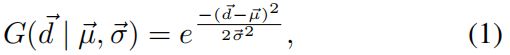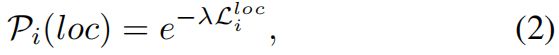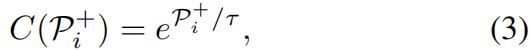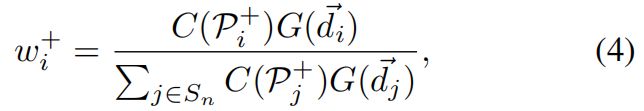AutoAssign: Differentiable Label Assignment for Dense Object Detection
论文 https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.03496
Center Weighting
在之前的目标检测模型中,大都依据中心先验(center prior)即物体在bounding box中的分布大体是围绕框的中心这一准则进行label assignment的。但是,目标的外观在不同的类别和场景中差异很大,比如像香蕉、雨伞,上述固定中心的采样策略可能会选择目标外的位置作为正样本,不能覆盖不同类别的不同分布。
因此作者提出了Center Weighting module,具体公式如下
其中\(\vec{d}\)表示gt box内任意一点沿x和y坐标方向与中心点的偏差,这意味着值可能为负。\(\vec{\mu }\)和\(\vec{\sigma }\)是维度为 (K, 2) 的可学习参数,K是类别数。\(\vec{\mu }\)控制每个类别目标中心的偏移量,\(\vec{\sigma }\)根据类别特征衡量每个位置的重要性。这样就可以根据不同类别物体的形状去自适应的学习center prior的分布。
具体对于一个目标,单独计算每个FPN stage中每个位置的权重,然后stack起来后续使用。此外,为了减少FPN不同stage不同scale带来的干扰,用stride对\(\vec{d}\)进行归一化。
Confidence Weighting
和之前的模型不同,在auto assign中,gt box中每个点既作为正样本同时又作为负样本,通过confidence weighting来控制一个位置正负样本的权重。
Classification confidence
错误的分配比如将背景分为正样本会严重影响模型的效果,因此作者提出了Implicit-Objectness (ImpObj)分支,该分支和FCOS中的centerness分支的形式是一样的,但是这里有一个问题,就是没有监督信息。考虑到这里的目的是为了动态的增强正样本点过滤有噪声的背景样本点,因此将其与分类的score相乘作为最终的分类置信度,这样就可以和分类分支共享监督信息而不需要额外的监督了。
Joint Confidene Indicator
在判断一个位置是前景还是背景时,不应该只考虑分类得分,回归的结果也应该考虑到,但是通常回归输出是的是位置的偏差,很难衡量回归分支的置信度。这里作者的做法是将回归的损失转换成似然,如下
其中\(\lambda\) 是平衡分类和回归的超参,\(L_{i}^{loc}\)用的是GIoU loss。然后将分类score和回归似然结合到一起作为联合置信度\(P_{i}\),前景置信度\(P_{i}^{+}=P_{i}(cls)\cdot P_{i}(loc)\),其中分类置信度\(P_{i}(cls)\)是分类score和ImpObj score的乘积。对于背景,考虑到背景位置只会进行分类操作,因此背景置信度\(P_{i}^{-}=P_{i}(cls)\),对于gt box外的所有位置也都是如此,这样所有的背景位置都可以统一处理了。
Positive weights
如果一个位置的前景置信度更高,理所当然更希望把它分到前景,因此基于前面提出的前景置信度\(P_{i}^{+}\),作者提出了前景置信度加权函数,如下所示
其中\( \tau \)是控制置信度高、低位置对positive loss贡献的超参。
对于一个目标,我们更应该关注bounding box内那些预测更准确的位置,但在训练初始阶段,因为随机初始化导致每个位置的预测并不合理,之前提出的center prior在这里就派上了用场,将\(G(\vec d_{i})\)与\(C(P_{i}^{+})\)进行结合得到前景的权重\(w_{i}^{+}\)
其中\(S_{n}\)表示目标\(n\)在所有scale level的bounding box中的所有位置。
Negative weights
背景权重\(w_{i}^{-}\)的定义如下
其中\(f(iou_{i})=1/(1-iou_{i})\),\(iou_{i}\)表示位置\(i\in S_{n}\)的proposal和所有gt box间的最大IoU。为了当做有效的权重,将\(f(iou_{i})\)按其值的范围归一化到[0, 1]区间,这样就确保IoU最大的位置获得零背景损失。对于gt box外的所有位置\(w_{i}^{-}\)设为1。
Loss function
通过生成正负权重map,实现了动态分配更合适的空间位置和自动为每个实例选择适当的FPN阶段的目的。因为权重map融入到了loss的计算中,AutoAssign能够以可微分的方式处理label assignment。最终的Loss函数定义如下
其中\(S\)表示所有scale stage的输出特征图上的所有位置,对于gt box内的一个位置,用不同的权重分别单独计算positive loss和negtive loss,为了解决样本不平衡问题,式(6)中的negative loss部分用了Focal Loss。
代码
代码是mmdetection中的实现,做了一些注释方便理解
class CenterPrior(nn.Module):
"""Center Weighting module to adjust the category-specific prior
distributions.
Args:
force_topk (bool): When no point falls into gt_bbox, forcibly
select the k points closest to the center to calculate
the center prior. Defaults to False.
topk (int): The number of points used to calculate the
center prior when no point falls in gt_bbox. Only work when
force_topk if True. Defaults to 9.
num_classes (int): The class number of dataset. Defaults to 80.
strides (tuple[int]): The stride of each input feature map. Defaults
to (8, 16, 32, 64, 128).
"""
def __init__(self,
force_topk=False, # False
topk=9, # 9
num_classes=80, # 20
strides=(8, 16, 32, 64, 128)): # [8,16,32,64,128]
super(CenterPrior, self).__init__()
self.mean = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_classes, 2))
self.sigma = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(num_classes, 2))
self.strides = strides
self.force_topk = force_topk
self.topk = topk
def forward(self, anchor_points_list, gt_bboxes, labels,
inside_gt_bbox_mask):
# [(13600,2),(3400,2),(850,2),(221,2),(63,2)], (2,4), (2), (18134,2)
"""Get the center prior of each point on the feature map for each
instance.
Args:
anchor_points_list (list[Tensor]): list of coordinate
of points on feature map. Each with shape
(num_points, 2).
gt_bboxes (Tensor): The gt_bboxes with shape of
(num_gt, 4).
labels (Tensor): The gt_labels with shape of (num_gt).
inside_gt_bbox_mask (Tensor): Tensor of bool type,
with shape of (num_points, num_gt), each
value is used to mark whether this point falls
within a certain gt.
Returns:
tuple(Tensor):
- center_prior_weights(Tensor): Float tensor with shape \
of (num_points, num_gt). Each value represents \
the center weighting coefficient.
- inside_gt_bbox_mask (Tensor): Tensor of bool type, \
with shape of (num_points, num_gt), each \
value is used to mark whether this point falls \
within a certain gt or is the topk nearest points for \
a specific gt_bbox.
"""
inside_gt_bbox_mask = inside_gt_bbox_mask.clone()
num_gts = len(labels) # 2
num_points = sum([len(item) for item in anchor_points_list]) # 18134
if num_gts == 0:
return gt_bboxes.new_zeros(num_points,
num_gts), inside_gt_bbox_mask
center_prior_list = []
for slvl_points, stride in zip(anchor_points_list, self.strides):
# slvl_points: points from single level in FPN, has shape (h*w, 2)
# single_level_points has shape (h*w, num_gt, 2)
single_level_points = slvl_points[:, None, :].expand(
(slvl_points.size(0), len(gt_bboxes), 2)) # (13600,2)->(13600,1,2)->(13600,2,2)
gt_center_x = ((gt_bboxes[:, 0] + gt_bboxes[:, 2]) / 2) # (2)
gt_center_y = ((gt_bboxes[:, 1] + gt_bboxes[:, 3]) / 2)
gt_center = torch.stack((gt_center_x, gt_center_y), dim=1) # (2,2)
gt_center = gt_center[None] # (1,2,2)
# instance_center has shape (1, num_gt, 2)
# tensor([12, 14], device='cuda:0'), torch.Size([2])
instance_center = self.mean[labels][None] # (20,2)[(2)]->(2,2)->(1,2,2)
# tensor([[[0., 0.],
# [0., 0.]]], device='cuda:0', grad_fn=)
# instance_sigma has shape (1, num_gt, 2)
instance_sigma = self.sigma[labels][None] # (1,2,2)
# distance has shape (num_points, num_gt, 2)
distance = (((single_level_points - gt_center) / float(stride) -
instance_center)**2) # (13600,2,2)-(1,2,2) -> (13600,2,2)
center_prior = torch.exp(-distance /
(2 * instance_sigma**2)).prod(dim=-1) # (13600,2),这里为什么要prod相乘?
center_prior_list.append(center_prior)
center_prior_weights = torch.cat(center_prior_list, dim=0) # (18134,2)
if self.force_topk:
gt_inds_no_points_inside = torch.nonzero(
inside_gt_bbox_mask.sum(0) == 0).reshape(-1)
if gt_inds_no_points_inside.numel():
topk_center_index = \
center_prior_weights[:, gt_inds_no_points_inside].topk(
self.topk,
dim=0)[1]
temp_mask = inside_gt_bbox_mask[:, gt_inds_no_points_inside]
inside_gt_bbox_mask[:, gt_inds_no_points_inside] = \
torch.scatter(temp_mask,
dim=0,
index=topk_center_index,
src=torch.ones_like(
topk_center_index,
dtype=torch.bool))
center_prior_weights[~inside_gt_bbox_mask] = 0
return center_prior_weights, inside_gt_bbox_mask
@HEADS.register_module()
class AutoAssignHead(FCOSHead):
"""AutoAssignHead head used in AutoAssign.
More details can be found in the `paper
`_ .
Args:
force_topk (bool): Used in center prior initialization to
handle extremely small gt. Default is False.
topk (int): The number of points used to calculate the
center prior when no point falls in gt_bbox. Only work when
force_topk if True. Defaults to 9.
pos_loss_weight (float): The loss weight of positive loss
and with default value 0.25.
neg_loss_weight (float): The loss weight of negative loss
and with default value 0.75.
center_loss_weight (float): The loss weight of center prior
loss and with default value 0.75.
"""
def __init__(self,
*args,
force_topk=False,
topk=9,
pos_loss_weight=0.25,
neg_loss_weight=0.75,
center_loss_weight=0.75,
**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, conv_bias=True, **kwargs)
self.center_prior = CenterPrior(
force_topk=force_topk,
topk=topk,
num_classes=self.num_classes,
strides=self.strides)
self.pos_loss_weight = pos_loss_weight # 0.25
self.neg_loss_weight = neg_loss_weight # 0.75
self.center_loss_weight = center_loss_weight # 0.75
self.prior_generator = MlvlPointGenerator(self.strides, offset=0)
def init_weights(self):
"""Initialize weights of the head.
In particular, we have special initialization for classified conv's and
regression conv's bias
"""
super(AutoAssignHead, self).init_weights()
bias_cls = bias_init_with_prob(0.02)
normal_init(self.conv_cls, std=0.01, bias=bias_cls)
normal_init(self.conv_reg, std=0.01, bias=4.0)
def forward_single(self, x, scale, stride): # (1,256,136,100), Scale(), 8
"""Forward features of a single scale level.
Args:
x (Tensor): FPN feature maps of the specified stride.
scale (:obj: `mmcv.cnn.Scale`): Learnable scale module to resize
the bbox prediction.
stride (int): The corresponding stride for feature maps, only
used to normalize the bbox prediction when self.norm_on_bbox
is True.
Returns:
tuple: scores for each class, bbox predictions and centerness \
predictions of input feature maps.
"""
cls_score, bbox_pred, cls_feat, reg_feat = super(
FCOSHead, self).forward_single(x) # 这里进入的是anchor_free_head.py中的forward_single,而不是fcos_head.py中的forward_single
# (1,20,136,100),(1,4,136,100),(1,256,136,100),(1,256,136,100)
centerness = self.conv_centerness(reg_feat) # (1,1,136,100)
# scale the bbox_pred of different level
# float to avoid overflow when enabling FP16
bbox_pred = scale(bbox_pred).float()
bbox_pred = F.relu(bbox_pred)
bbox_pred *= stride
return cls_score, bbox_pred, centerness # (1,20,136,100),(1,4,136,100),(1,1,136,100)
def get_pos_loss_single(self, cls_score, objectness, reg_loss, gt_labels,
center_prior_weights):
"""Calculate the positive loss of all points in gt_bboxes.
Args:
cls_score (Tensor): All category scores for each point on
the feature map. The shape is (num_points, num_class).
objectness (Tensor): Foreground probability of all points,
has shape (num_points, 1).
reg_loss (Tensor): The regression loss of each gt_bbox and each
prediction box, has shape of (num_points, num_gt).
gt_labels (Tensor): The zeros based gt_labels of all gt
with shape of (num_gt,).
center_prior_weights (Tensor): Float tensor with shape
of (num_points, num_gt). Each value represents
the center weighting coefficient.
Returns:
tuple[Tensor]:
- pos_loss (Tensor): The positive loss of all points
in the gt_bboxes.
"""
# p_loc: localization confidence
p_loc = torch.exp(-reg_loss)
# p_cls: classification confidence
p_cls = (cls_score * objectness)[:, gt_labels] # (18134,20)*(18134,1)->(18134,20)[:, [12,14]]->(18134,2)
# p_pos: joint confidence indicator
p_pos = p_cls * p_loc # (18134,2)*(18134,2)
# 3 is a hyper-parameter to control the contributions of high and
# low confidence locations towards positive losses.
confidence_weight = torch.exp(p_pos * 3)
p_pos_weight = (confidence_weight * center_prior_weights) / (
(confidence_weight * center_prior_weights).sum(
0, keepdim=True)).clamp(min=EPS) # (18134,2).sum(0)->(2), (18134,2).sum(0,keepdim=True)->(1,2)。(18134,2)
reweighted_p_pos = (p_pos * p_pos_weight).sum(0) # (2)
pos_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(
reweighted_p_pos,
torch.ones_like(reweighted_p_pos),
reduction='none') # (2)
pos_loss = pos_loss.sum() * self.pos_loss_weight
return pos_loss,
def get_neg_loss_single(self, cls_score, objectness, gt_labels, ious,
inside_gt_bbox_mask):
"""Calculate the negative loss of all points in feature map.
Args:
cls_score (Tensor): All category scores for each point on
the feature map. The shape is (num_points, num_class).
objectness (Tensor): Foreground probability of all points
and is shape of (num_points, 1).
gt_labels (Tensor): The zeros based label of all gt with shape of
(num_gt).
ious (Tensor): Float tensor with shape of (num_points, num_gt).
Each value represent the iou of pred_bbox and gt_bboxes.
inside_gt_bbox_mask (Tensor): Tensor of bool type,
with shape of (num_points, num_gt), each
value is used to mark whether this point falls
within a certain gt.
Returns:
tuple[Tensor]:
- neg_loss (Tensor): The negative loss of all points
in the feature map.
"""
num_gts = len(gt_labels) # 2
joint_conf = (cls_score * objectness) # (18134,20)*(18134,1)->(18134,20)
p_neg_weight = torch.ones_like(joint_conf)
if num_gts > 0:
# the order of dimension would affect the value of
# p_neg_weight, we strictly follow the original
# implementation.
inside_gt_bbox_mask = inside_gt_bbox_mask.permute(1, 0) # (18134,2)->(2,18134)
ious = ious.permute(1, 0) # (18134,2)->(2,18134)
foreground_idxs = torch.nonzero(inside_gt_bbox_mask, as_tuple=True) # len(foreground_idxs)=2
temp_weight = (1 / (1 - ious[foreground_idxs]).clamp_(EPS)) # (8409),为什么每次运行这里的维度不变?
def normalize(x): # (5970)
return (x - x.min() + EPS) / (x.max() - x.min() + EPS)
for instance_idx in range(num_gts):
idxs = foreground_idxs[0] == instance_idx
if idxs.any():
temp_weight[idxs] = normalize(temp_weight[idxs])
p_neg_weight[foreground_idxs[1],
gt_labels[foreground_idxs[0]]] = 1 - temp_weight
logits = (joint_conf * p_neg_weight)
neg_loss = (
logits**2 * F.binary_cross_entropy(
logits, torch.zeros_like(logits), reduction='none'))
neg_loss = neg_loss.sum() * self.neg_loss_weight
return neg_loss,
@force_fp32(apply_to=('cls_scores', 'bbox_preds', 'objectnesses'))
def loss(self,
cls_scores, # [(1,20,136,100),(1,20,68,50),(1,20,34,25),(1,20,17,13),(1,20,9,7)]
bbox_preds, # [(1,4, 136,100),(1,4, 68,50),(1,4, 34,25),(1,4, 17,13),(1,4, 9,7)]
objectnesses, # [(1,1, 136,100),(1,1, 68,50),(1,1, 34,25),(1,1, 17,13),(1,1, 9,7)]
gt_bboxes, # [(2,4)]
gt_labels, # [(2)]
img_metas,
gt_bboxes_ignore=None):
"""Compute loss of the head.
Args:
cls_scores (list[Tensor]): Box scores for each scale level,
each is a 4D-tensor, the channel number is
num_points * num_classes.
bbox_preds (list[Tensor]): Box energies / deltas for each scale
level, each is a 4D-tensor, the channel number is
num_points * 4.
objectnesses (list[Tensor]): objectness for each scale level, each
is a 4D-tensor, the channel number is num_points * 1.
gt_bboxes (list[Tensor]): Ground truth bboxes for each image with
shape (num_gts, 4) in [tl_x, tl_y, br_x, br_y] format.
gt_labels (list[Tensor]): class indices corresponding to each box
img_metas (list[dict]): Meta information of each image, e.g.,
image size, scaling factor, etc.
gt_bboxes_ignore (None | list[Tensor]): specify which bounding
boxes can be ignored when computing the loss.
Returns:
dict[str, Tensor]: A dictionary of loss components.
"""
assert len(cls_scores) == len(bbox_preds) == len(objectnesses)
all_num_gt = sum([len(item) for item in gt_bboxes]) # 2
featmap_sizes = [featmap.size()[-2:] for featmap in cls_scores] # [(136,100),(68,50),(34,25),(17,13),(9,7)]
all_level_points = self.prior_generator.grid_priors(
featmap_sizes,
dtype=bbox_preds[0].dtype,
device=bbox_preds[0].device) # [(13600,2),(3400,2),(850,2),(221,2),(63,2)], row first
inside_gt_bbox_mask_list, bbox_targets_list = self.get_targets(
all_level_points, gt_bboxes) # [(18134,2)], [(18134,2,4)]
center_prior_weight_list = []
temp_inside_gt_bbox_mask_list = []
for gt_bbox, gt_label, inside_gt_bbox_mask in zip(gt_bboxes, gt_labels, inside_gt_bbox_mask_list):
# (2,4),(2),(18134,2)
center_prior_weight, inside_gt_bbox_mask = self.center_prior(all_level_points,
gt_bbox, gt_label,
inside_gt_bbox_mask)
# (18134,2),(18134,2)
center_prior_weight_list.append(center_prior_weight)
temp_inside_gt_bbox_mask_list.append(inside_gt_bbox_mask)
inside_gt_bbox_mask_list = temp_inside_gt_bbox_mask_list
mlvl_points = torch.cat(all_level_points, dim=0) # (18134, 2)
bbox_preds = levels_to_images(bbox_preds) # [(1,4,136,100),(1,4,68,50),(1,4,34,25),(1,4,17,13),(1,4,9,7)] -> [(18134,4)]
cls_scores = levels_to_images(cls_scores) # [(18134, 20)]
objectnesses = levels_to_images(objectnesses) # [(18134, 1)]
reg_loss_list = []
ious_list = []
num_points = len(mlvl_points) # 18134
for bbox_pred, encoded_targets, inside_gt_bbox_mask in zip(
bbox_preds, bbox_targets_list, inside_gt_bbox_mask_list):
temp_num_gt = encoded_targets.size(1) # 2
expand_mlvl_points = mlvl_points[:, None, :].expand(
num_points, temp_num_gt, 2).reshape(-1, 2) # (18134,2)->(18134,1,2)->(18134,2,2)->(36268,2)
encoded_targets = encoded_targets.reshape(-1, 4) # (18134,2,4)->(36268,4)
expand_bbox_pred = bbox_pred[:, None, :].expand(
num_points, temp_num_gt, 4).reshape(-1, 4) # (18134,4)->(18134,1,4)->(18134,2,4)->(36268,4)
decoded_bbox_preds = self.bbox_coder.decode(
expand_mlvl_points, expand_bbox_pred) # (36268, 4), expand_bbox_pred是预测的每个点到四边的距离,decode根据点的坐标和到四边的距离还原出预测的框
decoded_target_preds = self.bbox_coder.decode(
expand_mlvl_points, encoded_targets) # (36268, 4)
# encoded_targets是expand_mlvl_points里的每个点到每个gt四条边的距离,这里decode又变回去了,decoded_target_preds里面全是gt_bboxes,两个gt_bbox交叉分布
with torch.no_grad():
ious = bbox_overlaps(
decoded_bbox_preds, decoded_target_preds, is_aligned=True) # (36268)
ious = ious.reshape(num_points, temp_num_gt) # (18134, 2)
if temp_num_gt:
ious = ious.max(
dim=-1, keepdim=True).values.repeat(1, temp_num_gt) # (18134,2)->(18134,1)->(18134,2)
else:
ious = ious.new_zeros(num_points, temp_num_gt)
ious[~inside_gt_bbox_mask] = 0
ious_list.append(ious)
loss_bbox = self.loss_bbox(
decoded_bbox_preds,
decoded_target_preds,
weight=None,
reduction_override='none') # (36268)
reg_loss_list.append(loss_bbox.reshape(num_points, temp_num_gt)) # [(18134,2)]
cls_scores = [item.sigmoid() for item in cls_scores]
objectnesses = [item.sigmoid() for item in objectnesses]
pos_loss_list, = multi_apply(self.get_pos_loss_single, cls_scores,
objectnesses, reg_loss_list, gt_labels,
center_prior_weight_list) # [tensor(4.03720760, device='cuda:0', grad_fn=)]
pos_avg_factor = reduce_mean(
bbox_pred.new_tensor(all_num_gt)).clamp_(min=1) # 2
pos_loss = sum(pos_loss_list) / pos_avg_factor # tensor(2.01860380, device='cuda:0', grad_fn=)
neg_loss_list, = multi_apply(self.get_neg_loss_single, cls_scores,
objectnesses, gt_labels, ious_list,
inside_gt_bbox_mask_list)
neg_avg_factor = sum(item.data.sum()
for item in center_prior_weight_list)
neg_avg_factor = reduce_mean(neg_avg_factor).clamp_(min=1)
neg_loss = sum(neg_loss_list) / neg_avg_factor
center_loss = []
for i in range(len(img_metas)):
if inside_gt_bbox_mask_list[i].any():
center_loss.append(
len(gt_bboxes[i]) /
center_prior_weight_list[i].sum().clamp_(min=EPS))
# when width or height of gt_bbox is smaller than stride of p3
else:
center_loss.append(center_prior_weight_list[i].sum() * 0)
center_loss = torch.stack(center_loss).mean() * self.center_loss_weight
# avoid dead lock in DDP
if all_num_gt == 0:
pos_loss = bbox_preds[0].sum() * 0
dummy_center_prior_loss = self.center_prior.mean.sum(
) * 0 + self.center_prior.sigma.sum() * 0
center_loss = objectnesses[0].sum() * 0 + dummy_center_prior_loss
loss = dict(
loss_pos=pos_loss, loss_neg=neg_loss, loss_center=center_loss)
return loss
def get_targets(self, points, gt_bboxes_list):
"""Compute regression targets and each point inside or outside gt_bbox
in multiple images.
Args:
points (list[Tensor]): Points of all fpn level, each has shape
(num_points, 2).
gt_bboxes_list (list[Tensor]): Ground truth bboxes of each image,
each has shape (num_gt, 4).
Returns:
tuple(list[Tensor]):
- inside_gt_bbox_mask_list (list[Tensor]): Each
Tensor is with bool type and shape of
(num_points, num_gt), each value
is used to mark whether this point falls
within a certain gt.
- concat_lvl_bbox_targets (list[Tensor]): BBox
targets of each level. Each tensor has shape
(num_points, num_gt, 4).
"""
concat_points = torch.cat(points, dim=0) # (18134,2)
# the number of points per img, per lvl
inside_gt_bbox_mask_list, bbox_targets_list = multi_apply(
self._get_target_single, gt_bboxes_list, points=concat_points) # len(gt_bboxes_list)=bs=1
return inside_gt_bbox_mask_list, bbox_targets_list # [(18134,2)], [(18134,2,4)]
def _get_target_single(self, gt_bboxes, points):
"""Compute regression targets and each point inside or outside gt_bbox
for a single image.
Args:
gt_bboxes (Tensor): gt_bbox of single image, has shape
(num_gt, 4).
points (Tensor): Points of all fpn level, has shape
(num_points, 2).
Returns:
tuple[Tensor]: Containing the following Tensors:
- inside_gt_bbox_mask (Tensor): Bool tensor with shape
(num_points, num_gt), each value is used to mark
whether this point falls within a certain gt.
- bbox_targets (Tensor): BBox targets of each points with
each gt_bboxes, has shape (num_points, num_gt, 4).
"""
# [tensor([[194.3503, 217.0000, 580.7910, 962.9376],
# [298.3051, 160.4896, 551.4124, 639.6979]], device='cuda:0')]
num_points = points.size(0) # 18134
num_gts = gt_bboxes.size(0) # 2
gt_bboxes = gt_bboxes[None].expand(num_points, num_gts, 4) # (2,4)->(1,2,4)->(18134,2,4)
xs, ys = points[:, 0], points[:, 1] # (18134), (18134)
xs = xs[:, None] # (18134,1)
ys = ys[:, None]
left = xs - gt_bboxes[..., 0] # (18134,1) - (18134,2) -> (18134,2)
right = gt_bboxes[..., 2] - xs
top = ys - gt_bboxes[..., 1]
bottom = gt_bboxes[..., 3] - ys
bbox_targets = torch.stack((left, top, right, bottom), -1) # (18134,2,4)
if num_gts:
inside_gt_bbox_mask = bbox_targets.min(-1)[0] > 0 # (18134,2)
else:
inside_gt_bbox_mask = bbox_targets.new_zeros((num_points, num_gts),
dtype=torch.bool)
return inside_gt_bbox_mask, bbox_targets 一些疑问
在看代码时发现一些论文中没提到的细节,在此记录一下
- 为什么center_prior_weight要把x, y两个方向的值相乘
- pos_avg_factor的含义
- neg_avg_factor的含义
- 对implicit-objectness的监督?
参考
From VanillaDet to AutoAssign - 知乎
大白话 《AutoAssign》by Face++ - 知乎