【SLAM】ORB-SLAM3解析——跟踪Track()(3)
在构建完最新的一帧Frame之后,就开始SLAM的正菜Tracking过程了。这个函数很长,有很多if-else看得很闹心。Track()干了一件什么事呢?
首先把active map找出来;然后IMU预积分还没干,这里需要补上;接下来还得判断是正常跟踪建图状态还是初始化状态,如果没初始化那就去初始化;如果初始化了,先进行帧间匹配,也就是短期数据关联获得当前帧位姿的初始值,先试试与相邻帧匹配,不行就和最近的关键帧匹配,还不行就重定位,还是不行就开张新图重新跑里程计;然后和local Map匹配,也就是中期数据关联让位姿更加准确。无论是和上一帧,和关键帧还是局部地图进行匹配,虽然细节不同,但是都经过找点,找匹配关系,优化求位姿这3大步。最后,如果需要创建KeyFrame的话,那就创建一个。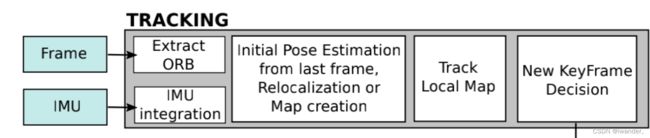
我们看一下论文中这个经典的流程图(部分),包括:Frame->Extract ORB对应Frame的构建(见链接),IMU integration(见3.1);接下来是求当前帧pose的初值,对应论文的短期数据关联,分别通过与上一帧匹配(见3.3)或者与最近的关键帧匹配(见3.2)实现;接下来是Track Local Map(见3.5)
提升位姿精度,对应论文的中期数据关联;最后就是增加KeyFrame了(见3.6)。
Step1:获取Altas多图系统的active map
首先用pCurrentMap指针把active map拿出来,如果没有,那么就CreateMapInAtlas()或者mpSystem->ResetActiveMap()。
Map* pCurrentMap = mpAtlas->GetCurrentMap();
if(mState!=NO_IMAGES_YET)
{
//时间戳错乱了
if(mLastFrame.mTimeStamp>mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp)
{
unique_lock lock(mMutexImuQueue);
mlQueueImuData.clear();
CreateMapInAtlas();
return;
}
//时间戳没错乱
else if(mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp>mLastFrame.mTimeStamp+1.0)
{
if(mpAtlas->isInertial())
{
if(mpAtlas->isImuInitialized())
{
if(!pCurrentMap->GetIniertialBA2()) mpSystem->ResetActiveMap();
else CreateMapInAtlas();
}
else mpSystem->ResetActiveMap();
return;
}
}
} Step2:IMU预积分
mCurrentFrame.SetNewBias(mpLastKeyFrame->GetImuBias());
PreintegrateIMU();Step3:初始化
if(mState==NOT_INITIALIZED)
{
if(mSensor==System::STEREO || mSensor==System::RGBD || mSensor==System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor==System::IMU_RGBD) StereoInitialization();
else MonocularInitialization();
if(mState!=OK) // If rightly initialized, mState=OK
{
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);
return;
}
if(mpAtlas->GetAllMaps().size() == 1) mnFirstFrameId = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
}Step4:(相邻帧间)短期数据匹配获取pose初值
本博客跳过纯定位模式,我们看看定位+建图(!mbOnlyTracking)的模式。在【SLAM】ORB-SLAM3解析——综述(1)介绍论文的时候,我们记得ORB-SLAM3的一大特点就是①短期数据匹配,②中期数据匹配和③长期数据匹配,这部分对应的就是短期数据匹配,也就是利用相邻帧间特征的匹配关系获取最新帧的位姿。当然这里误差是很大的,所以只能作为当前帧pose的初值。
// Initial camera pose estimation using motion model or relocalization (if tracking is lost)
if(!mbOnlyTracking)
{
...
}这个部分遇到3种情况,分别是mState很OK,刚跟丢,跟丢了,我们分别看看:
(1)情况1:状态很OK(mState==OK)
// State OK
// Local Mapping is activated. This is the normal behaviour, unless you explicitly activate the "only tracking" mode.
if(mState==OK)
{
// Local Mapping might have changed some MapPoints tracked in last frame
// 更新Local Mapping里的MapPoints
CheckReplacedInLastFrame();
if((!mbVelocity && !pCurrentMap->isImuInitialized()) || mCurrentFrame.mnIdKeyFramesInMap()>10)
{
mState = RECENTLY_LOST;
mTimeStampLost = mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp;
}
//没救了,8BQ了
else mState = LOST;
}
} (2)情况2:刚跟丢,还可以抢救一下(mState==RECENTLY_LOST)
else if (mState == RECENTLY_LOST)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("Lost for a short time", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
bOK = true;
if((mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD))
{
//VI模式下,用IMU数据抢救一波
if(pCurrentMap->isImuInitialized()) PredictStateIMU();
else bOK = false;
if (mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mTimeStampLost>time_recently_lost)
{
mState = LOST;
Verbose::PrintMess("Track Lost...", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
bOK=false;
}
}
else
{
//Visual模式下,Relocalization
bOK = Relocalization();
if(mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mTimeStampLost>3.0f && !bOK)
{
mState = LOST;
Verbose::PrintMess("Track Lost...", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
bOK=false;
}
}
}(3)情况3:跟丢了,这把重开吧(mState==LOST)
else if (mState == LOST)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("A new map is started...", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
if (pCurrentMap->KeyFramesInMap()<10)
{
mpSystem->ResetActiveMap();
Verbose::PrintMess("Reseting current map...", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
}else
CreateMapInAtlas();
if(mpLastKeyFrame) mpLastKeyFrame = static_cast(NULL);
Verbose::PrintMess("done", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
return;
}
} Step5:(与local map的)中期数据匹配让pose更精确
if(!mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF) mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
if(bOK) bOK = TrackLocalMap();
if(bOK) mState = OK;
else if (mState == OK)
{
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("Track lost for less than one second...", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
if(!pCurrentMap->isImuInitialized() || !pCurrentMap->GetIniertialBA2())
{
mpSystem->ResetActiveMap();
}
mState=RECENTLY_LOST;
}
else mState=RECENTLY_LOST; // visual to lost
mTimeStampLost = mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp;
}Step6:每隔若干帧更新IMU预积分
// Save frame if recent relocalization, since they are used for IMU reset (as we are making copy, it should be once mCurrFrame is completely modified)
if((mCurrentFrame.mnId<(mnLastRelocFrameId+mnFramesToResetIMU)) && (mCurrentFrame.mnId > mnFramesToResetIMU) &&
(mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD) && pCurrentMap->isImuInitialized())
{
// TODO check this situation
Verbose::PrintMess("Saving pointer to frame. imu needs reset...", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
Frame* pF = new Frame(mCurrentFrame);
pF->mpPrevFrame = new Frame(mLastFrame);
// Load preintegration
pF->mpImuPreintegratedFrame = new IMU::Preintegrated(mCurrentFrame.mpImuPreintegratedFrame);
}
if(pCurrentMap->isImuInitialized())
{
if(bOK)
{
//每过mnFramesToResetIMU帧就要ResetFrameIMU()一下
if(mCurrentFrame.mnId==(mnLastRelocFrameId+mnFramesToResetIMU))
{
ResetFrameIMU();
}
//如果当前帧的idx和mnLastRelocFrameId离得远了,那么mLastBias就应该是当前帧的bias
else if(mCurrentFrame.mnId>(mnLastRelocFrameId+30))
mLastBias = mCurrentFrame.mImuBias;
}
}Step7:保存恒速模型的速度
也就是当前帧和上一帧的相对位姿,下一轮循环的时候用这个相对位姿乘以上一帧位姿来找最新帧的位姿。注意Step7-10都在同一个if里面。
if(bOK || mState==RECENTLY_LOST)
{
// Update motion model
if(mLastFrame.isSet() && mCurrentFrame.isSet())
{
Sophus::SE3f LastTwc = mLastFrame.GetPose().inverse();
mVelocity = mCurrentFrame.GetPose() * LastTwc;
mbVelocity = true;
}
else mbVelocity = false;Step8:清空存放匹配数据的容器和临时路标点容器
// Clean VO matches
for(int i=0; iObservations()<1)
{
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i] = false;
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast(NULL);
}
}
// Delete temporal MapPoints
for(list::iterator lit = mlpTemporalPoints.begin(), lend = mlpTemporalPoints.end(); lit!=lend; lit++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *lit;
delete pMP;
}
mlpTemporalPoints.clear(); Step9:创建关键帧
bool bNeedKF = NeedNewKeyFrame();
// Check if we need to insert a new keyframe
// if(bNeedKF && bOK)
if(bNeedKF && (bOK || (mInsertKFsLost && mState==RECENTLY_LOST &&
(mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD))))
CreateNewKeyFrame();Step10:清除当前帧路标点中的外点
// We allow points with high innovation (considererd outliers by the Huber Function)
// pass to the new keyframe, so that bundle adjustment will finally decide
// if they are outliers or not. We dont want next frame to estimate its position
// with those points so we discard them in the frame. Only has effect if lastframe is tracked
for(int i=0; i(NULL);
} Step11:如果跟丢了,重开
// Reset if the camera get lost soon after initialization
if(mState==LOST)
{
if(pCurrentMap->KeyFramesInMap()<=10)
{
mpSystem->ResetActiveMap();
return;
}
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
if (!pCurrentMap->isImuInitialized())
{
Verbose::PrintMess("Track lost before IMU initialisation, reseting...", Verbose::VERBOSITY_QUIET);
mpSystem->ResetActiveMap();
return;
}
CreateMapInAtlas();
return;
}Step12:传递一些辅助的数据了
if(!mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF) mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);
}
if(mState==OK || mState==RECENTLY_LOST)
{
// Store frame pose information to retrieve the complete camera trajectory afterwards.
if(mCurrentFrame.isSet())
{
Sophus::SE3f Tcr_ = mCurrentFrame.GetPose() * mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF->GetPoseInverse();
mlRelativeFramePoses.push_back(Tcr_);
mlpReferences.push_back(mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF);
mlFrameTimes.push_back(mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp);
mlbLost.push_back(mState==LOST);
}
else
{
// This can happen if tracking is lost
mlRelativeFramePoses.push_back(mlRelativeFramePoses.back());
mlpReferences.push_back(mlpReferences.back());
mlFrameTimes.push_back(mlFrameTimes.back());
mlbLost.push_back(mState==LOST);
}
}3.1 IMU预积分
这部分的参考博客:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/374372286
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39266065/article/details/115703313
https://github.com/electech6/ORB_SLAM3_detailed_comments
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37835423/article/details/122370251?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502 推荐
这一部分涉及到复杂的公式推导,详情见上面的参考链接。
如果当前是第一帧,或者没有IMU数据,那就return。
void Tracking::PreintegrateIMU()
{
// Step 1.拿到两两帧之间待处理的预积分数据,组成一个集合
// 上一帧不存在,说明两帧之间没有imu数据,不进行预积分
if(!mCurrentFrame.mpPrevFrame)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("non prev frame ", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
mCurrentFrame.setIntegrated();
return;
}
mvImuFromLastFrame.clear();
mvImuFromLastFrame.reserve(mlQueueImuData.size());
// 没有imu数据,不进行预积分
if(mlQueueImuData.size() == 0)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("Not IMU data in mlQueueImuData!!", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
mCurrentFrame.setIntegrated();
return;
}然后把当前帧和上一帧之间的IMU数据都取出来。
while(true)
{
// 数据还没有时,会等待一段时间,直到mlQueueImuData中有imu数据.一开始不需要等待
bool bSleep = false;
{
unique_lock lock(mMutexImuQueue);
if(!mlQueueImuData.empty())
{
// 拿到第一个imu数据作为起始数据
IMU::Point* m = &mlQueueImuData.front();
cout.precision(17);
// imu起始数据会比当前帧的前一帧时间戳早,如果相差0.001则舍弃这个imu数据
if(m->tmTimeStamp-mImuPer)
{
mlQueueImuData.pop_front();
}
// 同样最后一个的imu数据时间戳也不能理当前帧时间间隔多余0.001
else if(m->t 对两帧之间进行中值积分处理。这里面对开头和结尾情况进行了特殊的分析,本质上就是线性插值。
// m个imu组数据会有m-1个预积分量
const int n = mvImuFromLastFrame.size()-1;
if(n==0) return;
// 构造imu预处理器,并初始化标定数据
IMU::Preintegrated* pImuPreintegratedFromLastFrame = new IMU::Preintegrated(mLastFrame.mImuBias,mCurrentFrame.mImuCalib);
// 针对预积分位置的不同做不同中值积分的处理
/**
* 根据上面imu帧的筛选,IMU与图像帧的时序如下:
* Frame---IMU0---IMU1---IMU2---IMU3---IMU4---------------IMUx---Frame---IMUx+1
* T_------T0-----T1-----T2-----T3-----T4-----------------Tx-----_T------Tx+1
* A_------A0-----A1-----A2-----A3-----A4-----------------Ax-----_T------Ax+1
* W_------W0-----W1-----W2-----W3-----W4-----------------Wx-----_T------Wx+1
* T_和_T分别表示上一图像帧和当前图像帧的时间戳,A(加速度数据),W(陀螺仪数据),同理
*/
for(int i=0; imTimeStamp;
// 设当前时刻imu的加速度a0,下一时刻加速度a1,时间间隔tab 为t10,tini t0p
// 正常情况下时为了求上一帧到当前时刻imu的一个平均加速度,但是imu时间不会正好落在上一帧的时刻,需要做补偿,要求得a0时刻到上一帧这段时间加速度的改变量
// 有了这个改变量将其加到a0上之后就可以表示上一帧时的加速度了。其中a0 - (a1-a0)*(tini/tab) 为上一帧时刻的加速度再加上a1 之后除以2就为这段时间的加速度平均值
// 其中tstep表示a1到上一帧的时间间隔,a0 - (a1-a0)*(tini/tab)这个式子中tini可以是正也可以是负表示时间上的先后,(a1-a0)也是一样,多种情况下这个式子依然成立
acc = (mvImuFromLastFrame[i].a+mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].a-
(mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].a-mvImuFromLastFrame[i].a)*(tini/tab))*0.5f;
// 计算过程类似加速度
angVel = (mvImuFromLastFrame[i].w+mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].w-
(mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].w-mvImuFromLastFrame[i].w)*(tini/tab))*0.5f;
tstep = mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].t-mCurrentFrame.mpPrevFrame->mTimeStamp;
}
else if(i<(n-1))
{
// 中间的数据不存在帧的干扰,正常计算
acc = (mvImuFromLastFrame[i].a+mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].a)*0.5f;
angVel = (mvImuFromLastFrame[i].w+mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].w)*0.5f;
tstep = mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].t-mvImuFromLastFrame[i].t;
}
// 直到倒数第二个imu时刻时,计算过程跟第一时刻类似,都需要考虑帧与imu时刻的关系
else if((i>0) && (i==(n-1)))
{
float tab = mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].t-mvImuFromLastFrame[i].t;
float tend = mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].t-mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp;
acc = (mvImuFromLastFrame[i].a+mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].a-
(mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].a-mvImuFromLastFrame[i].a)*(tend/tab))*0.5f;
angVel = (mvImuFromLastFrame[i].w+mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].w-
(mvImuFromLastFrame[i+1].w-mvImuFromLastFrame[i].w)*(tend/tab))*0.5f;
tstep = mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mvImuFromLastFrame[i].t;
}
// 就两个数据时使用第一个时刻的,这种情况应该没有吧,,回头应该试试看
else if((i==0) && (i==(n-1)))
{
acc = mvImuFromLastFrame[i].a;
angVel = mvImuFromLastFrame[i].w;
tstep = mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mCurrentFrame.mpPrevFrame->mTimeStamp;
}
// Step 3.依次进行预积分计算
// 应该是必存在的吧,一个是相对上一关键帧,一个是相对上一帧
mpImuPreintegratedFromLastKF->IntegrateNewMeasurement(acc,angVel,tstep);
pImuPreintegratedFromLastFrame->IntegrateNewMeasurement(acc,angVel,tstep);
}
// 记录当前预积分的图像帧
mCurrentFrame.mpImuPreintegratedFrame = pImuPreintegratedFromLastFrame;
mCurrentFrame.mpImuPreintegrated = mpImuPreintegratedFromLastKF;
mCurrentFrame.mpLastKeyFrame = mpLastKeyFrame;
mCurrentFrame.setIntegrated();
//Verbose::PrintMess("Preintegration is finished!! ", Verbose::VERBOSITY_DEBUG);
} 我们进入到IntegrateNewMeasurement(acc,angVel,tstep)函数看一下,这部分直接参考了参考链接里的注释版代码,它做了2件事,IMU预积分和误差传递矩阵的递推,关于后者,我目前
还没有完全理解不敢乱写,ctrl C+V 大法了:
void Preintegrated::IntegrateNewMeasurement(const Eigen::Vector3f &acceleration, const Eigen::Vector3f &angVel, const float &dt)
{
// 保存imu数据,利用中值积分的结果构造一个预积分类保存在mvMeasurements中
mvMeasurements.push_back(integrable(acceleration, angVel, dt));
// Position is updated firstly, as it depends on previously computed velocity and rotation.
// Velocity is updated secondly, as it depends on previously computed rotation.
// Rotation is the last to be updated.
// Matrices to compute covariance
// Step 1.构造协方差矩阵
// 噪声矩阵的传递矩阵,这部分用于计算i到j-1历史噪声或者协方差
Eigen::Matrix A;
A.setIdentity();
// 噪声矩阵的传递矩阵,这部分用于计算j-1新的噪声或协方差,这两个矩阵里面的数都是当前时刻的,计算主要是为了下一时刻使用
Eigen::Matrix B;
B.setZero();
// 考虑偏置后的加速度、角速度
Eigen::Vector3f acc(acceleration(0) - b.bax, acceleration(1) - b.bay, acceleration(2) - b.baz);
Eigen::Vector3f accW(angVel(0) - b.bwx, angVel(1) - b.bwy, angVel(2) - b.bwz);
// 记录平均加速度和角速度
avgA = (dT * avgA + dR * acc * dt) / (dT + dt);
avgW = (dT * avgW + accW * dt) / (dT + dt);
// Update delta position dP and velocity dV (rely on no-updated delta rotation)
// 根据没有更新的dR来更新dP与dV eq.(38)
dP = dP + dV * dt + 0.5f * dR * acc * dt * dt;
dV = dV + dR * acc * dt;
// Compute velocity and position parts of matrices A and B (rely on non-updated delta rotation)
// 根据η_ij = A * η_i,j-1 + B_j-1 * η_j-1中的A矩阵和B矩阵对速度和位移进行更新
Eigen::Matrix Wacc = Sophus::SO3f::hat(acc);
A.block<3, 3>(3, 0) = -dR * dt * Wacc;
A.block<3, 3>(6, 0) = -0.5f * dR * dt * dt * Wacc;
A.block<3, 3>(6, 3) = Eigen::DiagonalMatrix(dt, dt, dt);
B.block<3, 3>(3, 3) = dR * dt;
B.block<3, 3>(6, 3) = 0.5f * dR * dt * dt;
// Update position and velocity jacobians wrt bias correction
// 因为随着时间推移,不可能每次都重新计算雅克比矩阵,所以需要做J(k+1) = j(k) + (~)这类事,分解方式与AB矩阵相同
// 论文作者对forster论文公式的基础上做了变形,然后递归更新,参见 https://github.com/UZ-SLAMLab/ORB_SLAM3/issues/212
JPa = JPa + JVa * dt - 0.5f * dR * dt * dt;
JPg = JPg + JVg * dt - 0.5f * dR * dt * dt * Wacc * JRg;
JVa = JVa - dR * dt;
JVg = JVg - dR * dt * Wacc * JRg;
// Update delta rotation
// Step 2. 构造函数,会根据更新后的bias进行角度积分
IntegratedRotation dRi(angVel, b, dt);
// 强行归一化使其符合旋转矩阵的格式
dR = NormalizeRotation(dR * dRi.deltaR);
// Compute rotation parts of matrices A and B
// 补充AB矩阵
A.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = dRi.deltaR.transpose();
B.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = dRi.rightJ * dt;
// 小量delta初始为0,更新后通常也为0,故省略了小量的更新
// Update covariance
// Step 3.更新协方差,frost经典预积分论文的第63个公式,推导了噪声(ηa, ηg)对dR dV dP 的影响
C.block<9, 9>(0, 0) = A * C.block<9, 9>(0, 0) * A.transpose() + B * Nga * B.transpose(); // B矩阵为9*6矩阵 Nga 6*6对角矩阵,3个陀螺仪噪声的平方,3个加速度计噪声的平方
// 这一部分最开始是0矩阵,随着积分次数增加,每次都加上随机游走,偏置的信息矩阵
C.block<6, 6>(9, 9) += NgaWalk;
// Update rotation jacobian wrt bias correction
// 计算偏置的雅克比矩阵,r对bg的导数,∂ΔRij/∂bg = (ΔRjj-1) * ∂ΔRij-1/∂bg - Jr(j-1)*t
// 论文作者对forster论文公式的基础上做了变形,然后递归更新,参见 https://github.com/UZ-SLAMLab/ORB_SLAM3/issues/212
// ? 为什么先更新JPa、JPg、JVa、JVg最后更新JRg? 答:这里必须先更新dRi才能更新到这个值,但是为什么JPg和JVg依赖的上一个JRg值进行更新的?
JRg = dRi.deltaR.transpose() * JRg - dRi.rightJ * dt;
// Total integrated time
// 更新总时间
dT += dt;
} 3.2 TrackReferenceKeyFrame()
和关键帧匹配求解当前帧位姿,需求求出两帧各自的特征点的描述子,进而获取两帧特征点的匹配关系,随后3D-2D重投影误差求解当前帧位姿。
bool Tracking::TrackReferenceKeyFrame()
{
// Compute Bag of Words vector
// Step 1:将当前帧的描述子转化为BoW向量
mCurrentFrame.ComputeBoW();
// We perform first an ORB matching with the reference keyframe
// If enough matches are found we setup a PnP solver
ORBmatcher matcher(0.7,true);
vector vpMapPointMatches;
// Step 2:通过词袋BoW加速当前帧与参考帧之间的特征点匹配
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByBoW(mpReferenceKF,mCurrentFrame,vpMapPointMatches);
// 匹配数目小于15,认为跟踪失败
if(nmatches<15) return false;
// Step 3:将上一帧的位姿态作为当前帧位姿的初始值
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints = vpMapPointMatches;
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mLastFrame.GetPose()); // 用上一次的Tcw设置初值,在PoseOptimization可以收敛快一些
// Step 4:通过优化3D-2D的重投影误差来获得位姿
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
// Discard outliers
// Step 5:剔除优化后的匹配点中的外点
//之所以在优化之后才剔除外点,是因为在优化的过程中就有了对这些外点的标记
int nmatchesMap = 0;
for(int i =0; i= mCurrentFrame.Nleft) break;
if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i])
{
// 如果对应到的某个特征点是外点
if(mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i])
{
// 清除它在当前帧中存在过的痕迹
MapPoint* pMP = mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i];
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast(NULL);
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]=false;
if(i < mCurrentFrame.Nleft) pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
else pMP->mbTrackInViewR = false;
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
nmatches--;
}
else if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0)
// 匹配的内点计数++
nmatchesMap++;
}
}
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD) return true;
else return nmatchesMap>=10; // 跟踪成功的数目超过10才认为跟踪成功,否则跟踪失败
} 3.2.1 获取当前帧描述子
void Frame::ComputeBoW()
{
// 判断是否以前已经计算过了,计算过了就跳过
if(mBowVec.empty())
{
// 将描述子mDescriptors转换为DBOW要求的输入格式
vector vCurrentDesc = Converter::toDescriptorVector(mDescriptors);
// 将特征点的描述子转换成词袋向量mBowVec以及特征向量mFeatVec
mpORBvocabulary->transform(vCurrentDesc, //当前的描述子vector
mBowVec, //输出,词袋向量,记录的是单词的id及其对应权重TF-IDF值
mFeatVec, //输出,记录node id及其对应的图像 feature对应的索引
4); //4表示从叶节点向前数的层数
}
} 3.2.2 利用词袋进行特征匹配ORBmatcher::SearchByBoW()
这一步最重要的目的是用当前帧2D点的描述子和关键帧的2D点的描述子匹配,而关键帧的2D点和3D点是一一对应的,这样最终能找到当前帧2D点和关键帧3D点的匹配关系。
获取关键帧特征点和描述子,初始化存放当前帧匹配点的容器;
// 获取该关键帧的地图点
const vector vpMapPointsKF = pKF->GetMapPointMatches();
// 和普通帧F特征点的索引一致
vpMapPointMatches = vector(F.N,static_cast(NULL));
// 取出关键帧的词袋特征向量
const DBoW2::FeatureVector &vFeatVecKF = pKF->mFeatVec;
int nmatches=0;
// 特征点角度旋转差统计用的直方图
vector rotHist[HISTO_LENGTH];
for(int i=0;i 当然要确保属于同一节点(特定层)的ORB特征进行匹配:
// We perform the matching over ORB that belong to the same vocabulary node (at a certain level)
DBoW2::FeatureVector::const_iterator KFit = vFeatVecKF.begin();
DBoW2::FeatureVector::const_iterator Fit = F.mFeatVec.begin();
DBoW2::FeatureVector::const_iterator KFend = vFeatVecKF.end();
DBoW2::FeatureVector::const_iterator Fend = F.mFeatVec.end();
while(KFit != KFend && Fit != Fend)
{
// Step 1:分别取出属于同一node的ORB特征点(只有属于同一node,才有可能是匹配点)
// first 元素就是node id,遍历
if(KFit->first == Fit->first)
{
...
}
else if(KFit->first < Fit->first)
{
// 对齐
KFit = vFeatVecKF.lower_bound(Fit->first);
}
else
{
// 对齐
Fit = F.mFeatVec.lower_bound(KFit->first);
}如果是属于同一层,那么就遍历关键帧的每一个特征点,再用每一个当前帧上的特征点和它进行比对,找到描述子距离最小那个,我们进入上面代码中省略号的部分:
// Step 2:遍历KF中属于该node的特征点
for(size_t iKF=0; iKFisBad()) continue;
// 取出关键帧KF中该特征对应的描述子
const cv::Mat &dKF= pKF->mDescriptors.row(realIdxKF);
int bestDist1=256; // 最好的距离(最小距离)
int bestIdxF =-1 ;
int bestDist2=256; // 次好距离(倒数第二小距离)
int bestDist1R=256;
int bestIdxFR =-1 ;
int bestDist2R=256;
// Step 3:遍历F中属于该node的特征点,寻找最佳匹配点
for(size_t iF=0; iF= F.Nleft && dist= F.Nleft && dist 接下来,开始剔除外点了,首先根据阈值,然后是角度一致性:
// Step 4:根据阈值 和 角度投票剔除误匹配
// Step 4.1:第一关筛选:匹配距离必须小于设定阈值
if(bestDist1<=TH_LOW)
{
// Step 4.2:第二关筛选:最佳匹配比次佳匹配明显要好,那么最佳匹配才真正靠谱
if(static_cast(bestDist1)(bestDist2))
{
// Step 4.3:记录成功匹配特征点的对应的地图点(来自关键帧)
vpMapPointMatches[bestIdxF]=pMP;
// 这里的realIdxKF是当前遍历到的关键帧的特征点id
const cv::KeyPoint &kp =
(!pKF->mpCamera2) ? pKF->mvKeysUn[realIdxKF] :
(realIdxKF >= pKF -> NLeft) ? pKF -> mvKeysRight[realIdxKF - pKF -> NLeft]
: pKF -> mvKeys[realIdxKF];
// Step 4.4:计算匹配点旋转角度差所在的直方图
if(mbCheckOrientation)
{
cv::KeyPoint &Fkp = (!pKF->mpCamera2 || F.Nleft == -1) ? F.mvKeys[bestIdxF] :
(bestIdxF >= F.Nleft) ? F.mvKeysRight[bestIdxF - F.Nleft] : F.mvKeys[bestIdxF];
// 所有的特征点的角度变化应该是一致的,通过直方图统计得到最准确的角度变化值
float rot = kp.angle-Fkp.angle;
if(rot<0.0) rot+=360.0f;
int bin = round(rot*factor);// 将rot分配到bin组, 四舍五入, 其实就是离散到对应的直方图组中
if(bin==HISTO_LENGTH) bin=0;
assert(bin>=0 && bin 根据角度剔除外点:
// Step 5 根据方向剔除误匹配的点
if(mbCheckOrientation)
{
// index
int ind1=-1;
int ind2=-1;
int ind3=-1;
// 筛选出在旋转角度差落在在直方图区间内数量最多的前三个bin的索引
ComputeThreeMaxima(rotHist,HISTO_LENGTH,ind1,ind2,ind3);
for(int i=0; i(NULL);
nmatches--;
}
}
}
return nmatches;
} 3.2.3 3D-2D重投影求位姿
参考连接:https://blog.csdn.net/Walking_roll/article/details/119817174
int Optimizer::PoseOptimization(Frame *pFrame)
{
// Step 1:这里先构造了大boss--g2o稀疏优化器, BlockSolver_6_3表示:位姿为6维,路标点是3维
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;//图模型
g2o::BlockSolver_6_3::LinearSolverType * linearSolver;//线性求解器声明
// 创建一个线性求解器
linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense();
// 创建一个矩阵求解器并用上述线性求解器初始化
g2o::BlockSolver_6_3 * solver_ptr = new g2o::BlockSolver_6_3(linearSolver);
//创建一个总的求解器,并用上述矩阵求解器初始化,可以看到这里使用了LM算法
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(solver_ptr);
//设置求解器
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
// 输入的帧中,有效的,参与优化过程的2D-3D点对
int nInitialCorrespondences=0;
// Step 2:添加顶点:待优化当前帧的位姿
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap * vSE3 = new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap();//创建一个顶点
vSE3->setEstimate(Converter::toSE3Quat(pFrame->mTcw));//转化成四元数+平移向量得形式
// 设置id
vSE3->setId(0);
// 要优化的变量,所以不能固定
vSE3->setFixed(false);
optimizer.addVertex(vSE3);//添加顶点到优化器
// 地图点得个数,也就是要往优化器里添加得地图点个数。用于计算误差边(重投影误差)
const int N = pFrame->N;
vector vpEdgesMono;
vector vpEdgesMono_FHR;
vector vnIndexEdgeMono, vnIndexEdgeRight;
vpEdgesMono.reserve(N);
vpEdgesMono_FHR.reserve(N);
vnIndexEdgeMono.reserve(N);
vnIndexEdgeRight.reserve(N);
vector vpEdgesStereo;
vector vnIndexEdgeStereo;
vpEdgesStereo.reserve(N);
vnIndexEdgeStereo.reserve(N);
// 下面涉及卡方分布去除外点的知识,这里不做讲解
// 自由度为2的卡方分布,显著性水平为0.05,对应的临界阈值5.991
const float deltaMono = sqrt(5.991);
// 自由度为3的卡方分布,显著性水平为0.05,对应的临界阈值7.815
const float deltaStereo = sqrt(7.815);
// Step 3:添加一元边(因为此函数只优化当前位姿)
{
// 锁定地图点。因为系统是多线程,所以在取数据时要加锁才能保证线程安全。
// 另一方面,需要使用地图点来构造顶点和边,因此不希望在构造的过程中部分地图点被改写造成不一致甚至是段错误
unique_lock lock(MapPoint::mGlobalMutex);
// 遍历当前地图中的所有地图点
for(int i=0; imvpMapPoints[i];
// 如果这个地图点存在
if(pMP)
{
if(!pFrame->mpCamera2)
{
// 单目情况
if(pFrame->mvuRight[i]<0)
{
nInitialCorrespondences++;
pFrame->mvbOutlier[i] = false;// 先默认此地图点不是外点
// 对这个地图点的观测
const cv::KeyPoint &kpUn = pFrame->mvKeysUn[i];
Eigen::Matrix obs(kpUn.pt.x, kpUn.pt.y);
// 新建边,这个边只优化位姿Pose
ORB_SLAM3::EdgeSE3ProjectXYZOnlyPose* e = new ORB_SLAM3::EdgeSE3ProjectXYZOnlyPose();
e->setVertex(0, dynamic_cast(optimizer.vertex(0)));
e->setMeasurement(obs);//设置测量值
// 这个点的置信度,其与特征点所在的图层有关。用信息矩阵(协方差矩阵得逆)来表示。
const float invSigma2 = pFrame->mvInvLevelSigma2[kpUn.octave];
e->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity()*invSigma2);
// 在这里使用了鲁棒核函数
g2o::RobustKernelHuber* rk = new g2o::RobustKernelHuber;
e->setRobustKernel(rk);
rk->setDelta(deltaMono);
// 设置相机内参
e->pCamera = pFrame->mpCamera;
// 地图点的空间位置,作为迭代的初始值
cv::Mat Xw = pMP->GetWorldPos();
e->Xw[0] = Xw.at(0);
e->Xw[1] = Xw.at(1);
e->Xw[2] = Xw.at(2);
optimizer.addEdge(e);//将此边加入优化器
vpEdgesMono.push_back(e);//记录边属于单目情况
vnIndexEdgeMono.push_back(i);//记录索引
}
else // Stereo observation
{
nInitialCorrespondences++;
pFrame->mvbOutlier[i] = false;
// 观测多了一项右目的坐标
const cv::KeyPoint &kpUn = pFrame->mvKeysUn[i];
const float &kp_ur = pFrame->mvuRight[i];
Eigen::Matrix obs(kpUn.pt.x, kpUn.pt.y, kp_ur);
// 新建节点,注意这里也是只优化位姿
g2o::EdgeStereoSE3ProjectXYZOnlyPose* e = new g2o::EdgeStereoSE3ProjectXYZOnlyPose();
e->setVertex(0, dynamic_cast(optimizer.vertex(0)));
e->setMeasurement(obs);
// 置信程度主要是看左目特征点所在的图层
const float invSigma2 = pFrame->mvInvLevelSigma2[kpUn.octave];
Eigen::Matrix3d Info = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity()*invSigma2;
e->setInformation(Info);
g2o::RobustKernelHuber* rk = new g2o::RobustKernelHuber;
e->setRobustKernel(rk);
rk->setDelta(deltaStereo);
//获得内参和地图点坐标作为初始值
e->fx = pFrame->fx;
e->fy = pFrame->fy;
e->cx = pFrame->cx;
e->cy = pFrame->cy;
e->bf = pFrame->mbf;
cv::Mat Xw = pMP->GetWorldPos();
e->Xw[0] = Xw.at(0);
e->Xw[1] = Xw.at(1);
e->Xw[2] = Xw.at(2);
optimizer.addEdge(e);
vpEdgesStereo.push_back(e);
vnIndexEdgeStereo.push_back(i);
}
}
}
}
}
// 如果没有足够的匹配点,那么就只好放弃了
if(nInitialCorrespondences<3) return 0;
// Step 4:开始优化,总共优化四次,每次优化迭代10次,每次优化后,将观测分为outlier和inlier,outlier不参与下次优化
// 基于卡方检验计算出的阈值(假设测量有一个像素的偏差)
const float chi2Mono[4]={5.991,5.991,5.991,5.991}; // 单目
const float chi2Stereo[4]={7.815,7.815,7.815, 7.815}; // 双目
const int its[4]={10,10,10,10};// 四次迭代,每次迭代的次数
// bad 的地图点个数
int nBad=0;
// 一共进行四次优化
for(size_t it=0; it<4; it++)
{
//这里面计算了重投影误差。
vSE3->setEstimate(Converter::toSE3Quat(pFrame->mTcw));
// 其实就是初始化优化器,这里的参数0就算是不填写,默认也是0,也就是只对level为0的边进行优化
optimizer.initializeOptimization(0);
// 开始优化,优化10次
optimizer.optimize(its[it]);
nBad=0;
// 优化结束,开始遍历参与优化的每一条误差边(单目),其实就是重投影误差
for(size_t i=0, iend=vpEdgesMono.size(); imvbOutlier[idx]) e->computeError();
// 就是error*\Omega*error,表征了这个点的误差大小(考虑置信度以后)
const float chi2 = e->chi2();
//检验不通过
if(chi2>chi2Mono[it])
{
pFrame->mvbOutlier[idx]=true;
e->setLevel(1); // 设置为outlier , level 1 对应为外点,上面的过程中我们设置其为不优化
nBad++;
}
else
{
pFrame->mvbOutlier[idx]=false;
e->setLevel(0); // 设置为inlier, level 0 对应为内点,上面的过程中我们就是要优化这些关系
}
if(it==2) e->setRobustKernel(0); // 除了前两次优化需要RobustKernel以外, 其余的优化都不需要 -- 因为重投影的误差已经有明显的下降了
}
// ……
// Step 5 得到优化后的当前帧的位姿
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* vSE3_recov = static_cast(optimizer.vertex(0));
g2o::SE3Quat SE3quat_recov = vSE3_recov->estimate();
cv::Mat pose = Converter::toCvMat(SE3quat_recov);
pFrame->SetPose(pose);// 设置优化后得位姿
// 并且返回内点数目
return nInitialCorrespondences-nBad;
} 3.3 TrackWithMotionModel()
和上一个是很类似的,一样需要对当前帧位姿有一个初始估计,需要找到对应点的匹配关系,用3D-2D求位姿,只是匹配的对象变成上一帧的3D点了。还有对于IMU的情况,
直接用IMU积分得到的位姿给到当前帧,因此速度会快一些。
bool Tracking::TrackWithMotionModel()
{
// 最小距离 < 0.9*次小距离 匹配成功,检查旋转
ORBmatcher matcher(0.9,true);
// Update last frame pose according to its reference keyframe
// Create "visual odometry" points if in Localization Mode
// Step 1:更新上一帧的位姿;对于双目或RGB-D相机,还会根据深度值生成临时地图点
UpdateLastFrame();
// Step 2:根据IMU或者恒速模型得到当前帧的初始位姿。
if (mpAtlas->isImuInitialized() && (mCurrentFrame.mnId>mnLastRelocFrameId+mnFramesToResetIMU))
{
// Predict state with IMU if it is initialized and it doesnt need reset
// IMU完成初始化 并且 距离重定位挺久不需要重置IMU,用IMU来估计位姿,没有后面的这那那这的
PredictStateIMU();
return true;
}
else
{
// 根据之前估计的速度,用恒速模型得到当前帧的初始位姿。
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mVelocity * mLastFrame.GetPose());
}
// 清空当前帧的地图点
fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast(NULL));
// Project points seen in previous frame
// 设置特征匹配过程中的搜索半径
int th;
if(mSensor==System::STEREO)
th=7;
else
th=15;
// Step 3:用上一帧地图点进行投影匹配,如果匹配点不够,则扩大搜索半径再来一次
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR || mSensor==System::IMU_MONOCULAR);
// If few matches, uses a wider window search
// 如果匹配点太少,则扩大搜索半径再来一次
if(nmatches<20)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("Not enough matches, wider window search!!", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast(NULL));
nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,2*th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR || mSensor==System::IMU_MONOCULAR);
Verbose::PrintMess("Matches with wider search: " + to_string(nmatches), Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
}
// 这里不同于ORB-SLAM2的方式
if(nmatches<20)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("Not enough matches!!", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Optimize frame pose with all matches
// Step 4:利用3D-2D投影关系,优化当前帧位姿
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
// Discard outliers
// Step 5:剔除地图点中外点
int nmatchesMap = 0;
for(int i =0; i(NULL);
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]=false;
if(i < mCurrentFrame.Nleft){
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
}
else{
pMP->mbTrackInViewR = false;
}
pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
nmatches--;
}
else if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0)
// 累加成功匹配到的地图点数目
nmatchesMap++;
}
}
// 纯定位模式下:如果成功追踪的地图点非常少,那么这里的mbVO标志就会置位
if(mbOnlyTracking)
{
mbVO = nmatchesMap<10;
return nmatches>20;
}
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
return true;
else
return nmatchesMap>=10; // 匹配超过10个点就认为跟踪成功
} 3.3.1 对上一帧更新位姿并补充路标点UpdateLastFrame
上一帧的关键帧知道,上一帧的关键帧和上一帧之间的相对位姿关系知道,那么依此可以求出上一帧的位姿。补充路标点是之对于RGBD和双目的情况才这么做,因为特征点的深度值
在构建Frame的时候就求出来了,而单目模式没有特征点的深度信息。
Step 1:利用参考关键帧更新上一帧在世界坐标系下的位姿
void Tracking::UpdateLastFrame()
{
// Update pose according to reference keyframe
// 上一普通帧的参考关键帧,注意这里用的是参考关键帧(位姿准)而不是上上一帧的普通帧
KeyFrame* pRef = mLastFrame.mpReferenceKF;
// ref_keyframe 到 lastframe的位姿变换
Sophus::SE3f Tlr = mlRelativeFramePoses.back();
// 将上一帧的世界坐标系下的位姿计算出来
// l:last, r:reference, w:world
// Tlw = Tlr*Trw
mLastFrame.SetPose(Tlr * pRef->GetPose());
// 如果上一帧为关键帧,或者单目/单目惯性,SLAM模式的情况,则退出
if(mnLastKeyFrameId==mLastFrame.mnId || mSensor==System::MONOCULAR || mSensor==System::IMU_MONOCULAR || !mbOnlyTracking)
return;Step 2:对于双目或rgbd相机,为上一帧生成新的临时地图点
// 注意这些地图点只是用来跟踪,不加入到地图中,跟踪完后会删除
// Create "visual odometry" MapPoints
// We sort points according to their measured depth by the stereo/RGB-D sensor
// Step 2.1:得到上一帧中具有有效深度值的特征点(不一定是地图点)
vector > vDepthIdx;
const int Nfeat = mLastFrame.Nleft == -1? mLastFrame.N : mLastFrame.Nleft;
vDepthIdx.reserve(Nfeat);
for(int i=0; i0)
{
// vDepthIdx第一个元素是某个点的深度,第二个元素是对应的特征点id
vDepthIdx.push_back(make_pair(z,i));
}
}
// 如果上一帧中没有有效深度的点,那么就直接退出
if(vDepthIdx.empty()) return;
// 按照深度从小到大排序
sort(vDepthIdx.begin(),vDepthIdx.end());
// We insert all close points (depthObservations()<1)
// 地图点被创建后就没有被观测,认为不靠谱,也需要重新创建
bCreateNew = true;
if(bCreateNew)
{
// Step 2.3:需要创建的点,包装为地图点。只是为了提高双目和RGBD的跟踪成功率,并没有添加复杂属性,因为后面会扔掉
// 反投影到世界坐标系中
Eigen::Vector3f x3D;
if(mLastFrame.Nleft == -1){
mLastFrame.UnprojectStereo(i, x3D);
}
else{
x3D = mLastFrame.UnprojectStereoFishEye(i);
}
// 加入上一帧的地图点中
MapPoint* pNewMP = new MapPoint(x3D,mpAtlas->GetCurrentMap(),&mLastFrame,i);
mLastFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=pNewMP;
// 标记为临时添加的MapPoint,之后在CreateNewKeyFrame之前会全部删除
mlpTemporalPoints.push_back(pNewMP);
nPoints++;
}
else
{
// 因为从近到远排序,记录其中不需要创建地图点的个数
nPoints++;
}
// Step 2.4:如果地图点质量不好,停止创建地图点
// 停止新增临时地图点必须同时满足以下条件:
// 1、当前的点的深度已经超过了设定的深度阈值(35倍基线)
// 2、nPoints已经超过100个点,说明距离比较远了,可能不准确,停掉退出
if(vDepthIdx[j].first>mThDepth && nPoints>100) break;
}
} 3.3.2 用IMU估计当前状态量PredictStateIMU()
当前时刻的状态量用上一时刻状态量加上IMU预积分量转到world系下来估计。
/**
* @brief 跟踪不成功的时候,用初始化好的imu数据做跟踪处理,通过IMU预测状态
* 两个地方用到:
* 1. 匀速模型计算速度,但并没有给当前帧位姿赋值;
* 2. 跟踪丢失时不直接判定丢失,通过这个函数预测当前帧位姿看看能不能拽回来,代替纯视觉中的重定位
*
* @return true
* @return false
*/
bool Tracking::PredictStateIMU()
{
if(!mCurrentFrame.mpPrevFrame)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("No last frame", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
return false;
}
// 总结下都在什么时候地图更新,也就是mbMapUpdated为true
// 1. 回环或融合
// 2. 局部地图LocalBundleAdjustment
// 3. IMU三阶段的初始化
// 下面的代码流程一模一样,只不过计算时相对的帧不同,地图有更新后相对于上一关键帧做的,反之相对于上一帧
// 地图更新后会更新关键帧与MP,所以相对于关键帧更准
// 而没更新的话,距离上一帧更近,计算起来误差更小
// 地图更新时,并且上一个图像关键帧存在
if(mbMapUpdated && mpLastKeyFrame)
{
const Eigen::Vector3f twb1 = mpLastKeyFrame->GetImuPosition();
const Eigen::Matrix3f Rwb1 = mpLastKeyFrame->GetImuRotation();
const Eigen::Vector3f Vwb1 = mpLastKeyFrame->GetVelocity();
const Eigen::Vector3f Gz(0, 0, -IMU::GRAVITY_VALUE);
const float t12 = mpImuPreintegratedFromLastKF->dT;
// 计算当前帧在世界坐标系的位姿,原理都是用预积分的位姿(预积分的值不会变化)与上一帧的位姿(会迭代变化)进行更新
// 旋转 R_wb2 = R_wb1 * R_b1b2
Eigen::Matrix3f Rwb2 = IMU::NormalizeRotation(Rwb1 * mpImuPreintegratedFromLastKF->GetDeltaRotation(mpLastKeyFrame->GetImuBias()));
// 位移
Eigen::Vector3f twb2 = twb1 + Vwb1*t12 + 0.5f*t12*t12*Gz+ Rwb1*mpImuPreintegratedFromLastKF->GetDeltaPosition(mpLastKeyFrame->GetImuBias());
// 速度
Eigen::Vector3f Vwb2 = Vwb1 + t12*Gz + Rwb1 * mpImuPreintegratedFromLastKF->GetDeltaVelocity(mpLastKeyFrame->GetImuBias());
// 设置当前帧的世界坐标系的相机位姿
mCurrentFrame.SetImuPoseVelocity(Rwb2,twb2,Vwb2);
// 记录bias
mCurrentFrame.mImuBias = mpLastKeyFrame->GetImuBias();
mCurrentFrame.mPredBias = mCurrentFrame.mImuBias;
return true;
}
// 地图未更新时
else if(!mbMapUpdated)
{
const Eigen::Vector3f twb1 = mLastFrame.GetImuPosition();
const Eigen::Matrix3f Rwb1 = mLastFrame.GetImuRotation();
const Eigen::Vector3f Vwb1 = mLastFrame.GetVelocity();
const Eigen::Vector3f Gz(0, 0, -IMU::GRAVITY_VALUE);
// mpImuPreintegratedFrame是当前帧上一帧,不一定是关键帧
const float t12 = mCurrentFrame.mpImuPreintegratedFrame->dT;
Eigen::Matrix3f Rwb2 = IMU::NormalizeRotation(Rwb1 * mCurrentFrame.mpImuPreintegratedFrame->GetDeltaRotation(mLastFrame.mImuBias));
Eigen::Vector3f twb2 = twb1 + Vwb1*t12 + 0.5f*t12*t12*Gz+ Rwb1 * mCurrentFrame.mpImuPreintegratedFrame->GetDeltaPosition(mLastFrame.mImuBias);
Eigen::Vector3f Vwb2 = Vwb1 + t12*Gz + Rwb1 * mCurrentFrame.mpImuPreintegratedFrame->GetDeltaVelocity(mLastFrame.mImuBias);
mCurrentFrame.SetImuPoseVelocity(Rwb2,twb2,Vwb2);
mCurrentFrame.mImuBias = mLastFrame.mImuBias;
mCurrentFrame.mPredBias = mCurrentFrame.mImuBias;
return true;
}
return false;
}
3.3.3 利用投影找到当前帧与上一帧特征点的匹配关系SearchByProjection
根据当前帧位姿的初始值,把上一帧的3D点投影到当前帧上,然后在这个投影点所在的格子里依次比较所有特征点与该3D点描述子的距离,选择最小的那个。然后比较两者的
朝向的夹角,并放到对应的直方图里。所有匹配关系都找到后,它们的朝向应该是一致的,所以把直方图排名前三的方向的点找出来,这是最后保留的匹配结果。
Step1&2,把两帧相对pose计算出来,判断运动方向,并初始化容器
int ORBmatcher::SearchByProjection(Frame &CurrentFrame, const Frame &LastFrame, const float th, const bool bMono)
{
int nmatches = 0;
// Rotation Histogram (to check rotation consistency)
// Step 1 建立旋转直方图,用于检测旋转一致性
vector rotHist[HISTO_LENGTH];
for(int i=0;iCurrentFrame.mb && !bMono; // 非单目情况,如果Z大于基线,则表示相机明显前进
const bool bBackward = -tlc(2)>CurrentFrame.mb && !bMono; // 非单目情况,如果-Z小于基线,则表示相机明显后退 Step3&4,把上一帧的3D点投影到当前帧上,看看落到哪个格子里,然后把这个格子里的点全都揪出来
// Step 3 对于前一帧的每一个地图点,通过相机投影模型,得到投影到当前帧的像素坐标
for(int i=0; iGetWorldPos();
Eigen::Vector3f x3Dc = Tcw * x3Dw;
const float xc = x3Dc(0);
const float yc = x3Dc(1);
const float invzc = 1.0/x3Dc(2);
if(invzc<0) continue;
// 投影到当前帧中
Eigen::Vector2f uv = CurrentFrame.mpCamera->project(x3Dc);
if(uv(0)CurrentFrame.mnMaxX) continue;
if(uv(1)CurrentFrame.mnMaxY) continue;
// 认为投影前后地图点的尺度信息不变
int nLastOctave = (LastFrame.Nleft == -1 || i < LastFrame.Nleft) ? LastFrame.mvKeys[i].octave
: LastFrame.mvKeysRight[i - LastFrame.Nleft].octave;
// Search in a window. Size depends on scale
// 单目:th = 7,双目:th = 15
float radius = th*CurrentFrame.mvScaleFactors[nLastOctave]; // 尺度越大,搜索范围越大
// 记录候选匹配点的id
vector vIndices2;
// Step 4 根据相机的前后前进方向来判断搜索尺度范围。
// 以下可以这么理解,例如一个有一定面积的圆点,在某个尺度n下它是一个特征点
// 当相机前进时,圆点的面积增大,在某个尺度m下它是一个特征点,由于面积增大,则需要在更高的尺度下才能检测出来
// 当相机后退时,圆点的面积减小,在某个尺度m下它是一个特征点,由于面积减小,则需要在更低的尺度下才能检测出来
if(bForward) // 前进,则上一帧兴趣点在所在的尺度nLastOctave<=nCurOctave
vIndices2 = CurrentFrame.GetFeaturesInArea(uv(0),uv(1), radius, nLastOctave);
else if(bBackward) // 后退,则上一帧兴趣点在所在的尺度0<=nCurOctave<=nLastOctave
vIndices2 = CurrentFrame.GetFeaturesInArea(uv(0),uv(1), radius, 0, nLastOctave);
else // 在[nLastOctave-1, nLastOctave+1]中搜索
vIndices2 = CurrentFrame.GetFeaturesInArea(uv(0),uv(1), radius, nLastOctave-1, nLastOctave+1);
if(vIndices2.empty()) continue; 如何找到格子呢?
vector Frame::GetFeaturesInArea(
const float &x, const float &y, const float &r,
const int minLevel,const int maxLevel, const bool bRight) const
{
// 存储搜索结果的vector
vector vIndices;
vIndices.reserve(N);
float factorX = r, factorY = r;
// Step 1 计算半径为r圆左右上下边界所在的网格列和行的id
// 查找半径为r的圆左侧边界所在网格列坐标。这个地方有点绕,慢慢理解下:
// (mnMaxX-mnMinX)/FRAME_GRID_COLS:表示列方向每个网格可以平均分得几个像素(肯定大于1)
// mfGridElementWidthInv=FRAME_GRID_COLS/(mnMaxX-mnMinX) 是上面倒数,表示每个像素可以均分几个网格列(肯定小于1)
// (x-mnMinX-r),可以看做是从图像的左边界mnMinX到半径r的圆的左边界区域占的像素列数
// 两者相乘,就是求出那个半径为r的圆的左侧边界在哪个网格列中
// 保证nMinCellX 结果大于等于0
const int nMinCellX = max(0,(int)floor((x-mnMinX-factorX)*mfGridElementWidthInv));
// 如果最终求得的圆的左边界所在的网格列超过了设定了上限,那么就说明计算出错,找不到符合要求的特征点,返回空vector
if(nMinCellX>=FRAME_GRID_COLS) return vIndices;
// 计算圆所在的右边界网格列索引
const int nMaxCellX = min((int)FRAME_GRID_COLS-1,(int)ceil((x-mnMinX+factorX)*mfGridElementWidthInv));
// 如果计算出的圆右边界所在的网格不合法,说明该特征点不好,直接返回空vector
if(nMaxCellX<0) return vIndices;
// 后面的操作也都是类似的,计算出这个圆上下边界所在的网格行的id
const int nMinCellY = max(0,(int)floor((y-mnMinY-factorY)*mfGridElementHeightInv));
if(nMinCellY>=FRAME_GRID_ROWS) return vIndices;
const int nMaxCellY = min((int)FRAME_GRID_ROWS-1,(int)ceil((y-mnMinY+factorY)*mfGridElementHeightInv));
if(nMaxCellY<0) return vIndices;
// 检查需要搜索的图像金字塔层数范围是否符合要求
//? 疑似bug。(minLevel>0) 后面条件 (maxLevel>=0)肯定成立
//? 改为 const bool bCheckLevels = (minLevel>=0) || (maxLevel>=0);
const bool bCheckLevels = (minLevel>0) || (maxLevel>=0);
// Step 2 遍历圆形区域内的所有网格,寻找满足条件的候选特征点,并将其index放到输出里
for(int ix = nMinCellX; ix<=nMaxCellX; ix++)
{
for(int iy = nMinCellY; iy<=nMaxCellY; iy++)
{
// 获取这个网格内的所有特征点在 Frame::mvKeysUn 中的索引
const vector vCell = (!bRight) ? mGrid[ix][iy] : mGridRight[ix][iy];
// 如果这个网格中没有特征点,那么跳过这个网格继续下一个
if(vCell.empty()) continue;
// 如果这个网格中有特征点,那么遍历这个图像网格中所有的特征点
for(size_t j=0, jend=vCell.size(); j=0) if(kpUn.octave>maxLevel) continue;
}
// 通过检查,计算候选特征点到圆中心的距离,查看是否是在这个圆形区域之内
const float distx = kpUn.pt.x-x;
const float disty = kpUn.pt.y-y;
// 如果x方向和y方向的距离都在指定的半径之内,存储其index为候选特征点
if(fabs(distx) Step5 遍历格子里的候选匹配点,寻找描述子距离最小的最佳匹配点 Step 6 根据匹配点旋转角度差进行分类
// Step 6 计算匹配点旋转角度差所在的直方图
if(mbCheckOrientation)
{
cv::KeyPoint kpLF = (LastFrame.Nleft == -1) ? LastFrame.mvKeysUn[i]
: (i < LastFrame.Nleft) ? LastFrame.mvKeys[i]
: LastFrame.mvKeysRight[i - LastFrame.Nleft];
cv::KeyPoint kpCF = (CurrentFrame.Nleft == -1) ? CurrentFrame.mvKeysUn[bestIdx2]
: (bestIdx2 < CurrentFrame.Nleft) ? CurrentFrame.mvKeys[bestIdx2]
: CurrentFrame.mvKeysRight[bestIdx2 - CurrentFrame.Nleft];
float rot = kpLF.angle-kpCF.angle;
if(rot<0.0) rot+=360.0f;
int bin = round(rot*factor);
if(bin==HISTO_LENGTH) bin=0;
rotHist[bin].push_back(bestIdx2);
}
当然,对于右目,也要进行重投影,找格子,算描述子找匹配点,根据角度差进行分类的操作。
if(CurrentFrame.Nleft != -1){
...
}
}
}
} Step 7 进行旋转一致检测,剔除不一致的匹配
if(mbCheckOrientation)
{
int ind1=-1;
int ind2=-1;
int ind3=-1;
ComputeThreeMaxima(rotHist,HISTO_LENGTH,ind1,ind2,ind3);
for(int i=0; i(NULL);
nmatches--;
}
}
}
}
return nmatches;
}
3.4 重定位Relocalization()
如果根据恒速模型和上一帧进行匹配,或用词袋和KeyFrame进行匹配,或用IMU积分数据,如果这三招都不能预测出当前的位姿的话,那就只剩下最后绝招:重定位。
先根据词袋找到几个备选回环帧,再用MLPnP算法估计位姿,如果估计出来了再用BA优化位姿。
Step 1: 计算当前帧特征点的Bow映射
bool Tracking::Relocalization()
{
Verbose::PrintMess("Starting relocalization", Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
// Compute Bag of Words Vector
mCurrentFrame.ComputeBoW();Step 2:找到与当前帧相似的候选关键帧组
// Relocalization is performed when tracking is lost
// Track Lost: Query KeyFrame Database for keyframe candidates for relocalisation
vector vpCandidateKFs = mpKeyFrameDB->DetectRelocalizationCandidates(&mCurrentFrame, mpAtlas->GetCurrentMap());
if(vpCandidateKFs.empty()) return false;
const int nKFs = vpCandidateKFs.size();
// We perform first an ORB matching with each candidate
// If enough matches are found we setup a PnP solver
ORBmatcher matcher(0.75,true);
// 每个关键帧的解算器
vector vpMLPnPsolvers;
vpMLPnPsolvers.resize(nKFs);
// 每个关键帧和当前帧中特征点的匹配关系
vector > vvpMapPointMatches;
vvpMapPointMatches.resize(nKFs);
// 放弃某个关键帧的标记
vector vbDiscarded;
vbDiscarded.resize(nKFs);
// 有效的候选关键帧数目
int nCandidates=0; Step 3:遍历所有的候选关键帧,通过BoW进行快速匹配,用匹配结果初始化PnP Solver
for(int i=0; iisBad()) vbDiscarded[i] = true;
else
{
// 当前帧和候选关键帧用BoW进行快速匹配,匹配结果记录在vvpMapPointMatches,nmatches表示匹配的数目
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByBoW(pKF,mCurrentFrame,vvpMapPointMatches[i]);
// 如果和当前帧的匹配数小于15,那么只能放弃这个关键帧
if(nmatches<15)
{
vbDiscarded[i] = true;
continue;
}
else
{
// 如果匹配数目够用,用匹配结果初始化MLPnPsolver
// ? 为什么用MLPnP? 因为考虑了鱼眼相机模型,解耦某些关系?
// 参考论文《MLPNP-A REAL-TIME MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD SOLUTION TO THE PERSPECTIVE-N-POINT PROBLEM》
MLPnPsolver* pSolver = new MLPnPsolver(mCurrentFrame,vvpMapPointMatches[i]);
// 构造函数调用了一遍,这里重新设置参数
pSolver->SetRansacParameters(
0.99, // 模型最大概率值,默认0.9
10, // 内点的最小阈值,默认8
300, // 最大迭代次数,默认300
6, // 最小集,每次采样六个点,即最小集应该设置为6,论文里面写着I > 5
0.5, // 理论最少内点个数,这里是按照总数的比例计算,所以epsilon是比例,默认是0.4
5.991); // 卡方检验阈值 //This solver needs at least 6 points
vpMLPnPsolvers[i] = pSolver;
nCandidates++; // 1.0版本新加的
}
}
} Step 4: 通过一系列操作,直到找到能够匹配上的关键帧
// Alternatively perform some iterations of P4P RANSAC
// Until we found a camera pose supported by enough inliers
// 足够的内点才能匹配使用PNP算法,MLPnP需要至少6个点
// 是否已经找到相匹配的关键帧的标志
bool bMatch = false;
ORBmatcher matcher2(0.9,true);
// 为什么搞这么复杂?答:是担心误闭环
while(nCandidates>0 && !bMatch)
{
// 遍历当前所有的候选关键帧
for(int i=0; i vbInliers;
// 内点数
int nInliers;
// 表示RANSAC已经没有更多的迭代次数可用 -- 也就是说数据不够好,RANSAC也已经尽力了。。。
bool bNoMore;
// Step 4.1:通过MLPnP算法估计姿态,迭代5次
MLPnPsolver* pSolver = vpMLPnPsolvers[i];
Eigen::Matrix4f eigTcw;
// PnP算法的入口函数
bool bTcw = pSolver->iterate(5,bNoMore,vbInliers,nInliers, eigTcw);
// If Ransac reachs max. iterations discard keyframe
// bNoMore 为true 表示已经超过了RANSAC最大迭代次数,就放弃当前关键帧
if(bNoMore)
{
vbDiscarded[i]=true;
nCandidates--;
}
// If a Camera Pose is computed, optimize
if(bTcw)
{
// Step 4.2:如果MLPnP 计算出了位姿,对内点进行BA优化
Sophus::SE3f Tcw(eigTcw);
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(Tcw);
// Tcw.copyTo(mCurrentFrame.mTcw);
// MLPnP 里RANSAC后的内点的集合
set sFound;
const int np = vbInliers.size();
// 遍历所有内点
for(int j=0; j(NULL);
// If few inliers, search by projection in a coarse window and optimize again
// Step 4.3:如果内点较少,则通过投影的方式对之前未匹配的点进行匹配,再进行优化求解
// 前面的匹配关系是用词袋匹配过程得到的
if(nGood<50)
{
// 通过投影的方式将关键帧中未匹配的地图点投影到当前帧中, 生成新的匹配
int nadditional =matcher2.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,vpCandidateKFs[i],sFound,10,100);
// 如果通过投影过程新增了比较多的匹配特征点对
if(nadditional+nGood>=50)
{
// 根据投影匹配的结果,再次采用3D-2D pnp BA优化位姿
nGood = Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
// If many inliers but still not enough, search by projection again in a narrower window
// the camera has been already optimized with many points
// Step 4.4:如果BA后内点数还是比较少(<50)但是还不至于太少(>30),可以挽救一下, 最后垂死挣扎
// 重新执行上一步 4.3的过程,只不过使用更小的搜索窗口
// 这里的位姿已经使用了更多的点进行了优化,应该更准,所以使用更小的窗口搜索
if(nGood>30 && nGood<50)
{
// 用更小窗口、更严格的描述子阈值,重新进行投影搜索匹配
sFound.clear();
for(int ip =0; ip=50)
{
nGood = Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
// 更新地图点
for(int io =0; io=50)
{
bMatch = true;
// 只要有一个候选关键帧重定位成功,就退出循环,不考虑其他候选关键帧了
break;
}
}
}// 一直运行,知道已经没有足够的关键帧,或者是已经有成功匹配上的关键帧
}
// 折腾了这么久还是没有匹配上,重定位失败
if(!bMatch) return false;
else
{
// 如果匹配上了,说明当前帧重定位成功了(当前帧已经有了自己的位姿)
// 记录成功重定位帧的id,防止短时间多次重定位
mnLastRelocFrameId = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
return true;
}
} 3.4.1 通过MLPnP算法估计姿态MLPnPsolver::iterate()
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39266065/article/details/115614421
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/349773077
https://blog.csdn.net/joun772/article/details/119409329
https://github.com/electech6/ORB_SLAM3_detailed_comments
这部分没看懂,cv参考链接的内容了。
(1)构造函数
MLPnPsolver::MLPnPsolver(const Frame &F, // 输入帧的数据
const vector &vpMapPointMatches // 待匹配的特征点,是当前帧和候选关键帧用BoW进行快速匹配的结果
) : mnInliersi(0), // 内点的个数
mnIterations(0), // Ransac迭代次数
mnBestInliers(0), // 最佳内点数
N(0), // 所有2D点的个数
mpCamera(F.mpCamera) // 相机模型,利用该变量对3D点进行投影
{
mvpMapPointMatches = vpMapPointMatches; // 待匹配的特征点,是当前帧和候选关键帧用BoW进行快速匹配的结果
mvBearingVecs.reserve(F.mvpMapPoints.size()); // 初始化3D点的单位向量
mvP2D.reserve(F.mvpMapPoints.size()); // 初始化3D点的投影点
mvSigma2.reserve(F.mvpMapPoints.size()); // 初始化卡方检验中的sigma值
mvP3Dw.reserve(F.mvpMapPoints.size()); // 初始化3D点坐标
mvKeyPointIndices.reserve(F.mvpMapPoints.size()); // 初始化3D点的索引值
mvAllIndices.reserve(F.mvpMapPoints.size()); // 初始化所有索引值
// 一些必要的初始化操作
int idx = 0;
for (size_t i = 0, iend = mvpMapPointMatches.size(); i < iend; i++)
{
MapPoint *pMP = vpMapPointMatches[i];
// 如果pMP存在,则接下来初始化一些参数,否则什么都不做
if (pMP)
{
// 判断是否是坏点
if (!pMP->isBad())
{
// 如果记录的点个数超过总数,则不做任何事情,否则继续记录
if (i >= F.mvKeysUn.size()) continue;
const cv::KeyPoint &kp = F.mvKeysUn[i];
// 保存3D点的投影点
mvP2D.push_back(kp.pt);
// 保存卡方检验中的sigma值
mvSigma2.push_back(F.mvLevelSigma2[kp.octave]);
// Bearing vector should be normalized
// 特征点投影,并计算单位向量
cv::Point3f cv_br = mpCamera->unproject(kp.pt);
cv_br /= cv_br.z;
bearingVector_t br(cv_br.x, cv_br.y, cv_br.z);
mvBearingVecs.push_back(br);
// 3D coordinates
// 获取当前特征点的3D坐标
Eigen::Matrix posEig = pMP->GetWorldPos();
point_t pos(posEig(0), posEig(1), posEig(2));
mvP3Dw.push_back(pos);
// 记录当前特征点的索引值,挑选后的
mvKeyPointIndices.push_back(i);
// 记录所有特征点的索引值
mvAllIndices.push_back(idx);
idx++;
}
}
}
// 设置RANSAC参数
SetRansacParameters();
} (2)主函数
这里作者手写了RANSAC方法,对于候选匹配点集合,每次选6个点去拟合一个模型,对于剩下的点计算重投影误差,如果误差小于阈值则认为是内点;统计每个模型内点的数量,选择
最多的那个模型。
Step 1: 判断,如果2D点个数不足以启动RANSAC迭代过程的最小下限,则退出
// RANSAC methods
/**
* @brief MLPnP迭代计算相机位姿
*
* @param[in] nIterations 迭代次数
* @param[in] bNoMore 达到最大迭代次数的标志
* @param[in] vbInliers 内点的标记
* @param[in] nInliers 总共内点数
* @return cv::Mat 计算出来的位姿
*/
bool MLPnPsolver::iterate(int nIterations, bool &bNoMore, vector &vbInliers, int &nInliers, Eigen::Matrix4f &Tout)
{
Tout.setIdentity();
bNoMore = false; // 已经达到最大迭代次数的标志
vbInliers.clear(); // 清除保存判断是否是内点的容器
nInliers = 0; // 当前次迭代时的内点数
// N为所有2D点的个数, mRansacMinInliers为正常退出RANSAC迭代过程中最少的inlier数
// Step 1: 判断,如果2D点个数不足以启动RANSAC迭代过程的最小下限,则退出
if (N < mRansacMinInliers)
{
bNoMore = true; // 已经达到最大迭代次数的标志
return false; // 函数退出
} Step 2: 正常迭代计算进行相机位姿估计,如果满足效果上限,直接返回最佳估计结果,否则就继续利用最小集(6个点)估计位姿
// mvAllIndices为所有参与PnP的2D点的索引
// vAvailableIndices为每次从mvAllIndices中随机挑选mRansacMinSet组3D-2D对应点进行一次RANSAC
vector vAvailableIndices;
// 当前的迭代次数id
int nCurrentIterations = 0;
// 进行迭代的条件:
// 条件1: 历史进行的迭代次数少于最大迭代值
// 条件2: 当前进行的迭代次数少于当前函数给定的最大迭代值
while (mnIterations < mRansacMaxIts || nCurrentIterations < nIterations)
{
// 迭代次数更新加1,直到达到最大迭代次数
nCurrentIterations++;
mnIterations++;
// 清空已有的匹配点的计数,为新的一次迭代作准备
vAvailableIndices = mvAllIndices;
// Bearing vectors and 3D points used for this ransac iteration
// 初始化单位向量和3D点,给当前ransac迭代使用
bearingVectors_t bearingVecs(mRansacMinSet);
points_t p3DS(mRansacMinSet);
vector indexes(mRansacMinSet);
// Get min set of points
// 从vAvailableIndices中选取mRansacMinSet个点进行操作,这里应该是6
for (short i = 0; i < mRansacMinSet; ++i)
{
// 在所有备选点中随机抽取一个,通过随机抽取索引数组vAvailableIndices的索引[randi]来实现
int randi = DUtils::Random::RandomInt(0, vAvailableIndices.size() - 1);
// vAvailableIndices[randi]才是备选点真正的索引值,randi是索引数组的索引值,不要搞混了
int idx = vAvailableIndices[randi];
bearingVecs[i] = mvBearingVecs[idx];
p3DS[i] = mvP3Dw[idx];
indexes[i] = i;
// 把抽取出来的点从所有备选点数组里删除掉,概率论中不放回的操作
vAvailableIndices[randi] = vAvailableIndices.back();
vAvailableIndices.pop_back();
}
// By the moment, we are using MLPnP without covariance info
// 目前为止,还没有使用协方差的信息,所以这里生成一个size=1的值为0的协方差矩阵
// |0 0 0|
// covs[0] = |0 0 0|
// |0 0 0|
cov3_mats_t covs(1);
// Result
transformation_t result;
// Compute camera pose
// 相机位姿估计,MLPnP最主要的操作在这里
computePose(bearingVecs, p3DS, covs, indexes, result);
// Save result
// 论文中12个待求值赋值保存在mRi中,每个求解器都有保存各自的计算结果
mRi[0][0] = result(0, 0);
mRi[0][1] = result(0, 1);
mRi[0][2] = result(0, 2);
mRi[1][0] = result(1, 0);
mRi[1][1] = result(1, 1);
mRi[1][2] = result(1, 2);
mRi[2][0] = result(2, 0);
mRi[2][1] = result(2, 1);
mRi[2][2] = result(2, 2);
mti[0] = result(0, 3);
mti[1] = result(1, 3);
mti[2] = result(2, 3);
// Check inliers
// 卡方检验内点,和EPnP基本类似
CheckInliers();
if (mnInliersi >= mRansacMinInliers)
{
// If it is the best solution so far, save it
// 如果该结果是目前内点数最多的,说明该结果是目前最好的,保存起来
if (mnInliersi > mnBestInliers)
{
mvbBestInliers = mvbInliersi; // 每个点是否是内点的标记
mnBestInliers = mnInliersi; // 内点个数
cv::Mat Rcw(3, 3, CV_64F, mRi);
cv::Mat tcw(3, 1, CV_64F, mti);
Rcw.convertTo(Rcw, CV_32F);
tcw.convertTo(tcw, CV_32F);
mBestTcw.setIdentity();
mBestTcw.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Converter::toMatrix3f(Rcw);
mBestTcw.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = Converter::toVector3f(tcw);
Eigen::Matrix eigRcw(mRi[0]);
Eigen::Vector3d eigtcw(mti);
}
// 用新的内点对相机位姿精求解,提高位姿估计精度,这里如果有足够内点的话,函数直接返回该值,不再继续计算
if (Refine())
{
nInliers = mnRefinedInliers;
vbInliers = vector(mvpMapPointMatches.size(), false);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (mvbRefinedInliers[i]) vbInliers[mvKeyPointIndices[i]] = true;
}
Tout = mRefinedTcw;
return true;
}
}
} Step 3: 选择最小集中效果最好的相机位姿估计结果,如果没有,只能用6个点去计算这个值了
// 程序运行到这里,说明Refine失败了,说明精求解过程中,内点的个数不满足最小阈值,那就只能在当前结果中选择内点数最多的那个最小集
// 但是也意味着这样子的结果最终是用6个点来求出来的,近似效果一般
if (mnIterations >= mRansacMaxIts)
{
bNoMore = true;
if (mnBestInliers >= mRansacMinInliers)
{
nInliers = mnBestInliers;
vbInliers = vector(mvpMapPointMatches.size(), false);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (mvbBestInliers[i]) vbInliers[mvKeyPointIndices[i]] = true;
}
Tout = mBestTcw;
return true;
}
} step 4: 相机位姿估计失败,返回零值
// 程序运行到这里,那说明没有满足条件的相机位姿估计结果,位姿估计失败了
return false;(3)computePose()
void MLPnPsolver::computePose(const bearingVectors_t &f, const points_t &p, const cov3_mats_t &covMats,
const std::vector &indices, transformation_t &result)
{
// Step 1: 判断点的数量是否满足计算条件,否则直接报错
// 因为每个观测值会产生2个残差,所以至少需要6个点来计算公式12,所以要检验当前的点个数是否满足大于5的条件
size_t numberCorrespondences = indices.size();
// 当numberCorrespondences不满足>5的条件时会发生错误(如果小于6根本进不来)
assert(numberCorrespondences > 5);
// ? 用来标记是否满足平面条件,(平面情况下矩阵有相关性,秩为2,矩阵形式可以简化,但需要跟多的约束求解)
bool planar = false;
// compute the nullspace of all vectors
// compute the nullspace of all vectors
// step 2: 计算点的单位(方向向量)向量的零空间
// 利用公式7 Jvr(v) = null(v^T) = [r s]
// 给每个向量都开辟一个零空间,所以数量相等
std::vector nullspaces(numberCorrespondences);
// 存储世界坐标系下空间点的矩阵,3行N列,N是numberCorrespondences,即点的总个数
// |x1, x2, xn|
// points3 = |y1, y2, ..., yn|
// |z1, z2, zn|
Eigen::MatrixXd points3(3, numberCorrespondences);
// 空间点向量
// |xi|
// points3v = |yi|
// |zi|
points_t points3v(numberCorrespondences);
// 单个空间点的齐次坐标矩阵,TODO:没用到啊
// |xi|
// points4v = |yi|
// |zi|
// |1 |
points4_t points4v(numberCorrespondences);
// numberCorrespondences不等于所有点,而是提取出来的内点的数量,其作为连续索引值对indices进行索引
// 因为内点的索引并非连续,想要方便遍历,必须用连续的索引值,
// 所以就用了indices[i]嵌套形式,i表示内点数量numberCorrespondences范围内的连续形式
// indices里面保存的是不连续的内点的索引值
for (size_t i = 0; i < numberCorrespondences; i++)
{
// 当前空间点的单位向量,indices[i]是当前点坐标和向量的索引值,
bearingVector_t f_current = f[indices[i]];
// 取出当前点记录到 points3 空间点矩阵里
points3.col(i) = p[indices[i]];
// nullspace of right vector
// 求解方程 Jvr(v) = null(v^T) = [r s]
// A = U * S * V^T
// 这里只求解了V的完全解,没有求解U
Eigen::JacobiSVD
svd_f(f_current.transpose(), Eigen::ComputeFullV);
// 取特征值最小的那两个对应的2个特征向量
// |r1 s1|
// nullspaces = |r2 s2|
// |r3 s3|
nullspaces[i] = svd_f.matrixV().block(0, 1, 3, 2);
// 取出当前点记录到 points3v 空间点向量
points3v[i] = p[indices[i]];
}
// Step 3: 通过计算S的秩来判断是在平面情况还是在正常情况
// 令S = M * M^T,其中M = [p1,p2,...,pi],即 points3 空间点矩阵
//
// 1. test if we have a planar scene
// 在平面条件下,会产生4个解,因此需要另外判断和解决平面条件下的问题
//
// 令S = M * M^T,其中M = [p1,p2,...,pi],即 points3 空间点矩阵
// 如果矩阵S的秩为3且最小特征值不接近于0,则不属于平面条件,否则需要解决一下
Eigen::Matrix3d planarTest = points3 * points3.transpose();
// 为了计算矩阵S的秩,需要对矩阵S进行满秩的QR分解,通过其结果来判断矩阵S的秩,从而判断是否是平面条件
Eigen::FullPivHouseholderQR rankTest(planarTest);
// int r, c;
// double minEigenVal = abs(eigen_solver.eigenvalues().real().minCoeff(&r, &c));
// 特征旋转矩阵,用在平面条件下的计算
Eigen::Matrix3d eigenRot;
eigenRot.setIdentity();
// if yes -> transform points to new eigen frame
// if (minEigenVal < 1e-3 || minEigenVal == 0.0)
// rankTest.setThreshold(1e-10);
// 当矩阵S的秩为2时,属于平面条件,
if (rankTest.rank() == 2)
{
planar = true;
// self adjoint is faster and more accurate than general eigen solvers
// also has closed form solution for 3x3 self-adjoint matrices
// in addition this solver sorts the eigenvalues in increasing order
// 计算矩阵S的特征值和特征向量
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver eigen_solver(planarTest);
// 得到QR分解的结果
eigenRot = eigen_solver.eigenvectors().real();
// 把eigenRot变成其转置矩阵,即论文公式20的系数 R_S^T
eigenRot.transposeInPlace();
// 公式20: pi' = R_S^T * pi
for (size_t i = 0; i < numberCorrespondences; i++)
points3.col(i) = eigenRot * points3.col(i);
}
//
// 2. stochastic model
//
// Step 4: 计算随机模型中的协方差矩阵
// 但是作者并没有用到协方差信息
Eigen::SparseMatrix P(2 * numberCorrespondences,
2 * numberCorrespondences);
bool use_cov = false;
P.setIdentity(); // standard
// if we do have covariance information
// -> fill covariance matrix
// 如果协方差矩阵的个数等于空间点的个数,说明前面已经计算好了,表示有协方差信息
// 目前版本是没有用到协方差信息的,所以调用本函数前就把协方差矩阵个数置为1了
if (covMats.size() == numberCorrespondences)
{
use_cov = true;
int l = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < numberCorrespondences; ++i)
{
// invert matrix
cov2_mat_t temp = nullspaces[i].transpose() * covMats[i] * nullspaces[i];
temp = temp.inverse().eval();
P.coeffRef(l, l) = temp(0, 0);
P.coeffRef(l, l + 1) = temp(0, 1);
P.coeffRef(l + 1, l) = temp(1, 0);
P.coeffRef(l + 1, l + 1) = temp(1, 1);
l += 2;
}
}
// Step 5: 构造矩阵A来完成线性方程组的构建
//
// 3. fill the design matrix A
//
// 公式12,设矩阵A,则有 Au = 0
// u = [r11, r12, r13, r21, r22, r23, r31, r32, r33, t1, t2, t3]^T
// 对单位向量v的2个零空间向量做微分,所以有[dr, ds]^T,一个点有2行,N个点就有2*N行
const int rowsA = 2 * numberCorrespondences;
// 对应上面u的列数,因为旋转矩阵有9个元素,加上平移矩阵3个元素,总共12个元素
int colsA = 12;
Eigen::MatrixXd A;
// 如果世界点位于分别跨2个坐标轴的平面上,即所有世界点的一个元素是常数的时候,可简单地忽略矩阵A中对应的列
// 而且这不影响问题的结构本身,所以在计算公式20: pi' = R_S^T * pi的时候,忽略了r11,r21,r31,即第一列
// 对应的u只有9个元素 u = [r12, r13, r22, r23, r32, r33, t1, t2, t3]^T 所以A的列个数是9个
if (planar)
{
colsA = 9;
A = Eigen::MatrixXd(rowsA, 9);
}
else
A = Eigen::MatrixXd(rowsA, 12);
A.setZero();
// fill design matrix
// 构造矩阵A,分平面和非平面2种情况
if (planar)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < numberCorrespondences; ++i)
{
// 列表示当前点的坐标
point_t pt3_current = points3.col(i);
// r12 r12 的系数 r1*py 和 s1*py
A(2 * i, 0) = nullspaces[i](0, 0) * pt3_current[1];
A(2 * i + 1, 0) = nullspaces[i](0, 1) * pt3_current[1];
// r13 r13 的系数 r1*pz 和 s1*pz
A(2 * i, 1) = nullspaces[i](0, 0) * pt3_current[2];
A(2 * i + 1, 1) = nullspaces[i](0, 1) * pt3_current[2];
// r22 r22 的系数 r2*py 和 s2*py
A(2 * i, 2) = nullspaces[i](1, 0) * pt3_current[1];
A(2 * i + 1, 2) = nullspaces[i](1, 1) * pt3_current[1];
// r23 r23 的系数 r2*pz 和 s2*pz
A(2 * i, 3) = nullspaces[i](1, 0) * pt3_current[2];
A(2 * i + 1, 3) = nullspaces[i](1, 1) * pt3_current[2];
// r32 r32 的系数 r3*py 和 s3*py
A(2 * i, 4) = nullspaces[i](2, 0) * pt3_current[1];
A(2 * i + 1, 4) = nullspaces[i](2, 1) * pt3_current[1];
// r33 r33 的系数 r3*pz 和 s3*pz
A(2 * i, 5) = nullspaces[i](2, 0) * pt3_current[2];
A(2 * i + 1, 5) = nullspaces[i](2, 1) * pt3_current[2];
// t1 t1 的系数 r1 和 s1
A(2 * i, 6) = nullspaces[i](0, 0);
A(2 * i + 1, 6) = nullspaces[i](0, 1);
// t2 t2 的系数 r2 和 s2
A(2 * i, 7) = nullspaces[i](1, 0);
A(2 * i + 1, 7) = nullspaces[i](1, 1);
// t3 t3 的系数 r3 和 s3
A(2 * i, 8) = nullspaces[i](2, 0);
A(2 * i + 1, 8) = nullspaces[i](2, 1);
}
}
else
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < numberCorrespondences; ++i)
{
point_t pt3_current = points3.col(i);
// 不是平面的情况下,三个列向量都保留求解
// r11
A(2 * i, 0) = nullspaces[i](0, 0) * pt3_current[0];
A(2 * i + 1, 0) = nullspaces[i](0, 1) * pt3_current[0];
// r12
A(2 * i, 1) = nullspaces[i](0, 0) * pt3_current[1];
A(2 * i + 1, 1) = nullspaces[i](0, 1) * pt3_current[1];
// r13
A(2 * i, 2) = nullspaces[i](0, 0) * pt3_current[2];
A(2 * i + 1, 2) = nullspaces[i](0, 1) * pt3_current[2];
// r21
A(2 * i, 3) = nullspaces[i](1, 0) * pt3_current[0];
A(2 * i + 1, 3) = nullspaces[i](1, 1) * pt3_current[0];
// r22
A(2 * i, 4) = nullspaces[i](1, 0) * pt3_current[1];
A(2 * i + 1, 4) = nullspaces[i](1, 1) * pt3_current[1];
// r23
A(2 * i, 5) = nullspaces[i](1, 0) * pt3_current[2];
A(2 * i + 1, 5) = nullspaces[i](1, 1) * pt3_current[2];
// r31
A(2 * i, 6) = nullspaces[i](2, 0) * pt3_current[0];
A(2 * i + 1, 6) = nullspaces[i](2, 1) * pt3_current[0];
// r32
A(2 * i, 7) = nullspaces[i](2, 0) * pt3_current[1];
A(2 * i + 1, 7) = nullspaces[i](2, 1) * pt3_current[1];
// r33
A(2 * i, 8) = nullspaces[i](2, 0) * pt3_current[2];
A(2 * i + 1, 8) = nullspaces[i](2, 1) * pt3_current[2];
// t1
A(2 * i, 9) = nullspaces[i](0, 0);
A(2 * i + 1, 9) = nullspaces[i](0, 1);
// t2
A(2 * i, 10) = nullspaces[i](1, 0);
A(2 * i + 1, 10) = nullspaces[i](1, 1);
// t3
A(2 * i, 11) = nullspaces[i](2, 0);
A(2 * i + 1, 11) = nullspaces[i](2, 1);
}
}
// Step 6: 计算线性方程组的最小二乘解
//
// 4. solve least squares
//
// 求解方程的最小二乘解
Eigen::MatrixXd AtPA;
if (use_cov)
// 有协方差信息的情况下,一般方程是 A^T*P*A*u = N*u = 0
AtPA = A.transpose() * P * A; // setting up the full normal equations seems to be unstable
else
// 无协方差信息的情况下,一般方程是 A^T*A*u = N*u = 0
AtPA = A.transpose() * A;
// SVD分解,满秩求解V
Eigen::JacobiSVD svd_A(AtPA, Eigen::ComputeFullV);
// 解就是对应奇异值最小的列向量,即最后一列
Eigen::MatrixXd result1 = svd_A.matrixV().col(colsA - 1);
// Step 7: 根据平面和非平面情况下选择最终位姿解
// now we treat the results differently,
// depending on the scene (planar or not)
// transformation_t T_final;
rotation_t Rout;
translation_t tout;
if (planar) // planar case
{
rotation_t tmp;
// until now, we only estimated
// row one and two of the transposed rotation matrix
// 暂时只估计了旋转矩阵的第1行和第2行,先记录到tmp中
tmp << 0.0, result1(0, 0), result1(1, 0),
0.0, result1(2, 0), result1(3, 0),
0.0, result1(4, 0), result1(5, 0);
// double scale = 1 / sqrt(tmp.col(1).norm() * tmp.col(2).norm());
// row 3
// 第3行等于第1行和第2行的叉积(这里应该是列,后面转置后成了行)
tmp.col(0) = tmp.col(1).cross(tmp.col(2));
// 原来是:
// |r11 r12 r13|
// tmp = |r21 r22 r23|
// |r31 r32 r33|
// 转置变成:
// |r11 r21 r31|
// tmp = |r12 r22 r32|
// |r13 r23 r33|
tmp.transposeInPlace();
// 平移部分 t 只表示了正确的方向,没有尺度,需要求解 scale, 先求系数
double scale = 1.0 / std::sqrt(std::abs(tmp.col(1).norm() * tmp.col(2).norm()));
// find best rotation matrix in frobenius sense
// 利用Frobenious范数计算最佳的旋转矩阵,利用公式(19), R = U_R*V_R^T
// 本质上,采用矩阵,将其元素平方,将它们加在一起并对结果平方根。计算得出的数字是矩阵的Frobenious范数
// 由于列向量是单列矩阵,行向量是单行矩阵,所以这些矩阵的Frobenius范数等于向量的长度(L)
Eigen::JacobiSVD svd_R_frob(tmp, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
rotation_t Rout1 = svd_R_frob.matrixU() * svd_R_frob.matrixV().transpose();
// test if we found a good rotation matrix
// 如果估计出来的旋转矩阵的行列式小于0,则乘以-1(EPnP也是同样的操作)
if (Rout1.determinant() < 0)
Rout1 *= -1.0;
// rotate this matrix back using the eigen frame
// 因为是在平面情况下计算的,估计出来的旋转矩阵是要做一个转换的,根据公式(21),R = Rs*R
// 其中,Rs表示特征向量的旋转矩阵
// 注意eigenRot之前已经转置过了transposeInPlace(),所以这里Rout1在之前也转置了,即tmp.transposeInPlace()
Rout1 = eigenRot.transpose() * Rout1;
// 估计最终的平移矩阵,带尺度信息的,根据公式(17),t = t^ / three-party(||r1||*||r2||*||r3||)
// 这里是 t = t^ / sqrt(||r1||*||r2||)
translation_t t = scale * translation_t(result1(6, 0), result1(7, 0), result1(8, 0));
// 把之前转置过来的矩阵再转回去,变成公式里面的形态:
// |r11 r12 r13|
// Rout1 = |r21 r22 r23|
// |r31 r32 r33|
Rout1.transposeInPlace();
// 这里乘以-1是为了计算4种结果
Rout1 *= -1;
if (Rout1.determinant() < 0.0)
Rout1.col(2) *= -1;
// now we have to find the best out of 4 combinations
// |r11 r12 r13|
// R1 = |r21 r22 r23|
// |r31 r32 r33|
// |-r11 -r12 -r13|
// R2 = |-r21 -r22 -r23|
// |-r31 -r32 -r33|
rotation_t R1, R2;
R1.col(0) = Rout1.col(0);
R1.col(1) = Rout1.col(1);
R1.col(2) = Rout1.col(2);
R2.col(0) = -Rout1.col(0);
R2.col(1) = -Rout1.col(1);
R2.col(2) = Rout1.col(2);
// |R1 t|
// Ts = |R1 -t|
// |R2 t|
// |R2 -t|
vector> Ts(4);
Ts[0].block<3, 3>(0, 0) = R1;
Ts[0].block<3, 1>(0, 3) = t;
Ts[1].block<3, 3>(0, 0) = R1;
Ts[1].block<3, 1>(0, 3) = -t;
Ts[2].block<3, 3>(0, 0) = R2;
Ts[2].block<3, 1>(0, 3) = t;
Ts[3].block<3, 3>(0, 0) = R2;
Ts[3].block<3, 1>(0, 3) = -t;
// 遍历4种解
vector normVal(4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
point_t reproPt;
double norms = 0.0;
// 计算世界点p到切线空间v的投影的残差,对应最小的就是最好的解
// 用前6个点来验证4种解的残差
for (int p = 0; p < 6; ++p)
{
// 重投影的向量
reproPt = Ts[i].block<3, 3>(0, 0) * points3v[p] + Ts[i].block<3, 1>(0, 3);
// 变成单位向量
reproPt = reproPt / reproPt.norm();
// f[indices[p]] 是当前空间点的单位向量
// 利用欧氏距离来表示重投影向量(观测)和当前空间点向量(实际)的偏差
// 即两个n维向量a(x11,x12,…,x1n)与 b(x21,x22,…,x2n)间的欧氏距离
norms += (1.0 - reproPt.transpose() * f[indices[p]]);
}
// 统计每种解的误差和,第i个解的误差和放入对应的变量normVal[i]
normVal[i] = norms;
}
// 搜索容器中的最小值,并返回该值对应的指针
std::vector::iterator
findMinRepro = std::min_element(std::begin(normVal), std::end(normVal));
// 计算容器头指针到最小值指针的距离,即可作为该最小值的索引值
int idx = std::distance(std::begin(normVal), findMinRepro);
// 得到最终相机位姿估计的结果
Rout = Ts[idx].block<3, 3>(0, 0);
tout = Ts[idx].block<3, 1>(0, 3);
}
else // non-planar
{
rotation_t tmp;
// 从AtPA的SVD分解中得到旋转矩阵,先存下来
// 注意这里的顺序是和公式16不同的
// |r11 r21 r31|
// tmp = |r12 r22 r32|
// |r13 r23 r33|
rotation_t tmp(result1(0, 0), result1(3, 0), result1(6, 0),
result1(1, 0), result1(4, 0), result1(7, 0),
result1(2, 0), result1(5, 0), result1(8, 0));
// get the scale
// 计算尺度,根据公式(17),t = t^ / three-party(||r1||*||r2||*||r3||)
double scale = 1.0 /
std::pow(std::abs(tmp.col(0).norm() * tmp.col(1).norm() * tmp.col(2).norm()), 1.0 / 3.0);
// double scale = 1.0 / std::sqrt(std::abs(tmp.col(0).norm() * tmp.col(1).norm()));
// find best rotation matrix in frobenius sense
// 利用Frobenious范数计算最佳的旋转矩阵,利用公式(19), R = U_R*V_R^T
Eigen::JacobiSVD svd_R_frob(tmp, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
Rout = svd_R_frob.matrixU() * svd_R_frob.matrixV().transpose();
// test if we found a good rotation matrix
// 如果估计出来的旋转矩阵的行列式小于0,则乘以-1
if (Rout.determinant() < 0)
Rout *= -1.0;
// scale translation
// 从相机坐标系到世界坐标系的转换关系是 lambda*v = R*pi+t
// 从世界坐标系到相机坐标系的转换关系是 pi = R^T*v-R^Tt
// 旋转矩阵的性质 R^-1 = R^T
// 所以,在下面的计算中,需要计算从世界坐标系到相机坐标系的转换,这里tout = -R^T*t,下面再计算前半部分R^T*v
// 先恢复平移部分的尺度再计算
tout = Rout * (scale * translation_t(result1(9, 0), result1(10, 0), result1(11, 0)));
// find correct direction in terms of reprojection error, just take the first 6 correspondences
// 非平面情况下,一共有2种解,R,t和R,-t
// 利用前6个点计算重投影误差,选择残差最小的一个解
vector error(2);
vector> Ts(2);
for (int s = 0; s < 2; ++s)
{
// 初始化error的值为0
error[s] = 0.0;
// |1 0 0 0|
// Ts[s] = |0 1 0 0|
// |0 0 1 0|
// |0 0 0 1|
Ts[s] = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
// |. . . 0|
// Ts[s] = |. Rout . 0|
// |. . . 0|
// |0 0 0 1|
Ts[s].block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Rout;
if (s == 0)
// |. . . . |
// Ts[s] = |. Rout . tout|
// |. . . . |
// |0 0 0 1 |
Ts[s].block<3, 1>(0, 3) = tout;
else
// |. . . . |
// Ts[s] = |. Rout . -tout|
// |. . . . |
// |0 0 0 1 |
Ts[s].block<3, 1>(0, 3) = -tout;
// 为了避免Eigen中aliasing的问题,后面在计算矩阵的逆的时候,需要添加eval()条件
// a = a.transpose(); //error: aliasing
// a = a.transpose().eval(); //ok
// a.transposeInPlace(); //ok
// Eigen中aliasing指的是在赋值表达式的左右两边存在矩阵的重叠区域,这种情况下,有可能得到非预期的结果。
// 如mat = 2*mat或者mat = mat.transpose(),第一个例子中的alias是没有问题的,而第二的例子则会导致非预期的计算结果。
Ts[s] = Ts[s].inverse().eval();
for (int p = 0; p < 6; ++p)
{
// 从世界坐标系到相机坐标系的转换关系是 pi = R^T*v-R^Tt
// Ts[s].block<3, 3>(0, 0) * points3v[p] = Rout = R^T*v
// Ts[s].block<3, 1>(0, 3) = tout = -R^Tt
bearingVector_t v = Ts[s].block<3, 3>(0, 0) * points3v[p] + Ts[s].block<3, 1>(0, 3);
// 变成单位向量
v = v / v.norm();
// 计算重投影向量(观测)和当前空间点向量(实际)的偏差
error[s] += (1.0 - v.transpose() * f[indices[p]]);
}
}
// 选择残差最小的解作为最终解
if (error[0] < error[1])
tout = Ts[0].block<3, 1>(0, 3);
else
tout = Ts[1].block<3, 1>(0, 3);
Rout = Ts[0].block<3, 3>(0, 0);
}
// Step 8: 利用高斯牛顿法对位姿进行精确求解,提高位姿解的精度
//
// 5. gauss newton
//
// 求解非线性方程之前,需要得到罗德里格斯参数,来表达李群(SO3) -> 李代数(so3)的对数映射
rodrigues_t omega = rot2rodrigues(Rout);
// |r1|
// |r2|
// minx = |r3|
// |t1|
// |t2|
// |t3|
Eigen::VectorXd minx(6);
minx[0] = omega[0];
minx[1] = omega[1];
minx[2] = omega[2];
minx[3] = tout[0];
minx[4] = tout[1];
minx[5] = tout[2];
// 利用高斯牛顿迭代法来提炼相机位姿 pose
mlpnp_gn(minx, points3v, nullspaces, P, use_cov);
// 最终输出的结果
Rout = rodrigues2rot(rodrigues_t(minx[0], minx[1], minx[2]));
tout = translation_t(minx[3], minx[4], minx[5]);
// result inverse as opengv uses this convention
// 这里是用来计算世界坐标系到相机坐标系的转换,所以是Pc=R^T*Pw-R^T*t,反变换
result.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Rout; // Rout.transpose();
result.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = tout; //-result.block<3, 3>(0, 0) * tout;
} 3.5 中期数据匹配TrackLocalMap()
前面只是跟踪一帧得到初始位姿,这里搜索局部关键帧、局部地图点,和当前帧进行投影匹配,得到更多匹配的MapPoints后进行Pose优化,从而获得更准确的pose。前提是之前
pose的初值求出来了,否则的话就重开一张图。
Step 1:把当前帧的局部关键帧 mvpLocalKeyFrames 和局部地图点 mvpLocalMapPoints找出来
bool Tracking::TrackLocalMap()
{
// We have an estimation of the camera pose and some map points tracked in the frame.
// We retrieve the local map and try to find matches to points in the local map.
mTrackedFr++;
UpdateLocalMap();Step 2:筛选局部地图中新增的在视野范围内的地图点,投影到当前帧搜索匹配,得到更多的匹配关系
SearchLocalPoints(); Step 3:BA优化
// 在这个函数之前,在 Relocalization、TrackReferenceKeyFrame、TrackWithMotionModel 中都有位姿优化
int inliers;
// IMU未初始化,仅优化位姿
if (!mpAtlas->isImuInitialized()) Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
else
{
// 初始化,重定位,重新开启一个地图都会使mnLastRelocFrameId变化
if(mCurrentFrame.mnId<=mnLastRelocFrameId+mnFramesToResetIMU)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("TLM: PoseOptimization ", Verbose::VERBOSITY_DEBUG);
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
}
else // 如果积累的IMU数据量比较多,考虑使用IMU数据优化
{
// 未更新地图
if(!mbMapUpdated)
{
Verbose::PrintMess("TLM: PoseInertialOptimizationLastFrame ", Verbose::VERBOSITY_DEBUG);
// 使用上一普通帧以及当前帧的视觉信息和IMU信息联合优化当前帧位姿、速度和IMU零偏
inliers = Optimizer::PoseInertialOptimizationLastFrame(&mCurrentFrame); // , !mpLastKeyFrame->GetMap()->GetIniertialBA1());
}
else
{
Verbose::PrintMess("TLM: PoseInertialOptimizationLastKeyFrame ", Verbose::VERBOSITY_DEBUG);
// 使用上一关键帧以及当前帧的视觉信息和IMU信息联合优化当前帧位姿、速度和IMU零偏
inliers = Optimizer::PoseInertialOptimizationLastKeyFrame(&mCurrentFrame); // , !mpLastKeyFrame->GetMap()->GetIniertialBA1());
}
}
}Step 4:根据跟踪匹配数目及重定位情况决定是否跟踪成功
// Decide if the tracking was succesful
// More restrictive if there was a relocalization recently
mpLocalMapper->mnMatchesInliers=mnMatchesInliers;
// 如果最近刚刚发生了重定位,那么至少成功匹配50个点才认为是成功跟踪
if(mCurrentFrame.mnId10)&&(mState==RECENTLY_LOST)) return true;
// 单目IMU模式下做完初始化至少成功跟踪15个才算成功,没做初始化需要50个
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR)
{
if((mnMatchesInliers<15 && mpAtlas->isImuInitialized())||(mnMatchesInliers<50 && !mpAtlas->isImuInitialized())) return false;
else return true;
}
else if (mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
{
if(mnMatchesInliers<15) return false;
else return true;
}
else
{
//以上情况都不满足,只要跟踪的地图点大于30个就认为成功了
if(mnMatchesInliers<30) return false;
else return true;
}
} 3.5.1 找出当前帧的局部关键帧和局部地图点UpdateLocalMap()
void Tracking::UpdateLocalMap()
{
// This is for visualization
// 设置参考地图点用于绘图显示局部地图点(红色)
mpAtlas->SetReferenceMapPoints(mvpLocalMapPoints);
// 找出局部关键帧
UpdateLocalKeyFrames();
// 找出局部地图点
UpdateLocalPoints();
}(1)找出局部关键帧
首先是找出局部关键帧,遍历当前帧所有点,把观测到这些点的帧都找出来,然后把这些帧的相邻帧也找出来。
Step 1:遍历当前帧的地图点,记录所有能观测到当前帧地图点的关键帧
void Tracking::UpdateLocalKeyFrames()
{
// Each map point vote for the keyframes in which it has been observed
map keyframeCounter;
// 如果IMU未初始化 或者 刚刚完成重定位
for(int i=0; iisBad())
{
// 得到观测到该地图点的关键帧和该地图点在关键帧中的索引
const map> observations = pMP->GetObservations();
// 由于一个地图点可以被多个关键帧观测到,因此对于每一次观测,都对观测到这个地图点的关键帧进行累计投票
for(map>::const_iterator it=observations.begin(), itend=observations.end(); it!=itend; it++)
// 这里的操作非常精彩!
// map[key] = value,当要插入的键存在时,会覆盖键对应的原来的值。如果键不存在,则添加一组键值对
// it->first 是地图点看到的关键帧,同一个关键帧看到的地图点会累加到该关键帧计数
// 所以最后keyframeCounter 第一个参数表示某个关键帧,第2个参数表示该关键帧看到了多少当前帧(mCurrentFrame)的地图点,也就是共视程度
keyframeCounter[it->first]++;
}
else mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=NULL;
}
} Step 2:更新局部关键帧(mvpLocalKeyFrames),添加局部关键帧有3种类型
// 存储具有最多观测次数(max)的关键帧
int max=0;
KeyFrame* pKFmax= static_cast(NULL);
// 先清空局部关键帧
mvpLocalKeyFrames.clear();
// 先申请3倍内存,不够后面再加
mvpLocalKeyFrames.reserve(3*keyframeCounter.size());
// All keyframes that observe a map point are included in the local map. Also check which keyframe shares most points
// Step 2.1 类型1:能观测到当前帧地图点的关键帧作为局部关键帧 (将邻居拉拢入伙)(一级共视关键帧)
for(map::const_iterator it=keyframeCounter.begin(), itEnd=keyframeCounter.end(); it!=itEnd; it++)
{
KeyFrame* pKF = it->first;
// 如果设定为要删除的,跳过
if(pKF->isBad())
continue;
// 寻找具有最大观测数目的关键帧
if(it->second>max)
{
max=it->second;
pKFmax=pKF;
}
// 添加到局部关键帧的列表里
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pKF);
// 用该关键帧的成员变量mnTrackReferenceForFrame 记录当前帧的id
// 表示它已经是当前帧的局部关键帧了,可以防止重复添加局部关键帧
pKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
}
// Include also some not-already-included keyframes that are neighbors to already-included keyframes
// Step 2.2 遍历一级共视关键帧,寻找更多的局部关键帧
for(vector::const_iterator itKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.begin(), itEndKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.end(); itKF!=itEndKF; itKF++)
{
// Limit the number of keyframes
// 处理的局部关键帧不超过80帧
if(mvpLocalKeyFrames.size()>80) // 80
break;
KeyFrame* pKF = *itKF;
// 类型2:一级共视关键帧的共视(前10个)关键帧,称为二级共视关键帧(将邻居的邻居拉拢入伙)
// 如果共视帧不足10帧,那么就返回所有具有共视关系的关键帧
const vector vNeighs = pKF->GetBestCovisibilityKeyFrames(10);
// vNeighs 是按照共视程度从大到小排列
for(vector::const_iterator itNeighKF=vNeighs.begin(), itEndNeighKF=vNeighs.end(); itNeighKF!=itEndNeighKF; itNeighKF++)
{
KeyFrame* pNeighKF = *itNeighKF;
if(!pNeighKF->isBad())
{
// mnTrackReferenceForFrame防止重复添加局部关键帧
if(pNeighKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame!=mCurrentFrame.mnId)
{
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pNeighKF);
pNeighKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
break;
}
}
}
// 类型3:将一级共视关键帧的子关键帧作为局部关键帧(将邻居的孩子们拉拢入伙)
const set spChilds = pKF->GetChilds();
for(set::const_iterator sit=spChilds.begin(), send=spChilds.end(); sit!=send; sit++)
{
KeyFrame* pChildKF = *sit;
if(!pChildKF->isBad())
{
if(pChildKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame!=mCurrentFrame.mnId)
{
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pChildKF);
pChildKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
break;
}
}
}
// 类型3:将一级共视关键帧的父关键帧(将邻居的父母们拉拢入伙)
KeyFrame* pParent = pKF->GetParent();
if(pParent)
{
// mnTrackReferenceForFrame防止重复添加局部关键帧
if(pParent->mnTrackReferenceForFrame!=mCurrentFrame.mnId)
{
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pParent);
pParent->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
break;
}
}
}
// Add 10 last temporal KFs (mainly for IMU)
// IMU模式下增加了临时的关键帧
if((mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD) &&mvpLocalKeyFrames.size()<80)
{
KeyFrame* tempKeyFrame = mCurrentFrame.mpLastKeyFrame;
const int Nd = 20;
for(int i=0; imnTrackReferenceForFrame!=mCurrentFrame.mnId)
{
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(tempKeyFrame);
tempKeyFrame->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
tempKeyFrame=tempKeyFrame->mPrevKF;
}
}
} (2)找出局部地图点
把这些帧上的点捞出来。
void Tracking::UpdateLocalPoints()
{
// Step 1:清空局部地图点
mvpLocalMapPoints.clear();
int count_pts = 0;
// Step 2:遍历局部关键帧 mvpLocalKeyFrames
for(vector::const_reverse_iterator itKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.rbegin(), itEndKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.rend(); itKF!=itEndKF; ++itKF)
{
KeyFrame* pKF = *itKF;
const vector vpMPs = pKF->GetMapPointMatches();
// step 3:将局部关键帧的地图点添加到mvpLocalMapPoints
for(vector::const_iterator itMP=vpMPs.begin(), itEndMP=vpMPs.end(); itMP!=itEndMP; itMP++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *itMP;
if(!pMP) continue;
// 用该地图点的成员变量mnTrackReferenceForFrame 记录当前帧的id
// 表示它已经是当前帧的局部地图点了,可以防止重复添加局部地图点
if(pMP->mnTrackReferenceForFrame==mCurrentFrame.mnId) continue;
if(!pMP->isBad())
{
count_pts++;
mvpLocalMapPoints.push_back(pMP);
pMP->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
}
}
}
} 3.5.2 确定curFrame与LocalMap特征点的匹配关系SearchLocalPoints()
Step 1:对于当前帧上已经和路标点匹配上了的特征点,跳过它们
// Do not search map points already matched
for(vector::iterator vit=mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(), vend=mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(); vit!=vend; vit++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *vit;
if(pMP)
{
if(pMP->isBad()) *vit = static_cast(NULL);
else
{
// 更新能观测到该点的帧数加1(被当前帧观测了)
pMP->IncreaseVisible();
// 标记该点被当前帧观测到
pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
// 标记该点在后面搜索匹配时不被投影,因为已经有匹配了
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
pMP->mbTrackInViewR = false;
}
}
} Step 2:判断所有局部地图点中除当前帧地图点外的点,是否在当前帧视野范围内
// 准备进行投影匹配的点的数目
int nToMatch=0;
// Project points in frame and check its visibility
for(vector::iterator vit=mvpLocalMapPoints.begin(), vend=mvpLocalMapPoints.end(); vit!=vend; vit++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *vit;
// 已经被当前帧观测到的地图点肯定在视野范围内,跳过
if(pMP->mnLastFrameSeen == mCurrentFrame.mnId) continue;
// 跳过坏点
if(pMP->isBad()) continue;
// Project (this fills MapPoint variables for matching)
// 判断地图点是否在在当前帧视野内
if(mCurrentFrame.isInFrustum(pMP,0.5))
{
// 观测到该点的帧数加1
pMP->IncreaseVisible();
// 只有在视野范围内的地图点才参与之后的投影匹配
nToMatch++;
}
if(pMP->mbTrackInView)
{
mCurrentFrame.mmProjectPoints[pMP->mnId] = cv::Point2f(pMP->mTrackProjX, pMP->mTrackProjY);
}
} Step 3:如果需要进行投影匹配的点的数目大于0,就进行投影匹配,增加更多的匹配关系
if(nToMatch>0)
{
ORBmatcher matcher(0.8);
int th = 1;
if(mSensor==System::RGBD || mSensor==System::IMU_RGBD) // RGBD相机输入的时候,搜索的阈值会变得稍微大一些
th=3;
if(mpAtlas->isImuInitialized())
{
if(mpAtlas->GetCurrentMap()->GetIniertialBA2())
th=2;
else
th=6; // 0.4版本这里是3
}
else if(!mpAtlas->isImuInitialized() && (mSensor==System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor==System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD))
{
th=10;
}
// If the camera has been relocalised recently, perform a coarser search
// 如果不久前进行过重定位,那么进行一个更加宽泛的搜索,阈值需要增大
if(mCurrentFrame.mnIdmbFarPoints, mpLocalMapper->mThFarPoints);
}
} 这里有一个新函数,判断地图点是否在在当前帧视野内isInFrustum():
bool Frame::isInFrustum(MapPoint *pMP, float viewingCosLimit)
{
// mbTrackInView是决定一个地图点是否进行重投影的标志
// 这个标志的确定要经过多个函数的确定,isInFrustum()只是其中的一个验证关卡。这里默认设置为否
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
pMP->mTrackProjX = -1;
pMP->mTrackProjY = -1;
// 3D in absolute coordinates
// Step 1 获得这个地图点的世界坐标
Eigen::Matrix P = pMP->GetWorldPos();
// 3D in camera coordinates
// 根据当前帧(粗糙)位姿转化到当前相机坐标系下的三维点Pc
const Eigen::Matrix Pc = mRcw * P + mtcw;
const float Pc_dist = Pc.norm();
// Check positive depth
const float &PcZ = Pc(2);
const float invz = 1.0f/PcZ;
// Step 2 关卡一:检查这个地图点在当前帧的相机坐标系下,是否有正的深度.如果是负的,表示出错,直接返回false
if(PcZ<0.0f)
return false;
const Eigen::Vector2f uv = mpCamera->project(Pc);
// Step 3 关卡二:将MapPoint投影到当前帧的像素坐标(u,v), 并判断是否在图像有效范围内
// 判断是否在图像边界中,只要不在那么就说明无法在当前帧下进行重投影
if(uv(0)mnMaxX)
return false;
if(uv(1)mnMaxY)
return false;
pMP->mTrackProjX = uv(0);
pMP->mTrackProjY = uv(1);
// Check distance is in the scale invariance region of the MapPoint
// Step 4 关卡三:计算MapPoint到相机中心的距离, 并判断是否在尺度变化的距离内
// 得到认为的可靠距离范围:[0.8f*mfMinDistance, 1.2f*mfMaxDistance]
const float maxDistance = pMP->GetMaxDistanceInvariance();
const float minDistance = pMP->GetMinDistanceInvariance();
// 得到当前地图点距离当前帧相机光心的距离,注意P,mOw都是在同一坐标系下才可以
// mOw:当前相机光心在世界坐标系下坐标
const Eigen::Vector3f PO = P - mOw;
// 取模就得到了距离
const float dist = PO.norm();
// 如果不在允许的尺度变化范围内,认为重投影不可靠
if(distmaxDistance)
return false;
// Check viewing angle
// Step 5 关卡四:
// 计算当前相机指向地图点向量和地图点的平均观测方向夹角的余弦值,
// 若小于cos(viewingCosLimit), 即夹角大于viewingCosLimit弧度则返回
Eigen::Vector3f Pn = pMP->GetNormal();
// 计算当前相机指向地图点向量和地图点的平均观测方向夹角的余弦值,注意平均观测方向为单位向量
const float viewCos = PO.dot(Pn)/dist;
// 如果大于给定的阈值 cos(60°)=0.5,认为这个点方向太偏了,重投影不可靠,返回false
if(viewCosPredictScale(dist,this);
// Step 7 记录计算得到的一些参数
// Data used by the tracking
// 通过置位标记 MapPoint::mbTrackInView 来表示这个地图点要被投影
pMP->mbTrackInView = true;
// 该地图点投影在当前图像(一般是左图)的像素横坐标
pMP->mTrackProjX = uv(0);
// bf/z其实是视差,相减得到右图(如有)中对应点的横坐标
pMP->mTrackProjXR = uv(0) - mbf*invz;
pMP->mTrackDepth = Pc_dist;
// 该地图点投影在当前图像(一般是左图)的像素纵坐标
pMP->mTrackProjY = uv(1);
// 根据地图点到光心距离,预测的该地图点的尺度层级
pMP->mnTrackScaleLevel= nPredictedLevel;
// 保存当前视角和法线夹角的余弦值
pMP->mTrackViewCos = viewCos;
// 执行到这里说明这个地图点在相机的视野中并且进行重投影是可靠的,返回true
return true;
} 3.6 判断是否添加关键帧NeedNewKeyFrame()
之前的内容非常的多,考虑了这样那样的case,分了这样那样的步骤,但是目的只有一个,就是求出当前帧位姿。现在位姿求好了,接下来就是要增加地图规模了。
这里是做一个判断,就是当前帧是否作为关键帧保存下来。
bool Tracking::NeedNewKeyFrame()
{
// 如果是IMU模式并且当前地图中未完成IMU初始化
if((mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD) && !mpAtlas->GetCurrentMap()->isImuInitialized())
{
// 如果是IMU模式,当前帧距离上一关键帧时间戳超过0.25s,则说明需要插入关键帧,不再进行后续判断
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR && (mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mpLastKeyFrame->mTimeStamp)>=0.25)
return true;
else if ((mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD) && (mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mpLastKeyFrame->mTimeStamp)>=0.25)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Step 1:纯VO模式下不插入关键帧
if(mbOnlyTracking)
return false;
// If Local Mapping is freezed by a Loop Closure do not insert keyframes
// Step 2:如果局部地图线程被闭环检测使用,则不插入关键帧
if(mpLocalMapper->isStopped() || mpLocalMapper->stopRequested()) {
return false;
}
// 获取当前地图中的关键帧数目
const int nKFs = mpAtlas->KeyFramesInMap();
// Do not insert keyframes if not enough frames have passed from last relocalisation
// mCurrentFrame.mnId是当前帧的ID
// mnLastRelocFrameId是最近一次重定位帧的ID
// mMaxFrames等于图像输入的帧率
// Step 3:如果距离上一次重定位比较近,并且关键帧数目超出最大限制,不插入关键帧
if(mCurrentFrame.mnIdmMaxFrames)
{
return false;
}
// Tracked MapPoints in the reference keyframe
// Step 4:得到参考关键帧跟踪到的地图点数量
// UpdateLocalKeyFrames 函数中会将与当前关键帧共视程度最高的关键帧设定为当前帧的参考关键帧
// 地图点的最小观测次数
int nMinObs = 3;
if(nKFs<=2)
nMinObs=2;
// 参考关键帧地图点中观测的数目>= nMinObs的地图点数目
int nRefMatches = mpReferenceKF->TrackedMapPoints(nMinObs);
// Local Mapping accept keyframes?
// Step 5:查询局部地图线程是否繁忙,当前能否接受新的关键帧
bool bLocalMappingIdle = mpLocalMapper->AcceptKeyFrames();
// Check how many "close" points are being tracked and how many could be potentially created.
// Step 6:对于双目或RGBD摄像头,统计成功跟踪的近点的数量,如果跟踪到的近点太少,没有跟踪到的近点较多,可以插入关键帧
int nNonTrackedClose = 0; // 双目或RGB-D中没有跟踪到的近点
int nTrackedClose= 0; // 双目或RGB-D中成功跟踪的近点(三维点)
if(mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR && mSensor!=System::IMU_MONOCULAR)
{
int N = (mCurrentFrame.Nleft == -1) ? mCurrentFrame.N : mCurrentFrame.Nleft;
for(int i =0; i0 && mCurrentFrame.mvDepth[i] closed points: " + to_string(nTrackedClose) + "; non tracked closed points: " + to_string(nNonTrackedClose), Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);// Verbose::VERBOSITY_DEBUG);
}
// 双目或RGBD情况下:跟踪到的地图点中近点太少 同时 没有跟踪到的三维点太多,可以插入关键帧了
// 单目时,为false
bool bNeedToInsertClose;
bNeedToInsertClose = (nTrackedClose<100) && (nNonTrackedClose>70);
// Step 7:决策是否需要插入关键帧
// Thresholds
// Step 7.1:设定比例阈值,当前帧和参考关键帧跟踪到点的比例,比例越大,越倾向于增加关键帧
float thRefRatio = 0.75f;
// 关键帧只有一帧,那么插入关键帧的阈值设置的低一点,插入频率较低
if(nKFs<2)
thRefRatio = 0.4f;
/*int nClosedPoints = nTrackedClose + nNonTrackedClose;
const int thStereoClosedPoints = 15;
if(nClosedPoints < thStereoClosedPoints && (mSensor==System::STEREO || mSensor==System::IMU_STEREO))
{
//Pseudo-monocular, there are not enough close points to be confident about the stereo observations.
thRefRatio = 0.9f;
}*/
// 单目情况下插入关键帧的频率很高
if(mSensor==System::MONOCULAR)
thRefRatio = 0.9f;
if(mpCamera2) thRefRatio = 0.75f;
// 单目+IMU情况下如果,匹配内点数目超过350,插入关键帧的频率可以适当降低
if(mSensor==System::IMU_MONOCULAR)
{
if(mnMatchesInliers>350) // Points tracked from the local map
thRefRatio = 0.75f;
else
thRefRatio = 0.90f;
}
// Condition 1a: More than "MaxFrames" have passed from last keyframe insertion
// Step 7.2:很长时间没有插入关键帧,可以插入
const bool c1a = mCurrentFrame.mnId>=mnLastKeyFrameId+mMaxFrames;
// Condition 1b: More than "MinFrames" have passed and Local Mapping is idle
// Step 7.3:满足插入关键帧的最小间隔并且localMapper处于空闲状态,可以插入
const bool c1b = ((mCurrentFrame.mnId>=mnLastKeyFrameId+mMinFrames) && bLocalMappingIdle); //mpLocalMapper->KeyframesInQueue() < 2);
//Condition 1c: tracking is weak
// Step 7.4:在双目,RGB-D的情况下当前帧跟踪到的点比参考关键帧的0.25倍还少,或者满足bNeedToInsertClose
const bool c1c = mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR && mSensor!=System::IMU_MONOCULAR && mSensor!=System::IMU_STEREO && mSensor!=System::IMU_RGBD && (mnMatchesInliers15);
// Temporal condition for Inertial cases
// 新增的条件c3:单目/双目+IMU模式下,并且IMU完成了初始化(隐藏条件),当前帧和上一关键帧之间时间超过0.5秒,则c3=true
bool c3 = false;
if(mpLastKeyFrame)
{
if (mSensor==System::IMU_MONOCULAR)
{
if ((mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mpLastKeyFrame->mTimeStamp)>=0.5)
c3 = true;
}
else if (mSensor==System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
{
if ((mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp-mpLastKeyFrame->mTimeStamp)>=0.5)
c3 = true;
}
}
// 新增的条件c4:单目+IMU模式下,当前帧匹配内点数在15~75之间或者是RECENTLY_LOST状态,c4=true
bool c4 = false;
if ((((mnMatchesInliers<75) && (mnMatchesInliers>15)) || mState==RECENTLY_LOST) && (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR)) // MODIFICATION_2, originally ((((mnMatchesInliers<75) && (mnMatchesInliers>15)) || mState==RECENTLY_LOST) && ((mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR)))
c4=true;
else
c4=false;
// 相比ORB-SLAM2多了c3,c4
if(((c1a||c1b||c1c) && c2)||c3 ||c4)
{
// If the mapping accepts keyframes, insert keyframe.
// Otherwise send a signal to interrupt BA
// Step 7.6:local mapping空闲时或者正在做imu初始化时可以直接插入,不空闲的时候要根据情况插入
if(bLocalMappingIdle || mpLocalMapper->IsInitializing())
{
// 可以插入关键帧
return true;
}
else
{
mpLocalMapper->InterruptBA();
if(mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR && mSensor!=System::IMU_MONOCULAR)
{
// 双目或双目+IMU或RGB-D模式下,如队列里没有阻塞太多关键帧,可以插入
// tracking插入关键帧不是直接插入,而且先插入到mlNewKeyFrames中,
// 然后localmapper再逐个pop出来插入到mspKeyFrames
if(mpLocalMapper->KeyframesInQueue()<3)
// 队列中的关键帧数目不是很多,可以插入
return true;
else
// 队列中缓冲的关键帧数目太多,暂时不能插入
return false;
}
else
{
//对于单目情况,就直接无法插入关键帧了
//? 为什么这里对单目情况的处理不一样?
//回答:可能是单目关键帧相对比较密集
return false;
}
}
}
else
// 不满足上面的条件,自然不能插入关键帧
return false;
} 3.7 添加关键帧CreateNewKeyFrame()
如果当前帧符合关键帧条件的话,那就根据它创建一个新的关键帧,重置IMU预积分,创建新的路标点,传给localMapping线程。
Step 1:将当前帧构造成关键帧并将当前关键帧设置为当前帧的参考关键帧
void Tracking::CreateNewKeyFrame()
{
// 如果局部建图线程正在初始化且没做完或关闭了,就无法插入关键帧
if(mpLocalMapper->IsInitializing() && !mpAtlas->isImuInitialized())
return;
if(!mpLocalMapper->SetNotStop(true))
return;
KeyFrame* pKF = new KeyFrame(mCurrentFrame,mpAtlas->GetCurrentMap(),mpKeyFrameDB);
if(mpAtlas->isImuInitialized()) // || mpLocalMapper->IsInitializing())
pKF->bImu = true;
pKF->SetNewBias(mCurrentFrame.mImuBias);
// 在UpdateLocalKeyFrames函数中会将与当前关键帧共视程度最高的关键帧设定为当前帧的参考关键帧
mpReferenceKF = pKF;
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = pKF;
if(mpLastKeyFrame)
{
pKF->mPrevKF = mpLastKeyFrame;
mpLastKeyFrame->mNextKF = pKF;
}
// Reset preintegration from last KF (Create new object)
if (mSensor == System::IMU_MONOCULAR || mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
{
mpImuPreintegratedFromLastKF = new IMU::Preintegrated(pKF->GetImuBias(),pKF->mImuCalib);
}Step 2:对于双目或rgbd摄像头,为当前帧生成新的地图点;单目无操作
if(mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR && mSensor != System::IMU_MONOCULAR) // TODO check if incluide imu_stereo
{
// 根据Tcw计算mRcw、mtcw和mRwc、mOw
mCurrentFrame.UpdatePoseMatrices();
// We sort points by the measured depth by the stereo/RGBD sensor.
// We create all those MapPoints whose depth < mThDepth.
// If there are less than 100 close points we create the 100 closest.
int maxPoint = 100;
if(mSensor == System::IMU_STEREO || mSensor == System::IMU_RGBD)
maxPoint = 100;
// Step 3.1:得到当前帧有深度值的特征点(不一定是地图点)
vector > vDepthIdx;
int N = (mCurrentFrame.Nleft != -1) ? mCurrentFrame.Nleft : mCurrentFrame.N;
vDepthIdx.reserve(mCurrentFrame.N);
for(int i=0; i0)
{
// 第一个元素是深度,第二个元素是对应的特征点的id
vDepthIdx.push_back(make_pair(z,i));
}
}
if(!vDepthIdx.empty())
{
// Step 3.2:按照深度从小到大排序
sort(vDepthIdx.begin(),vDepthIdx.end());
// Step 3.3:从中找出不是地图点的生成临时地图点
// 处理的近点的个数
int nPoints = 0;
for(size_t j=0; jObservations()<1)
{
bCreateNew = true;
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i] = static_cast(NULL);
}
// 如果需要就新建地图点,这里的地图点不是临时的,是全局地图中新建地图点,用于跟踪
if(bCreateNew)
{
Eigen::Vector3f x3D;
if(mCurrentFrame.Nleft == -1){
mCurrentFrame.UnprojectStereo(i, x3D);
}
else{
x3D = mCurrentFrame.UnprojectStereoFishEye(i);
}
MapPoint* pNewMP = new MapPoint(x3D,pKF,mpAtlas->GetCurrentMap());
// 这些添加属性的操作是每次创建MapPoint后都要做的
pNewMP->AddObservation(pKF,i);
//Check if it is a stereo observation in order to not
//duplicate mappoints
if(mCurrentFrame.Nleft != -1 && mCurrentFrame.mvLeftToRightMatch[i] >= 0){
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[mCurrentFrame.Nleft + mCurrentFrame.mvLeftToRightMatch[i]]=pNewMP;
pNewMP->AddObservation(pKF,mCurrentFrame.Nleft + mCurrentFrame.mvLeftToRightMatch[i]);
pKF->AddMapPoint(pNewMP,mCurrentFrame.Nleft + mCurrentFrame.mvLeftToRightMatch[i]);
}
pKF->AddMapPoint(pNewMP,i);
pNewMP->ComputeDistinctiveDescriptors();
pNewMP->UpdateNormalAndDepth();
mpAtlas->AddMapPoint(pNewMP);
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=pNewMP;
nPoints++;
}
else
{
// 因为从近到远排序,记录其中不需要创建地图点的个数
nPoints++;
}
// Step 3.4:停止新建地图点必须同时满足以下条件:
// 1、当前的点的深度已经超过了设定的深度阈值(35倍基线)
// 2、nPoints已经超过100个点,说明距离比较远了,可能不准确,停掉退出
if(vDepthIdx[j].first>mThDepth && nPoints>maxPoint)
{
break;
}
}
//Verbose::PrintMess("new mps for stereo KF: " + to_string(nPoints), Verbose::VERBOSITY_NORMAL);
}
} Step 3:插入关键帧
// 关键帧插入到列表 mlNewKeyFrames中,等待local mapping线程临幸
mpLocalMapper->InsertKeyFrame(pKF);
// 插入好了,允许局部建图停止
mpLocalMapper->SetNotStop(false);
// 当前帧成为新的关键帧,更新
mnLastKeyFrameId = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
mpLastKeyFrame = pKF;
}