Spring注解之@Value
@Value注解位于spring-beans中,以下是@Value注解的源码:
package org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Value {
String value();
}
由上可以看出:
- @Value可以修饰属性、方法、参数、注释类型。
- 编译器会将 @Value注解的信息保留在 .class 文件中,并且能被虚拟机读取。
- @Value可以出现在 javadoc 中。
- 该注解中的
String value();意味着,@Value能指定参数。
@Value的用法
@Value可以获取配置文件中的值,设置给属性,也可以引用Bean的属性值。下面通过SpringBoot项目讲解@Value的用法。
一、@Value引用配置文件中的属性值
使用@Value引用配置文件中的属性值的方式为
@Value("${属性名}")
application.yml的配置
application.yml文件的配置如下:
ymlname: only-yml
student:
name: yml里的name
age: 20
tel : 666
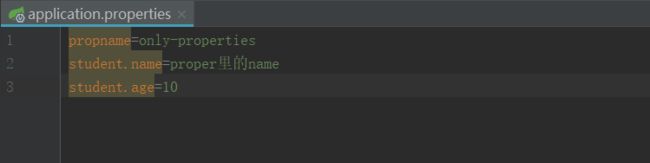
application.properties的配置
application.properties文件的配置如下:
测试用Controller
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class TestValueController {
// 只在application.yml中配置
@Value("${ymlname}")
private String ymlname;
// 只在application.properties中配置
@Value("${propname}")
private String propname;
// application.yml和application.properties均有该配置
@Value("${student.name}")
private String name;
// 配置文件中的字段名和属性名不一致
@Value("${student.age}")
private int nianling;
// application.yml和application.properties均没有该配置,设置默认值
@Value("${student.score:100}")
private int score;
// application.yml有该配置,同时设置默认值
@Value("${student.tel:888}")
public int tel;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/test")
public String testValue() {
return "ymlname —— " + ymlname + "
" +
"propname —— " + propname + "
" +
"name —— " + name + "
" +
"nianling —— " + nianling + "
" +
"score —— " + score + "
" +
"tel —— " + tel;
}
}
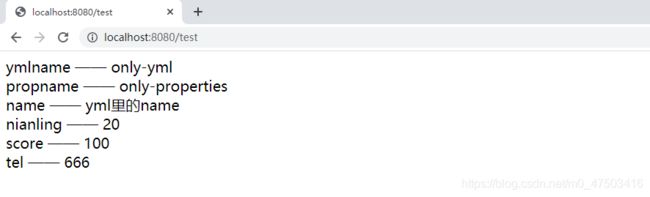
启动项目,查看结果
启动SpringBoot项目,浏览器输入localhost:8080/test,界面显示如下。
二、@Value作用于静态变量
正常情况下 @Value不可作用于静态属性。如下例。
启动类上做如下修改:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootTestApplication {
@Value("${student.name}")
public static String name;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootTestApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("name: " + name);
}
}
打印结果如下:

通过上例可以看出,使用@Value注解修饰静态属性,启动项目时不会报错,但是也不会给该静态属性设置值。
可以通过set方法给静态属性设置配置文件中的属性值。
public static String name;
@Value("${student.name}")
public void setName(String param) {
name = param;
}
三、@Value引用Bean的属性值
使用@Value引用Bean的属性值的方式和引用配置文件中的属性值方式类似。使用方式为
@Value("#{bean的名字.属性值}")
以通过@Value注解引用User实例的name属性值为例;
User类:
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String name;
private String password;
}
配置一个TestConfig类,用于产生一个name为zhangsan,password为66666的名为user的bean实例交由spring容器管理。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TestConfig {
@Bean(name = "user")
public User getUser() {
return new User("zhangsan","66666");
}
}
TestBeanPro 类用于测试,其有一个userName属性,通过@Value注解将容器中名为user的bean的name属性注入给userName。@PostConstruct注解的方法于该类的构造方法执行完成后执行。在本例中,该初始化方法用于打印user的name属性是否引用成功。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TestBeanPro {
@Value("#{user.name}")
private String userName;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
log.info("***************************** userName:{}.", userName);
}
}
启动项目后通过控制台日志可以看到,userName的值为zhangsan。控制台日志如下
![]()
总结
从以上测试结果可以看出:
- application.yml和application.properties中配置的值都可以通过@Value注解获取;
- 若application.yml和application.properties同时配有同一个变量的值,则以application.yml的值为主;
- 配置文件中的字段名和@Value修饰的属性名可以不一致
- @Value若从配置文件中获取不到值,则设置的默认值才生效。
- 若配置文件中有配置,则默认值不生效。
通过对@Value的以上分析,我们还不难看出,SpringBoot加载配置文件的顺序为.yml > .properties。即yml类型的优先级高于properties类型的配置文件。