FigDraw 25. SCI文章中绘图二维密度图及组合图
点击关注,桓峰基因
桓峰基因公众号推出基于R语言绘图教程并配有视频在线教程,目前整理出来的教程目录如下:
FigDraw 1. SCI 文章的灵魂 之 简约优雅的图表配色
FigDraw 2. SCI 文章绘图必备 R 语言基础
FigDraw 3. SCI 文章绘图必备 R 数据转换
FigDraw 4. SCI 文章绘图之散点图 (Scatter)
FigDraw 5. SCI 文章绘图之柱状图 (Barplot)
FigDraw 6. SCI 文章绘图之箱线图 (Boxplot)
FigDraw 7. SCI 文章绘图之折线图 (Lineplot)
FigDraw 8. SCI 文章绘图之饼图 (Pieplot)
FigDraw 9. SCI 文章绘图之韦恩图 (Vennplot)
FigDraw 10. SCI 文章绘图之直方图 (HistogramPlot)
FigDraw 11. SCI 文章绘图之小提琴图 (ViolinPlot)
FigDraw 12. SCI 文章绘图之相关性矩阵图(Correlation Matrix)
FigDraw 13. SCI 文章绘图之桑葚图及文章复现(Sankey)
FigDraw 14. SCI 文章绘图之和弦图及文章复现(Chord Diagram)
FigDraw 15. SCI 文章绘图之多组学圈图(OmicCircos)
FigDraw 16. SCI 文章绘图之树形图(Dendrogram)
FigDraw 17. SCI 文章绘图之主成分绘图(pca3d)
FigDraw 18. SCI 文章绘图之矩形树状图 (treemap)
FigDraw 19. SCI 文章中绘图之坡度图(Slope Chart)
FigDraw 20. SCI文章中绘图之马赛克图 (mosaic)
FigDraw 21. SCI文章中绘图之三维散点图 (plot3D)
FigDraw 22. SCI文章中绘图之核密度及山峦图 (ggridges)
FigDraw 23. SCI文章中绘图二维散点图与统计图组合
FigDraw 24. SCI文章中绘图二维直方图及组合图
前言
二维密度图显示了两个数值变量之间的关系,一个在x轴上表示,另一个在Y轴上表示,与散点图类似,然后计算二维空间中特定区域内的观测数,并用颜色梯度表示。
软件包安装
这里我们利用 ggplot2 软件包里面 geom_density() 和 stat_density2d(), 即可实现二维密度图的绘制。
if(!require(ellipse))
install.packages("ellipse")
例子实操
一般例子
等高线密度图
library(ggplot2)
#### 二维密度图
head(faithful)
## eruptions waiting
## 1 3.600 79
## 2 1.800 54
## 3 3.333 74
## 4 2.283 62
## 5 4.533 85
## 6 2.883 55
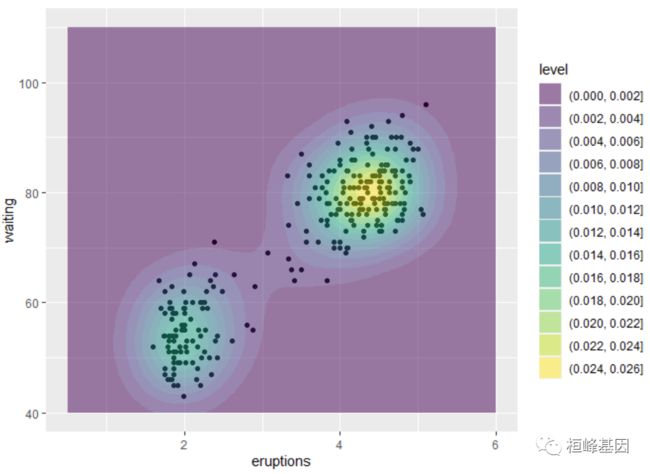
m <- ggplot(faithful, aes(x = eruptions, y = waiting)) + geom_point() + xlim(0.5,
6) + ylim(40, 110)
# contour lines
m + geom_density_2d()
等高带
# contour bands
m + geom_density_2d_filled(alpha = 0.5)
等高线和等高带
# contour bands and contour lines
m + geom_density_2d_filled(alpha = 0.5) + geom_density_2d(size = 0.25, colour = "black")
分组变量绘制等高线
set.seed(4393)
dsmall <- diamonds[sample(nrow(diamonds), 1000), ]
d <- ggplot(dsmall, aes(x, y))
# If you map an aesthetic to a categorical variable, you will get a set of
# contours for each value of that variable
d + geom_density_2d(aes(colour = cut))
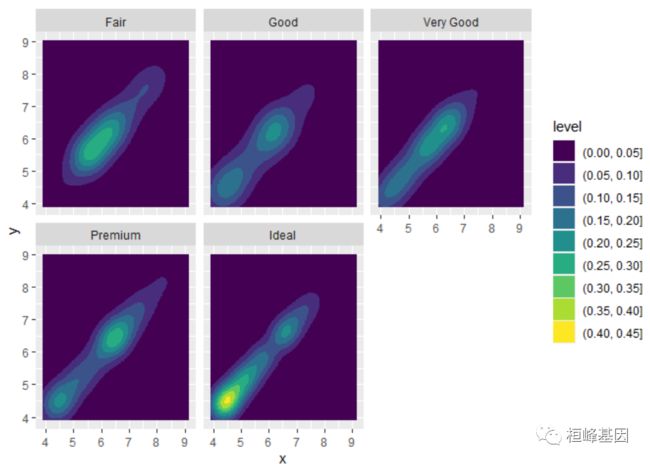
多面密度图
多么填充密度图绘制参数 facet_wrap(vars(cut))
# If you draw filled contours across multiple facets, the same bins are used
# across all facets
d + geom_density_2d_filled() + facet_wrap(vars(cut))
峰值强度相同
如果你想确保每个方面的峰值强度是相同的,可是使用contour_var = "ndensity
# If you want to make sure the peak intensity is the same in each facet, use
# `contour_var = 'ndensity'`.
d + geom_density_2d_filled(contour_var = "ndensity") + facet_wrap(vars(cut))
数据的强度衡量
如果你想根据每组观察的数量来衡量强度,使用 contour_var = “count”:
# If you want to scale intensity by the number of observations in each group,
# use `contour_var = 'count'`.
d + geom_density_2d_filled(contour_var = "count") + facet_wrap(vars(cut))
关闭等高线
如果我们关闭等高线,我们可以使用其他geoms,geom = “raster”,如下:
# If we turn contouring off, we can use other geoms, such as tiles:
d + stat_density_2d(geom = "raster", aes(fill = after_stat(density)), contour = FALSE) +
scale_fill_viridis_c()
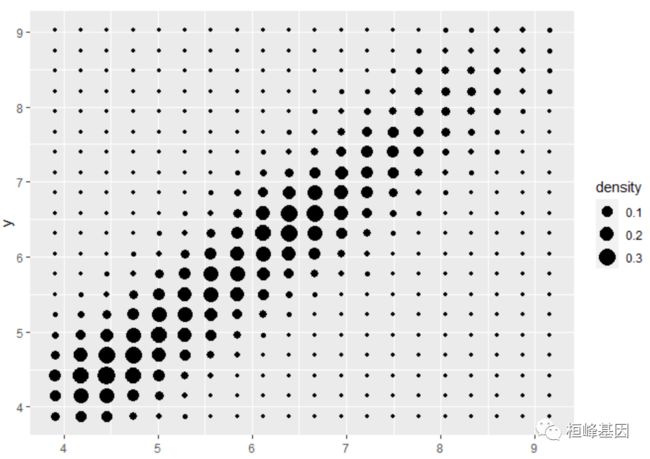
geom = “point”:
# Or points:
d + stat_density_2d(geom = "point", aes(size = after_stat(density)), n = 20, contour = FALSE)
不同类型的二维核密度统计图
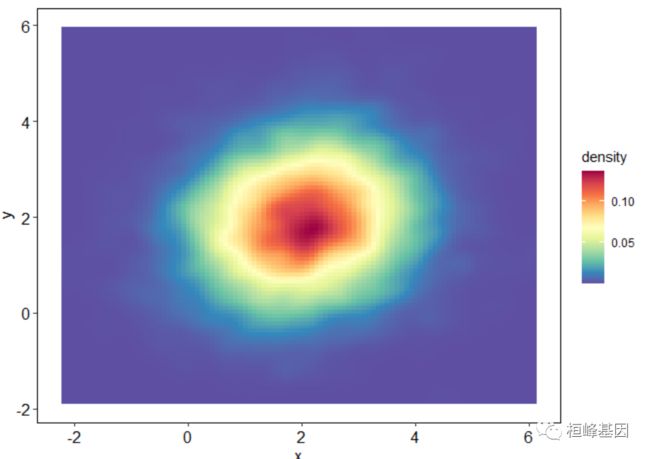
矩形二维密度图
矩形二维密度图使用函数 stat_density_2d()
library(ggplot2)
library(RColorBrewer)
colormap<- rev(brewer.pal(11,'Spectral'))
# Create normally distributed data for plotting
x1 <- rnorm(mean=1.5, 5000)
y1 <- rnorm(mean=1.6, 5000)
x2 <- rnorm(mean=2.5, 5000)
y2 <- rnorm(mean=2.2, 5000)
x<-c(x1,x2)
y<-c(y1,y2)
df <- data.frame(x,y)
ggplot(df, aes(x,y))+
stat_density_2d(geom ="raster",aes(fill = ..density..),contour = F)+# "polygon")+#geom_raster(aes(fill = density)) +
scale_fill_gradientn(colours=colormap)+#, trans="log"scale_fill_gradientn(colours=c("#CEF5FF","#00B8E5","#005C72"),name = "Frequency",na.value=NA)+
#scale_fill_gradientn(colours=c(brewer.pal(7,"Set2")[3],"white",brewer.pal(7,"Set2")[2]),na.value=NA)+
#geom_contour(acolour = "white") +
theme_classic()+
theme(panel.background=element_rect(fill="white",colour="black",size=0.25),
#panel.grid.major = element_line(colour = "grey60",size=.25,linetype ="dotted" ),
#panel.grid.minor = element_line(colour = "grey60",size=.25,linetype ="dotted" ),
#text=element_text(size=15),
#plot.title=element_text(size=15,family="myfont",hjust=.5),
axis.line=element_line(colour="black",size=0.25),
axis.title=element_text(size=13,face="plain",color="black"),
axis.text = element_text(size=12,face="plain",color="black"),
legend.position="right"
)
圆形二维密度图
圆形二维密度图使用stat_density2d()
ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) +
stat_density2d(geom ="polygon",aes(fill = ..level..),bins=30 )+#alpha=..level..,aes( fill=..level..), size=2, bins=10, geom="polygon") +
#stat_density_2d(geom = "point", aes(size = ..density..), n = 20, contour = FALSE)
scale_fill_gradientn(colours=colormap)+#scale_fill_gradient(low = "yellow", high = "red") +
#scale_alpha(range = c(0.00, 0.5), guide = FALSE) +
#geom_density2d( colour=NA,bins=30) +#
#geom_point() +
guides(alpha=FALSE) +
xlim(-2,6)+
ylim(-2,6)+
theme_classic()+
theme(panel.background=element_rect(fill="white",colour="black",size=0.25),
#panel.grid.major = element_line(colour = "grey60",size=.25,linetype ="dotted" ),
#panel.grid.minor = element_line(colour = "grey60",size=.25,linetype ="dotted" ),
#text=element_text(size=15),
#plot.title=element_text(size=15,family="myfont",hjust=.5),
axis.line=element_line(colour="black",size=0.25),
axis.title=element_text(size=13,face="plain",color="black"),
axis.text = element_text(size=12,face="plain",color="black"),
legend.position="right"
)
组合图
二维核密度估计图+一维核密度估计图
library(ggplot2)
library(ellipse)
library(gridExtra)
library(plyr)
library(RColorBrewer)
Colormap <- colorRampPalette(rev(brewer.pal(11,'Spectral')))(32)
N<-300
x1 <- rnorm(mean=1.5, N)
y1 <- rnorm(mean=1.6, N)
x2 <- rnorm(mean=2.5, N)
y2 <- rnorm(mean=2.2, N)
data <- data.frame(x=c(x1,x2),y=c(y1,y2))
# 绘制上边的直方图,并将各种标注去除
hist_top <- ggplot(data, aes(x)) +
geom_density(colour="black",fill='#5E4FA2',size=0.25)+
theme_void()
# 同样绘制右边的直方图
hist_right <- ggplot(data, aes(y)) +
geom_density(colour="black",fill='#5E4FA2',size=0.25)+
theme_void()+
coord_flip()
scatter<-ggplot(data, aes(x, y)) +
stat_density2d(geom ="polygon",aes(fill = ..level..),bins=30 )+#alpha=..level..,aes( fill=..level..), size=2, bins=10, geom="polygon") +
scale_fill_gradientn(colours=Colormap)+#, trans="log"
#geom_point(size=1) +
theme_minimal()+
theme(panel.background=element_rect(fill="white",colour="black",size=0.25),
#panel.grid.major = element_line(colour = "grey60",size=.25,linetype ="dotted" ),
#panel.grid.minor = element_line(colour = "grey60",size=.25,linetype ="dotted" ),
#text=element_text(size=15),
#plot.title=element_text(size=15,family="myfont",hjust=.5),
axis.line=element_line(colour="black",size=0.25),
axis.title=element_text(size=13,face="plain",color="black"),
axis.text = element_text(size=12,face="plain",color="black"),
legend.position=c(0.9,0.22),
legend.background=element_blank()
)
empty <- ggplot() +
theme(panel.background=element_blank(),
axis.title.x=element_blank(),
axis.title.y=element_blank(),
axis.text.x=element_blank(),
axis.text.y=element_blank(),
axis.ticks=element_blank())
# 最终的组合
grid.arrange(hist_top, empty, scatter, hist_right, ncol=2, nrow=2, widths=c(4,1), heights=c(1,4))
例子
library(cowplot)
top_hist <- ggplot(df, aes(x)) + geom_density(bins = 35, fill = "#FF0000", colour = "black") +
theme_void()
right_hist <- ggplot(df, aes(y)) + geom_density(bins = 35, fill = "#FF0000", colour = "black") +
coord_flip() + theme_void()
center <- ggplot(df, aes(x, y)) + stat_density2d(geom = "polygon", aes(fill = ..level..),
bins = 30) + scale_fill_gradientn(colours = rainbow(10)) + theme(panel.background = element_rect(fill = "white",
colour = "black", size = 0.25), axis.line = element_line(colour = "black", size = 0.25),
axis.title = element_text(size = 13, face = "plain", color = "black"), axis.text = element_text(size = 12,
face = "plain", color = "black"), legend.position = c(0.1, 0.8), legend.background = element_blank())
p1 <- plot_grid(top_hist, center, align = "v", nrow = 2, rel_heights = c(1, 4))
p2 <- plot_grid(NULL, right_hist, align = "v", nrow = 2, rel_heights = c(1, 4))
plot_grid(p1, p2, ncol = 2, rel_widths = c(4, 1))
软件包里面自带的例子,我这里都展示了一遍为了方便大家选择适合自己的图形,另外需要代码的将这期教程转发朋友圈,并配文“学生信,找桓峰基因,铸造成功的你!”即可获得!
桓峰基因,铸造成功的您!
有想进生信交流群的老师可以扫最后一个二维码加微信,备注“单位+姓名+目的”,有些想发广告的就免打扰吧,还得费力气把你踢出去!