PyTorch深度学习实践 Lecture13 RNN进阶篇
Author :Horizon Max
✨ 编程技巧篇:各种操作小结
机器视觉篇:会变魔术 OpenCV
深度学习篇:简单入门 PyTorch
神经网络篇:经典网络模型
算法篇:再忙也别忘了 LeetCode
视频链接:Lecture 13 RNN_Classifier
文档资料:
//Here is the link:
课件链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1vZ27gKp8Pl-qICn_p2PaSw
提取码:cxe4
文章目录
- RNN_Classifier
-
- 概述
- Code
- 运行结果
- 数据集链接
- 附录:相关文档资料
RNN_Classifier
概述
训练一个模型,能够通过输入名字预测是哪个国家的

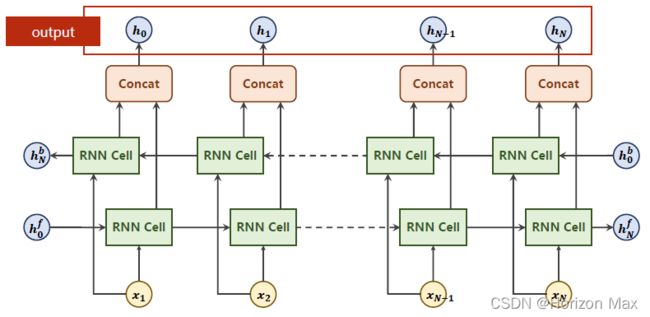
结果只需要对名字对应的国家这个大类进行训练,所以保留最后一个输出即可 h(N)

最后利用 GRU 搭建模型:

名字 利用 ASCII码 记录字符,并进行空值填充:

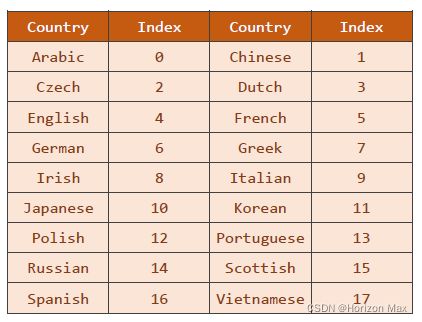
国家 进行编号:
双向神经网络:
Code
# Here is the code :
import torch
import gzip
import csv
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import numpy as np
from torch.nn.utils import rnn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
Hidden_size = 100
Batch_size = 256
Num_layers = 2
Num_epoch = 10
Num_chars = 128
use_gpu = False
# Prepare Data
class NameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, is_train_set=True):
super(NameDataset, self).__init__()
filename = './names_train.csv.gz' if is_train_set else './names_test.csv.gz'
with gzip.open(filename, 'rt') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
rows = list(reader)
self.names = [row[0] for row in rows]
self.len = len(self.names)
self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows]
self.country_list = list(sorted(set(self.countries))) # 去重
self.country_dict = self.getCountryDict() # 将 list 转换成 dict
self.country_num = len(self.country_list)
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.names[index], self.country_dict[self.countries[index]]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
def getCountryDict(self):
country_dict = dict()
for idx, country_name in enumerate(self.country_list, 0):
country_dict[country_name] = idx
return country_dict
def idx2country(self,index):
return self.country_list[index]
def getCountryNum(self):
return self.country_num
train_sets = NameDataset(is_train_set=True)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_sets, batch_size = Batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_sets = NameDataset(is_train_set=False)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_sets, batch_size=Batch_size, shuffle=False)
Num_country = train_sets.getCountryNum()
def create_tensor(tensor):
if use_gpu:
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
tensor = tensor.to(device)
return tensor
def name2list(name):
arr = [ord(c) for c in name]
return arr, len(arr)
def make_tensors(names, countries):
sequences_and_lengths = [name2list(name) for name in names]
name_sequences = [sl[0] for sl in sequences_and_lengths]
seq_lengths = torch.LongTensor([sl[1] for sl in sequences_and_lengths])
countries = countries.long()
# make tensor of name, Batchsize * seqlen
seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences), seq_lengths.max()).long()
for idx, (seq, seq_len) in enumerate(zip(name_sequences, seq_lengths), 0):
seq_tensor[idx, :seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq)
# sort by length to use pack_padded_sequence
seq_lengths, perm_idx = seq_lengths.sort(dim=0, descending=True)
seq_tensor = seq_tensor[perm_idx]
countries = countries[perm_idx]
return create_tensor(seq_tensor),\
create_tensor(seq_lengths),\
create_tensor(countries)
# Modle Design
class RNNClassifier(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1,bidirectional=True):
super(RNNClassifier, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1
self.embadding = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = torch.nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers,
bidirectional=bidirectional)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size * self.directions, output_size)
def _init_hidden(self,batch_size):
hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers * self.directions,
batch_size, self.hidden_size)
return create_tensor(hidden)
def forward(self, input, seq_lengths):
# input shape : B * S - > S * B
input = input.t()
batch_size = input.size(1) # save batch_size for make initial hidden
hidden = self._init_hidden(batch_size)
embadding = self.embadding(input)
# pack them up
gru_input = rnn.pack_padded_sequence(embadding, seq_lengths)
output, hidden = self.gru(gru_input, hidden)
if self.directions==2:
hidden_cat = torch.cat([hidden[-1], hidden[-2]], dim=1)
else:
hidden_cat = hidden[-1]
fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat) # Use linear classifier
return fc_output
def time_since(since):
s = time.time()-since
m = math.floor(s/60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
def trainModel():
total_loss = 0
for i, (names,countries) in enumerate(train_loader,1):
inputs, seq_lengths, targets = make_tensors(names,countries)
output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths)
loss = criterion(output, targets)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if i % 10 == 0:
print(f'[{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch}', end='')
print(f'[{i * len(inputs)}/{len(train_sets)}]',end='')
print(f'loss={total_loss / (i * len(inputs))}')
return total_loss
def testModel():
correct = 0
total = len(test_sets)
print('evaluating trained model...')
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(test_loader, 1):
inputs, seq_lengths, targets = make_tensors(names, countries)
output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths)
pred = output.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(targets.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
percent = '%.2f' % (100 * correct / total)
print(f'Test set:Accuracy {correct} / {total} {percent}%')
return correct / total
if __name__=="__main__":
classifier = RNNClassifier(Num_chars, Hidden_size, Num_country, Num_layers)
# 字符数,隐层大小、国家类数、网络层数
if use_gpu:
device = torch.device('cuda:0')
classifier.to(device)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=0.001)
start = time.time() # 打印训练时间
print('Training for %d epochs...' % Num_epoch)
acc_list = []
for epoch in range(1,Num_epoch+1):
trainModel()
acc = testModel()
acc_list.append(acc)
epoch = np.arange(1, len(acc_list) + 1, 1)
acc_list = np.array(acc_list)
plt.plot(epoch, acc_list)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
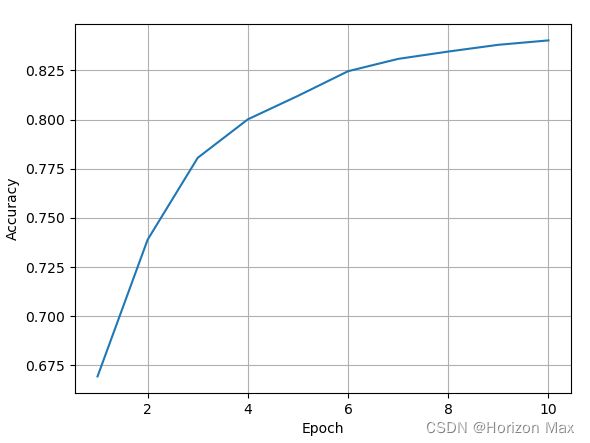
运行结果
在将参数 use_gpu = False 改成 “True” 的时候就会发现 惊喜 :
RuntimeError: 'lengths' argument should be a 1D CPU int64 tensor, but got 1D cuda:0 Long tensor
解决方案参考:链接
数据集链接
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1l_r_S2AE7i2vvgKs5HawOQ
提取码:6666
附录:相关文档资料
PyTorch 官方文档: PyTorch Documentation
PyTorch 中文手册: PyTorch Handbook
《PyTorch深度学习实践》系列链接:
Lecture01 Overview
Lecture02 Linear_Model
Lecture03 Gradient_Descent
Lecture04 Back_Propagation
Lecture05 Linear_Regression_with_PyTorch
Lecture06 Logistic_Regression
Lecture07 Multiple_Dimension_Input
Lecture08 Dataset_and_Dataloader
Lecture09 Softmax_Classifier
Lecture10 Basic_CNN
Lecture11 Advanced_CNN
Lecture12 Basic_RNN
Lecture13 RNN_Classifier