MATLAB | 面向对象编程基础 | 类的创建及运算符重载
很多人发现我的很多绘图函数都写成了类哈,这一期讲讲MATLAB面向对象编程基础知识之《类的创建及运算符的重载》。
首先点击图示位置创建类:
classdef untitled
%UNTITLED 此处提供此类的摘要
% 此处提供详细说明
properties
Property1
end
methods
function obj = untitled(inputArg1,inputArg2)
%UNTITLED 构造此类的实例
% 此处提供详细说明
obj.Property1 = inputArg1 + inputArg2;
end
function outputArg = method1(obj,inputArg)
%METHOD1 此处提供此方法的摘要
% 此处提供详细说明
outputArg = obj.Property1 + inputArg;
end
end
end
我们看到自动生成的文件具有properties属性,methods方法等组成部分,对于基础的类有这俩部分已经足够了更复杂的类还会有比如events事件等一系列组成部分,
复数类与基础知识讲解
属性与构造函数
这里我们今天做示范就讲解一下如何建立一个复数类,复数类要包含实部和虚部两个属性,我们将这个自动生成的类进行一下改写,改成输入实部虚部两个参数创建新的对象,并将这两个属性分别存到对象的real和imag属性:
classdef complexS
properties
real,imag
end
methods
function obj=complexS(real,imag)
obj.real=real;
obj.imag=imag;
end
end
end
这样我们就可以通过如下方式创建复数:
a=complexS(3,4)
a =
complexS - 属性:
real: 3
imag: 4
类的方法
我们定义一个名为sum的方法函数,实现实部加实部,虚部加虚部:
classdef complexS
properties
real,imag
end
methods
function obj=complexS(real,imag)
obj.real=real;
obj.imag=imag;
end
function obj=sum(obj,arg)
obj.real=obj.real+arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag+arg.imag;
end
end
end
这样我们就可以通过sum实现俩复数的加法:
a=complexS(3,4);
b=complexS(1,-2);
c=sum(a,b)
c =
complexS - 属性:
real: 4
imag: 2
运算符的重载
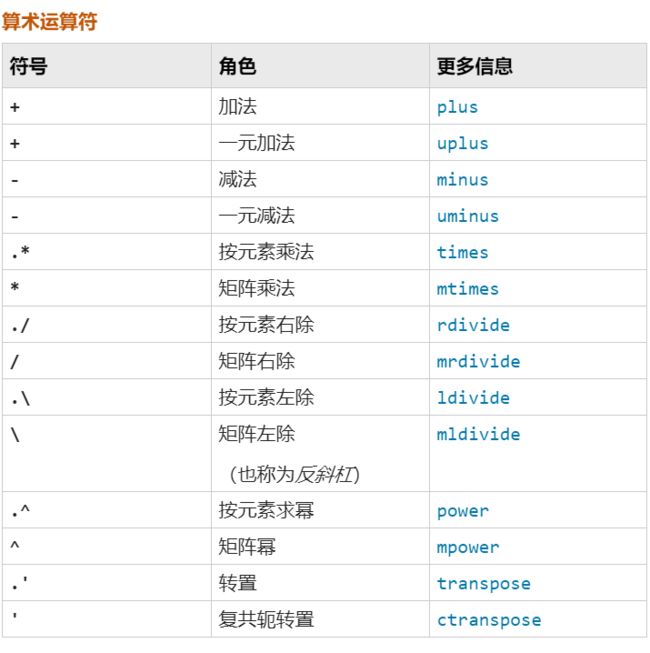
但是sum(a,b)的形式太麻烦,我们有没有办法直接a+b就直接进行加法呢?MATLAB运算符的重载不像是C++的operater+的形式,它是直接每个运算符有专门的名字,例如算符+的名称为plus,将类改写:
classdef complexS
properties
real,imag
end
methods
function obj=complexS(real,imag)
obj.real=real;
obj.imag=imag;
end
function obj=plus(obj,arg)
obj.real=obj.real+arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag+arg.imag;
end
end
end
运行一下加法:
a=complexS(3,4);
b=complexS(1,-2);
c=a+b
c =
complexS - 属性:
real: 4
imag: 2
给一下常见运算符的名称:
当然还有一些比如@,:等运算符,详细信息请参见:
https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/matlab_prog/matlab-operators-and-special-characters.html?s_tid=srchtitle_operator_5
单目运算符
有了上面的写法和思路,我们非常容易能使用minus定义出减法,但是这样的减法必须两个复数做减法,我只想把a变成-a咋办呢?我们注意到上面表里还有个叫做一元减法的玩意uminus这个能够实现相反数功能:
classdef complexS
properties
real,imag
end
methods
function obj=complexS(real,imag)
obj.real=real;
obj.imag=imag;
end
% 加法
function obj=plus(obj,arg)
obj.real=obj.real+arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag+arg.imag;
end
% 减法
function obj=minus(obj,arg)
obj.real=obj.real-arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag-arg.imag;
end
% 一元减法
function obj=uminus(obj)
obj.real=-obj.real;
obj.imag=-obj.imag;
end
end
end
试试正常减法和一元减法:
a=complexS(3,4);
b=complexS(1,-2);
a-b
-a
ans =
complexS - 属性:
real: 2
imag: 6
ans =
complexS - 属性:
real: -3
imag: -4
输入参数类型
我们有时候只想在右侧加个实数,而不一定加个复数咋办,我们可以在编写函数的时候用isa判断一下输入变量的类型再做出不同的处理,比如把之前的加法函数改为:
% 加法
function obj=plus(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
obj.real=obj.real+arg;
else
obj.real=obj.real+arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag+arg.imag;
end
end
a=complexS(3,4);
b=complexS(1,-2);
a+1
ans =
complexS - 属性:
real: 4
imag: 4
输出函数的重载
我们每次运行完的结果显示都是
ans =
complexS - 属性:
real: 4
imag: 4
这种形式,我们怎么能很简洁的显示x+yi这种格式呢?想不到吧disp这个函数也能重载,将类改为如下形式:
classdef complexS
properties
real,imag
end
methods
function obj=complexS(real,imag)
obj.real=real;
obj.imag=imag;
end
% 显示
function disp(obj)
if obj.real==0
switch true
case obj.imag==0,fprintf('%s','0');
case obj.imag>0,fprintf('%s',[num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
case obj.imag<0,fprintf('%s',[num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
end
else
fprintf('%s',num2str(obj.real))
switch true
case obj.imag==0
case obj.imag>0,fprintf('%s',['+',num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
case obj.imag<0,fprintf('%s',[num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
end
end
fprintf('\n');
end
% 加法
function obj=plus(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
obj.real=obj.real+arg;
else
obj.real=obj.real+arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag+arg.imag;
end
end
% 减法
function obj=minus(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
obj.real=obj.real-arg;
else
obj.real=obj.real-arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag-arg.imag;
end
end
% 一元减法
function obj=uminus(obj)
obj.real=-obj.real;
obj.imag=-obj.imag;
end
end
end
这样不管是不加分号还是disp都是正常的复数:
disp(complexS(3,-4))
complexS(-1,-4)
3-4i
ans =
-1-4i
完整复数类
一个支持四则运算及一些简单运算的复数类,此例子只用于简单的类练习:
classdef complexS
properties
real,imag
end
methods
function obj=complexS(real,imag)
obj.real=real;
obj.imag=imag;
end
% 显示
function disp(obj)
if obj.real==0
switch true
case obj.imag==0,fprintf('%s','0');
case obj.imag>0,fprintf('%s',[num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
case obj.imag<0,fprintf('%s',[num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
end
else
fprintf('%s',num2str(obj.real))
switch true
case obj.imag==0
case obj.imag>0,fprintf('%s',['+',num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
case obj.imag<0,fprintf('%s',[num2str(obj.imag),'i']);
end
end
fprintf('\n');
end
% 加法
function obj=plus(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
obj.real=obj.real+arg;
else
obj.real=obj.real+arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag+arg.imag;
end
end
% 减法
function obj=minus(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
obj.real=obj.real-arg;
else
obj.real=obj.real-arg.real;
obj.imag=obj.imag-arg.imag;
end
end
% 一元减法
function obj=uminus(obj)
obj.real=-obj.real;
obj.imag=-obj.imag;
end
% 乘法
function obj=mtimes(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
obj.real=obj.real.*arg;
obj.imag=obj.imag.*arg;
else
[obj.real,obj.imag]=...
deal(obj.real*arg.real-obj.imag*arg.imag,...
obj.real*arg.imag+obj.imag*arg.real);
end
end
% 除法
function obj=mrdivide(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
obj.real=obj.real./arg;
obj.imag=obj.imag./arg;
else
[obj.real,obj.imag]=...
deal(obj.real*arg.real+obj.imag*arg.imag,...
-obj.real*arg.imag+obj.imag*arg.real);
obj.real=obj.real./(arg.real.^2+arg.imag.^2);
obj.imag=obj.imag./(arg.real.^2+arg.imag.^2);
end
end
% 共轭
function obj=conj(obj)
obj.imag=-obj.imag;
end
% 模长
function normval=norm(obj)
normval=norm([obj.real,obj.imag]);
end
end
end
调用:
fprintf('\n创建:a=')
a=complexS(3,4);
disp(a)
fprintf('\n创建:b=')
b=complexS(1,-2);
disp(b)
fprintf('\n加法:a+b=')
disp(a+b)
fprintf('\n减法:a-b=')
disp(a-b)
fprintf('\n乘法:a*b=')
disp(a*b)
fprintf('\n除法:a/b=')
disp(a/b)
fprintf('\n共轭:conj(a)=')
disp(conj(a))
fprintf('\n模长:||a||=')
disp(norm(a))
创建:a=3+4i
创建:b=1-2i
加法:a+b=4+2i
减法:a-b=2+6i
乘法:a*b=11-2i
除法:a/b=-1+2i
共轭:conj(a)=3-4i
模长:||a||= 5
小作业:多项式类
请创建多项式类并具有基本的加减乘带余除法,积分求导等功能:
示例代码:
classdef polynom
properties
coe
end
methods
function obj=polynom(coe)
obj.coe=coe;
end
% =========================================================================
% 输出 --------------------------------------------------------------------
function disp(obj)
if all(obj.coe==0)
disp('0')
else
baseStr=char(32.*ones([1,length(obj.coe)*10]));
for i=1:length(obj.coe)
tStr='';
if obj.coe(i)~=0
if obj.coe(i)>0
oStr='+';
else
oStr='';
end
nStr=num2str(obj.coe(i));
if i~=length(obj.coe)
if str2double(nStr)==1,nStr='';end
if str2double(nStr)==-1,nStr='-';end
end
if i==(length(obj.coe)-1)
tStr=[oStr,nStr,'x'];
else
tStr=[oStr,nStr,'x^',num2str(length(obj.coe)-i)];
end
end
ind=find(abs(baseStr)==32,1);
baseStr(ind:ind+length(tStr)-1)=tStr;
end
baseStr(abs(baseStr)==32)=[];
if strcmp(baseStr(end-2:end),'x^0'),baseStr(end-2:end)=[];end
if strcmp(baseStr(1),'+'),baseStr(1)=[];end
disp(baseStr)
end
end
% 加法 --------------------------------------------------------------------
function obj=plus(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
tcoe=arg;
else
tcoe=arg.coe;
end
L1=length(obj.coe);
L2=length(tcoe);
baseCoe=zeros([1,max(L1,L2)+1]);
baseCoe(end+1-L1:end)=baseCoe(end+1-L1:end)+obj.coe;
baseCoe(end+1-L2:end)=baseCoe(end+1-L2:end)+tcoe;
obj.coe=baseCoe(find(baseCoe~=0,1):end);
end
% 减法 --------------------------------------------------------------------
function obj=minus(obj,arg)
if isa(arg,'double')
tcoe=arg;
else
tcoe=arg.coe;
end
L1=length(obj.coe);
L2=length(tcoe);
baseCoe=zeros([1,max(L1,L2)+1]);
baseCoe(end+1-L1:end)=baseCoe(end+1-L1:end)+obj.coe;
baseCoe(end+1-L2:end)=baseCoe(end+1-L2:end)-tcoe;
obj.coe=baseCoe(find(baseCoe~=0,1):end);
end
function obj=uminus(obj)
obj.coe=-obj.coe;
end
% 乘法 --------------------------------------------------------------------
function obj=mtimes(obj,arg)
L1=length(obj.coe);
L2=length(arg.coe);
tmat=zeros(L2,L1+L2-1);
for i=1:L2
tmat(i,i:(i+L1-1))=arg.coe(i).*obj.coe;
end
obj.coe=sum(tmat);
end
% 带余除法 -----------------------------------------------------------------
function [obj1,obj2]=mrdivide(obj,arg)
L1=length(obj.coe);
L2=length(arg.coe);
tCoe=obj.coe;
obj1=polynom(0);
for i=1:(L1+1-L2)
obj1.coe(i)=1./(arg.coe(1)).*(tCoe(1));
tCoe(1:L2)=tCoe(1:L2)-arg.coe.*obj1.coe(i);
tCoe(1)=[];
end
obj2=polynom(tCoe);
end
% 数值计算 -----------------------------------------------------------------
function value=val(obj,x)
value=x.^(length(obj.coe)-1:-1:0)*(obj.coe.');
end
% 积分 --------------------------------------------------------------------
function output=int(obj,a,b)
if nargin<2
output=polynom([obj.coe./(length(obj.coe):-1:1),0]);
else
tcoe=[obj.coe./(length(obj.coe):-1:1),0];
output=b.^(length(tcoe)-1:-1:0)*(tcoe.')-...
a.^(length(tcoe)-1:-1:0)*(tcoe.');
end
end
% 求导 --------------------------------------------------------------------
function obj=diff(obj)
obj.coe=obj.coe.*(length(obj.coe)-1:-1:0);
obj.coe(end)=[];
end
% 比较 --------------------------------------------------------------------
function bool=eq(obj,arg)
if length(obj.coe)~=length(arg.coe)
bool=false;
else
bool=all(obj.coe==arg.coe);
end
end
function bool=ne(obj,arg)
if length(obj.coe)~=length(arg.coe)
bool=true;
else
bool=~all(obj.coe==arg.coe);
end
end
end
end
fprintf('\n创建:a(x)=')
a=polynom([3,4,1,0]);
disp(a)
fprintf('\n创建:b(x)=')
b=polynom([3,2]);
disp(b)
fprintf('\n加法:a(x)+b(x)=')
disp(a+b)
fprintf('\n加法:a(x)+5x+6=')
disp(a+[5,6])
fprintf('\n减法:a(x)-b(x)=')
disp(a-b)
fprintf('\n相反数:-a(x)=')
disp(-a)
fprintf('\n乘法:a(x)*b(x)=')
disp(a*b)
fprintf('\n除法:a(x)/b(x)')
[c,d]=a/b;
fprintf('\n商=')
disp(c)
fprintf('余数=')
disp(d)
fprintf('\n积分:int(a(x))=')
disp(int(a))
fprintf('\n求导:diff(a(x))=')
disp(diff(a))
fprintf('\n数值计算:a(5)=')
disp(val(a,5))
fprintf('数值积分:int(a(x),0,1)=')
disp(int(a,0,1))
fprintf('比较:a(x)==b(x)=')
disp(a==b)
fprintf('比较:a(x)~=b(x)=')
disp(a~=b)
创建:a(x)=3x3+4x2+x
创建:b(x)=3x+2
加法:a(x)+b(x)=3x3+4x2+4x+2
加法:a(x)+5x+6=3x3+4x2+6x+6
减法:a(x)-b(x)=3x3+4x2-2x-2
相反数:-a(x)=-3x3-4x2-x
乘法:a(x)*b(x)=9x4+18x3+11x^2+2x
除法:a(x)/b(x)
商=x^2+0.66667x-0.11111
余数=0.22222积分:int(a(x))=0.75x4+1.3333x3+0.5x^2
求导:diff(a(x))=9x^2+8x+1
数值计算:a(5)= 480
数值积分:int(a(x),0,1)= 2.5833
比较:a(x)==b(x)= 0
比较:a(x)~=b(x)= 1