后缀自动机(SAM)构造实现过程演示+习题集锦
文章目录
- 后缀自动机
- 算法实现过程
- 模板
- 习题
-
- 洛谷后缀自动机模板题
- 品酒大会
- [HEOI2015]最短不公共子串
- 字符串
蒟蒻写这篇 b l o g blog blog主要是存一下,后缀自动机的详细搭建过程,方便以后复习
具体的某些证明,为什么这么做,正确性劈里啪啦一大堆就不赘述了讲解指路☞
后缀自动机
后缀自动机上每一条到 i i i的路径对应一个子串,整个自动机包含了字符串的所有子串
很多时候可以和后缀数组等价使用
e n d p o s endpos endpos:一个子串 i i i在整个字符串中出现的位置 最后一个字符的下标 构成的集合
举个栗子 a b c b c d e a b c abcbcdeabc abcbcdeabc,(从 0 0 0开始标号)
子串 a b c abc abc对应的 e n d p o s endpos endpos为 { 2 , 9 } \{2,9\} {2,9},子串 b c bc bc的 e n d p o s endpos endpos为 { 2 , 4 , 9 } \{2,4,9\} {2,4,9}
后缀自动机的编号对应的就是 e n d p o s endpos endpos完全相同的所有子串
依旧是上面的粒子 a b c b c d e a b c abcbcdeabc abcbcdeabc
子串 b c bc bc的 e n d p o s endpos endpos为 { 2 , 4 , 9 } \{2,4,9\} {2,4,9},子串 c c c的 e n d p o s endpos endpos也为 { 2 , 4 , 9 } \{2,4,9\} {2,4,9}
那么后缀自动机上对应的 i d id id编号既表示 b c bc bc子串,也表示 c c c子串
算法实现过程
- e . g . 1 e.g.1 e.g.1,构建 a b c d abcd abcd的后缀自动机
Ⅰ最初始状态,仅有一个空根, l a s t = 1 last=1 last=1, l a s t last last表示后缀自动机的最后一个节点

Ⅱ 将 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′扔进去,新建一个节点 c n t = 2 cnt=2 cnt=2, l e n = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 1 len=len[last]+1=1 len=len[last]+1=1
从 l a s t last last开始跳,发现 1 1 1没有 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边
则建立一条 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,并指向新点 2 2 2
此时跳到了初始源点, 2 2 2的后缀链接只能指向 1 1 1, l a s t last last变为 2 2 2

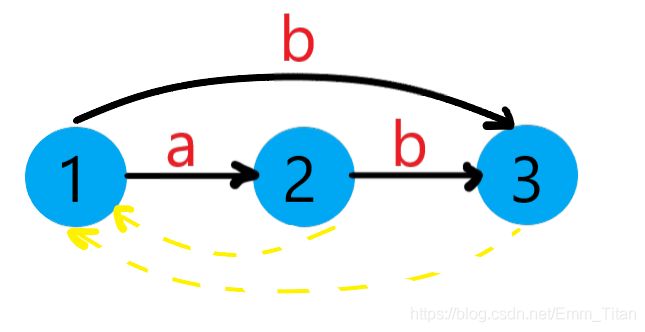
Ⅲ 将 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′扔进去,新建一个节点 c n t = 3 , l e n = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 2 cnt=3,len=len[last]+1=2 cnt=3,len=len[last]+1=2
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
2 2 2没有 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,新建一条并指向 3 3 3,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1没有 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,新建一条并指向 3 3 3
此时已经到了根节点, 3 3 3的后缀链接只能指向 1 1 1, l a s t = 3 last=3 last=3
Ⅳ 将 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′扔进去,新建一个节点 c n t = 4 , l e n = 3 cnt=4,len=3 cnt=4,len=3
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
3 3 3没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 4 4 4,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 4 4 4
此时已经到了根节点, 4 4 4的后缀链接只能指向 1 1 1, l a s t = 4 last=4 last=4
 Ⅴ 将 ′ d ′ 'd' ′d′扔进去,新建一个节点 c n t = 5 , l e n = 4 cnt=5,len=4 cnt=5,len=4
Ⅴ 将 ′ d ′ 'd' ′d′扔进去,新建一个节点 c n t = 5 , l e n = 4 cnt=5,len=4 cnt=5,len=4
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
4 4 4没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 5 5 5,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 5 5 5
此时已经到了根节点, 5 5 5的后缀链接只能指向 1 1 1, l a s t = 5 last=5 last=5

最简单的一种后缀自动机就完成了
接下来就尝试一下进阶版
- e . g . 2 e.g.2 e.g.2,构建 a b a b e ababe ababe的后缀自动机
Ⅰ先搭建空源点, l a s t = 1 last=1 last=1

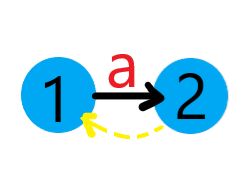
Ⅱ 加入 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′,新建一个节点 c n t = 2 , l e n [ 2 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 1 cnt=2,len[2]=len[last]+1=1 cnt=2,len[2]=len[last]+1=1
1 1 1没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 2 2 2,
此时已经到了根节点, 2 2 2的后缀链接只能指向 1 1 1, l a s t = 2 last=2 last=2
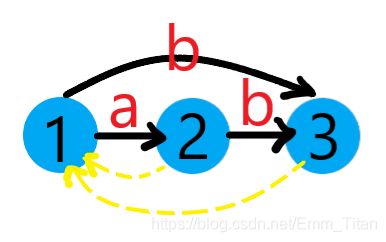
Ⅲ 加入 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′,新建一个节点 c n t = 3 , l e n [ 3 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 2 cnt=3,len[3]=len[last]+1=2 cnt=3,len[3]=len[last]+1=2
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
2 2 2没有 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,新建一条并指向 3 3 3,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1没有 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,新建一条并指向 3 3 3
此时已经到了根节点, 3 3 3的后缀链接只能指向 1 1 1, l a s t = 3 last=3 last=3
Ⅳ 再加入 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′,新建一个节点 c n t = 4 , l e n [ 4 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 3 cnt=4,len[4]=len[last]+1=3 cnt=4,len[4]=len[last]+1=3
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
3 3 3没有 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,新建一条并指向 4 4 4,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1有一条指向 2 2 2的 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,满足 l e n [ 2 ] = l e n [ 1 ] + 1 len[2]=len[1]+1 len[2]=len[1]+1,则直接将 4 4 4后缀链接指向 2 2 2
结束, l a s t = 4 last=4 last=4

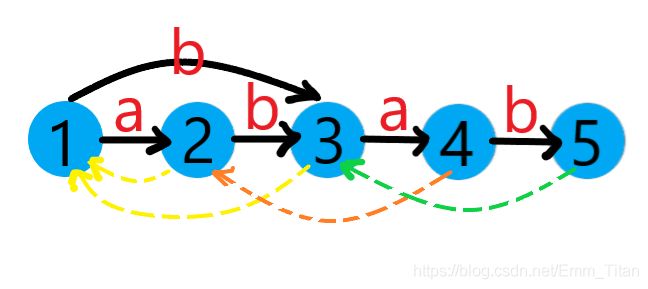
Ⅴ 再加入 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′,新建一个节点 c n t = 5 , l e n [ 5 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 4 cnt=5,len[5]=len[last]+1=4 cnt=5,len[5]=len[last]+1=4
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
4 4 4没有 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,新建一条并指向 5 5 5,跳后缀链接到 2 2 2
2 2 2有一条指向 3 3 3的 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,满足 l e n [ 3 ] = l e n [ 2 ] + 1 len[3]=len[2]+1 len[3]=len[2]+1,直接将 5 5 5后缀链接指向 3 3 3
结束, l a s t = 5 last=5 last=5
Ⅵ 加入新 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′,新建一个节点 c n t = 6 , l e n [ 6 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 5 cnt=6,len[6]=len[last]+1=5 cnt=6,len[6]=len[last]+1=5
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
5 5 5没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 6 6 6,跳后缀链接到 3 3 3
3 3 3没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 6 6 6,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 6 6 6
此时已到根节点, 6 6 6只能链接 1 1 1, l a s t = 6 last=6 last=6结束
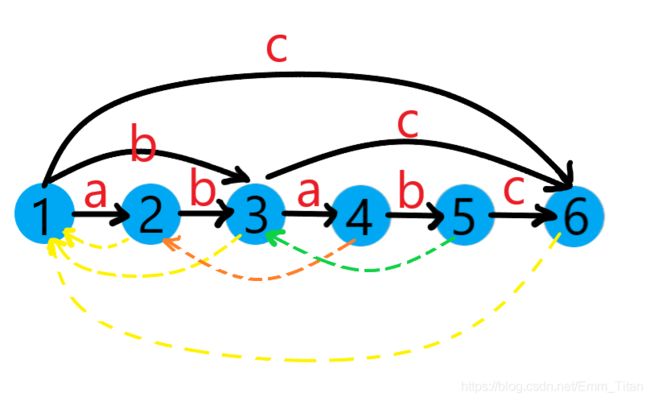 这就是进阶版了,没有涉及到最终版的点复制
这就是进阶版了,没有涉及到最终版的点复制
最后让我们一起携手走进最终版的后缀自动机构造
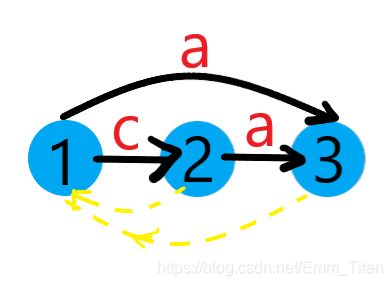
- e . g . 3 e.g.3 e.g.3,构建 c a b a b cabab cabab的后缀自动机
Ⅰ 创造新源点, l a s t = 1 , c n t = 1 last=1,cnt=1 last=1,cnt=1

Ⅱ 加入 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′,新建一个节点 c n t = 2 , l e n [ 2 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 1 cnt=2,len[2]=len[last]+1=1 cnt=2,len[2]=len[last]+1=1
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
1 1 1没有 ′ c ′ 'c' ′c′边,新建一条并指向 2 2 2
此时已到根节点, 2 2 2只能链接 1 , l a s t = 2 1,last=2 1,last=2

Ⅲ 加入 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′,新建一个节点 c n t = 3 , l e n [ 3 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 2 cnt=3,len[3]=len[last]+1=2 cnt=3,len[3]=len[last]+1=2
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
2 2 2没有 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,新建一条并指向 3 3 3,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1没有 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,新建一条并指向 3 3 3
此时已到根节点, 3 3 3只能链接 1 , l a s t = 3 1,last=3 1,last=3
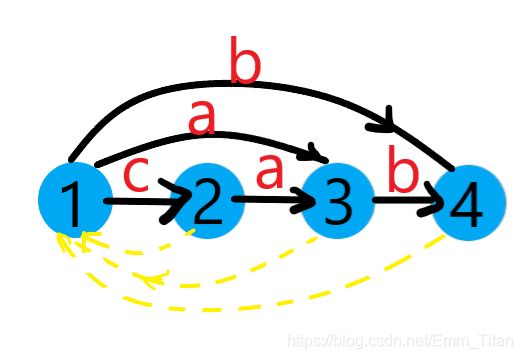
Ⅳ 加入 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′,新建一个节点 c n t = 4 , l e n [ 4 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 3 cnt=4,len[4]=len[last]+1=3 cnt=4,len[4]=len[last]+1=3
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
3 3 3没有 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,新建一条并指向 4 4 4,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1没有 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,新建一条并指向 4 4 4
此时已到根节点, 4 4 4只能链接 1 , l a s t = 4 1,last=4 1,last=4
Ⅴ 加入 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′,新建一个节点 c n t = 5 , l e n [ 5 ] = l e n [ l a s t ] + 1 = 4 cnt=5,len[5]=len[last]+1=4 cnt=5,len[5]=len[last]+1=4
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
4 4 4没有 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,新建一条并指向 5 5 5,跳后缀链接到 1 1 1
1 1 1有 ′ a ′ 'a' ′a′边,指向 3 3 3,但是!!! l e n [ 3 ] ≠ l e n [ 1 ] + 1 len[3]≠len[1]+1 len[3]=len[1]+1,不能像进阶版直接链接,这里必须要点复制
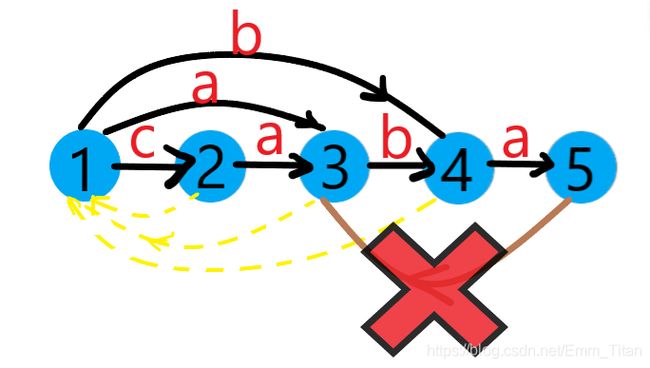 新建一个 3 3 3的分身节点 c n t = 6 cnt=6 cnt=6
新建一个 3 3 3的分身节点 c n t = 6 cnt=6 cnt=6
3 3 3的所有信息(出入边)除了原字符串间的边(图中黑色边)全部修改为分点 6 6 6的边,直接覆盖
并且 6 6 6成为 3 3 3的直接后缀链接,替代 1 1 1
l e n [ 6 ] = l e n [ 1 ] + 1 = 1 len[6]=len[1]+1=1 len[6]=len[1]+1=1
相当于 6 6 6做了 1 , 3 1,3 1,3后缀链之间的承接点,保证了每一条边上 l e n len len只会带来 + 1 +1 +1的影响
5 5 5直接链接 6 6 6后结束, l a s t = 5 last=5 last=5
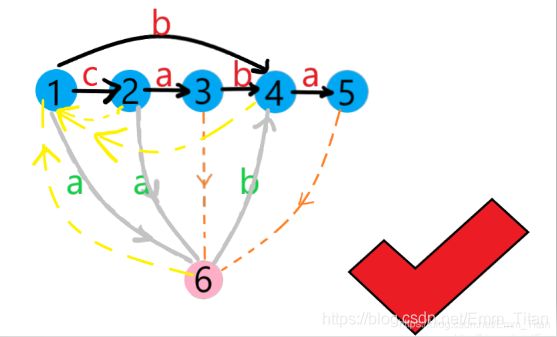
Ⅵ 加入 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′,新建节点 c n t = 7 cnt=7 cnt=7
从 l a s t last last开始跳后缀链接
5 5 5没有 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,新建一条指向 7 7 7,跳后缀链接到 6 6 6
6 6 6有一条 ′ b ′ 'b' ′b′边,指向 4 4 4,判断 l e n [ 4 ] ≠ l e n [ 6 ] + 1 len[4]≠len[6]+1 len[4]=len[6]+1

再次执行复制操作
新建一个 4 4 4的分身节点 c n t = 8 cnt=8 cnt=8
4 4 4的所有信息(出入边)除了原字符串间的边(图中黑色边)全部修改为分点 8 8 8的边,直接进行覆盖
8 8 8成为 4 4 4的直接后缀链接, l e n [ 8 ] = l e n [ 6 ] + 1 = 2 len[8]=len[6]+1=2 len[8]=len[6]+1=2
7 7 7直接链接 8 8 8后结束, l a s t = 7 last=7 last=7
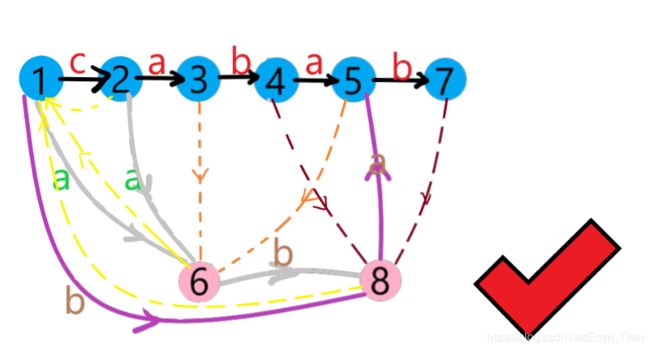
⚡
l e n [ x ] len[x] len[x]复制点的 l e n len len不等于被复制点的原后缀链接的 l e n + 1 len+1 len+1,而是谁触发的 l e n + 1 len+1 len+1
模板
struct node {
int len; //长度
int fa; //后缀链接
int son[maxc]; //字符集大小
}t[maxn];
模拟从主链的前一个开始跳后缀链接,并对于链接上的没有该字符边的每一个点都连出一条新字符边
while( pre && ! t[pre].son[c] ) t[pre].son[c] = now, pre = t[pre].fa;
跳到根,代表这是首个出现的字符,他只能链接最初的根节点了
if( ! pre ) t[now].fa = 1;
否则,如果路上找到了,满足 l e n len len的关系,直接后缀链接指过去即可
int u = t[pre].son[c];
if( t[u].len == t[pre].len + 1 ) t[now].fa = u;
复制该点,并进行有关该点的所有信息重改
①原点连出的点,新点也要连出
②连入原点的点,变成连入新点
③原点和新点间也需建立联系,新点是原点的后缀链接
else {
int v = ++ tot;
t[v] = t[u];//利用结构体巧妙将原点连出的点进行复制
t[v].len = t[pre].len + 1;//由谁触发 len就是触发点len+1
t[u].fa = t[now].fa = v;//原点与复制点与新建点的关系
while( pre && t[pre].son[c] == u ) t[pre].son[c] = v, pre = t[pre].fa;//暴力复制修改连入原点的点
}
习题
洛谷后缀自动机模板题
- code
#include 品酒大会
- solution
有一个 S A M SAM SAM常用结论:前缀 i , j i,j i,j的最长公共后缀 = p a r e n t t r e e =parent\ tree =parent tree上前缀 i , j i,j i,j分别指向的点 u , v u,v u,v的 l c a lca lca反映在后缀自动机上的节点代表的最长子串
将本题的字符串倒过来建后缀自动机,在自动机上进行树上 d p dp dp,最后从后往前进行更新即可 - code
#include [HEOI2015]最短不公共子串
- solution
做此题需要了解序列自动机
然后就是很无脑的四个 b f s bfs bfs跑
子串就是跑后缀自动机
子序列就是跑序列自动机 - code
#include 字符串
- solution
这题运用的思想主要是广义后缀自动机,即将多个字符串建在一个后缀自动机上
其实并没有什么新颖之处,只需在扩展的时候带一个这个字符属于哪个字符串的编号即可
假设已经建好了自动机,接下来考虑两个长度为 k k k的子串之间如何一一对应修改
这个时候如果将其放到 p a r e n t t r e e parent\ tree parent tree上考虑的话,就简单了
其实可以猜想一下,刚开始我就想到了虚树的性质,即相邻两两配对
不难证明,的确应该相邻两个不同属类的子串配对
前缀 i , j i,j i,j的最长公共后缀 = p a r e n t t r e e =parent\ tree =parent tree上前缀 i , j i,j i,j分别指向的点 u , v u,v u,v的 l c a lca lca反映在后缀自动机上的节点代表的最长子串
也就是最后变成深搜一棵树的模样,记得特判可能 l c a lca lca代表的最长子串长度 ≥ k \ge k ≥k
此时是不需要代价的
- code
#include