RabbitMQ之交换机的讲解
一、交换机
1、Exchange
在RabbitMQ中,生产者发送消息不会直接将消息投递到队列中,而是先将消息投递到交换机中, 在由交换机转发到具体的队列, 队列再将消息以推送或者拉取方式给消费者进行消费
生产者将消息发送到Exchange, 由Exchange再路由到一个或多个队列中:
2、路由键 ( RoutingKey)
生产者将消息发送给交换机的时候, 会指定RoutingKey指定路由规则。
3、绑定键 ( BindingKey)
通过绑定键将交换机与队列关联起来, 这样RabbitMQ就知道如何正确地将消息路由到队列。
4、关系
生产者将消息发送给哪个Exchange是需要由RoutingKey决定的,生产者需要将Exchange与哪个队列绑定时需要由 BindingKey决定的。
二、交换机类型
1、直连交换机: Direct exchange
直连交换机的路由算法非常简单: 将消息推送到binding key与该消息的routing key相同的队列。
直连交换机X上绑定了两个队列。第一个队列绑定了绑定o键range, 第二个队列有两个绑定键: black和green。
在这种场景下,一 个消息在布时指定了路由键为orange将会只被路由到队列Q1 I 路由键为black 和green的消息都将被路由到队列Q2。其他的消息都将被丢失。
同一个绑定键可以绑定到不同的队列上去, 可以增加一个交换机X与队列Q2的绑定键,在这种清况下,直连交换机将会和广播交换机有着相同的行为, 将消息推送到所有匹配的队列。一个路由键为black的消息将会同时被推送到队列Q1和Q2。
2、 主题交换机: Topic exchange
直连交换机的缺点:
直连交换机的 routing_key方案非常简单 ,如果我们希望一 条消息发送给多个队列 ,那么这个交换机需 要绑定上非常多的 routing_key.
假设每个交换机上都绑定一堆的 routing_key连接到各个队列上。那么消息的管理 就会异常地困难。
主题交换机的特点:
发送到主题交换机的 消息不能有任意的 routing key, 必须是由点号分开的一串单词,这些单词可以是任意的,但通常是与消息相关的一些特征。
如以下是几个有效的routing key:
"stock.usd.nyse", "nyse.vmw", "quick.orange.rabb 代", routing key的单词可以 有很多,最大限制是255 bytes。
Topic 交换机的 逻辑与 direct 交换机有点 相似 使用特定路由键发送的消息 将被发送到所有使用匹配绑定键绑定的队列 ,然而 ,绑定键有两个特殊的情况:
*表示匹配任意一个单词
#表示匹配任意—个或多个单词
如:
routing key quick.orange.rabbit-> queue Ql, Q2
routing key lazy.orange.elephant-> queue Ql,Q2
延申:
当一个队列的绑定键是"#",它将会接收所有的消息,而不再考虑所接收消息的路由键。
当一个队列的绑定键没有用到"#"和'*"时,它又像 direct 交换一样工作。
2、扇形交换机: Fanout exchange
扇形交换机是最基本的交换机类型,它所能做的事清非常简单广播消息。
扇形交换机会把能接收到的消息全部发送给绑定在自己身上的队列。因为广播不需要'思考”,所以扇形交换机处理消息的速度也是所有的交换机类型里面最快的。
3、首部交换机: Headers exchange
首部交换机和扇形交换机都不需 要路由键routingKey,交换机时通过 Headers 头部来将消息映射到队列的 ,有点像 HTTP的 Headers.
Hash结构中要求携带一个键 "x-match", 这个键的Val ue可以是any或者all, 这代表消息携带的 Hash是需要全部匹配(all), 还是仅匹配一个键(any) 就可以了。
相比直连交换机 ,首部交换机的优势是匹配的规则不被限定为字符串(string)而是 Object 类型。
all: 在发布消息时携带的所有Entry必须和绑定在队列上的所有 Entry完全匹配
any: 只要在发布消息时携带的有一对键值对 headers满足队列定义的多个参数 arguments的其中一 个就能 匹配上 ,注意这里是键值对的完全匹配,只匹配到键了,值却不—样是不行的;
4、默认交换机
实际上是— 个由 RabbitMQ预先声明好的名字为空字符串的直连交换机 (direct exchange) 。
它有一个特殊的属性使得它对于简单应用特别有用处 :那就是每个新建队列 (queue) 都会自动绑定到默认交换机上,绑定的 路由键(routing key) 名称与队列名称相同。
当你声明了一个名为“hello”的队列,RabbitMQ会自动将其绑定到默认交换机上,绑定(binding)的路由键名称也是为“hello”。
当携带着名为“hello”的路由键的信息被发送到默认交换机的时候,此消息会被默认交换机路由至名为“hello”的队列中
类似amq.*的名称的交换机:这些是RabbitMQ默认创建的交换机。
这些队列名称被预留做RabbitMQ内部使用,不能被应用使用,否则抛出403错误
5、Dead Letter Exchange(死信交换机)
演示链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60389087/article/details/123167193
RabbitMQ作为一个高级消息中间件,提出了死信交换器的概念。
这种交互器专门处理死了的信息(被拒绝可以重新投递的信息不能算死的)。
消息变成死信一般是以下三种情况:
①、消息被拒绝,并且设置requeue参数为false。
②、消息过期(默认情况下Rabbit中的消息不过期,但是可以设置队列的过期时间和信息的过期的效果)
③、队列达到最大长度(一般当设置了最大队列长度或大小并达到最大值时)
当满足上面三种情况时,消息会变成死信消息,并通过死信交换机投递到相应的队列中。
我们只需要监听相应队列,就可以对死信消息进行最后的处理。
订单超时处理:
生产者生产一条1分钟后超时的订单信息到正常交换机exchange-a中,消息匹配到队列queue-a,但一分钟后仍未消费。
消息会被投递到死信交换机dlx-exchange中,并发送到私信队列中。
死信队列dlx-queue的消费者拿到信息后,根据消息去查询订单的状态,如果仍然是未支付状态,将订单状态更新为超时状态。
三、交换机的属性
Name:交换机名称
Type:交换机类型,direct,topic,fanout,headers
Durability:是否需要持久化,如果持久性,则RabbitMQ重启后,交换机还存在
Auto Delete:当最后一个绑定到Exchange上的队列删除后,自动删除该Exchange
Internal:当前Exchange是否用于RabbitMQ内部使用,默认为false。
Arguments:扩展参数,用于扩展AMQP协议定制使用
四、演示直连交换机(生产者)
1、导入yml文件
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: provider
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.218.130
password: 123456
port: 5672
username: springboot
virtual-host: my_vhost2、创建队列,交换机以及绑定
DirectConfig :
package com.lv.code.mq;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class DirectConfig {
// 创建队列
@Bean
public Queue directQueueA(){
return new Queue("directQueueA",true);
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueueB(){
return new Queue("directQueueB",true);
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueueC(){
return new Queue("directQueueC",true);
}
// 创建交换机
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("directExchange");
}
// 进行交换机和队列的绑定:设置bindingkey
@Bean
public Binding bingingA(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueueA()).to(directExchange()).with("AA");
}
@Bean
public Binding bingingB(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueueB()).to(directExchange()).with("BB");
}
@Bean
public Binding bingingC(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueueC()).to(directExchange()).with("CC");
}
}
3、ProviderController
package com.lv.code;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ProviderController {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
@RequestMapping("/directSend")
public String directSend(String routingKey){
template.convertAndSend("directExchange",routingKey,"hello world");
return "yes";
}
}
启动时出现以下错误:进程结束快
解决方案:
导入依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
成功解决:
五、演示直连交换机(消费者)
1、导入yml文件
server:
port: 8082
spring:
application:
name: consumer
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.218.130
password: 123456
port: 5672
username: springboot
virtual-host: my_vhost2、在消费者内创建三个接收者
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "directQueueA")
@Slf4j
public class DirectReceiverA {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.info("A接到"+message);
}
}
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "directQueueB")
@Slf4j
public class DirectReceiverB {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.info("B接到"+message);
}
}
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "directQueueC")
@Slf4j
public class DirectReceiverC {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.info("C接到"+message);
}
}
六、主题交换机
1、在生产者内定义键,创建队列,创建交换机以及进行绑定
package com.lv.code.mq;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TopicConfig {
// 定义键
public final static String KEY_A="*.orange.*";
public final static String KEY_B="*.*.rabbit";
public final static String KEY_C="lazy.#";
// 创建队列
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueA(){
return new Queue("topicQueueA",true);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueB(){
return new Queue("topicQueueB",true);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueC(){
return new Queue("topicQueueC",true);
}
// 创建交换机
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("topicExchange");
}
// 进行交换机和队列的绑定:设置bindingkey
@Bean
public Binding topicBingingA(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueA()).to(topicExchange()).with(KEY_A);
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBingingB(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueB()).to(topicExchange()).with(KEY_B);
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBingingC(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueC()).to(topicExchange()).with(KEY_C);
}
}
2、在ProviderController内增加方法
@RequestMapping("/topicSend")
public String topicSend(String routingKey){
template.convertAndSend("topicExchange",routingKey,"hello world");
return "yes";
}3、消费者接收信息
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "topicQueueA")
@Slf4j
public class TopicReceiverA {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.info("A接到"+message);
}
}
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "topicQueueB")
@Slf4j
public class TopicReceiverB {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.info("B接到"+message);
}
}
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "topicQueueC")
@Slf4j
public class TopicReceiverC {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.warn("C接到"+message);
}
}
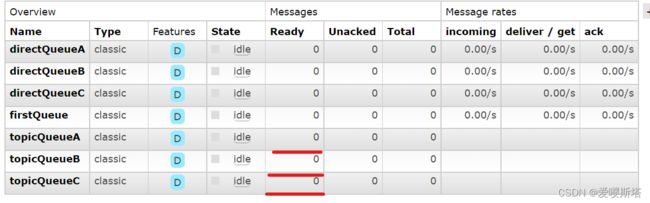
4、执行
规则:
aa不符合规则,不产生任何数据:
符合规则:出现数据
启动消费者,接收数据:
![]()
七、扇形交换机
1、在生产者内创建队列,创建交换机以及进行绑定,绑定时不需要键
FanoutConfig :
package com.lv.code.mq;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
// 创建队列
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueA(){
return new Queue("fanoutQueueA",true);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueB(){
return new Queue("fanoutQueueB",true);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueC(){
return new Queue("fanoutQueueC",true);
}
// 创建交换机
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");
}
// 进行交换机和队列的绑定:不需要键
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBingingA(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueA()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBingingB(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueB()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBingingC(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueC()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}
2、ProviderController新增方法
@RequestMapping("/fanoutSend")
public String fanoutSend(){
template.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange",null,"hello world");
return "yes";
}3、执行
 4、定义消费者接收
4、定义消费者接收
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "topicQueueA")
@Slf4j
public class TopicReceiverA {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.info("A接到"+message);
}
}
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "topicQueueB")
@Slf4j
public class TopicReceiverB {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.info("B接到"+message);
}
}
package com.lv.consumer1.mq;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
//消息队的监听器
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanoutQueueC")
@Slf4j
public class FanoutReceiverC {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message){
log.error("C接到"+message);
}
}
接收到信息:
本期内容结束~~~~~~~~··