理解ggplot2颜色的标尺函数(scale_color_*,scale_color_*)
关于颜色的标尺函数在ggplot2中竟然多达22种,如此多的标尺函数未免使人感到疑惑
library(ggplot2)
grep('scale_color_*', x = ls('package:ggplot2'), value = TRUE)#在这里fill同理
[1] “scale_color_binned” “scale_color_brewer”
[3] “scale_color_continuous” “scale_color_date”
[5] “scale_color_datetime” “scale_color_discrete”
[7] “scale_color_distiller” “scale_color_fermenter”
[9] “scale_color_gradient” “scale_color_gradient2”
[11] “scale_color_gradientn” “scale_color_grey”
[13] “scale_color_hue” “scale_color_identity”
[15] “scale_color_manual” “scale_color_ordinal”
[17] “scale_color_steps” “scale_color_steps2”
[19] “scale_color_stepsn” “scale_color_viridis_b”
[21] “scale_color_viridis_c” “scale_color_viridis_d”
对颜色标尺函数的理解
让我们直入正题,虽然ggplot2拥有多达22种的标尺函数,但我们可以根据关键性质(一共分为三种),这样我们可以大体知道在不同的情形下具体使用哪个标尺函数。
- 数据映射的自然属性:
aes()图形映射里描述的数据是连续的还是离散的?连续的典型如时间,温度,长度,离散的典型如分类结果ABCD。 - 颜色空间:
简单来说就是你在画图内使用的调色板,在默认情况下ggplot2已经给你设置了调色板,此外ggplot2还内置了RcolorBrewer调色板以及Viridis调色板 - 层级的控制:
一旦指定映射数据是否离散,规定颜色空间之后,用户就需要在颜色的层级上描述差异,例如*_continuous(),*_gradient,*_gradient2(),*_gradientn(),
连续的标尺
我们以连续的标尺开始示例,在映射数据是连续的时候,我们选择continous函数族,这些函数可以进一步指定它们是否是分箱的,(分箱是指将连续的变量分组为数个分组,每个组都被指定到特定的颜色中),在后续示例你会在图例中注意到分箱和连续颜色的区别。
默认情况下:
library(ggplot2)
cont <- ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp, color=cyl)) + geom_point(size=4)
cont + scale_color_continuous()# scale_color_continuous可以不用添加
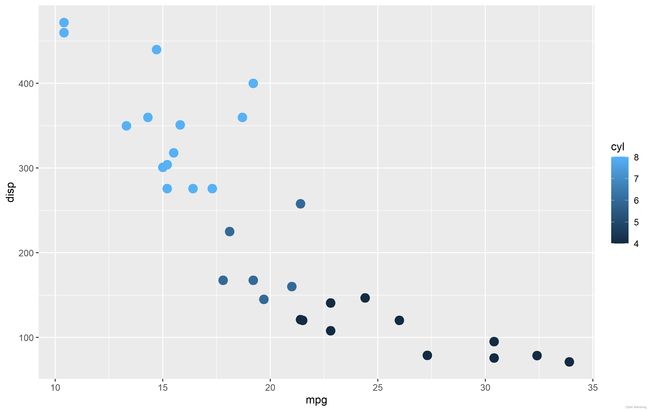
需要指出的是,scale_color_continuous当ggplot2检测到cyl是numeric向量后,会自动调用,为了直观,我们手动将这一函数写了出来。
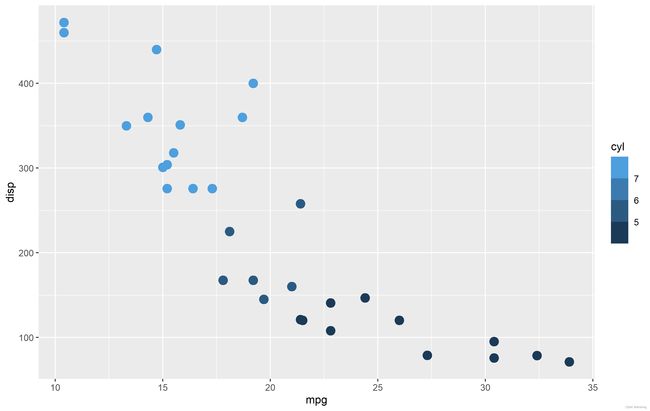
在我们指定了颜色分箱之后,图例也发生了变化:
cont + scale_color_binned()
以下是连续的颜色标尺,(作用就不需要翻译了,很简单的英语,ggplot2官网也有这些函数详细的介绍):
| 连续的标尺函数 | 颜色空间(调色板) | 显示的图例 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| scale_color_continuous() | default | Colorbar | 默认 |
| scale_color_gradient() | user-defined | Colorbar | define low and high values |
| scale_color_gradient2() | user-defined | Colorbar | define low mid and high values |
| scale_color_gradientn() | user_defined | Colorbar | define any number of incremental val |
| scale_color_binned() | default | Colorsteps | basic scale, but binned |
| scale_color_steps() | user-defined | Colorsteps | define low and high values |
| scale_color_steps2() | user-defined | Colorsteps | define low, mid, and high vals |
| scale_color_stepsn() | user-defined | Colorsteps | define any number of incremental vals |
| scale_color_viridis_c() | Viridis | Colorbar | viridis color scale. Change palette via option=. |
| scale_color_viridis_b() | Viridis | Colorsteps | Viridis color scale, binned. Change palette via option=. |
| scale_color_distiller() | Brewer | Colorbar | Brewer color scales. Change palette via palette=. |
| scale_color_fermenter() | Brewer | Colorsteps | Brewer color scale, binned. Change palette via palette=. |
当映射数据是离散的情况下,scale_color_discrete就会被调用,同样是上面的示例,我们用as.factor函数将数值向量强行转化为因子向量后,就可以得到离散的颜色标尺。
discrete <- ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp, color=as.factor(cyl))) + geom_point(size=4)
discrete# 在这里写不写scale_color_discrete没有区别,因为它是被默认调用的
如下是有关离散的函数,如英文原文示意:
| 标尺函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| scale_color_discrete() | 默认 |
| scale_color_hue() | Same as scale_color_discrete(), but you can define the range of hues and colors used |
| scale_color_grey() | Uses a greyscale. Can define the range. |
| scale_color_manual() | Must define specifically every color used. You can apply to your mapping by supplying a named vector for values=. |
| scale_color_identity() | A special-case function where your data is made up of names of colors - not names of factor levels |
| scale_color_brewer() | The discrete version of the Brewer colorspaces. Change palette via palette=. |
| scale_color_viridis_d() | The discrete version of the viridis colorspaces. Can change palette via option=. |
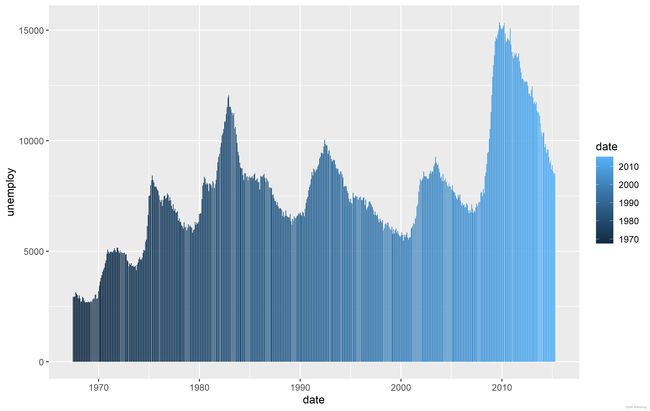
日期标尺
将日期映射到颜色我个人觉得是种很奇怪的行为(起码我一次都没遇到过),但既然ggplot2还是给了这种标尺(tidyverse就是喜欢重复造轮子),在文章的最后还是要介绍一下。
日期标尺主要分为scale_color_date() ,scale_color_datetime(), 顾名思义,但它们的本质和scale_color_continous没有区别,它们两都在定义函数的内部包装了scale_color_continous,使得在标签的显示上更令人易懂。
ggplot(economics, aes(x=date, y=unemploy, fill=date)) + geom_col() +scale_fill_date()
回顾曾经
如果你看到这里的话,那么下面的错误显然不用多加解释了。
> discrete + scale_color_continuous()
Error: Discrete value supplied to continuous scale
> cont + scale_color_discrete()
Error: Continuous value supplied to discrete scale