Pytorch搭建ResNet(附完整代码)
Pytorch搭建ResNet
1. 问题描述
1.1 ResNet
卷积神经网络逐渐取代传统算法,成为处理计算机视觉任务的核心,ResNet[1]的提出更是CNN图像史上一件里程碑事件。当网络深度增加时,网络准确度出现饱和甚至下降,残差学习的提出解决了网络退化的问题。ResNet通过shortcut的方法让信息跨层传播,被跨越的层拟合的就是shortcut连接的两层之间的残差。
Shortcut的具体方法如下:
存在 H ( x ) = F ( x ) + x H(x)=F(x)+x H(x)=F(x)+x,
当 F ( x ) = 0 F(x)=0 F(x)=0时, H ( x ) H(x) H(x)就是恒等映射;
当 F ( x ) ≠ 0 F(x)\neq 0 F(x)=0时,就能在恒等映射的基础上补充学习残差。
本文的改进包括:
- 调整残差块内部顺序为,先经过ReLU后再进行加和
- 通过方法
res_layer_maker动态地生成含有多个连续卷积核的残差块 - 在网络中尝试加入Bottlenck结构节省计算开销,先压缩通道数,经过3x3卷积核后再提升通道数
- 先使用Adam算法进行快速下降,再用SGD调优[5]
2. 数据集描述
2.1 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10数据集由6万张尺寸大小为32x32的图片组成,其中图片分为10类,每类有6千张图片。这些图片中有5万张被划分为训练集,1万张被划分为测试集。

3. 实验结果与分析
3.1 ResNet
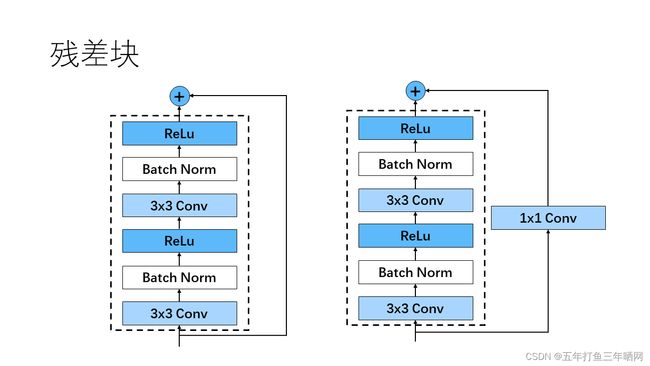
3.1.1 残差块
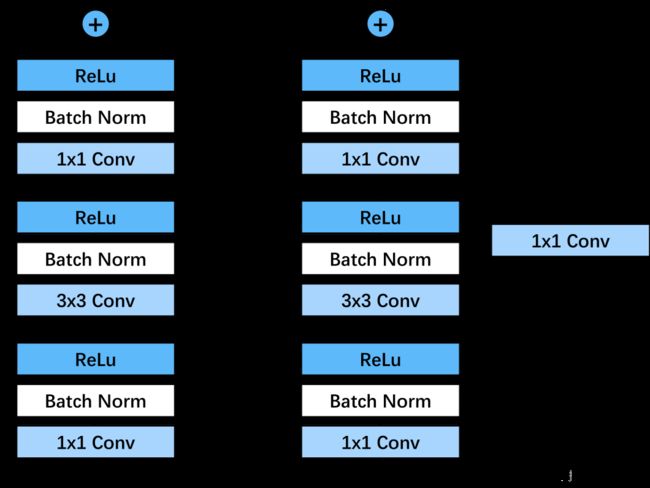
ResNet继承了VGG的经典网络结构,将其中细节部分替换为一个个残差块。其中,我设计的残差块分为图示两种:
这两种残差块相较原论文更改了与shortcut相加的位置,他们的区别是shortcut有无一个1x1的卷积核,该1x1卷积核主要用于跨层时匹配输入特征和输出特征的通道数。
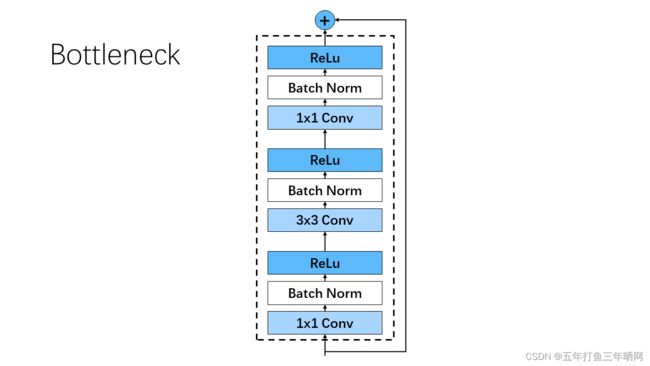
3.1.2 Bottleneck
Bottleneck一般使用在较深的神经网络中,比如ResNet101。其主要目的是为了减少参数的数量,从而减少计算量。我搭建的Bottleneck功能为先压缩通道数,再提升通道数,具体架构如下图所示:
其中,首尾的两个1x1卷积核分别用于降低和升高特征通道数,使特征通道数经过Bottleneck后不发生改变。中间是一个常规3x3卷积核,每次通过卷积核后都进行数据归一化与ReLu激活处理。
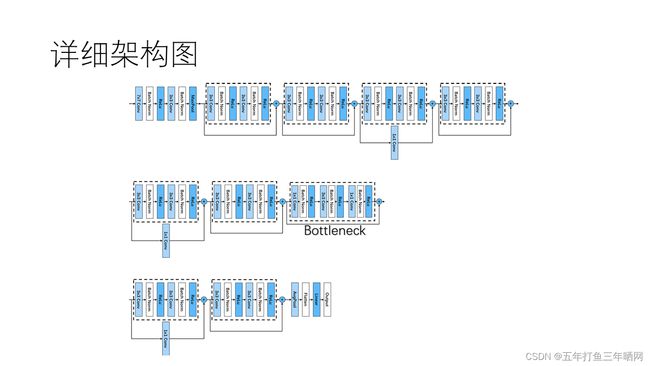
3.1.3 架构图与描述
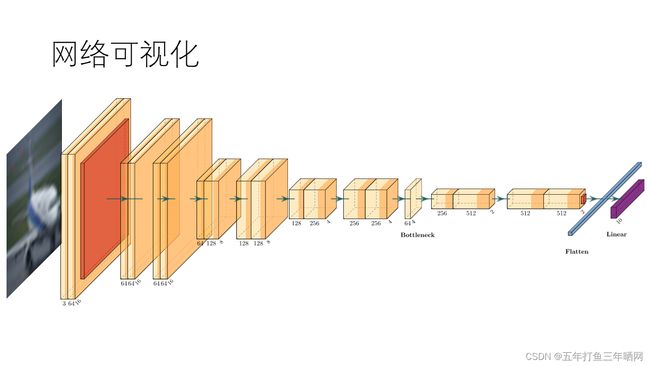
详细的网络架构图见文末附录,以下是使用基于LaTeX的PlotNeuralNet[4]绘制的可视化架构图:
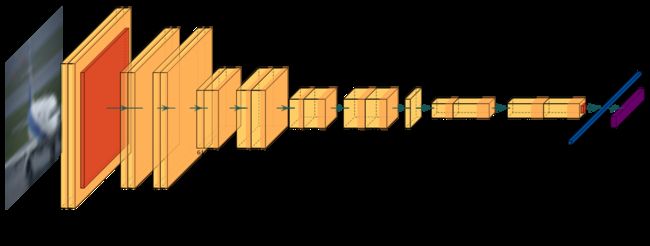
其中,特征先进入一个7x7的卷积核,步长取2,填充取3,经过BatchNorm与ReLU激活后,通过一个3x3的最大池化层,这是经典的VGG网络结构。
然后,特征通过8个设计结构相同的残差块,残差块的两种设计结构已经在上文中给出。当经过了6个残差块后,接上了一个Bottleneck,后续连接剩下的残差块。从我绘制的简化架构图中可以看出,特征在部分残差块中宽高减半,通道数加倍;在通过Bottleneck时,通道数发生压缩与提高,图片宽高不发生改变。
最后,特征通过一个自适应平均池化层将宽高尺寸压缩到1x1,经过Flatten后变成长度为512的向量,通过一个全连接层将输出降至10维,以对应10种分类。
3.1.4 损失函数变化
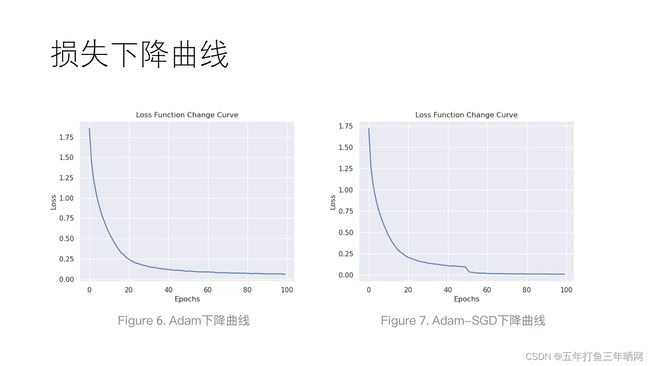
在模型训练过程中,我选取交叉熵作为损失函数。以下是训练100epochs的损失下降曲线:

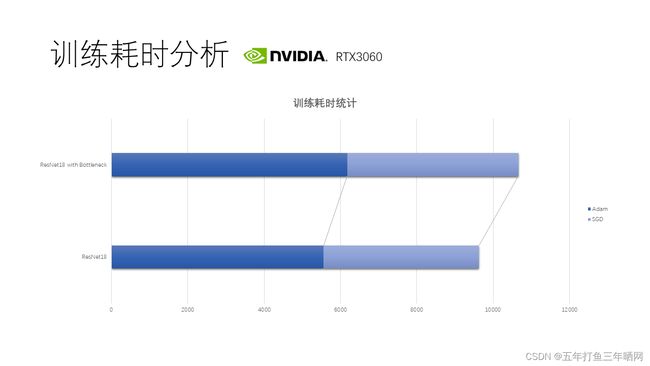
第一次训练全程使用Adam优化器,第二次训练中先使用Adam训练50epochs至损失下降平缓处,后切换至SGD优化器训练50epochs。训练在RTX3060上进行,Adam训练50epochs耗时93分钟,SGD训练耗时68分钟,总耗时161分钟。使用Adam优化器比SGD在相同网络结构与损失函数下耗时增加30%左右。
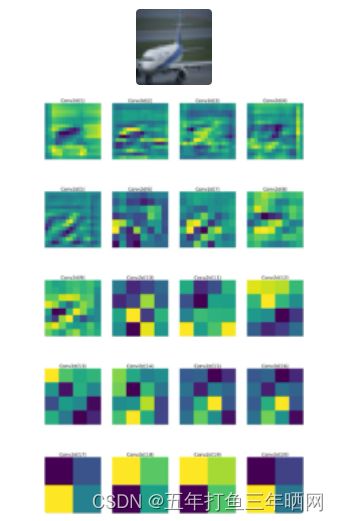
3.1.5 可视化卷积层输出
模型完成训练后,选取数据集中的一架飞机图片作为输入,除shortcut外所有卷积核的输出可视化呈现如下:
从图中可以看出,conv1提取的是背景特征,conv2提取了飞机的上边缘轮廓,conv3提取了机身的大致轮廓。随着网络层的深入,后续卷积核提取的特征逐渐变得抽象。
3.1.6 测试正确率与计算耗时
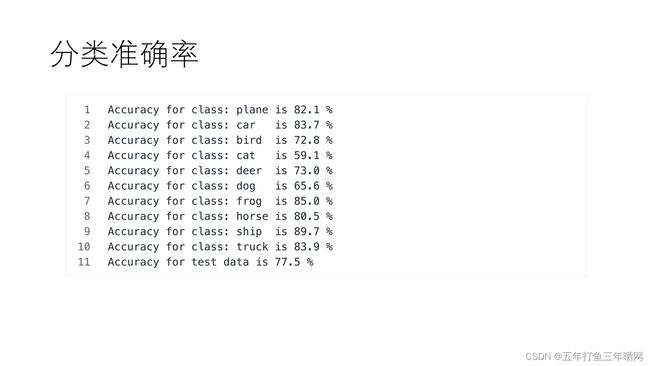
从以下输出可以看出模型对船的分类准确率最高,对猫的分类准确率最低,对测试集的平均分类准确率为77.5%。
Accuracy for class: plane is 82.1 %
Accuracy for class: car is 83.7 %
Accuracy for class: bird is 72.8 %
Accuracy for class: cat is 59.1 %
Accuracy for class: deer is 73.0 %
Accuracy for class: dog is 65.6 %
Accuracy for class: frog is 85.0 %
Accuracy for class: horse is 80.5 %
Accuracy for class: ship is 89.7 %
Accuracy for class: truck is 83.9 %
Accuracy for test data is 77.5 %
在网络中增加bottleneck结构,与之前采取相同的训练方案后,在测试集上的分类正确率几乎无变化,训练时间增加了10%。我认为bottleneck结构用在更深的网络中才能发挥出减少参数量、减少计算量的优点,本网络中计算耗时增加是因为网络较浅,新增卷积核需要的计算量多于其结构节省的计算量。
与网络上其它resnet相比,准确率过低,分析认为是对图片进行的预处理与图像变换过于简单(transforms)。
4. 引用
[1] He, Kaiming, et al. “Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition.” [1512.03385] Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition, 10 Dec. 2015, http://export.arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.
[2] Goodfellow, Ian J., et al. “Generative Adversarial Networks.” ArXiv.org, 10 June 2014, https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661.
[3] Radford, Alec, et al. “Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks.” ArXiv.org, 7 Jan. 2016, https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434.
[4] Iqbal, Haris. “Harisiqbal88/PlotNeuralNet v1.0.0.” Zenodo, 25 Dec. 2018, https://zenodo.org/record/2526396.
[5] Bottou, Léon. “Stochastic Gradient Descent Tricks.” Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2012, pp. 421–436., https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35289-8_25.
5. 附录
5.1 ResNet总架构图
5.2 完整代码
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import time
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
"""
残差块
"""
def __init__(self, input_channels, output_channels, use_1x1conv=False, strides=1):
"""
:param input_channels: 输入的通道数
:param output_channels: 输出的通道数
:param use_1x1conv: 是否使用1x1的卷积核[默认不使用]
:param strides: 滑动步长
"""
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=strides)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(output_channels, output_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=strides)
else:
self.conv3 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channels)
def forward(self, x):
y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
y = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(y)))
if self.conv3:
x = self.conv3(x)
y = y + x
return y
class BottleNeck(nn.Module):
"""
Bottleneck瓶颈层
"""
def __init__(self, input_channels, output_channels, use_1x1conv=False, strides=1):
"""
:param input_channels: 输入的通道数
:param output_channels: 输出的通道数
:param use_1x1conv: 是否使用1x1的卷积核[默认不使用]
:param strides: 滑动步长
"""
super().__init__()
mid_channels = input_channels
if input_channels / 4 != 0:
mid_channels = int(mid_channels / 4)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=strides)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, output_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=strides)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=strides)
else:
self.conv4 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channels)
def forward(self, x):
y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
y = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(y)))
y = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(y)))
if self.conv4:
x = self.conv4(x)
y = y + x
return y
class MyResNet(nn.Module):
"""
残差网络
"""
_loss = []
_loss4epochs = []
model_weights = []
conv_layers = []
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self._loss.clear()
self._loss4epochs.clear()
self.bl1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
self.bl2 = nn.Sequential(*self.res_layer_maker(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
self.bl3 = nn.Sequential(*self.res_layer_maker(64, 128, 2))
self.bl4 = nn.Sequential(*self.res_layer_maker(128, 256, 2))
self.bottleneck = BottleNeck(256, 256)
self.bl5 = nn.Sequential(*self.res_layer_maker(256, 512, 2))
self.pool1 = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear = nn.Linear(512, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.bl1(x)
x = self.bl2(x)
x = self.bl3(x)
x = self.bl4(x)
x = self.bottleneck(x)
x = self.bl5(x)
x = self.linear(self.flatten(self.pool1(x)))
return x
@staticmethod
def res_layer_maker(input_channels, output_channels, num_residuals,
first_block=False):
"""
调用残差块,对第一个残差块进行处理(1x1卷积核),并连接重复的残差块
:param input_channels: 输入的通道数
:param output_channels: 输出的通道数
:param num_residuals: 残差块重复的次数
:param first_block: 是否是第一个残差块
:return: 处理好的残差块
"""
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(ResBlock(input_channels, output_channels,
use_1x1conv=True, strides=2))
else:
blk.append(ResBlock(output_channels, output_channels))
return blk
def train_net(self, dataloader, epochs=2, device=None, criterion='CrossEntropyLoss',
optimizer='SGD'):
"""
训练网络
:param dataloader: 加载数据集
:param epochs: 训练的epochs数
:param device: 运行在cpu或gpu
:param criterion: 损失函数种类
:param optimizer: 优化算法种类
"""
self.train() # 模型设置为训练模式
if optimizer == 'SGD':
optimizer = optim.SGD(self.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
elif optimizer == 'Adam':
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.001)
if criterion == 'CrossEntropyLoss':
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
if not device:
# 如果未给出device,就将第一个网络层所在位置设成device
device = next(iter(self.parameters())).device
self.to(device)
start_time = time.perf_counter()
for epoch in range(epochs): # 对数据集循环多次
running_loss = 0.0
loss4epoch = []
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
# 获取输入; data是[inputs, labels]的列表
inputs, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)
# 清空梯度,否则梯度会累加
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前向传播 + 反向传播 + 优化
outputs = self(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 打印统计
running_loss += loss.item()
loss4epoch.append(loss.item())
if i % 2000 == 1999: # 每2000 mini-batches打印损失
print(f'[{epoch + 1}, {i + 1:5d}] loss: {running_loss / 2000:.3f}')
self._loss.append(running_loss / 2000)
running_loss = 0.0
self._loss4epochs.append(sum(loss4epoch) / len(loss4epoch))
loss4epoch.clear()
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('Finished Training')
print('Training time: %s Seconds' % (end_time - start_time))
def test_net(self, testloader, classes, device=None):
"""
在测试集上测试网络
:param testloader: 加载测试集
:param classes: 类别的标签
:param device: 训练在cpu或是gpu
"""
self.eval() # 设置为评估模式,节省资源开销
dataiter = iter(testloader)
if not device:
# 如果未给出device,就将第一个网络层所在位置设成device
device = next(iter(self.parameters())).device
self.to(device)
x, labels = dataiter.next()
x, labels = x.to(device), labels.to(device)
output = self(x)
# 准备计算总正确率和各类正确率
correct_pred = {classname: 0 for classname in classes}
total_pred = {classname: 0 for classname in classes}
correct = 0
total = 0
# 不需要计算梯度,节省资源
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = net(images)
energy, predictions = torch.max(outputs, 1)
# 为每个类统计正确的预测数
for label, prediction in zip(labels, predictions):
if label == prediction:
correct += 1
correct_pred[classes[label]] += 1
total += 1
total_pred[classes[label]] += 1
# 打印每个类别的预测准确率
for classname, correct_count in correct_pred.items():
accuracy = 100 * float(correct_count) / total_pred[classname]
print(f'Accuracy for class: {classname:5s} is {accuracy:.1f} %')
total_accuracy = 100 * float(correct) / total
print(f'Accuracy for test data is {total_accuracy:.1f} %')
def save_net(self, path='./cifar_net.pth'):
"""
保存网络训练结果
:param path: 保存的路径
"""
torch.save(self.state_dict(), path)
def load_net(self, path=None):
"""
加载已经训练好的网络
:param path: 网络路径
"""
if path:
self.load_state_dict(torch.load(path))
else:
print("Path not given!")
def draw_loss(self):
"""
绘制损失函数下降曲线
"""
# 按每2000 mini-batches绘制损失曲线
s1 = pd.Series(self._loss, name="Loss")
sns.set_theme(style='darkgrid')
sns.lineplot(data=s1)
plt.xlabel("Every 2000 mini-batches")
plt.title("Loss Function Change Curve")
plt.show()
# 按epochs绘制Loss曲线
s2 = pd.Series(self._loss4epochs, name="Loss")
sns.set_theme(style='darkgrid')
sns.lineplot(data=s2)
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.title("Loss Function Change Curve")
plt.savefig('Adam_loss.png')
plt.show()
def count_cov(self, device=None):
"""
统计卷积核个数及信息
:param device: 计算设备为CPU或GPU
"""
if not device:
# 如果未给出device,就将第一个网络层所在位置设成device
device = next(iter(self.parameters())).device
# 保存模型权重
self.model_weights.clear()
# 保存卷积层
self.conv_layers.clear()
# 把model children转为list
model_children = list(self.children())
# print(model_children)
cnt = 0
# 把所有卷积层及对应权重加入list中
for i in range(len(model_children)):
# 遍历最外层网络寻找卷积层
if type(model_children[i]) == nn.Conv2d:
cnt += 1
self.model_weights.append(model_children[i].weight)
self.conv_layers.append(model_children[i])
# 遍历Sequential寻找卷积层
elif type(model_children[i]) == nn.Sequential:
for child in model_children[i].children():
if type(child) == nn.Conv2d:
cnt += 1
self.model_weights.append(child.weight)
self.conv_layers.append(child)
# 遍历ResBlock残差块寻找卷积层
elif type(child) == ResBlock:
for sub_child in child.children():
if type(sub_child) == nn.Conv2d:
# 如果是1x1卷积核(一般是shortcut)则跳过
if sub_child.kernel_size == (1, 1):
continue
cnt += 1
self.model_weights.append(sub_child.weight)
self.conv_layers.append(sub_child)
# 遍历Bottleneck寻找卷积层,代码仅在shortcut上无卷积核情况下有效
elif type(model_children[i]) == BottleNeck:
for child in model_children[i].children():
if type(child) == nn.Conv2d:
cnt += 1
self.model_weights.append(child.weight)
self.conv_layers.append(child)
print(f"Total convolution layers: {cnt} (ignore conv on shortcut)")
def draw_feature_map(self, input_path, output_path, test_transform, device=None):
"""
卷积层输出可视化
:param input_path: 输入的图片的路径
:param device: 在cpu或是gpu上运行网络
"""
if not device:
# 如果未给出device,就将第一个网络层所在位置设成device
device = next(iter(self.parameters())).device
self.to(device)
if len(self.conv_layers) == 0:
self.count_cov()
from PIL import Image
image = Image.open(input_path)
image = test_transform(image)
# print(f"Image shape before: {image.shape}")
image = image.unsqueeze(0)
# print(f"Image shape after: {image.shape}")
image = image.to(device)
outputs = []
names = []
# print(self.conv_layers[0:])
cnt = 0
# 将数据输入卷积核,并获取输出
for layer in self.conv_layers[0:]:
cnt += 1
image = layer(image)
outputs.append(image)
names.append(str(layer))
processed = []
# 压缩并去除颜色维度
for feature_map in outputs:
feature_map = feature_map.squeeze(0)
gray_scale = torch.sum(feature_map, 0)
gray_scale = gray_scale / feature_map.shape[0]
processed.append(gray_scale.data.cpu().numpy())
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(30, 50))
for i in range(len(processed)):
a = fig.add_subplot(5, 4, i + 1)
# 将数组的值以图片的形式展示出来
plt.imshow(processed[i])
a.axis("off")
a.set_title(names[i].split('(')[0] + '(' + str(i + 1) + ')', fontsize=30)
plt.savefig(output_path + str('feature_maps.jpg'), bbox_inches='tight')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 串联多个图片变换的操作,对RGB图像先转为张量,后做归一化
transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
batch_size = 4
# 如果cuda加速可用,则使用cuda加速,否则使用CPU
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 加载训练集
train_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
# 加载测试集
test_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)
# 设置分类标签
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
# 实例化网络
net = MyResNet()
# 用Adam训练网络
net.train_net(train_loader, device=device, epochs=50, optimizer='Adam')
# 保存训练好的参数
net.save_net(path='./cifar_ResNet_Adam_100epochs.pth')
net.draw_loss()
# 加载网络
net.load_net(path='./cifar10_ResNet_bottleneck_Adam-SGD_100epochs.pth')
# 用SGD训练网络
net.train_net(train_loader, device=device, epochs=50, optimizer='SGD')
net.save_net(path='./cifar10_ResNet_bottleneck_Adam-SGD_100epochs.pth')
# 画损失图
net.draw_loss()
# 在测试集上测试网络
net.test_net(test_loader, classes, device=device)
# 卷积核输出可视化
net.draw_feature_map(input_path='./airplane7.png', output_path='',
test_transform=transform, device=device)