C#学习笔记一 委托、事件
C# 委托、事件
1、Action委托、Func委托
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
Calculator calculator=new Calculator();
//Action委托
Action Cal=new Action(calculator.Report);
//直接调用函数
Calculator.Report();
//通过委托调用函数
Cal.Invoke();
//简便写法
Cal();
//Func委托
int a=100,b=200,c=0;
Func<int,int,int> func1=new Func<int,int,int>(Calculator.Add);
//尖括号中为<参数1,参数2,返回值>
Func<int,int,int> func2=new Func<int,int,int>(Calculator.Sub);
//利用委托调用函数
c=func1.Invoke(a,b);//简便写法 c=func1(a,b)
Console.WriteLine(c);
c=func2.Invoke(a,b);//简便写法 c=func1(a,b)
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public void Report(){
console.WriteLine("123");
}
public int Add(int a,int b){
int result=a+b;
return result;
}
public int Sub(int a,int b){
int result=a-b;
return result;
}
}
}
2、自定义委托
避免写错地方结果声明成嵌套类型:
一般委托的声明在命名空间内,和Program类同级,如果声明在Program类中,会声明成为嵌套类 类型。
namespace DelegateExample
{
//自定义委托声明格式
public delegate double Cal(double x,double y);
class Program
{
static void main(string[] args){
Calculator calculator=new Calculator();
Cal cal1=new Cal(calculator.Add);
Cal cal2=new Cal(calculator.Sub);
Cal cal3=new Cal(calculator.Mul);
Cal cal4=new Cal(calculator.Div);
double a=200,b=100,c=0;
c=cal1.invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c=cal2.invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c=cal3.invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c=cal4.invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public double Add(double a,double b){
return a+b;
}
public double Sub(double a,double b){
return a-b;
}
public double Mul(double a,double b){
return a*b;
}
public double Div(double a,double b){
return a/b;
}
}
}
3、委托的一般使用
3.1 模板方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name{ get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct)
{
Product product = getProduct.Invoke();
Box box = new Box();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
return product;
}
}
}
//使用模板方法的好处,代码复用性高,只需要扩充ProductFactory类中的方法
//Product类、WrapFactory类,均不用修改
3.2 回调方法
需求:
使用委托的回调方法,在上述代码中实现,若产品价格大于等于50时,打印输出商品信息
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Logger logger = new Logger();
Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1,log);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2,log);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Logger
{
public void Log(Product product)
{
Console.WriteLine("Product '{0}' created at {1}. Price is {2}.", product.Name, DateTime.UtcNow, product.Price);
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name{ get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct,Action<Product> logCallback)
{
Product product = getProduct.Invoke();
if (product.Price >= 50)
{
logCallback(product);
}
Box box = new Box();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
product.Price = 20;
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
product.Price = 99;
return product;
}
}
}
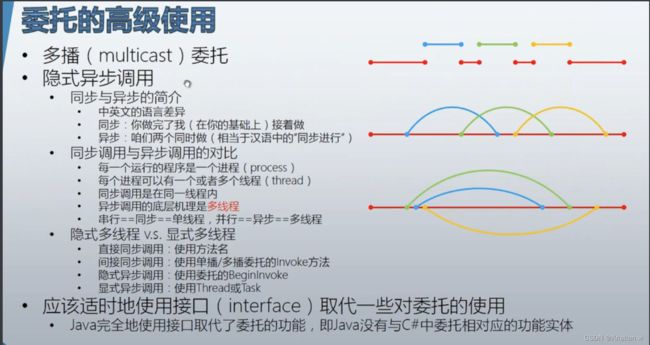
3.3 委托的高级使用
同步与异步的概念:与中文不同
多播委托
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomeWork);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomeWork);
Action action3= new Action(stu3.DoHomeWork);
//单播委托
/*action1.Invoke();
action2.Invoke();
action3.Invoke();*/
//多播委托
action1 += action2;
action1 += action3;
action1.Invoke();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomeWork()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
隐式异步调用
首先了解一下同步调用
直接同步调用与间接同步调用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
//直接同步调用
/*stu1.DoHomeWork();
stu2.DoHomeWork();
stu3.DoHomeWork();*/
//间接同步调用
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomeWork);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomeWork);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomeWork);
action1.Invoke();
action2.Invoke();
action3.Invoke();
//或者使用多播委托,也是同步调用的
//action1+=action2;action1+=action3;action1.Invoke();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}.", i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomeWork()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
异步调用
隐式异步调用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
//隐式异步调用
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomeWork);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomeWork);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomeWork);
action1.BeginInvoke(null,null);
action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);
action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}.", i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomeWork()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
显式异步调用(古老的方式:使用Thread进行显示异步调用)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
/*
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomeWork);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomeWork);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomeWork);
//隐式异步调用
action1.BeginInvoke(null,null);
action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);
action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);
*/
//使用Thread进行显式异步调用
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.DoHomeWork));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu2.DoHomeWork));
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu3.DoHomeWork));
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}.", i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomeWork()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
显式异步调用更高级的方式:Task,需要引用System.Threading.Tasks命名空间
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
public static object TTask { get; private set; }
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
Student stu2 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student stu3 = new Student() { ID = 1, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
/*
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomeWork);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomeWork);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomeWork);
//隐式异步调用
action1.BeginInvoke(null,null);
action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);
action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);
*/
//使用Thread进行显式异步调用
/*Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.DoHomeWork));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu2.DoHomeWork));
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu3.DoHomeWork));
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();*/
//更高级的方式,使用Task进行显式异步调用
Task task1 = new Task(new Action(stu1.DoHomeWork));
Task task2 = new Task(new Action(stu2.DoHomeWork));
Task task3 = new Task(new Action(stu3.DoHomeWork));
task1.Start();
task2.Start();
task3.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}.", i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomeWork()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).", this.ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
最好用接口代替委托
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Mhj2pXf5-1670512875811)(C:\Users\Wu\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20221208185431055.png)]
用接口代替第一个案例中的委托
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IProductFactory pizzaFactory = new PizzaFactory();
IProductFactory toyCarFactory = new ToyCarFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(pizzaFactory);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(toyCarFactory);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
interface IProductFactory
{
Product Make();
}
class PizzaFactory : IProductFactory
{
public Product Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
}
class ToyCarFactory : IProductFactory
{
public Product Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
return product;
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
public Box WrapProduct(IProductFactory productFactory)
{
Product product = productFactory.Make();
Box box = new Box();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
}
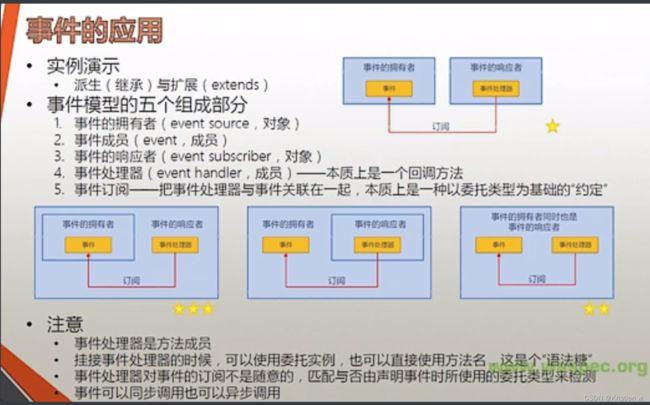
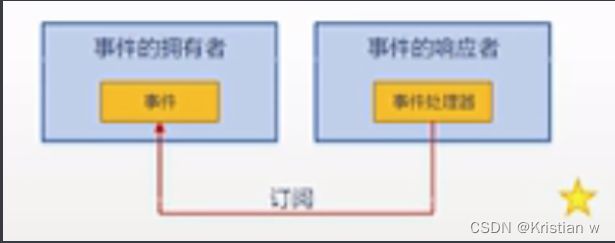
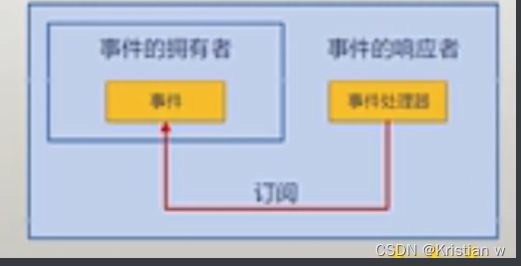
事件
1.初步了解
1.事件的简单示例
using System;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();//timer为事件的拥有者
timer.Interval = 1000;
Boy boy = new Boy();//boy为事件的订阅者
Girl girl = new Girl();
timer.Elapsed += boy.Action;
timer.Elapsed += girl.Action;
timer.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Boy
{
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Jump!");
}
}
class Girl
{
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Sing!");
}
}
}
- 示例2
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form form = new Form();//form是事件的拥有者
Controller controller = new Controller(form);//controller是事件的订阅者
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class Controller
{
private Form form;
public Controller(Form form)
{
if (form != null)
{
this.form = form;
this.form.Click += this.FormClicked;//form.Click是事件成员,FromClicked是事件处理器
}
}
private void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
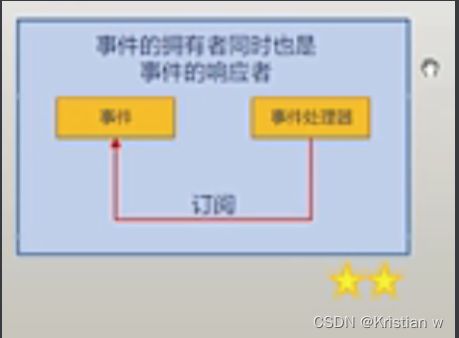
MyForm form = new MyForm();//form事件拥有者
form.Click += form.FormClicked;//事件成员form.Click;事件处理器form.FormClicked;
//事件订阅者也是form;
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form
{
internal void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
4.示例4
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form
{
private TextBox textBox;
private Button button;//事件拥有者是实例化的 Form.button
public MyForm()
{
this.textBox = new TextBox();
this.button = new Button();
this.Controls.Add(this.button);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);
this.button.Click += ButtonClicked;//button.Click是事件成员,
//ButtonClicked是事件处理器
//事件订阅者是MyForm的实例
}
private void ButtonClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.textBox.Text = "Hello, World!";
}
}
}
事件的声明
1.完整声明
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
}
}
public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
public class Customer
{
private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;
public event OrderEventHandler Order
{
add
{
this.orderEventHandler += value;
}
remove
{
this.orderEventHandler -= value;
}
}
public double Bill { get; set; }
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}.", this.Bill);
}
public void WalkIn()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant.", this.Bill);
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit Down");
}
public void Think()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me think...");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
if (this.orderEventHandler != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";
e.Size = "large";
this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadLine();
this.WalkIn();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
public class Waiter
{
public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}.", e.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch (e.Size)
{
case "small":
price = price * 0.5;
break;
case "large":
price = price * 1.5;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}
2.简略声明格式
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
}
}
public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
public class Customer
{
public event OrderEventHandler Order;
public double Bill { get; set; }
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}.", this.Bill);
}
public void WalkIn()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walk into the restaurant.", this.Bill);
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit Down");
}
public void Think()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me think...");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
if (this.Order != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";
e.Size = "large";
this.Order.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadLine();
this.WalkIn();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
public class Waiter
{
public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}.", e.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch (e.Size)
{
case "small":
price = price * 0.5;
break;
case "large":
price = price * 1.5;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}
委托、事件
- C# 委托、事件
-
- 1、Action委托、Func委托
- 2、自定义委托
- 3、委托的一般使用
-
- 3.1 模板方法
- 3.2 回调方法
- 3.3 委托的高级使用
-
- 同步与异步的概念:与中文不同
- 多播委托
- **隐式异步调用**
- **异步调用**
- 最好用接口代替委托
- 事件