Spring BOOT 手写一个starter并使用这个starter
1、stater工程的命名
starter 是一个开箱即用的组件,减少不必要的重复代码,重复配置。例如,在mavne项目进行配置的时候,我们需要引用 spring-boot-starter-parent。
Spring 官方定义的 starter 通常命名遵循的格式为 spring-boot-starter-{name},例如 spring-boot-starter-web。
非官方 starter 命名应遵循 {name}-spring-boot-starter 的格式,例如,dubbo-spring-boot-starter。
2、需求
写一个序列化的插件,并且可以自由的选择 fastjson 还是 gson,如果没选的情况下默认选择fastjson。
3、stater步骤
创建一个Spring Boot项目,这里项目名字叫 jackformat-spring-boot-starter
3.1 引入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-autoconfigure
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.56
com.google.code.gson
gson
2.2.4
注意: 如果在后续引用stater工程中出现 :Unable to read meta-data for class 这个错误
处理意见,可以参考这篇博客意见:传送门
参考博客里面是对依赖进行处理,防止stater引用失败。
3.2 格式化接口
3.3 配置类
先定义一个配置类,具体的实现逻辑在具体的实现类里面实现。
public interface FormatProcessor {
/**
* 定义一个格式化的方法
*/
String format(T obj);
} 下面是两个具体的配置类
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class GsonFormatProcessor implements FormatProcessor{
@Override
public String format(T obj) {
return "GsonFormatProcessor" + new Gson().toJson(obj);
}
} import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class FastJsonFormatProcessor implements FormatProcessor{
@Override
public String format(T obj) {
return "FastJsonFormatProcessor:" + JSON.toJSONString(obj);
}
} 3.3.1 条件配置
这个条件配置里面用到了条件注解,如果fastjson和gson类存在的情况下才加载对应的实现类。
因为在pom文件里面都引用了,所以在这里是都会被加载的。
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
@Configuration
public class FormatAutoConfiguration {
/**
* @return
* @ConditionalOnClass条件注解。如果 fastjson 类存在的情况下才加载对应的实现类
* 同一个接口,有几种不同的实现类时,@Autowired 是按类型注入的,不知道要选哪一个.
* 按照第二点需求,用户在没选的情况下默认选择 fastjson,所以这里给 fastjson 的实现上打上 @Primary
*/
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON")
@Bean
@Primary
public FormatProcessor fastJsonFormat() {
return new FastJsonFormatProcessor();
}
/**
* 如果 Gson 类存在的情况下才加载对应的实现类
*
* @return
*/
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "com.google.gson.Gson")
@Bean
public FormatProcessor gsonJsonFormat() {
return new FastJsonFormatProcessor();
}
}代码段里面有 @Primary 注解,这是为了用户在没有手动选择的时候,默认选择fastjson。(如果自动注入选的是@Autowired的话,因为@Autowired默认是类型注入的,不知道选择哪一种类型)
3.3.2 读取配置
这个配置类主要是用来读取用户的选择,作用和@Value作用一致
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = FormatProperties.ORMAT_PREFIX)
public class FormatProperties {
public static final String ORMAT_PREFIX = "jackluo.format";
private String type;
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}3.4 序列化实现类
import com.jackluo.autoconfiguration.FormatProcessor;
public class FormatTemplate {
private FormatProcessor formatProcessor;
public FormatTemplate(FormatProcessor formatProcessor) {
this.formatProcessor = formatProcessor;
}
public String doFormat(T obj) {
return formatProcessor.format(obj);
}
} 序列化实现类,这个是来提供给用户序列化的。
3.5 逻辑配置类
import com.jackluo.format.FormatTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Import(FormatAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(FormatProperties.class)
@Configuration
public class JackluoFormatConfiguration {
@Bean
public FormatTemplate helloFormatTemplate(FormatProperties formatProperties, @Qualifier("fastJsonFormat") FormatProcessor formatProcessor) {
if ("fastjson".equals(formatProperties.getType())) {
return new FormatTemplate(new FastJsonFormatProcessor());
}
if ("gson".equals(formatProperties.getType())) {
return new FormatTemplate(new GsonFormatProcessor());
}
return new FormatTemplate(formatProcessor);
}
}@Import 导入配置类,就是将该配置类中的 Bean 注入到容器
@EnableConfigurationProperties 这是在将属性类激活,注入到容器中,也可以用 @Bean 的方式
@Configuration 说明这是一个配置类
流程是 FormatProperties 属性类注入到容器当中,如果是fastjson就去走fastjaon的逻辑实现类;反之是gson也是一样。如果没有以上情况,就走上面配置的默认项。
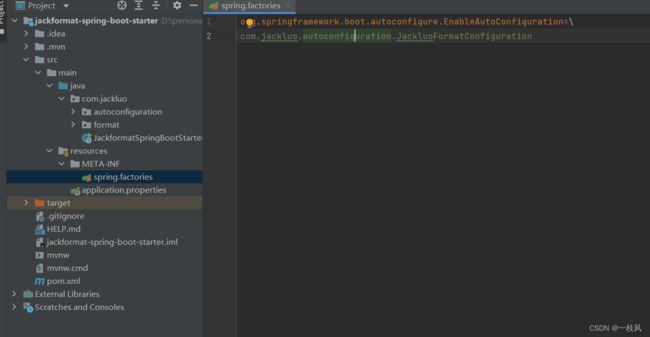
3.6 创建 META-INF/spring.factories
因为springboot在启动的时候是读取该文件下面的配置类,从而将Bean加载到容器当中。所以我们写stater也是一样的道理。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
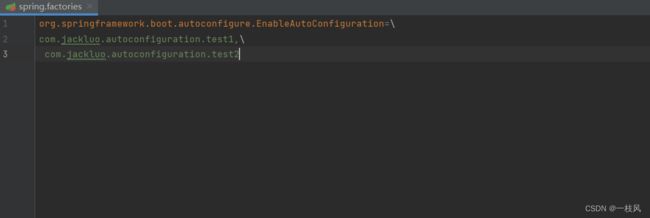
com.jackluo.autoconfiguration.JackluoFormatConfiguration注意:有多个文件的时候是需要用 ,\ 来隔开的。如:
以上。一个手写的stater就OK了,我们需要引用直接打jar包在其他项目直接引用即可。
下面是引用过程。
4、 引用-测试
4.1 打包
4.2 引入依赖
com.jackluo
jackformat-spring-boot-starter
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
这个依赖命名方式就是我们写的stater工程的名称,这个一眼就是能看出来的。
4.3 选用序列化
在.yml文件中配置我们需要选用的序列化方式。
我们选用gson。测试完可以试试什么也不选出来什么结果
4.4 调用
定义一个实体类,定义一个controller,直接调用即可。
4.5结果
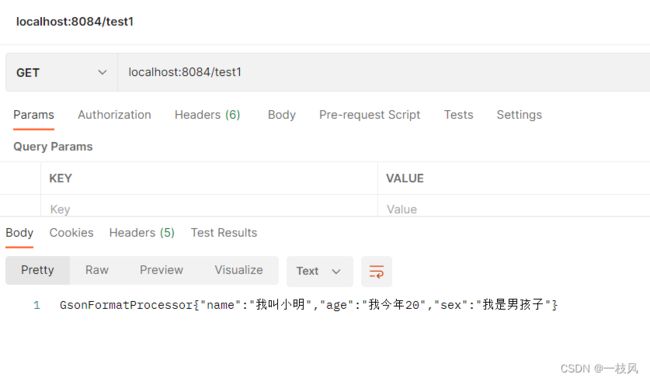
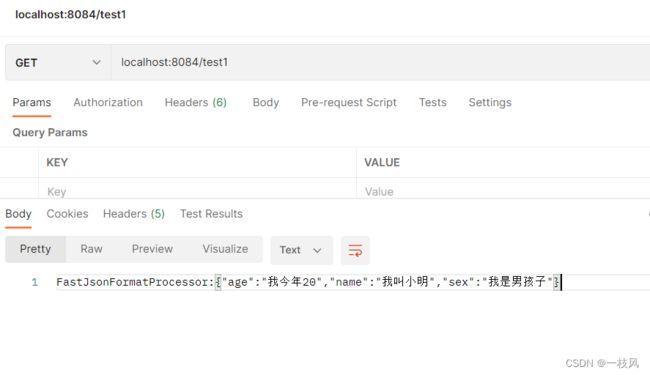
当选用gson的时候出来的是:GsonFormatProcessor。
默认什么也不选的时候,出现的是:FastJsonFormatProcessor。
和我们在stater的结果是一样的。
至此,一个完整的stater和引用已经OK了。