要作为 RNN 的一个输入
outs = [] # 保存所有时间点的预测值
for time_step in range(r_out.size(1)): # 对每一个时间点计算 output
outs.append(self.out(r_out[:, time_step, :]))
return torch.stack(outs, dim=1), h_state
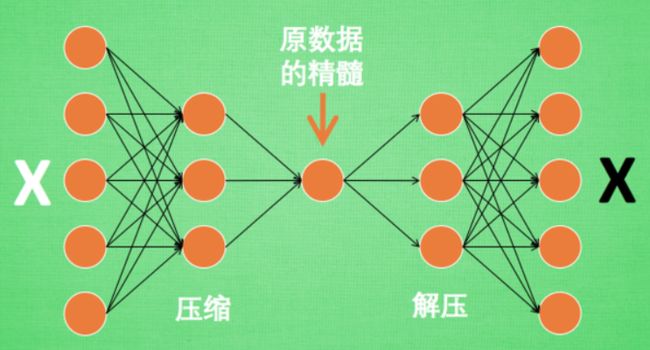
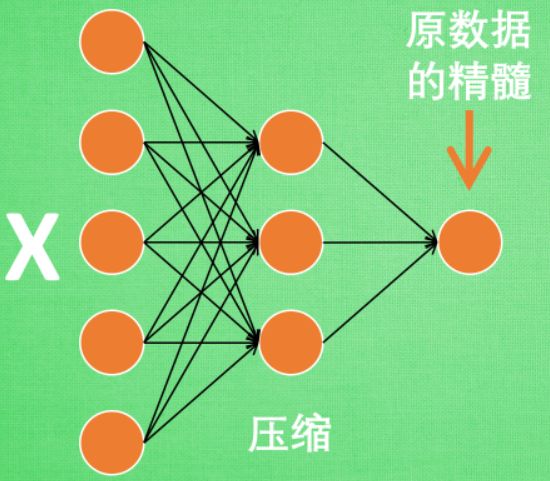
自编码(Autoencoder)
AutoEncoder
class AutoEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(AutoEncoder, self).__init__()
# 压缩
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28, 128), 28*28->128
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(128, 64), 128->64
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(64, 12), 64->12
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(12, 3), # 压缩成3个特征, 进行 3D 图像可视化
)
# 解压
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(3, 12),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(12, 64),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(64, 128),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(128, 28*28),
nn.Sigmoid(), # 激励函数让输出值在 (0, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return encoded, decoded
autoencoder = AutoEncoder()
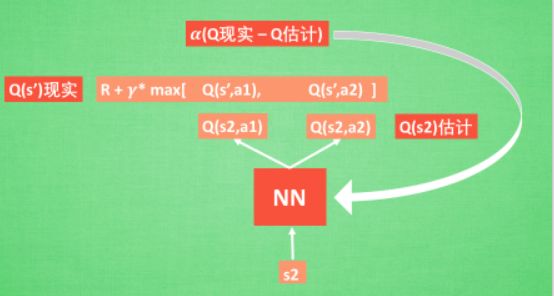
DQN
- 通过NN预测出Q(s2, a1) 和 Q(s2,a2) 的值,即Q估计
- 选取Q估计中最大值的动作来换取还清中的奖励reward
- Q现实是之前在Q-learing中的值
- 更新神经网络中的参数
- 显示网络和估计网络建立的基本体系
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(N_STATES, 10)
self.fc1.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.1) # initialization
self.out = nn.Linear(10, N_ACTIONS)
self.out.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.1) # initialization
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
actions_value = self.out(x)
return actions_value
- DQN
class DQN(object):
def __init__(self):
# 建立 target net 和 eval net 还有 memory
def choose_action(self, x):
# 根据环境观测值选择动作的机制
return action
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
# 存储记忆
#如果记忆满了,就覆盖老数据
def learn(self):
# target 网络更新
# 学习记忆库中的记忆
GAN
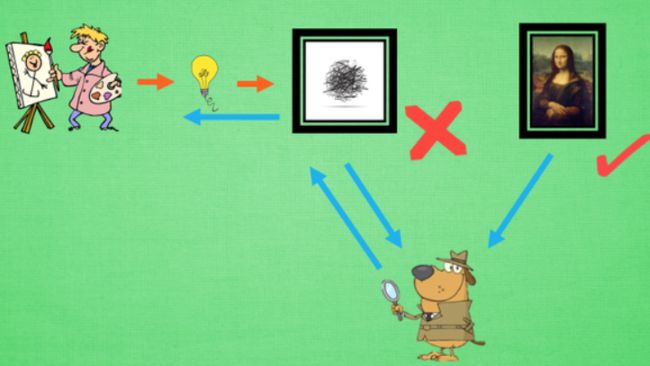
大白话解释GAN:新手画家随机灵感画画,新手鉴赏家接受画作(不知道是新手画还是著名画),说出判断,一边还告诉新手怎么画,然后新手就画的越来越像著名画家的画。
G = nn.Sequential( # Generator
nn.Linear(N_IDEAS, 128), # random ideas (could from normal distribution)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, ART_COMPONENTS), # making a painting from these random ideas
)
D = nn.Sequential( # Discriminator
nn.Linear(ART_COMPONENTS, 128), # receive art work either from the famous artist or a newbie like G
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 1),
nn.Sigmoid(), # tell the probability that the art work is made by artist
)
Dropout缓解过拟合
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5) 这里的 0.5 指的是随机有 50% 的神经元会被关闭/丢弃.
net_dropped = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5), # drop 50% of the neuron
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, N_HIDDEN),
torch.nn.Dropout(0.5), # drop 50% of the neuron
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(N_HIDDEN, 1),
)
批标准化(Batch Normalization)BN
- 将分散的数据统一的一种做法,使数据具有统一规格。
- BN被添加在每一个全连接和激励函数之间,对每一层神经网络进行标准化
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, batch_normalization=False):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.do_bn = batch_normalization
self.fcs = [] # 太多层了, 我们用 for loop 建立
self.bns = []
self.bn_input = nn.BatchNorm1d(1, momentum=0.5) # 给 input 的 BN
for i in range(N_HIDDEN): # 建层
input_size = 1 if i == 0 else 10
fc = nn.Linear(input_size, 10)
setattr(self, 'fc%i' % i, fc) # 注意! pytorch 一定要你将层信息变成 class 的属性! 我在这里花了2天时间发现了这个 bug
self._set_init(fc) # 参数初始化
self.fcs.append(fc)
if self.do_bn:
bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(10, momentum=0.5)
setattr(self, 'bn%i' % i, bn) # 注意! pytorch 一定要你将层信息变成 class 的属性! 我在这里花了2天时间发现了这个 bug
self.bns.append(bn)
self.predict = nn.Linear(10, 1) # output layer
self._set_init(self.predict) # 参数初始化
def _set_init(self, layer): # 参数初始化
init.normal_(layer.weight, mean=0., std=.1)
init.constant_(layer.bias, B_INIT)
def forward(self, x):
pre_activation = [x]
if self.do_bn: x = self.bn_input(x) # 判断是否要加 BN
layer_input = [x]
for i in range(N_HIDDEN):
x = self.fcs[i](x)
pre_activation.append(x) # 为之后出图
if self.do_bn: x = self.bns[i](x) # 判断是否要加 BN
x = ACTIVATION(x)
layer_input.append(x) # 为之后出图
out = self.predict(x)
return out, layer_input, pre_activation
# 建立两个 net, 一个有 BN, 一个没有
nets = [Net(batch_normalization=False), Net(batch_normalization=True)]