01.CCNA 200-301 题库_1-50
title: CCNA 200-301 题库_1-50
date: 2022-07-13 12:29:58
permalink: /pages/55766c/
categories:
- 网络运维
- CCNA
- CCNA题库
tags: - https://jonas-wolfxin.github.io/pages/55766c/
CCNA 200-301 题库_1-50
-
A network engineer must create a diagram of a multivendor network. Which command must be configured on the Cisco devices so that the topology of the network can be mapped?
A. Device(config)# lldp run
B. Device(config)# cdp run
C. Device(config)# cdp enable
D. Device(config)# flow-sampler-map topology
Correct Answer A
Explanation:- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a proprietary Data Link Layer Protocol developed by Cisco Systems. It is used to share information about other directly connected Cisco equipment, such as the operating system version and IP address. CDP is already enabled on Cisco devices by default.
- LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) and CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) are Data Link Layer Protocols for directly-connected LLDP and CDP-capable neighbors to advertise themselves and their capabilities. By default, the device sends an LLDP/CDP advertisement periodically to all its interfaces and processes incoming LLDP and CDP packets as required by the protocols. In LLDP and CDP, advertisements are encoded as TLV (Type, Length, Value) in the packet.
- In order to ensure discovery in a multivendor network, you would need to enable LLDP on the Cisco devices; it isn't enabled by default, and it can be run on non-Cisco devices, where CDP can't be.
-
Which feature on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller when enabled restricts management access from specific networks?
A. CPU ACL
B. TACACS
C. Flex ACL
D. RADIUS
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- For any traffic to the CPU, for example, management protocols such as SNMP, HTTPS, SSH, Telnet, or network services protocols such as Radius or DHCP, use a “CPU ACL”
- Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wireless-mobility/wlan-security/71978-acl-wlc.html
-
When a site-to-site VPN is used, which protocol is responsible for the transport of user data?
A. IKEv2
B. IKEv1
C. IPsec
D. MD5
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a secure network protocol suite that authenticates and encrypts packets of data to provide secure encrypted communication between two computers over an Internet Protocol network. It is used in virtual private networks (VPNs).
- IPsec The term referring to the IP Security protocols, which is an architecture for providing encryption and authentication services, usually when creating VPN tunnel through an IP network. Site-to-site IPSec VPNs offer scalability as a benefit. This is because each remote office only needs an Internet connection to create a VPN tunnel back to the main office.
- IPsec can protect data flows between a pair of hosts (host-to-host), between a pair of security gateways (network-to-network), or between a security gateway and a host (network-to-host).
- A site-to-site VPN allows offices in multiple fixed locations to establish secure connections with each other over a public network such as the Internet. A site-to-site VPN means that two sites create a VPN tunnel by encrypting and sending data between two devices. One set of rules for creating a site-to-site VPN is defined by IPsec.
- IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2) is a VPN encryption protocol responsible for request and response actions. It handles the SA (security association) attribute within an authentication suite called IPSec. IKEv2 is the mechanism that generates encryption keys, ensuring safe data flow between your device and the VPN server you’re connected to.
-
How do TCP and UDP differ in the way that they establish a connection between two endpoints?
A. TCP use the three-way handshake, and UDP dose no guarantee message delivery
B. TCP use synchronization packets,and UDP uses acknowledgement packets
C. UDP provides reliable message transfer,and TCP is a connectionless protocol.
D. UDP use SYN,SYN ACK,and FIN bits in the frame header while TCP uses SYN,SYN ACK,and ACK bis.
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- TCP Vs UDP
-
What are two reasons that cause late collisions to increment on an Ethernet interface?(choose two)
A. when the sending device waits 15 seconds before sending the frame again
B. when the cable length limits are exceeded
C. when one side of the connection is configured for half-duplex
D. when Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection is used
E. when a collision occurs after the 32nd byte of a frame has been transmitted
Correct Answer B, CExplanation:
- A late collision is defined as any collision that occurs after the first 512 bits (or 64th byte) of the frame have been transmitted. The usual possible causes are
- full- duplex/half-duplex mismatch,
- exceeded Ethernet cable length limits,
- or defective hardware such as incorrect cabling,
- non-compliant number of hubs in the network,
- or a bad NIC.
- Late collisions should never occur in a properly designed Ethernet network.
- A late collision is defined as any collision that occurs after the first 512 bits (or 64th byte) of the frame have been transmitted. The usual possible causes are
-
A Cisco IP phone receive untagged data traffic from an attached PC. Which action is taken by the phone?
A. It allows the traffic to pass through unchanged
B. It drops the traffic
C. It tags the traffic with the default VLAN
D. It tags the traffic with the native VLAN
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2960x/software/15-0_2_EX/vlan/configuration_guide/b_vlan_152ex_2960-x_cg/b_vlan_152ex_2960-x_cg_chapter_0110.pdf
-
Refer to the exhibit. The
show ip ospf interfacecommand has been executed on R1. How is OSPF configured?[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-V6wioEt7-1661764193961)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/202207131255792.png)]
A. The interface is not participating in OSPF
B. A point-to-point network type is configured
C. The default Hello and Dead timers are in use
D. There are six OSPF neighbors on this interface
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13689-17.html
-
What benefit does controller-based networking provide versus traditional networking?
A. provides an added layer of security to protect from DDoS attacks
B. combines control and data plane functionality on a single device to minimize latency
C. moves from a two-tier to a three-tier network architecture to provide maximum redundancy
D. allows configuration and monitoring of the network from one centralized point
Correct Answer DExplanation:
-
When a floating static route is configured, which action ensures that the backup route is used when the primary route fails?
A. The floating static route must have a higher administrative distance than the primary route so it is used as a backup
B. The administrative distance must be higher on the primary route so that the backup route becomes secondary.
C. The floating static route must have a lower administrative distance than the primary route so it is used as a backup
D. The default-information originate command must be configured for the route to be installed into the routing table
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- By default, IOS considers static routes better than OSPF-learned routes. By default, IOS gives static routes an administrative distance of 1.
- A floating static route floats or moves into and out of the IP routing table depending on whether the better (lower) administrative distance route learned by the routing protocol happens to exist currently.
-
Which mode must be used to configure EtherChannel between two switches without using a negotiation protocol?
A. on
B. auto
C. active
D. desirable
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- on
Mode that forces the LAN port to form Etherchannel without using negotiation protocol. In the on mode, a usable EtherChannel exists only when a LAN port group in the on mode is connected to another LAN port group in the on mode. Because ports configured in the on mode do not negotiate, there is no negotiation traffic between the ports. You cannot configure the on mode with an EtherChannel protocol. If one end uses the on mode, the other end must also. - PAgP 协议
- auto
PAgP mode that places a LAN port into a passive negotiating state, in which the port responds to PAgP packets it receives but does not initiate PAgP negotiation. (Default) - desirable
PAgP mode that places a LAN port into an active negotiating state, in which the port initiates negotiations with other LAN ports by sending PAgP packets. - LACP 协议
- passive
LACP mode that places a port into a passive negotiating state, in which the port responds to LACP packets it receives but does not initiate LACP negotiation. (Default) - active
LACP mode that places a port into an active negotiating state, in which the port initiates negotiations with other ports by sending LACP packets. - Ref: Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4500/12-2/3-1-1SG/configuration/guide/config/channel.html
PAgP(Port Aggregration Protocol 端口聚合协议): Cisco Proprietary protocol;
LACP(Link Aggregration Control Protocol)是属于IEEE规范(802.3ad),允许将多个物理端口捆绑形成单个逻辑通道。它的功能类似于思科的以太通道协议PAgP。: Open Standard used by most of Vendors - on
-
What are two descriptions of three-tier network topologies? (Choose two.)
A. The distribution layer runs Layer 2 and Layer 3 technologies.
B. The network core is designed to maintain continuous connectivity when devices fail.
C. The core layer maintains wired connections for each host.
D. The core and distribution layers perform the same functions
E. The access layer manages routing between devices in different domains.
Correct Answer A, BExplanation:
- Access: Provides a connection point (access) for end-user devices. Does not forward frames between two other access switches under normal circumstances.
- Distribution: Provides an aggregation point for access switches, providing connectivity to the rest of the devices in the LAN, forwarding frames between switches, but not connecting directly to end-user devices. The distribution layer is where redistribution of routing protocols should be performed. It should never be performed at the core or access layer.
- Core: Aggregates distribution switches in very large campus LANs, providing very high forwarding rates for the larger volume of traffic due to the size of the network. Only switching between campus (distribution) switches should be performed at the core layer. Nothing should be done to slow down forwarding of traffic, such as using ACLs, supporting clients, or routing between VLANs. Core layer switches are commonly set up in a star topology. This is because core layer switches connect multiple campuses via distribution layer switches
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement explains the configuration error message that is received?
A. it belongs to a private IP address range
B. the router dose not support /28 mask
C. it is a network IP address
D. it is a broadcast IP address
Correct Answer DExplanation:
- https://bbs.hh010.com/ipv4.html
-
What is the expected outcome when an EUI-64 address is generated?
A. The seventh bit of original MAC address of the interface is inverted
B. The interface ID is configured as a random 64-bit value
C. The characters FE80 are inserted at the beginning of the MAC address of the interface
D. The MAC address of the interface is used as the interface ID without modification
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- EUI-64 (Extended Unique Identifier) is a method we can use to automatically configure IPv6 host addresses. An IPv6 device will use the MAC address of its interface to generate a unique 64-bit interface ID. However, a MAC address is 48 bit and the interface ID is 64 bit. What are we going to do with the missing bits?
- Split Mac Address in to two ( 00:BB:CC | DD:11:22)
- Insert FFFE Hexa in the middle, Eg: 00:BB:CC:DD:11:22 --> 02BB:CCFF:FEDD:1122
- Invert the 7th Bit of the MAC address (0 to 1)
- Reference: https://geek-university.com/ccna/ipv6-eui-64-calculation/
- EUI-64 (Extended Unique Identifier) is a method we can use to automatically configure IPv6 host addresses. An IPv6 device will use the MAC address of its interface to generate a unique 64-bit interface ID. However, a MAC address is 48 bit and the interface ID is 64 bit. What are we going to do with the missing bits?
-
Which function does an SNMP agent perform?
A. It manages routing between Layer 3 devices in a network,
B. It coordinates user authentication between a network device and a TACACS+ or RADIUS server.
C. It sends information about MIB variables in response to requests from the NMS.
D. It requests information from remote network nodes about catastrophic system events.
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/snmp/configuration/xe-16/snmp-xe-16-book/nm-snmp-cfg-snmp-support.html
-
Refer to the exhibit. The
default-information originatecommand is configured under the R1 OSPF configuration. After testing, workstation on VLAN 20 at Site B cannot reach a DNS server on the Internet.
wihch action corrects the configuration issue?[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Zossw1Kr-1661764193962)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/202207131255815.png)]
A. Add the
default-information originatecommand on R2B. Add the always keyword to the
default-information originatecommand on R1C. Configure the
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.18command on R1D. Configure the
Correct Answer Cip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.2command on R2Explanation:
- Ref: Reference: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.08/HTML/ip_route_6300-6400-83xx/Content/Chp_OSPFv2/OSPFv2_cmds/def-inf-ori-10.htm
- Reference: https://study-ccna.com/ospf-default-information-originate/
-
What are two benefits of network automation? (Choose two)
A. reduced operational costs
B. reduced hardware footprint
C. faster changes with more reliable results
D. fewer network failures
E. increased network security
Correct Answer A, CExplanation:
- Operational cost is reduced due to automation of configuration, IOS update and group deployment of policies
- You can auto configure new device(s) based on their type/function which is more reliable than human configuration which is prone to errors.
-
Which two command sequences must you configure on a switch to establish a Layer 3 EtherChannel with an open-standard protocol? (choose two)
A. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Channel-group 10 mode activeB. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Channel-group 10 mode autoC. interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Channel-group 10 mode onD. interface port-channel 10
no switchport
ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.0E. interface port-channel 10
Correct Answer A, D
switchport
Switchport mode trunkExplanation:
- B is discarded: PAgP configuration
- C is discarded: manual configuration ("On" mode)
- E is discarded: It is configuration of trunk mode, not Etherchannel
-
Which command prevents passwords from being stored in the configuration as plaintext on a router or switch?
A. enable secret
B. service password-encryption
C. username Cisco password encrypt
D. enable password
Correct Answer BExplanation:
- enable secret - Sets the enable password, and stores that password as an md5 hash in the config.
- enable password - Sets the enable password, and stores that password in plaintext in the config.
- service password-encryption - For any passwords in the config that are stored in plaintext, this command changes them to be stored as hashed values instead.
- Ref: Reference: https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/hardening-cisco-routers/0596001665/ch04.html#:~:text=service%20password%2Dencryption&text=This%20command%20obscures%20all%20clear,feature%20from%20global%20configuration%20mode.&text=Now%20a%20show%20run%20command,password%20in%20humanly%20readable%20format.
-
R1 has learned route 10.10.10.0/24 via numerous routing protocols, which route is installed?
A. route with the lowest cost
B. route with the shortest prefix length
C. route with the next hop that has the highest IP
D. route with the lowest administrative distance
Correct Answer DExplanation:
The longest prefix match always wins among the routes actually installed in the routing table, while the routing protocol with the lowest administrative distance always wins when installing routes into the routing table.
Supplementary:
- Route Selection Preference:
- Longest Prefix
- Administrative Distance
- Metric
-
which network allows devices to communicate without the need to access the internet?
A. 172.9.0.0/16
B. 172.28.0.0/16
C. 192.0.0.0/18
D. 209.165.201.0/24
Correct Answer BExplanation:
- Private IP address range:
- 10.0.0.0 ~ 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 ~ 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 ~ 192.168.255.255
-
Which attribute does a router use to select the best path when two or more different routes to the same destination exist from two different routing protocols?
A. dual algorithm
B. metric
C. administrative distance
D. hop count
Correct Answer CExplanation:
The longest prefix match always wins among the routes actually installed in the routing table, while the routing protocol with the lowest administrative distance always wins when installing routes into the routing table.
Supplementary:
- Route Selection Preference:
- Longest Prefix
- Administrative Distance
- Metric
-
which command must be entered when a device is configured as an NTP server?
A. ntp master
B. ntp sever
C. ntp authenticate
D. ntp peer
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- To configure a Cisco device as an Authoritative NTP Server, use the ntp master [stratum] command. the device acts only as an NTP server, and not as an NTP client. The device gets its time information from the internal clock on the device.
- To configure a Cisco device as a NTP client, use the command ntp server [IP address]. First, it acts as an NTP client, to synchronize time with a server. Once synchronized, the device could then act as an NTP server, to supply time to other NTP clients. For example:
Router(config)#ntp server 192.168.1.1
This command will instruct the router to query 192.168.1.1 for the time.
-
When OSPF learns multiple paths to a network, how does it select a route?
A. It multiple the active K value by 256 to calculate the route with the lowest metric.
B. For each existing interface, it adds the metric from the source router to the destination to calculate the route with the lowest bandwidth.
C. It divides a reference bandwidth of 100 Mbps by the actual bandwidth of the existing interface to calculate the router with the lowest cost.
D. It count the number of hops between the source router and the destination to determine the router with the lowest metric
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- Reference: https://networktechstudy.com/home/learning-ospf-path-selection
- A: EIGRP
- D: Rip
-
What is a characteristic of spine-and-leaf architecture?
A. It provides variable latency.
B. Each link between leaf switches allows for higher bandwidth.
C. Each device is separated by the same number of hops.
D. It provides greater predictability on STP blocked ports.
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- With a spine-and-leaf architecture, no matter which leaf switch to which a server is connected, its traffic always has to cross the same number of devices to get to another server (unless the other server is located on the same leaf). This approach keeps latency at a predictable level because a payload only has to hop to a spine switch and another leaf switch to reach its destination.
- In this two-tier Clos architecture, every lower-tier switch (leaf layer) is connected to each of the top-tier switches (spine layer) in a full-mesh topology. The leaf layer consists of access switches that connect to devices such as servers. The spine layer is the backbone of the network and is responsible for interconnecting all leaf switches. Every leaf switch connects to every spine switch in the fabric. The path is randomly chosen so that the traffic load is evenly distributed among the top-tier switches. If one of the top tier switches were to fail, it would only slightly degrade performance throughout the data center.
- Ref: Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/nexus-7000-series-switches/white-paper-c11-737022.html
- Reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xjc7WLBb-nI
-
Which two outcomes are predictable behaviors for HSRP? (Choose two)
A. The two routers share a virtual IP address that is used as the default gateway for devices on the LAN.
B. The two routers negotiate one router as the active router and the other as the standby router
C. Each router has a different IP address both routers act as the default gateway on the LAN, and traffic is load balanced between them.
D. The two routers synchronize configurations to provide consistent packet forwarding
E. The two routed share the same IP address, and default gateway traffic is load-balanced between them
Correct Answer A, BExplanation:
- Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) A Cisco proprietary protocol that allows two (or more) routers to share the duties of being the default router on a subnet, with an active/standby model, with one router acting as the default router and the other sitting by waiting to take over that role if the first router fails
-
Which action must be taken to assign a global unicast IPv6 address on an interface that is derived from the MAC address of that interface?
A. explicitly assign a link-local address
B. disable the EUI-64 bit process
C. enable SLAAC on an interface
D. configure a stateful DHCPv6 server on the network
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- Reference: https://howdoesinternetwork.com/2013/slaac-ipv6-stateless-address-autoconfiguration
-
Refer to the exhibit. What is the effect of this configuration?
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aztP5W8Y-1661764193962)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/202207131255759.png)]
A. The switch port interface trust state becomes untrusted
B. The switch port remains administratively down until the interface is connected to another switch
C. Dynamic ARP inspection is disabled because the ARP ACL is missing
D. The switch port remains down until it is configured to trust or untrust incoming packets
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- Dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) is a security feature that validates(验证) ARP packets in a network. It intercepts(拦截), logs, and discards ARP packets with invalid IP-to-MAC address bindings. This capability protects the network from certain man-in-the-middle attacks. After enabling DAI, all ports become untrusted ports.
- To make this port trusted you need to add the 'ip arp inpection trust' command on int fa0/1
-
In which way does a spine-and-leaf architecture allow for scalability in a network when additional access ports are required?
A. A spine switch and a leaf switch can be added with redundant connections between them
B. A spine switch can be added with at least 40 GB uplinks
C. A leaf switch can be added with connections to every spine switch
D. A leaf switch can be added with a single connection to a core spine switch
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- Spine-leaf architecture is typically deployed as two layers: spines (such as an aggregation layer), and leaves (such as an access layer). Spine-leaf topologies provide high-bandwidth, low-latency, nonblocking server-to-server connectivity.
- Leaf (aggregation) switches are what provide devices access to the fabric (the network of spine and leaf switches) and are typically deployed at the top of the rack. Generally, devices connect to the leaf switches. Devices can include servers, Layer 4-7 services (firewalls and load balancers), and WAN or Internet routers. Leaf switches do not connect to other leaf switches. In spine-and-leaf architecture, every leaf should connect to every spine in a full mesh.
- Spine (aggregation) switches are used to connect to all leaf switches and are typically deployed at the end or middle of the row. Spine switches do not connect to other spine switches.
- Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/nexus-9000-series-switches/guide-c07-733228.html
-
Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 is running three different routing protocols. Which route characteristic is used by the router to forward the packet that receives for destination IP 172.16.32.1?
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-pk9TaYLV-1661764193963)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/0013100001.png)]
A. metric
B. longest prefix
C. cost
D. administrative distance
Correct Answer BExplanation:
Route Selection Preference:
- Longest Prefix
- Administrative Distance
- Metric
-
Which configuration is needed to generate an RSA key for SSH on a router?
A. Configure the version of SSH
B. Configure VTY access.
C. Create a user with a password
D. Assign a DNS domain name
Correct Answer DExplanation:
- Ref: Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_usr_ssh/configuration/15-s/sec-usr-ssh-15-s-book/sec-secure-shell-v2.html
-
Which API is used in controller-based architectures to interact with edge devices?
A. overlay
B. northbound
C. underlay
D. southbound
Correct Answer DExplanation:
- overlay: the virtual network
- underlay: the physical network
- nothbound: interacts with the server
-
Router R1 must send all traffic without a matching routing-table entry to 192.168.1.1. Which configuration accomplishes this task?
A. R1# config t
R1(config)# ip routing
R1(config)# ip route default-route 192.168.1.1B. R1# config t
R1(config)# ip routing
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1C. R1# config t
R1(config)# ip routing
R1(config)# ip route 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0D. R1# config t
Correct Answer B
R1(config)# ip routing
R1(config)# ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1Explanation:
- "ip default-gateway" is usually used on Layer 2 switches and on hosts.
- "ip route 0.0.0.0" is usually used on Layer 3 switches and on routers.
-
What is the benefit of using a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller?
A. Central AP management requires more complex configurations
B. Unique SSIDs cannot use the same authentication method
C. It supports autonomous and lightweight APs
D. It eliminates the need to configure each access point individually
Correct Answer DExplanation:
- Autonomous doesn't support LWAPP protocol ( Autonomous APs are standalone APs which does not support CAPWAP/LWAPP) that Wireless Lan Controller uses)
- Autonomous APs do not understand the Lightweight AP Protocol (LWAPP) or the CAPWAP protocol that the WLC uses. In order to connect an autonomous AP to a WLC, you must first convert the autonomous AP to lightweight mode.
-
An engineer must configure a /30 subnet between two routers. which usable IP address and subnet mask combination meets this criteria?
A. interface e0/0
description to HQ-A370:98968
ip address 10.2.1.3 255.255.255.252B. interface e0/0
description to HQ-A370:98968
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.248C. interface e0/0
description to HQ-A370:98968
ip address 172.16.1.4 255.255.255.248D. interface e0/0
Correct Answer D
description to HQ-A370:98968
ip address 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252Explanation:
- ip address 10.2.1.3 255.255.255.252 is a Broadcast Address
-
Which unified access point mode continues to serve wireless clients after losing connectivity to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller?
A. sniffer
B. mesh
C. flexconnect
D. local
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- When a FlexConnect access point can reach the controller (referred to as the connected mode), the controller assists in client authentication.
- When a FlexConnect access point cannot access the controller, the access point enters the standalone mode and authenticates clients by itself.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the LACP neighbor status, in which mode is the SW1 port channel configured?
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-99PGBfnH-1661764193963)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/image-20220701161216684.png)]
A. passive
B. mode on
C. auto
D. active
Correct Answer DExplanation:
- LACP 协议
- passive
LACP mode that places a port into a passive negotiating state, in which the port responds to LACP packets it receives but does not initiate LACP negotiation. (Default) - active
LACP mode that places a port into an active negotiating state, in which the port initiates negotiations with other ports by sending LACP packets. - Ref: Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4500/12-2/3-1-1SG/configuration/guide/config/channel.html
-
which WPA3 enhancement protects against hackers viewing traffic on the Wi-Fi network?
A. TKIP encryption
B. SAE encryption
C. AES encryption
D. scrambled encryption key
Correct Answer BExplanation:
- Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE): A strong authentication method used in WPA3 to authenticate wireless clients and APs and to prevent dictionary attacks for discovering pre-shared keys.
- Ref: Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/9800/17-2/config-guide/b_wl_17_2_cg/wi_fi_protected_access_3.html
-
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is bringing up a new circuit to the MPLS provider on the Gi0/1 interface of Router1. The new circuit uses eBGP and learns the route to VLAN25 from the BGP path. What is the expected behavior for the traffic flow for route 10.10.13.0/25?
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LWGEAw79-1661764193964)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/0003200001.png)]
A. Traffic to 10.10.13.0.25 is load balanced out of multiple interfaces
B. Route 10.10.13.0/25 is updated in the routing table as being learned from interface Gi0/1.
C. Traffic to 10.10.13.0/25 is a symmetrical
D. Route 10.10.13.0/25 learned via the Gi0/0 interface remains in the routing table
Correct Answer D, 但 此题有争议 BExplanation:
- Reference: https://community.cisco.com/t5/routing/ospf-wins-over-bgp/td-p/420248
- Multiprotocol Label Switching, or MPLS, is a networking technology that routes traffic using the shortest path based on “labels,” rather than network addresses, to handle forwarding over private wide area networks. As a scalable and protocol-independent solution, MPLS assigns labels to each data packet, controlling the path the packet follows. MPLS greatly improves the speed of traffic, so users don’t experience downtime when connected to the network.
-
Refer to the exhibit.How does router R1 handle traffic to 192.168.10.16?
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5ztxHT2q-1661764193964)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/202207131255335.png)]
A. It selects the EIGRP route because it has the lowest administrative distance
B. It selects the RIP route because it has the longest prefix inclusive of the destination address
C. It selects the OSFP route because it has the lowest cost
D. It selects the IS-IS route because it has the shortest prefix inclusive of the destination address
Correct Answer BExplanation:
Route Selection Preference:
1. Longest Prefix
2. Administrative distance
3. Metric- Reference: https://packetlife.net/blog/2010/aug/16/route-preference/
-
Which two actions influence the EIGRP route selection process? (Choose two)
A. The router calculates the reported distance by multiplying the delay on the exiting Interface by 256.
B. The router calculates the best backup path to the destination route and assigns it as the feasible successor.
C. The router calculates the feasible distance of all paths to the destination route
D. The advertised distance is calculated by a downstream neighbor to inform the local router of the bandwidth on the link
E. The router must use the advertised distance as the metric for any given route
Correct Answer B, CExplanation:
DUAL算法中的几个术语:
- 可行距离(Feasible Distance): 本路由器到达目标网络的开销Cost;
- 通告距离(Advertised Distance): 当前路由器的下一跳路由器到达目标网络的开销Cost
- 后继路由器(Successor): 到达目的网络的最优(FD最小)的下一跳路由器
- 可行后继路由器(Feasible Successor): A backup route if the successor fails. The FS must have a AD that is less than the Successor FD.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which two commands were used to create port channel 10?(choose two)
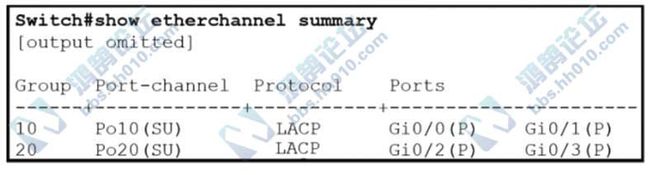
A. int range g0/0-1
Channel-group 10 mode activeB. Bint range g0/0-1
Channel-group 10 mode desirableC. int range g0/0-1
Channel-group 10 mode passiveD. int range g0/0-1
Channel-group 10 mode autoE. int range g0/0-1
Correct Answer A, C
Channel-group 10 mode onExplanation:
- PAGP: Desirable/Auto
- LACP: Active/Passive
-
What is a difference between RADIUS and TACACS+?
A. TACACS+ encrypts only password information and RADIUS encrypts the entire payload
B. RADIUS logs all commands that are entered by the administrator, but TACACS+ logs only start, stop, and interim commands
C. RADIUS is most appropriate for dial authentication, but TACACS+ can be used for multiple types of authentication
D. TACACS+ separates authentication and authorization, and RADIUS merges them
Correct Answer DExplanation:
- Reference: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-tacacs-and-radius/
- Ref: Reference: https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos-space-apps/network-director4.0/topics/concept/radius-tacacs-understanding.html#:~:text=RADIUS%20was%20designed%20to%20authenticate,devices%20like%20routers%20and%20switches.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer must block access for all computers on VLAN 20 to the web server via HTTP. All other computers must be able to access the web server. Which configuration when applied to switch A accomplishes this task?
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mdeFDXa5-1661764193964)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/0005500001.png)]
A.
config t ip access-list extended wwwblock permit ip any any deny tcp any host 10.30.0.100 eq 80 int vlan 20 ip access-group wwwblock inB.
config t ip access-list extended wwwblock permit ip any any deny tcp any host 10.30.0.100 eq 80 int vlan 30 ip access-group wwwblock inC.
config t ip access-list extended wwwblock deny tcp any host 10.30.0.100 eq 80 int vlan 10 ip access-group wwwblock inD.
Correct Answer Dconf t ip access-list extended wwwblock deny tcp any host 10.30.0.100 eq 80 permit ip any any int vlan 20 ip access-group wwwblock inExplanation:
- ACL
-
Refer to the exhibit. How does the router manage traffic to 192.168.12.16?
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bvmbQVis-1661764193964)(https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/Wolfxin/MyPicGo/img/0013400001.png)]
A. It selects RIP route because it has the longest prefix inclusive of the destination address
B. It chooses the EIGRP route because it has the lowest administrative distance
C. It load-balances traffic between all three routes
D. It chooses the OSPF route because it has the longest prefix inclusive of the destination address
Correct Answer AExplanation:
- The router can't use the network OSPF because it's another network and not include the destination address (192.168.12.0/28 --> from 192.168.12.0 to 192.168.12.15).
- The correct answer is A because the RIP route use a /27 subnet and include the destination address (192.168.12.0/27 --> from 192.168.12.0 to 192.168.12.31).
-
What is an advantage of Cisco DNA Center versus traditional campus device management?
A. It supports numerous extensibility options including cross-domain adapters and third-party SDKs.
B. It supports high availability for management functions when operating in cluster mode.
C. It enables easy auto-discovery of network elements m a brownfield deployment.
D. It is designed primarily to provide network assurance
Correct Answer AExplanation:
-
While examining excessive traffic on the network, it is noted that all incoming packets on an interface appear to be allowed even though an IPv4 ACL is applied to the interface. Which two misconfigurations cause this behavior? (Choose two)
A. The packets fail to match any permit statement
B. A matching permit statement is too high in the access test
C. A matching deny statement is too high in the access list
D. A matching permit statement is too broadly defined
E. The ACL is empty
Correct Answer B, DExplanation:
- A: Then teh packets will be blocked rather than allowed
- B: correct. Mormally the permit statement should be low in the access list
- E: The fact is that acl can never be empty because of deny statement at the end which is by default.
-
Which design element is a best practice when deploying an 802.11b wireless infrastructure?
A. disabling TPC so that access points can negotiate signal levels with their attached wireless devices.
B. setting the maximum data rate to 54 Mbps on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
C. allocating non-overlapping channels to access points that are in close physical proximity to one another
D. configuring access points to provide clients with a maximum of 5 Mbps
Correct Answer CExplanation:
- Selecting the proper WiFi channel can significantly improve your WiFi coverage and performance. In the 2.4 GHz band, 1, 6, and 11 are the only non-overlapping channels. Selecting one or more of these channels is an important part of setting up your network correctly.
-
How do traditional campus device management and Cisco DNA Center device management differ in regards to deployment?
A. Cisco DNA Center device management can be implemented at a lower cost than most traditional campus device management options
B. Traditional campus device management schemes can typically deploy patches and updates more quickly than Cisco DNA Center device management.
C. Cisco DNA Center device management can deploy a network more quickly than traditional campus device management
D. Traditional campus device management allows a network to scale more quickly than with Cisco DNA Center device management.
Correct Answer CExplanation:
-
Which two actions are performed by the Weighted Random Early Detection mechanism?(Choose two)
A. It drops lower-priority packets before it drops higher-priority packets
B. It can identify different flows with a high level of granularity
C. It guarantees the delivery of high-priority packets
D. It can mitigate congestion by preventing the queue from filling up
E. IT supports protocol discovery
Correct Answer A, DExplanation:
Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) is just a congestion avoidance mechanism. WRED drops packets selectively based on IP precedence. Edge routers assign IP precedences to packets as they enter the network. When a packet arrives, the following events occur:
1. The average queue size is calculated.
2. If the average is less than the minimum queue threshold, the arriving packet is queued.
3. If the average is between the minimum queue threshold for that type of traffic and the maximum threshold for the interface, the packet is either dropped or queued, depending on the packet drop probability for that type of traffic.
4. If the average queue size is greater than the maximum threshold, the packet is dropped.
WRED reduces the chances of tail drop (when the queue is full, the packet is dropped) by selectively dropping packets when the output interface begins to show signs of congestion (thus it can mitigate congestion by preventing the queue from filling up). By dropping some packets early rather than waiting until the queue is full, WRED avoids dropping large numbers of packets at once and minimizes the chances of global synchronization. Thus, WRED allows the transmission line to be used fully at all times.
WRED generally drops packets selectively based on IP precedence. Packets with a higher IP precedence are less likely to be dropped than packets with a lower precedence. Thus, the higher the priority of a packet, the higher the probability that the packet will be delivered.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/qos_conavd/configuration/15-mt/qos-conavd-15-mt-book/qos-conavd-cfg-wred.html -
Which set of action satisfy the requirement for multi-factor authentication?
A. The user swipes a key fob, then clicks through an email link
B. The user enters a user name and password, and then clicks a notification in an authentication app on a mobile device
C. The user enters a PIN into an RSA token, and then enters the displayed RSA key on a login screen
D. The user enters a user name and password and then re-enters the credentials on a second screen
Correct Answer BExplanation:
This is an example of how two-factor authentication (2FA) works:
- The user logs in to the website or service with their username and password.
- The password is validated by an authentication server and, if correct, the user becomes eligible for the second factor.
- The authentication server sends a unique code to the user's second-factor method (such as a smartphone app).
- The user confirms their identity by providing the additional authentication for their second-factor method.
- something you know - password, pin
- something you have - card, badge
- something you are - retina, voice, facial recognition
s the displayed RSA key on a login screen
D. The user enters a user name and password and then re-enters the credentials on a second screen
Correct Answer
B
Explanation:
This is an example of how two-factor authentication (2FA) works:
- The user logs in to the website or service with their username and password.
- The password is validated by an authentication server and, if correct, the user becomes eligible for the second factor.
- The authentication server sends a unique code to the user's second-factor method (such as a smartphone app).
- The user confirms their identity by providing the additional authentication for their second-factor method.
multi factor can be 2 of the 3:
- something you know - password, pin
- something you have - card, badge
- something you are - retina, voice, facial recognition