C# 学习笔记 (极速版)
本篇文章参照 菜鸟教程 后的学习笔记 针对有点c 基础
我觉得能看懂的就没有解释 想看原文章 文章最后我给了网站地址
第一个函数
test.cs 文件代码:
using System;
namespace HelloWorldApplication
{
class HelloWorld
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 我的第一个 C# 程序*/
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}程序的第一行 using System; - using 关键字用于在程序中包含 System 命名空间。 一个程序一般有多个 using 语句。
下一行是 namespace 声明。一个 namespace 里包含了一系列的类。HelloWorldApplication 命名空间包含了类 HelloWorld。
下一行是 class 声明。类 HelloWorld 包含了程序使用的数据和方法声明。类一般包含多个方法。方法定义了类的行为。在这里,HelloWorld 类只有一个 Main 方法。
下一行定义了 Main 方法,是所有 C# 程序的 入口点。Main 方法说明当执行时 类将做什么动作。
下一行 /*...*/ 将会被编译器忽略,且它会在程序中添加额外的 注释。
Main 方法通过语句 Console.WriteLine("Hello World"); 指定了它的行为。
WriteLine 是一个定义在 System 命名空间中的 Console 类的一个方法。该语句会在屏幕上显示消息 "Hello World"。
最后一行 Console.ReadKey(); 是针对 VS.NET 用户的。这使得程序会等待一个按键的动作,防止程序从 Visual Studio .NET 启动时屏幕会快速运行并关闭。
C# 占位符{}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("A:{0},a:{1}",65,97);
Console.ReadLine();
}
占位符从零开始计数,且占位符中的数字不能大于第二个及后面的参数的总个数减一(要求占位符必须有可替换的值)。
占位符数字与第二个及后面的参数字符位置一一对应。
对象(Object)类型
当一个值类型转换为对象类型时,则被称为装箱;另一方面,当一个对象类型转换为值类型时,则被称为拆箱。
int val = 8;
object obj = val;//整型数据转换为了对象类型(装箱)
拆箱:之前由值类型转换而来的对象类型再转回值类型, 实例
int val = 8;
object obj = val;//先装箱
int nval = (int)obj;//再拆箱
动态(Dynamic)类型
可以存储任何类型的值在动态数据类型变量中。这些变量的类型检查是在运行时发生的。
声明动态类型的语法:
dynamic = value;
eg:
dynamic d = 20;
字符串(String)类型
字符串(String)类型 允许您给变量分配任何字符串值。字符串(String)类型是 System.String 类的别名。它是从对象(Object)类型派生的。字符串(String)类型的值可以通过两种形式进行分配:引号和 @引号。
eg:
string str = "runoob.com";
@"runoob.com";
string str = @"C:\Windows";
string str = "C:\\Windows";
上面三种方式都可以
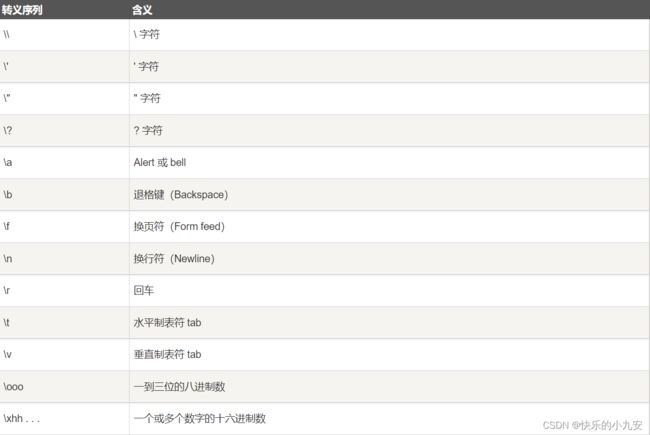
转义字符(\)
指针类型(Pointer types)
char* cptr;
int* iptr;
和c指针一样
子类
namespace TypeConvertion
{ class Class1
{
}
class Class2 : Class1 //类Class2是类Class1的子类
{
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int inum = 100;
long lnum = inum; // 进行了隐式转换,将 int 型(数据范围小)数据转换为了 long 型(数据范围大)的数据
Class1 c1 = new Class2(); // 这里也是隐式转换,将一个新建的 Class2 实例转换为了其基类 Class1 类型的实例 C1
}
}
}
C# 类型转换方法
将不同类型转换为字符川型
namespace TypeConversionApplication
{
class StringConversion
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i = 75;
float f = 53.005f;
double d = 2345.7652;
bool b = true;
Console.WriteLine(i.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(f.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(d.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(b.ToString());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
强制转换
i = (int)d;Convert.ToInt32()的取整
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double a = 1.35;
double b = 1.65;
int a1 = Convert.ToInt32(a);
int a2 = (int)(a);
int b1 = Convert.ToInt32(b);
int b2 = (int)(b);
Console.WriteLine("{0}使用convert方法转化的结果为:{1}",a,a1);
Console.WriteLine("{0}使用int强制转换的结果为:{1}",a,a2);
Console.WriteLine("{0}使用convert方法转化的结果为:{1}", b, b1);
Console.WriteLine("{0}使用int强制转换的结果为:{1}", b, b2);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
int 直接去掉小数点,Convert.ToInt32()的取整是四舍五入
C# 变量
C# 中的变量定义
变量通过在等号后跟一个常量表达式进行初始化(赋值)
int i, j, k;
char c, ch;
float f, salary;
double d;
int i = 100;//您可以在变量定义时进行初始化:
C# 中的变量初始化
变量可以在声明时被初始化(指定一个初始值)。初始化由一个等号后跟一个常量表达式组成,如下所示:
int d = 3, f = 5; /* 初始化 d 和 f. */
byte z = 22; /* 初始化 z. */
double pi = 3.14159; /* 声明 pi 的近似值 */
char x = 'x'; /* 变量 x 的值为 'x' */
接受来自用户的值
System 命名空间中的 Console 类提供了一个函数 ReadLine(),用于接收来自用户的输入,并把它存储到一个变量中 相当于c的scanf自己理解的可能不对
int num;
num = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
为什么要转换为整型 因为函数 Convert.ToInt32() 把用户输入的数据转换为 int 数据类型,因为 Console.ReadLine() 只接受字符串格式的数据
C# 中的 Lvalues 和 Rvalues
正确
int g = 20;
错误
10 = 20;
C# 常量
整数常量可以是十进制、八进制或十六进制的常量。前缀指定基数:0x 或 0X 表示十六进制,0 表示八进制,没有前缀则表示十进制。
整数常量也可以有后缀,可以是 U 和 L 的组合,其中,U 和 L 分别表示 unsigned 和 long。后缀可以是大写或者小写,多个后缀以任意顺序进行组合。
212 /* 合法 */
215u /* 合法 */
0xFeeL /* 合法 */
078 /* 非法:8 不是一个八进制数字 */
032UU /* 非法:不能重复后缀 */
85 /* 十进制 */
0213 /* 八进制 */
0x4b /* 十六进制 */
30 /* int */
30u /* 无符号 int */
30l /* long */
30ul /* 无符号 long */
浮点常量
一个浮点常量是由整数部分、小数点、小数部分和指数部分组成。您可以使用小数形式或者指数形式来表示浮点常量。
使用小数形式表示时,必须包含小数点、指数或同时包含两者。使用指数形式表示时,必须包含整数部分、小数部分或同时包含两者。有符号的指数是用 e 或 E 表示的。
3.14159 /* 合法 */
314159E-5L /* 合法 */
510E /* 非法:不完全指数 */
210f /* 非法:没有小数或指数 */
.e55 /* 非法:缺少整数或小数 */
字符常量
namespace EscapeChar
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello\tWorld\n\n");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
可以看见有一个\t 等于tab
字符串常量
字符串常量是括在双引号""里,或者是括在@""里。字符串常量包含的字符与字符常量相似,可以是:普通字符、转义序列和通用字符
使用字符串常量时,可以把一个很长的行拆成多个行,可以使用空格分隔各个部分
string a = "hello, world"; // hello, world
string b = @"hello, world"; // hello, world
string c = "hello \t world"; // hello world
string d = @"hello \t world"; // hello \t world
string e = "Joe said \"Hello\" to me"; // Joe said "Hello" to me
string f = @"Joe said ""Hello"" to me"; // Joe said "Hello" to me
string g = "\\\\server\\share\\file.txt"; // \\server\share\file.txt
string h = @"\\server\share\file.txt"; // \\server\share\file.txt
string i = "one\r\ntwo\r\nthree";
string j = @"one
two
three";
@""不认转义符 ""认转义符
定义常量
常量是使用 const 关键字来定义的 。定义一个常量的语法
using System;
public class ConstTest
{
class SampleClass
{
public int x;
public int y;
public const int c1 = 5;
public const int c2 = c1 + 5;
public SampleClass(int p1, int p2)
{
x = p1;
y = p2;
}
}
static void Main()
{
int p1;
int p2;
p1 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
p2 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
SampleClass mC = new SampleClass(p1,p2);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0}, y = {1}", mC.x, mC.y);
Console.WriteLine("c1 = {0}, c2 = {1}",SampleClass.c1, SampleClass.c2);
}
}
静态常量(编译时常量)const
在编译时就确定了值,必须在声明时就进行初始化且之后不能进行更改,可在类和方法中定义
const double a=3.14;// 正确声明常量的方法
const int b; // 错误,没有初始化
动态常量(运行时常量)readonly
在运行时确定值,只能在声明时或构造函数中初始化
class Program
{
readonly int a=1; // 声明时初始化
readonly int b; // 构造函数中初始化
Program()
{
b=2;
}
static void Main()
{
}
}
静态常量与动态常量的使用场景
在下面两种情况下,可以使用 const 常量:
取值永久不变(比如圆周率、一天包含的小时数、地球的半径等)。
对程序性能要求非常苛刻。
除此之外的其他情况都应该优先采用 readonly 常量。
C# 运算符
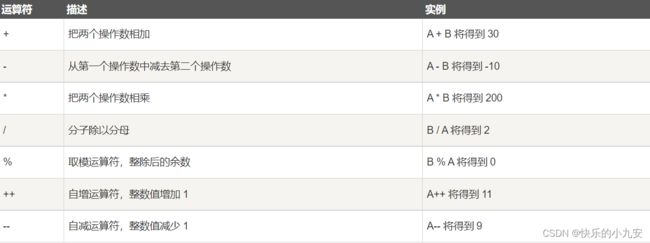
下表显示了 C# 支持的所有算术运算符。假设变量 A 的值为 10,变量 B 的值为 20,则:
eg:
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 21;
int b = 10;
int c;
c = a + b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = a - b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = a * b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = a / b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = a % b;
Console.WriteLine("Line 5 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
// ++a 先进行自增运算再赋值
c = ++a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 6 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
// 此时 a 的值为 22
// --a 先进行自减运算再赋值
c = --a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 7 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
c = a++: 先将 a 赋值给 c,再对 a 进行自增运算 1
c = ++a: 先将 a 进行自增运算,再将 a 赋值给 c 2
c = a --: 先将 a 赋值给 c,再对 a 进行自减运算 1
c = --a: 先将 a 进行自减运算,再将 a 赋值给 c 0
关系运算符
下表显示了 C# 支持的所有关系运算符。假设变量 A 的值为 10,变量 B 的值为 20,则:
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 21;
int b = 10;
if (a == b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - a 等于 b");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - a 不等于 b");
}
if (a < b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - a 小于 b");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - a 不小于 b");
}
if (a > b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - a 大于 b");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - a 不大于 b");
}
/* 改变 a 和 b 的值 */
a = 5;
b = 20;
if (a <= b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - a 小于或等于 b");
}
if (b >= a)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 5 - b 大于或等于 a");
}
}
}
逻辑运算符
下表显示了 C# 支持的所有逻辑运算符。假设变量 A 为布尔值 true,变量 B 为布尔值 false,
与&& 或 || 非!
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool a = true;
bool b = true;
if (a && b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - 条件为真");
}
if (a || b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - 条件为真");
}
/* 改变 a 和 b 的值 */
a = false;
b = true;
if (a && b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - 条件为真");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - 条件不为真");
}
if (!(a && b))
{
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - 条件为真");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
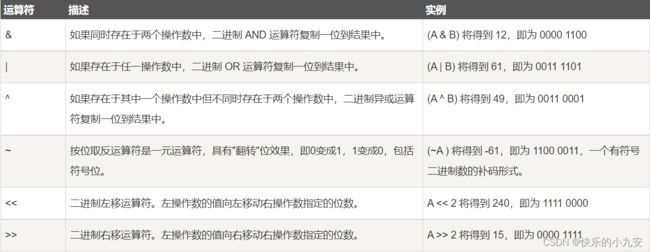
位运算符
位运算符作用于位,并逐位执行操作。&、 | 和 ^ 的真值表如下所示:
假设如果 A = 60,且 B = 13,现在以二进制格式表示,它们如下所示:
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
-----------------
A&B = 0000 1100
A|B = 0011 1101
A^B = 0011 0001 相同为False(0) 不同为True(1)
~A = 1100 0011
下表列出了 C# 支持的位运算符。假设变量 A 的值为 60,变量 B 的值为 13,则:
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 60; /* 60 = 0011 1100 */
int b = 13; /* 13 = 0000 1101 */
int c = 0;
c = a & b; /* 12 = 0000 1100 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - c 的值是 {0}", c );
c = a | b; /* 61 = 0011 1101 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = a ^ b; /* 49 = 0011 0001 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = ~a; /*-61 = 1100 0011 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = a << 2; /* 240 = 1111 0000 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 5 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
c = a >> 2; /* 15 = 0000 1111 */
Console.WriteLine("Line 6 - c 的值是 {0}", c);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
赋值运算符
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 21;
int c;
c = a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 1 - = c 的值 = {0}", c);
c += a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 2 - += c 的值 = {0}", c);
c -= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 3 - -= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c *= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 4 - *= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c /= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 5 - /= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c = 200;
c %= a;
Console.WriteLine("Line 6 - %= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c <<= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 7 - <<= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c >>= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 8 - >>= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c &= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 9 - &= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c ^= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 10 - ^= c 的值 = {0}", c);
c |= 2;
Console.WriteLine("Line 11 - |= c 的值 = {0}", c);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
其他运算符
using System;
namespace OperatorsAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* sizeof 运算符的实例 */
Console.WriteLine("int 的大小是 {0}", sizeof(int));
Console.WriteLine("short 的大小是 {0}", sizeof(short));
Console.WriteLine("double 的大小是 {0}", sizeof(double));
/* 三元运算符的实例 */
int a, b;
a = 10;
b = (a == 1) ? 20 : 30;
Console.WriteLine("b 的值是 {0}", b);
b = (a == 10) ? 20 : 30;
Console.WriteLine("b 的值是 {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
最后是先a是不是等于1 是为真则执行20 为假则执行30
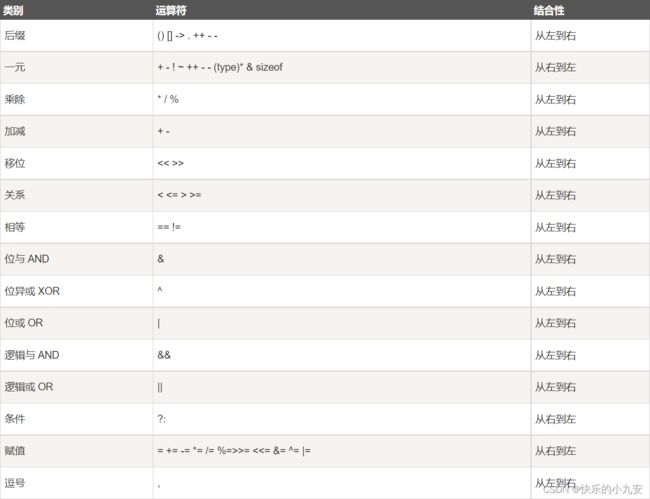
C# 中的运算符优先级
下表将按运算符优先级从高到低列出各个运算符,具有较高优先级的运算符出现在表格的上面,具有较低优先级的运算符出现在表格的下面
if 语句
if (boolean_expression)
{
/* 如果布尔表达式为真将执行的语句 */
}
eg:
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 10;
/* 使用 if 语句检查布尔条件 */
if (a < 20)
{
/* 如果条件为真,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("a 小于 20");
}
Console.WriteLine("a 的值是 {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
if…else语句
if(boolean_expression)
{
/* 如果布尔表达式为真将执行的语句 */
}
else
{
/* 如果布尔表达式为假将执行的语句 */
}
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
/* 检查布尔条件 */
if (a < 20)
{
/* 如果条件为真,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("a 小于 20");
}
else
{
/* 如果条件为假,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("a 大于 20");
}
Console.WriteLine("a 的值是 {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
if…else if…else 语句
if(boolean_expression 1)
{
/* 当布尔表达式 1 为真时执行 */
}
else if( boolean_expression 2)
{
/* 当布尔表达式 2 为真时执行 */
}
else if( boolean_expression 3)
{
/* 当布尔表达式 3 为真时执行 */
}
else
{
/* 当上面条件都不为真时执行 */
}
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
/* 检查布尔条件 */
if (a == 10)
{
/* 如果 if 条件为真,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("a 的值是 10");
}
else if (a == 20)
{
/* 如果 else if 条件为真,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("a 的值是 20");
}
else if (a == 30)
{
/* 如果 else if 条件为真,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("a 的值是 30");
}
else
{
/* 如果上面条件都不为真,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("没有匹配的值");
}
Console.WriteLine("a 的准确值是 {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
嵌套if语句
if( boolean_expression 1)
{
/* 当布尔表达式 1 为真时执行 */
if(boolean_expression 2)
{
/* 当布尔表达式 2 为真时执行 */
}
}
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
/* 检查布尔条件 */
if (a == 100)
{
/* 如果条件为真,则检查下面的条件 */
if (b == 200)
{
/* 如果条件为真,则输出下面的语句 */
Console.WriteLine("a 的值是 100,且 b 的值是 200");
}
}
Console.WriteLine("a 的准确值是 {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("b 的准确值是 {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
switch语句
switch(expression){
case constant-expression :
statement(s);
break;
case constant-expression :
statement(s);
break;
/* 您可以有任意数量的 case 语句 */
default : /* 可选的 */
statement(s);
break;
}
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
char grade = 'B';
switch (grade)
{
case 'A':
Console.WriteLine("很棒!");
break;
case 'B':
case 'C':
Console.WriteLine("做得好");
break;
case 'D':
Console.WriteLine("您通过了");
break;
case 'F':
Console.WriteLine("最好再试一下");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("无效的成绩");
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("您的成绩是 {0}", grade);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
嵌套 switch 语句
switch(ch1)
{
case 'A':
printf("这个 A 是外部 switch 的一部分" );
switch(ch2)
{
case 'A':
printf("这个 A 是内部 switch 的一部分" );
break;
case 'B': /* 内部 B case 代码 */
}
break;
case 'B': /* 外部 B case 代码 */
}
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
switch (a)
{
case 100:
Console.WriteLine("这是外部 switch 的一部分");
switch (b)
{
case 200:
Console.WriteLine("这是内部 switch 的一部分");
break;
}
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("a 的准确值是 {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("b 的准确值是 {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
?:运算符
Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3;
其中,Exp1、Exp2 和 Exp3 是表达式。请注意,冒号的使用和位置。
while 循环
while(condition)
{
statement(s);
}
using System;
namespace Loops
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 10;
/* while 循环执行 */
while (a < 20)
{
Console.WriteLine("a 的值: {0}", a);
a++;
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
for/foreach 循环
for ( init; condition; increment )
{
statement(s);
}
for循环
using System;
namespace Loops
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* for 循环执行 */
for (int a = 10; a < 20; a = a + 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("a 的值: {0}", a);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
C# 也支持 foreach 循环,使用foreach可以迭代数组或者一个集合对象
oreach循环
class ForEachTest
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] fibarray = new int[] { 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 };
foreach (int element in fibarray)//依次迭代数组内的整型,迭代一次执行一次循环语句
{
System.Console.WriteLine(element);//每次循环需要执行的内容
}
System.Console.WriteLine();
// 类似 foreach 循环
for (int i = 0; i < fibarray.Length; i++)//确定i的值,
{
System.Console.WriteLine(fibarray[i]);//输出数组中第i个值
}
System.Console.WriteLine();
// 设置集合中元素的计算器
int count = 0;
foreach (int element in fibarray)
{
count += 1;
System.Console.WriteLine("Element #{0}: {1}", count, element);//count值反映了循环主体的执行次数,从1开始代表了数组中第一个整型,依次往后
}
System.Console.WriteLine("Number of elements in the array: {0}", count);
}
}
fibarray.Length和python中len函数一样相当于求元素长度
do…while 循环
do
{
statement(s);
}while( condition );
using System;
namespace Loops
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 10;
/* do 循环执行 */
do
{
Console.WriteLine("a 的值: {0}", a);
a = a + 1;
} while (a < 20);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
嵌套循环
for for嵌套
for ( init; condition; increment )
{
for ( init; condition; increment )
{
statement(s);
}
statement(s);
}
while while嵌套
while(condition)
{
while(condition)
{
statement(s);
}
statement(s);
}
break 语句
using System;
namespace Loops
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 10;
/* while 循环执行 */
while (a < 20)
{
Console.WriteLine("a 的值: {0}", a);
a++;
if (a > 15)
{
/* 使用 break 语句终止 loop */
break;
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
continue 语句
using System;
namespace Loops
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 10;
/* do 循环执行 */
do
{
if (a == 15)
{
/* 跳过迭代 */
a = a + 1;
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine("a 的值: {0}", a);
a++;
} while (a < 20);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
无限循环
using System;
namespace Loops
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (; ; )
{
Console.WriteLine("Hey! I am Trapped");
}
}
}
}
当条件表达式不存在时,它被假设为真。您也可以设置一个初始值和增量表达式,但是一般情况下,程序员偏向于使用 for(;;) 结构来表示一个无限循环。
C# 封装
public:所有对象都可以访问;
private:对象本身在对象内部可以访问;
protected:只有该类对象及其子类对象可以访问
internal:同一个程序集的对象可以访问;
protected internal:访问限于当前程序集或派生自包含类的类型。
using System;
namespace RectangleApplication
{
class Rectangle
{
//成员变量
public double length;
public double width;
public double GetArea()
{
return length * width;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("长度: {0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("宽度: {0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("面积: {0}", GetArea());
}
}// Rectangle 结束
class ExecuteRectangle
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.length = 4.5;
r.width = 3.5;
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}网上看见一个大哥的比喻很有意思
比如说:一个人A为父类,他的儿子B,妻子C,私生子D(注:D不在他家里)
如果我们给A的事情增加修饰符:
public事件,地球人都知道,全公开
protected事件,A,B,D知道(A和他的所有儿子知道,妻子C不知道)
private事件,只有A知道(隐私?心事?)
internal事件,A,B,C知道(A家里人都知道,私生子D不知道)
protected internal事件,A,B,C,D都知道,其它人不知道
Console.WriteLine("请输入长度:");
相当于c中的printf("请输入长度:");
length = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
相当于c中的scanf("%d"&length)
C# 中定义方法
(Parameter List)
{
Method Body
} class NumberManipulator
{
public int FindMax(int num1, int num2)
{
/* 局部变量声明 */
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}
...
}C# 中调用方法
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public int FindMax(int num1, int num2)
{
/* 局部变量声明 */
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
int ret;
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
//调用 FindMax 方法
ret = n.FindMax(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("最大值是: {0}", ret );
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}您也可以使用类的实例从另一个类中调用其他类的公有方法。例如,方法 FindMax 属于 NumberManipulator 类,您可以从另一个类 Test 中调用它。
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public int FindMax(int num1, int num2)
{
/* 局部变量声明 */
int result;
if (num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
return result;
}
}
class Test
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
int ret;
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
//调用 FindMax 方法
ret = n.FindMax(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("最大值是: {0}", ret );
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}递归方法调用
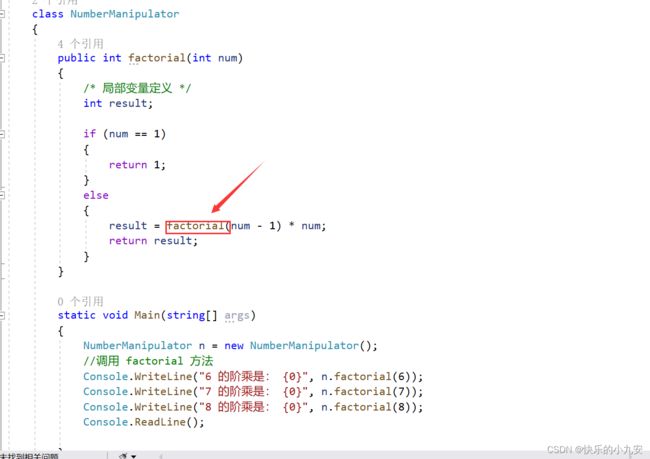
一个方法可以自我调用。这就是所谓的 递归。下面的实例使用递归函数计算一个数的阶乘:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public int factorial(int num)
{
/* 局部变量定义 */
int result;
if (num == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
result = factorial(num - 1) * num;
return result;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
//调用 factorial 方法
Console.WriteLine("6 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(6));
Console.WriteLine("7 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(7));
Console.WriteLine("8 的阶乘是: {0}", n.factorial(8));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}本身的阶层函数
参数传递
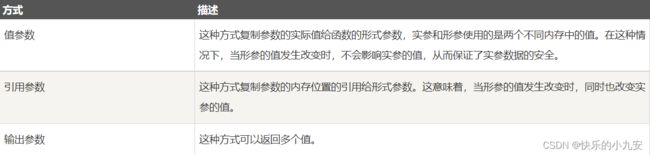
当调用带有参数的方法时,您需要向方法传递参数。在 C# 中,有三种向方法传递参数的方式:
按值传递参数
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void swap(int x, int y)
{
int temp;
temp = x; /* 保存 x 的值 */
x = y; /* 把 y 赋值给 x */
y = temp; /* 把 temp 赋值给 y */
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,b 的值: {0}", b);
/* 调用函数来交换值 */
n.swap(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,b 的值: {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}形参的值发生改变时,不会影响实参的值
按引用传递参数
ref 关键字指示按引用传递的值
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void swap(ref int x, ref int y)
{
int temp;
temp = x; /* 保存 x 的值 */
x = y; /* 把 y 赋值给 x */
y = temp; /* 把 temp 赋值给 y */
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之前,b 的值: {0}", b);
/* 调用函数来交换值 */
n.swap(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在交换之后,b 的值: {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}形参的值发生改变时,实参的值也跟着改变
按输出传递参数
out
如果你在一个方法中,返回多个相同类型的值得时候,可以考虑返回一个数组。
但是,如果返回多个不同类型的值得时候,返回数组就不行了,那么这个时候,
我们可以考虑使用out参数。
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void getValue(out int x )
{
int temp = 5;
x = temp;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a = 100;
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之前,a 的值: {0}", a);
/* 调用函数来获取值 */
n.getValue(out a);
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NumberManipulator
{
public void getValues(out int x, out int y )
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入第一个值: ");
x = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("请输入第二个值: ");
y = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NumberManipulator n = new NumberManipulator();
/* 局部变量定义 */
int a , b;
/* 调用函数来获取值 */
n.getValues(out a, out b);
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,a 的值: {0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("在方法调用之后,b 的值: {0}", b);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}这种方式可以返回多个值。
C# 可空类型(Nullable)(?)
C# 提供了一个特殊的数据类型,nullable 类型(可空类型),可空类型可以表示其基础值类型正常范围内的值,再加上一个 null 值。
例如,Nullable< Int32 >,读作"可空的 Int32",可以被赋值为 -2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647 之间的任意值,也可以被赋值为 null 值。类似的,Nullable< bool > 变量可以被赋值为 true 或 false 或 null。
在处理数据库和其他包含可能未赋值的元素的数据类型时,将 null 赋值给数值类型或布尔型的功能特别有用。例如,数据库中的布尔型字段可以存储值 true 或 false,或者,该字段也可以未定义。
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NullablesAtShow
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int? num1 = null;
int? num2 = 45;
double? num3 = new double?();
double? num4 = 3.14157;
bool? boolval = new bool?();
// 显示值
Console.WriteLine("显示可空类型的值: {0}, {1}, {2}, {3}",
num1, num2, num3, num4);
Console.WriteLine("一个可空的布尔值: {0}", boolval);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Null 合并运算符( ?? )
Null 合并运算符用于定义可空类型和引用类型的默认值。Null 合并运算符为类型转换定义了一个预设值,以防可空类型的值为 Null。Null 合并运算符把操作数类型隐式转换为另一个可空(或不可空)的值类型的操作数的类型。
如果第一个操作数的值为 null,则运算符返回第二个操作数的值,否则返回第一个操作数的值。下面的实例演示了这点:
using System;
namespace CalculatorApplication
{
class NullablesAtShow
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double? num1 = null;
double? num2 = 3.14157;
double num3;
num3 = num1 ?? 5.34; // num1 如果为空值则返回 5.34
Console.WriteLine("num3 的值: {0}", num3);
num3 = num2 ?? 5.34;
Console.WriteLine("num3 的值: {0}", num3);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}声明数组
datatype 用于指定被存储在数组中的元素的类型。
[ ] 指定数组的秩(维度)。秩指定数组的大小。
arrayName 指定数组的名称。
double[] balance;//datatype[] arrayName;初始化数组
声明一个数组不会在内存中初始化数组。当初始化数组变量时,您可以赋值给数组。
数组是一个引用类型,所以您需要使用 new 关键字来创建数组的实例。
double[] balance = new double[10];赋值给数组
您可以通过使用索引号赋值给一个单独的数组元素,比如:
double[] balance = new double[10];
balance[0] = 4500.0;您可以在声明数组的同时给数组赋值,比如:
double[] balance = { 2340.0, 4523.69, 3421.0};您也可以创建并初始化一个数组,比如:
int [] marks = new int[5] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};在上述情况下,你也可以省略数组的大小,比如:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};您也可以赋值一个数组变量到另一个目标数组变量中。在这种情况下,目标和源会指向相同的内存位置:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
int[] score = marks;访问数组元素
元素是通过带索引的数组名称来访问的。这是通过把元素的索引放置在数组名称后的方括号中来实现的
double salary = balance[9];using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */
int i,j;
/* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
n[ i ] = i + 100;
}
/* 输出每个数组元素的值 */
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++ )
{
Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", j, n[j]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}使用 foreach 循环
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */
/* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
n[i] = i + 100;
}
/* 输出每个数组元素的值 */
foreach (int j in n )
{
int i = j-100;
Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", i, j);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}看不懂回看循环部分
C# 多维数组
string [,] names;//二维数组
int [ , , ] m;//三维数组初始化二维数组
多维数组可以通过在括号内为每行指定值来进行初始化。下面是一个带有 3 行 4 列的数组
int [,] a = new int [3,4] {
{0, 1, 2, 3} , /* 初始化索引号为 0 的行 */
{4, 5, 6, 7} , /* 初始化索引号为 1 的行 */
{8, 9, 10, 11} /* 初始化索引号为 2 的行 */
};访问二维数组元素
二维数组中的元素是通过使用下标(即数组的行索引和列索引)来访问的
int val = a[2,3];eg:
using System;
namespace ArrayApplication
{
class MyArray
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 一个带有 5 行 2 列的数组 */
int[,] a = new int[5, 2] {{0,0}, {1,2}, {2,4}, {3,6}, {4,8} };
int i, j;
/* 输出数组中每个元素的值 */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i,j]);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}C# 交错数组 传递数组给函数 参数数组 Array 类 (后面补写)
C# 字符串(String)
在 C# 中,您可以使用字符数组来表示字符串,但是,更常见的做法是使用 string 关键字来声明一个字符串变量。string 关键字是 System.String 类的别名。
您可以使用以下方法之一来创建 string 对象:
通过给 String 变量指定一个字符串
通过使用 String 类构造函数
通过使用字符串串联运算符( + )
通过检索属性或调用一个返回字符串的方法
通过格式化方法来转换一个值或对象为它的字符串表示形式
using System;
namespace StringApplication
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//字符串,字符串连接
string fname, lname;
fname = "Rowan";
lname = "Atkinson";
string fullname = fname + lname;
Console.WriteLine("Full Name: {0}", fullname);
//通过使用 string 构造函数
char[] letters = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l','o' };
string greetings = new string(letters);
Console.WriteLine("Greetings: {0}", greetings);
//方法返回字符串
string[] sarray = { "Hello", "From", "Tutorials", "Point" };
string message = String.Join(" ", sarray);
Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", message);
//用于转化值的格式化方法
DateTime waiting = new DateTime(2012, 10, 10, 17, 58, 1);
string chat = String.Format("Message sent at {0:t} on {0:D}",
waiting);
Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", chat);
Console.ReadKey() ;
}
}
}后续每天补
网站
C# 运算符 | 菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)