ATSS:Adaptive Training Sample Selection原理与代码解读
论文 Bridging the Gap Between Anchor-based and Anchor-free Detection via Adaptive Training Sample Selection
官方代码 GitHub - sfzhang15/ATSS: Bridging the Gap Between Anchor-based and Anchor-free Detection via Adaptive Training Sample Selection, CVPR, Oral, 2020
Anchor-based和Anchor-free方法的差异
作者以RetinaNet和Fcos两个one-stage detector为例,比较了anchor-based和anchor-free两种方法的差异。
原始的RetinaNet和Fcos主要有三个区别:
- 每个位置设置的anchor数量。RetinaNet设置多个(一般是9个)anchor,Fcos设置1个(Fcos中的一个点等价于一个anchor)。
- 正负样本的定义。RetinaNet根据IoU的不同来区分正负样本,Fcos根据spatial和scale两个维度的约束来区分正负样本。
- 边框回归的方法。RetinaNet基于预设的anchor回归中心坐标和宽高,Fcos回归每个点到gt box四条边的距离。
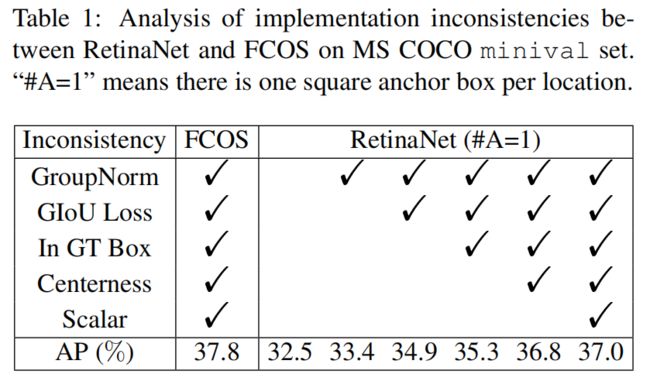
为了找到效果差异的原因,作者去除了两者不一致的地方,首先将RetinaNet每个位置设置的anchor数量改为1即RetinaNet(#A=1),然后将Fcos新增的一些trick也加到RetinaNet上
通过上表可以看出,将这些不一致去除后,RetinaNet最终的AP为37,与Fcos的37.8仍有差距。此时二者还有两点不一致,一是正负样本的定义,二是回归的方法。
正负样本定义的区别如下所示
回归方式的区别如下所示
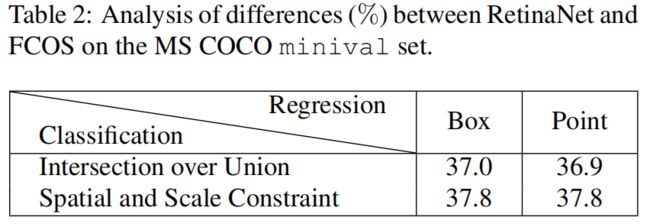
作者进一步进行实验,比较这两点不同造成的效果差异,结果如下所示
当RetinaNet采用Fcos的spatial and scale constraint的正负样本采样方式后,AP由37上升到37.8,而Fcos采用RetinaNet的IoU采样方式后,AP由37.8降到36.9。而当两者改变回归方法后,AP几乎没有变化。由此可见,anchor-based和anchor-free性能差异的根本原因在于正负样本的定义。
ATSS
在了解了anchor-based和anchor-free方法性能差异的根本原因后,作者提出了一种新的正负样本定义方法Adaptive Training Sample Selection(ATSS)。
具体步骤如下:
- 遍历每个gt box,遍历每个输出层,找出每层中topk(超参,默认是9)个L2距离(anchor和gt box中心点)最小的anchor。假设一共L层输出层,则每个gt会挑选出topk×L个候选anchor。
- 计算该gt和所有候选anchor的IoU。
- 计算IoU的均值\(m_{g}\)和方差\(v_{g}\),两者相加得到该gt的自适应阈值\(t_{g}\)。
- 从候选anchor中挑选出IoU大于该阈值的anchor,并过滤掉中心不在gt box内部的anchor,剩下的就是挑选出的正样本。
- 候选anchor中去掉正样本,剩下的都是负样本。
均值代表了anchor对gt box的正样本概率适应度值,其值越高,代表候选样本质量普遍越高。而标准差代表哪些输出层适合预测该 gt box,标准差越大越能区分层和层之间的 anchor 质量差异。均值和标准差相加就能够很好的反应出哪些层的哪些 anchor 适合作为正样本。
需要特别强调,ATSS 自定义分配策略可以用于 anchor-free,也可以用于 anchor-based,当用于 anchor-free 后,其 anchor 设置仅仅用于计算特征图上面点的正负样本属性,不会参数后续任何计算,而且由于其自适应策略,anchor 的设置不当影响没有 anchor-based 类算法大。
分析
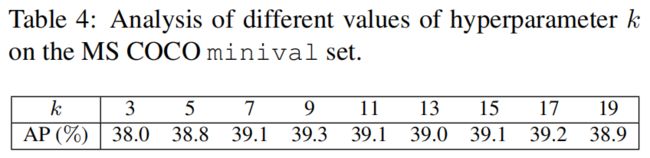
Hyperparameter k
可以看出,当k在7~17范围内,结果还是比较鲁棒的。当k过小时,比如k=3,正样本太少模型训练困难。当k过大时,会引入质量差的正样本,也会导致模型性能变差。
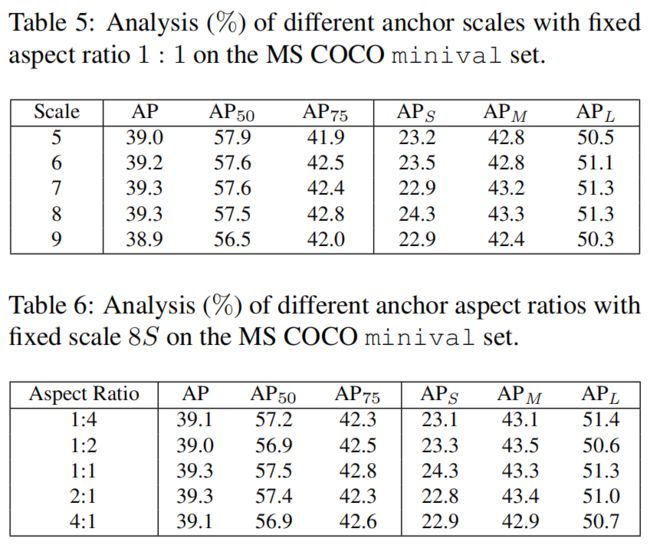
Anchor Size
通过上面结果可以看出,不论是scale还是ratio,模型的性能对其变化都不敏感,表明ATSS对不同的anchor设置都具有很好的鲁棒性。
Anchor Num
作者在之前的实验中为了和Fcos保持一致,直接将RetinaNet每个位置放置的anchor数量由9改为1,并没有讨论anchor数量的影响。这里作者研究了这点,从上面的结果可以看出,在原始的根据IoU定义正负样本的情况下,每个位置放置更多的anchor会带来性能的提升,AP 38.4 vs. 37.0。但当采用ATSS后,anchor数量对结果并没有影响。
代码
class ATSSAssigner(BaseAssigner):
"""Assign a corresponding gt bbox or background to each bbox.
Each proposals will be assigned with `0` or a positive integer
indicating the ground truth index.
- 0: negative sample, no assigned gt
- positive integer: positive sample, index (1-based) of assigned gt
Args:
topk (float): number of bbox selected in each level
"""
def __init__(self,
topk,
iou_calculator=dict(type='BboxOverlaps2D'),
ignore_iof_thr=-1):
self.topk = topk
self.iou_calculator = build_iou_calculator(iou_calculator)
self.ignore_iof_thr = ignore_iof_thr
# https://github.com/sfzhang15/ATSS/blob/master/atss_core/modeling/rpn/atss/loss.py
def assign(self,
bboxes, # shape=(1939,4)
num_level_bboxes, # [1444, 361, 100, 25, 9]
gt_bboxes, # tensor([[157.2000, 168.0000, 193.8000, 270.4000], [98.4000, 210.4000, 151.2000, 296.8000], [144.0000, 154.4000, 176.4000, 238.4000]], device='cuda:0')
gt_bboxes_ignore=None, # None
gt_labels=None): # tensor([8, 8, 8], device='cuda:0')
"""Assign gt to bboxes.
The assignment is done in following steps
1. compute iou between all bbox (bbox of all pyramid levels) and gt
2. compute center distance between all bbox and gt
3. on each pyramid level, for each gt, select k bbox whose center
are closest to the gt center, so we total select k*l bbox as
candidates for each gt
4. get corresponding iou for the these candidates, and compute the
mean and std, set mean + std as the iou threshold
5. select these candidates whose iou are greater than or equal to
the threshold as positive
6. limit the positive sample's center in gt
Args:
bboxes (Tensor): Bounding boxes to be assigned, shape(n, 4).
num_level_bboxes (List): num of bboxes in each level
gt_bboxes (Tensor): Groundtruth boxes, shape (k, 4).
gt_bboxes_ignore (Tensor, optional): Ground truth bboxes that are
labelled as `ignored`, e.g., crowd boxes in COCO.
gt_labels (Tensor, optional): Label of gt_bboxes, shape (k, ).
Returns:
:obj:`AssignResult`: The assign result.
"""
INF = 100000000
bboxes = bboxes[:, :4]
num_gt, num_bboxes = gt_bboxes.size(0), bboxes.size(0) # (3, 4), (1939, 4)
# compute iou between all bbox and gt
overlaps = self.iou_calculator(bboxes, gt_bboxes) # torch.Size([1939, 3])
# assign 0 by default
assigned_gt_inds = overlaps.new_full((num_bboxes, ),
0,
dtype=torch.long) # torch.Size([1939])
if num_gt == 0 or num_bboxes == 0:
# No ground truth or boxes, return empty assignment
max_overlaps = overlaps.new_zeros((num_bboxes, ))
if num_gt == 0:
# No truth, assign everything to background
assigned_gt_inds[:] = 0
if gt_labels is None:
assigned_labels = None
else:
assigned_labels = overlaps.new_full((num_bboxes, ),
-1,
dtype=torch.long)
return AssignResult(
num_gt, assigned_gt_inds, max_overlaps, labels=assigned_labels)
# compute center distance between all bbox and gt
gt_cx = (gt_bboxes[:, 0] + gt_bboxes[:, 2]) / 2.0 # torch.Size([3])
gt_cy = (gt_bboxes[:, 1] + gt_bboxes[:, 3]) / 2.0
gt_points = torch.stack((gt_cx, gt_cy), dim=1) # torch.Size([3, 2]), tensor([[175.5000, 219.2000], [124.8000, 253.6000], [160.2000, 196.4000]], device='cuda:0')
bboxes_cx = (bboxes[:, 0] + bboxes[:, 2]) / 2.0 # torch.Size([1939])
bboxes_cy = (bboxes[:, 1] + bboxes[:, 3]) / 2.0
bboxes_points = torch.stack((bboxes_cx, bboxes_cy), dim=1) # torch.Size([1939, 2])
distances = (bboxes_points[:, None, :] -
gt_points[None, :, :]).pow(2).sum(-1).sqrt() # L2 distance
# (1939,1,2) - (1,3,2) -> (1939,3,2) -> (1939,3)
if (self.ignore_iof_thr > 0 and gt_bboxes_ignore is not None
and gt_bboxes_ignore.numel() > 0 and bboxes.numel() > 0): # -1,
ignore_overlaps = self.iou_calculator(
bboxes, gt_bboxes_ignore, mode='iof')
ignore_max_overlaps, _ = ignore_overlaps.max(dim=1)
ignore_idxs = ignore_max_overlaps > self.ignore_iof_thr
distances[ignore_idxs, :] = INF
assigned_gt_inds[ignore_idxs] = -1
# Selecting candidates based on the center distance
candidate_idxs = []
start_idx = 0
for level, bboxes_per_level in enumerate(num_level_bboxes):
# on each pyramid level, for each gt,
# select k bbox whose center are closest to the gt center
end_idx = start_idx + bboxes_per_level
distances_per_level = distances[start_idx:end_idx, :]
selectable_k = min(self.topk, bboxes_per_level)
_, topk_idxs_per_level = distances_per_level.topk(
selectable_k, dim=0, largest=False) # (9,3)
candidate_idxs.append(topk_idxs_per_level + start_idx)
start_idx = end_idx
candidate_idxs = torch.cat(candidate_idxs, dim=0) # (45,3)
# get corresponding iou for the these candidates, and compute the
# mean and std, set mean + std as the iou threshold
candidate_overlaps = overlaps[candidate_idxs, torch.arange(num_gt)] # (1939,3) -> (45, 3)
overlaps_mean_per_gt = candidate_overlaps.mean(0) # torch.Size([3])
overlaps_std_per_gt = candidate_overlaps.std(0) # torch.Size([3])
overlaps_thr_per_gt = overlaps_mean_per_gt + overlaps_std_per_gt # torch.Size([3])
is_pos = candidate_overlaps >= overlaps_thr_per_gt[None, :] # (45,3)
# limit the positive sample's center in gt
for gt_idx in range(num_gt):
candidate_idxs[:, gt_idx] += gt_idx * num_bboxes # 每个gt的candidate_idxs的范围都是[0,1939),这里的操作相当于展平拼接在后面
ep_bboxes_cx = bboxes_cx.view(1, -1).expand(
num_gt, num_bboxes).contiguous().view(-1) # (1939)->(1,1939)->(3,1939)->(5817)
ep_bboxes_cy = bboxes_cy.view(1, -1).expand(
num_gt, num_bboxes).contiguous().view(-1)
candidate_idxs = candidate_idxs.view(-1) # (45,3)->(135)
# calculate the left, top, right, bottom distance between positive
# bbox center and gt side
l_ = ep_bboxes_cx[candidate_idxs].view(-1, num_gt) - gt_bboxes[:, 0] # (5817)->(135)->(45,3)-(3)->(45,3)
t_ = ep_bboxes_cy[candidate_idxs].view(-1, num_gt) - gt_bboxes[:, 1]
r_ = gt_bboxes[:, 2] - ep_bboxes_cx[candidate_idxs].view(-1, num_gt)
b_ = gt_bboxes[:, 3] - ep_bboxes_cy[candidate_idxs].view(-1, num_gt)
is_in_gts = torch.stack([l_, t_, r_, b_], dim=1).min(dim=1)[0] > 0.01 # (45,4,3) -> (45,3)
is_pos = is_pos & is_in_gts # (45,3)
# if an anchor box is assigned to multiple gts,
# the one with the highest IoU will be selected.
overlaps_inf = torch.full_like(overlaps,
-INF).t().contiguous().view(-1) # (1939,3)->(3,1939)->(5817)
index = candidate_idxs.view(-1)[is_pos.view(-1)] # (135)->(135)[(45,3)->(135)] -> (21)
overlaps_inf[index] = overlaps.t().contiguous().view(-1)[index]
overlaps_inf = overlaps_inf.view(num_gt, -1).t() # (5817)->(3,1939)->(1939,3)
max_overlaps, argmax_overlaps = overlaps_inf.max(dim=1) # (1939),(1939)
assigned_gt_inds[
max_overlaps != -INF] = argmax_overlaps[max_overlaps != -INF] + 1
if gt_labels is not None:
assigned_labels = assigned_gt_inds.new_full((num_bboxes, ), -1)
pos_inds = torch.nonzero(
assigned_gt_inds > 0, as_tuple=False).squeeze()
if pos_inds.numel() > 0:
assigned_labels[pos_inds] = gt_labels[
assigned_gt_inds[pos_inds] - 1]
else:
assigned_labels = None
return AssignResult(
num_gt, assigned_gt_inds, max_overlaps, labels=assigned_labels)参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/358125611