Go语言实现AI五子棋智能算法
文章目录
- 前言
- 博弈树
- 博弈算法
-
- 打分机制的确定
- 极大极小算法
- alpha-beta剪枝
- 启发式搜索
- 代码实现
前言
周末在家闲来无事,下起了五子棋。其中人机对战部分引起了我的好奇,机器人如何实现自动下棋的功能的呢?带着如此疑问,我踏上了探寻真相的旅程!
博弈树
众所周知,评判一个人棋力如何就是判断其思考的深度。一个人棋力越厉害,其思考深度越深。对于AI来说也是一样,最常用的对弈数据结构为博弈树,博弈树(game tree)是一种特殊的根树,博弈树可以表示两名游戏参与者之间的一场博弈(游戏),他们交替行棋,试图获胜。我们以最简单的井字棋为例:

对于9宫格我们进行标号,如果我方先走一步5,那么就形成以下博弈树,也就是落子枚举:
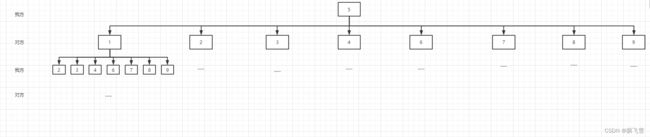
然而如果想要确定最优解,就需要引入评分机制,这就引出了极大极小算法。
博弈算法
常用的博弈算法为极大极小算法:
对于博弈树而言,树的叶子节点就是游戏的一个局面。极大极小算法利用的原理就是对手与自己都会选择最有利于自己的局面。这就需要一套打分机制,越有利于对手的局面,所得的分数越少,越有利于自己的局面,所得的分数越高。
打分机制的确定
对于五子棋而言,为了满足越有利于对手的局面,所得的分数越少,越有利于自己的局面,所得的分数越高的设定,如何进行局面分数评估呢?这边确定了如下规则:
- 如果我方局面中出现活1,+10分
- 如果我方局面中出现活2,+100分
- 如果我方局面中出现活3,+1000分
- 如果我方局面中出现活4,+10000分
- 如果我方局面中出现五连,+100000分
- 如果我方局面中出现死2,+10分
- 如果我方局面中出现死3,+100分
- 如果我方局面中出现死4,+1000分
- 如果对方局面中出现活1,-10分
- 如果对方局面中出现活2,-100分
- 如果对方局面中出现活3,-1000分
- 如果对方局面中出现活4,-10000分
- 如果对方局面中出现五连,-100000分
- 如果对方局面中出现死2,-10分
- 如果对方局面中出现死3,-100分
- 如果对方局面中出现死4,-1000分
对于一个局面,遍历棋盘所有位置,根据以上规则所有分数总和即为当前局面的分数。
go语言实现:
type ScoreMap struct {
role []int
score int
}
func InitScoreMapList() []ScoreMap {
scoreMapList := []ScoreMap{}
//活1 10分
r1 := []int{0, 1, 0}
s1 := ScoreMap{r1, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s1)
//活2 100分
r2 := []int{0, 1, 1, 0}
s2 := ScoreMap{r2, 100}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s2)
//活3 1000分
r3 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s3 := ScoreMap{r3, 1000}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s3)
//活4 10000分
r4 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s4 := ScoreMap{r4, 10000}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s4)
//五连 100000分
r5 := []int{1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
s5 := ScoreMap{r5, 100000}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s5)
//死2 10分
r6 := []int{0, 1, 1, -1}
s6 := ScoreMap{r6, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s6)
r7 := []int{-1, 1, 1, 0}
s7 := ScoreMap{r7, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s7)
//死3 100分
r8 := []int{-1, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s8 := ScoreMap{r8, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s8)
r9 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, -1}
s9 := ScoreMap{r9, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s9)
//死4 1000分
r10 := []int{-1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s10 := ScoreMap{r10, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s10)
r11 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, -1}
s11 := ScoreMap{r11, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s11)
//对手情况再copy一遍
scoreMapList2 := []ScoreMap{}
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
newScoreMap := ScoreMap{}
deepCopy(newScoreMap, scoreMap)
newScoreMap.score = -scoreMap.score
for _, v := range scoreMap.role {
newScoreMap.role = append(newScoreMap.role, -v)
}
scoreMapList2 = append(scoreMapList2, newScoreMap)
}
return append(scoreMapList, scoreMapList2...)
}
func eval(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, step int) int {
/*
评估当前局势分数
*/
total++
sum := 0
//对于每一行进行评估,从上到下,从左往右
//行,模拟从上到下
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//列,模拟从左到右
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > step {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[i][j+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
//if j == 1 {
// fmt.Println(scoreMap.role)
//}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//对每一列进行评估
//列
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//行
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > step {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[j+k][i] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//自左上到右下遍历
//行
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//列
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > l || i+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[j+k][i+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//列
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//行
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > l || i+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[i+k][j+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//自右上到左下遍历
//列
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//行
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if i < len(scoreMap.role) || j+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[j+k][i-k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//行
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//列
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if i < len(scoreMap.role) || j+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[i-k][j+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
return sum
}
极大极小算法
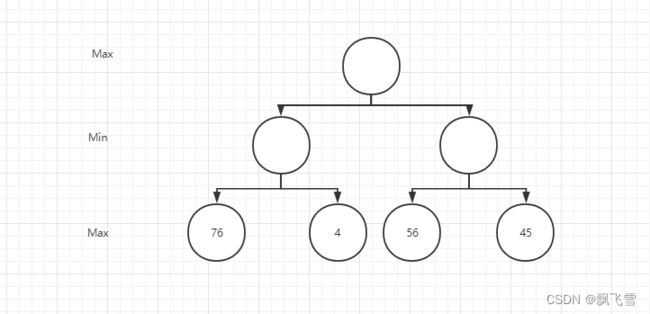
这是一个最简单的博弈树,深度为3,max层代表自己要下的地方,min层代表对方要走的地方。图中博弈树最终生成4种局面,每一种局面的分数分别为76,4,56,45。第二层为min层,对于min层而言,肯定希望局面对对方更有利,于是min层就会选择分数最少的来走。
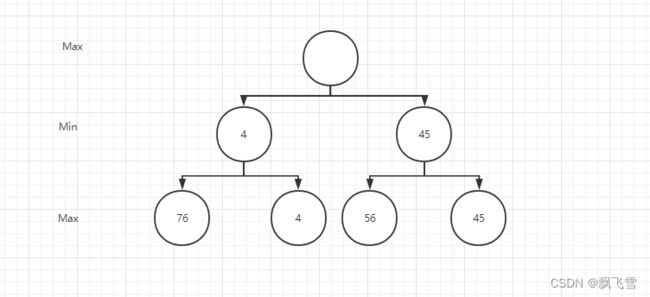
第一层为max层,max层为自己要走的棋,肯定希望分数越大越好,于是就有了以下的极大极小搜索树。

根据分数的大小,我方就可以选择分数最大的地方进行落子。
alpha-beta剪枝
Alpha Beta 剪枝算法的基本依据是:棋手不会做出对自己不利的选择。依据这个前提,如果一个节点明显是不利于自己的节点,那么就可以直接剪掉这个节点。
具体见:https://blog.csdn.net/lihongxun945/article/details/50668253
下面是极大极小算法go语言实现:
func min(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, nowDeep int, maxDeep int, step int, resList *ResList, alpha int, beta int) int {
/*
极小值
*/
if nowDeep > maxDeep {
return eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
}
res := Res{score: 99999999, x: 0, y: 0, deep: nowDeep}
heuristicsList := heuristicsMin(chess, scoreMapList, step)
for _, v := range heuristicsList {
i := v.x
j := v.y
chess[j][i] = -1
if res.score < alpha {
alpha = res.score
}
score := max(chess, scoreMapList, nowDeep+1, maxDeep, step, resList, alpha, beta)
chess[j][i] = 0
if score < res.score {
res.score = score
res.x = i
res.y = j
}
if score < beta { //AB剪枝
abc++
break
}
}
return res.score
}
func max(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, nowDeep int, maxDeep int, step int, resList *ResList, alpha int, beta int) int {
/*
极大值
*/
if nowDeep > maxDeep {
return eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
}
res := Res{score: -99999999, x: 0, y: 0, deep: nowDeep}
heuristicsList := heuristicsMax(chess, scoreMapList, step)
for _, v := range heuristicsList {
i := v.x
j := v.y
chess[j][i] = 1
if res.score > beta {
beta = res.score
}
score := min(chess, scoreMapList, nowDeep+1, maxDeep, step, resList, alpha, beta)
//if nowDeep == 0 {
// fmt.Println(score)
//}
chess[j][i] = 0
if score > res.score {
res.score = score
res.x = i
res.y = j
}
if score > alpha { //AB 剪枝
abc++
break
}
}
if nowDeep == 0 {
resList.resList = append(resList.resList, res)
}
return res.score
}
启发式搜索
极大极小搜索算法与在alpha-beta剪枝的实现采用前序遍历的方式,所以如果将分数高的节点提前,那么剪枝的效率就越高。于是就有了启发式函数。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/lihongxun945/article/details/50668622
func heuristicsMax(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, step int) []Res {
heuristicsList := []Res{}
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
if chess[j][i] == 0 {
if !isHavePiece(chess, i, j, n, step) {
continue
}
chess[j][i] = 1
score := eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
chess[j][i] = 0
heuristicsList = append(heuristicsList, Res{score, i, j, 0})
}
}
}
sort.Sort(HeuristicsListMax(heuristicsList))
return heuristicsList
}
func heuristicsMin(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, step int) []Res {
heuristicsList := []Res{}
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
if chess[j][i] == 0 {
if !isHavePiece(chess, i, j, n, step) {
continue
}
chess[j][i] = -1
score := eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
chess[j][i] = 0
heuristicsList = append(heuristicsList, Res{score, i, j, 0})
}
}
}
sort.Sort(HeuristicsListMin(heuristicsList))
return heuristicsList
}
对于当前局势先做一轮初步判断,将分数进行排序。
代码实现
以下是最终AI算法的代码实现,
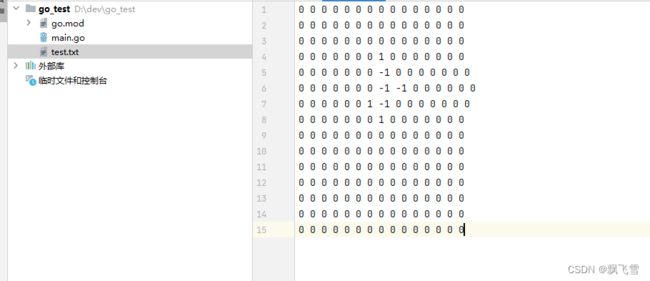
- 输入为test.txt文件,保存棋盘信息,0代表空,1代表AI方子位,-1代表对手子位
- 输出为resList,为切片,从左往右代表每一深度AI的思考落子结果以及分数,total代表调用评估函数次数,abc代表剪枝次数
package main
import (
"bufio"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"sort"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
const n = 1
var abc = 0
var total = 0
type ScoreMap struct {
role []int
score int
}
type Res struct {
score int
x int
y int
deep int
}
type HeuristicsListMax []Res
type HeuristicsListMin []Res
func (h HeuristicsListMax) Len() int {
return len(h)
}
func (h HeuristicsListMax) Less(i, j int) bool {
return h[i].score > h[j].score
}
func (h HeuristicsListMax) Swap(i, j int) {
h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i]
}
func (h HeuristicsListMin) Len() int {
return len(h)
}
func (h HeuristicsListMin) Less(i, j int) bool {
return h[i].score < h[j].score
}
func (h HeuristicsListMin) Swap(i, j int) {
h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i]
}
type ResList struct {
resList []Res
}
// 泛型深拷贝
func deepCopy(dst, src interface{}) {
bytes, _ := json.Marshal(src)
_ = json.Unmarshal(bytes, dst)
}
func InitScoreMapList() []ScoreMap {
scoreMapList := []ScoreMap{}
//活1 10分
r1 := []int{0, 1, 0}
s1 := ScoreMap{r1, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s1)
//活2 100分
r2 := []int{0, 1, 1, 0}
s2 := ScoreMap{r2, 100}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s2)
//活3 1000分
r3 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s3 := ScoreMap{r3, 1000}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s3)
//活4 10000分
r4 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s4 := ScoreMap{r4, 10000}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s4)
//五连 100000分
r5 := []int{1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
s5 := ScoreMap{r5, 100000}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s5)
//死2 10分
r6 := []int{0, 1, 1, -1}
s6 := ScoreMap{r6, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s6)
r7 := []int{-1, 1, 1, 0}
s7 := ScoreMap{r7, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s7)
//死3 100分
r8 := []int{-1, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s8 := ScoreMap{r8, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s8)
r9 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, -1}
s9 := ScoreMap{r9, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s9)
//死4 1000分
r10 := []int{-1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}
s10 := ScoreMap{r10, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s10)
r11 := []int{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, -1}
s11 := ScoreMap{r11, 10}
scoreMapList = append(scoreMapList, s11)
//对手情况再copy一遍
scoreMapList2 := []ScoreMap{}
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
newScoreMap := ScoreMap{}
deepCopy(newScoreMap, scoreMap)
newScoreMap.score = -scoreMap.score
for _, v := range scoreMap.role {
newScoreMap.role = append(newScoreMap.role, -v)
}
scoreMapList2 = append(scoreMapList2, newScoreMap)
}
return append(scoreMapList, scoreMapList2...)
}
func ReadChessFromFile(filepath string, step int) [][]int {
/*
从文件获取棋盘信息
*/
fi, _ := os.Open(filepath)
r := bufio.NewReader(fi)
chess := make([][]int, step)
j := 0
for {
lineBytes, err := r.ReadBytes('\n')
line := strings.Split(strings.TrimSpace(string(lineBytes)), " ")
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
num, _ := strconv.Atoi(line[i])
chess[j] = append(chess[j], num)
}
j++
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
}
return chess
}
func isHavePiece(chess [][]int, x int, y int, n int, step int) bool {
/*
n格之内是否有棋子
*/
xMin := x - n
xMax := x + n
yMin := y - n
yMax := y + n
if xMin < 0 {
xMin = 0
}
if xMax > step-1 {
xMax = step - 1
}
if yMin < 0 {
yMin = 0
}
if yMax > step-1 {
yMax = step - 1
}
for i := xMin; i <= xMax; i++ {
for j := yMin; j <= yMax; j++ {
if chess[j][i] != 0 {
return true
}
}
}
return false
}
func min(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, nowDeep int, maxDeep int, step int, resList *ResList, alpha int, beta int) int {
/*
极小值
*/
if nowDeep > maxDeep {
return eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
}
res := Res{score: 99999999, x: 0, y: 0, deep: nowDeep}
heuristicsList := heuristicsMin(chess, scoreMapList, step)
for _, v := range heuristicsList {
i := v.x
j := v.y
chess[j][i] = -1
if res.score < alpha {
alpha = res.score
}
score := max(chess, scoreMapList, nowDeep+1, maxDeep, step, resList, alpha, beta)
chess[j][i] = 0
if score < res.score {
res.score = score
res.x = i
res.y = j
}
if score < beta { //AB剪枝
abc++
break
}
}
return res.score
}
func max(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, nowDeep int, maxDeep int, step int, resList *ResList, alpha int, beta int) int {
/*
极大值
*/
if nowDeep > maxDeep {
return eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
}
res := Res{score: -99999999, x: 0, y: 0, deep: nowDeep}
heuristicsList := heuristicsMax(chess, scoreMapList, step)
for _, v := range heuristicsList {
i := v.x
j := v.y
chess[j][i] = 1
if res.score > beta {
beta = res.score
}
score := min(chess, scoreMapList, nowDeep+1, maxDeep, step, resList, alpha, beta)
//if nowDeep == 0 {
// fmt.Println(score)
//}
chess[j][i] = 0
if score > res.score {
res.score = score
res.x = i
res.y = j
}
if score > alpha { //AB 剪枝
abc++
break
}
}
if nowDeep == 0 {
resList.resList = append(resList.resList, res)
}
return res.score
}
func eval(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, step int) int {
/*
评估当前局势分数
*/
total++
sum := 0
//对于每一行进行评估,从上到下,从左往右
//行,模拟从上到下
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//列,模拟从左到右
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > step {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[i][j+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
//if j == 1 {
// fmt.Println(scoreMap.role)
//}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//对每一列进行评估
//列
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//行
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > step {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[j+k][i] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//自左上到右下遍历
//行
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//列
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > l || i+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[j+k][i+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//列
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//行
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if j+len(scoreMap.role) > l || i+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[i+k][j+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//自右上到左下遍历
//列
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//行
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if i < len(scoreMap.role) || j+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[j+k][i-k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
//行
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
//列
l := step - i
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
for _, scoreMap := range scoreMapList {
if i < len(scoreMap.role) || j+len(scoreMap.role) > l {
continue
}
isOk := true
for k := 0; k < len(scoreMap.role); k++ {
if scoreMap.role[k] != chess[i-k][j+k] {
isOk = false
break
}
}
if isOk {
sum += scoreMap.score
}
}
}
}
return sum
}
func heuristicsMax(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, step int) []Res {
heuristicsList := []Res{}
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
if chess[j][i] == 0 {
if !isHavePiece(chess, i, j, n, step) {
continue
}
chess[j][i] = 1
score := eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
chess[j][i] = 0
heuristicsList = append(heuristicsList, Res{score, i, j, 0})
}
}
}
sort.Sort(HeuristicsListMax(heuristicsList))
return heuristicsList
}
func heuristicsMin(chess [][]int, scoreMapList []ScoreMap, step int) []Res {
heuristicsList := []Res{}
for i := 0; i < step; i++ {
for j := 0; j < step; j++ {
if chess[j][i] == 0 {
if !isHavePiece(chess, i, j, n, step) {
continue
}
chess[j][i] = -1
score := eval(chess, scoreMapList, step)
chess[j][i] = 0
heuristicsList = append(heuristicsList, Res{score, i, j, 0})
}
}
}
sort.Sort(HeuristicsListMin(heuristicsList))
return heuristicsList
}
//func beginGame(chess [][]int) {
// scoreMapList := InitScoreMapList()
// //fmt.Println(scoreMapList)
// //num := eval(chess, scoreMapList, 15)
// //fmt.Println(num)
// resList := ResList{resList: []Res{}}
// for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
// max(chess, scoreMapList, 0, i, 15, &resList, 999999999, -999999999)
// fmt.Println(resList, total, abc)
// }
//}
func main() {
chess := ReadChessFromFile("./test.txt", 15)
//fmt.Println(chess)
scoreMapList := InitScoreMapList()
fmt.Println(scoreMapList)
num := eval(chess, scoreMapList, 15)
fmt.Println(num)
resList := ResList{resList: []Res{}}
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
max(chess, scoreMapList, 0, i, 15, &resList, 999999999, -999999999)
fmt.Println(resList, total, abc)
}
}