图像超分辨率:Efficient and Degradation-Adaptive Network for Real-World Image Super-Resolution(DASR,oppo)
文章目录
- Efficient and Degradation-Adaptive Network for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
- Efficient and Degradation-Adaptive Network for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
-
- 1. 本文主要解决问题
- 2. 网络结构
-
- 2.1 degradation prediction 阶段
- 2.2 main sr net
- 3. 数据集
-
- 1. 训练数据集
- 2. 测试数据集
- 4. degradation strategy
- 5. 损失函数
-
- 1. pixel 重建损失L1 loss:
- 2. degradation regression 损失函数也是 L1 loss
- 3. 感知损失的配置如下:
- 4. gan 损失函数
- 6. 判别器
- 7. 训练步骤
Efficient and Degradation-Adaptive Network for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Efficient and Degradation-Adaptive Network for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
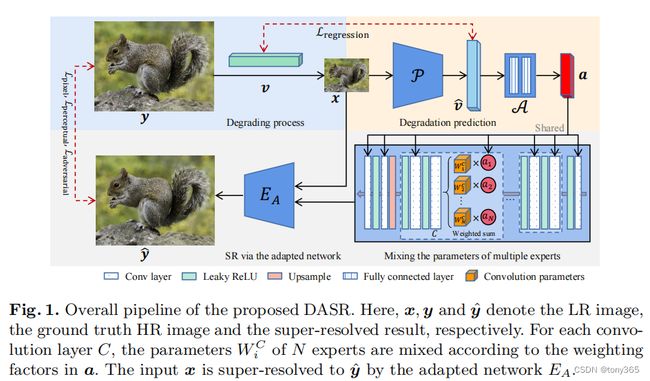
oppo的blind sr方法,思路是显式训练和预测 退化。并apply 到 main sr net中。
1. 本文主要解决问题
适应于各种退化方式的blind sr。
如下图 y是真实HR, 通过各种degradation 方法生成 LR图像x, 再通过一个分支网络预测x的degradation represetation.
将退化方式融入主超分网络
2. 网络结构
2.1 degradation prediction 阶段
损失函数:v是退化类型的表示。关于退化方法在本文稍后讲解。
- 退化预测网络6个卷积 + 1个池化层 -> batch * 33
- condition net(map) 两层全连接网络 -> batch * 5 这里5个数表示的是 主超分网络中的 expert 的weight
class Degradation_Predictor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_nc=3, nf=64, num_params=100, num_networks=5, use_bias=True):
super(Degradation_Predictor, self).__init__()
self.ConvNet = nn.Sequential(*[
nn.Conv2d(in_nc, nf, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(nf, nf, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=use_bias),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(nf, nf, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=use_bias),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(nf, nf, kernel_size=5, stride=2, padding=2, bias=use_bias),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(nf, nf, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=use_bias),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(nf, num_params, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=use_bias),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
])
self.globalPooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.MappingNet = nn.Sequential(*[
nn.Linear(num_params, 15),
nn.Linear(15, num_networks),
])
def forward(self, input):
conv = self.ConvNet(input)
flat = self.globalPooling(conv)
out_params = flat.view(flat.size()[:2])
mapped_weights = self.MappingNet(out_params)
return out_params, mapped_weights
2.2 main sr net
# 动态卷积,就是输入 feature 和 5个conv expert的weight,
# 5个conv expert 通过weight加权融合后 得到最终的weight, 然后对 feature进行卷积。
class Dynamic_conv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1, if_bias=True, K=5, init_weight=False):
super(Dynamic_conv2d, self).__init__()
assert in_planes % groups == 0
self.in_planes = in_planes
self.out_planes = out_planes
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.stride = stride
self.padding = padding
self.dilation = dilation
self.groups = groups
self.if_bias = if_bias
self.K = K
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(K, out_planes, in_planes//groups, kernel_size, kernel_size), requires_grad=True)
if self.if_bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(K, out_planes), requires_grad=True)
else:
self.bias = None
if init_weight:
self._initialize_weights()
def _initialize_weights(self):
for i in range(self.K):
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight[i])
if self.if_bias:
nn.init.constant_(self.bias[i], 0)
def forward(self, inputs):
x = inputs['x']
softmax_attention = inputs['weights']
batch_size, in_planes, height, width = x.size()
x = x.contiguous().view(1, -1, height, width)
weight = self.weight.view(self.K, -1)
aggregate_weight = torch.mm(softmax_attention, weight).view(-1, self.in_planes, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size)
if self.bias is not None:
aggregate_bias = torch.mm(softmax_attention, self.bias).view(-1)
output = F.conv2d(x, weight=aggregate_weight, bias=aggregate_bias, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding,
dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups*batch_size)
else:
output = F.conv2d(x, weight=aggregate_weight, bias=None, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding,
dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups * batch_size)
output = output.view(batch_size, self.out_planes, output.size(-2), output.size(-1))
return output
MSRResNet卷积 转换为 动态卷积后,得到动态网络
class MSRResNetDynamic(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_in_ch=3, num_out_ch=3, num_feat=64, num_block=16, num_models=5, upscale=4):
super(MSRResNetDynamic, self).__init__()
self.upscale = upscale
self.conv_first = Dynamic_conv2d(num_in_ch, num_feat, 3, groups=1, if_bias=True, K=num_models)
self.body = make_layer(ResidualBlockNoBNDynamic, num_block, num_feat=num_feat, num_models=num_models)
# upsampling
if self.upscale in [2, 3]:
self.upconv1 = Dynamic_conv2d(num_feat, num_feat * self.upscale * self.upscale, 3, groups=1, if_bias=True, K=num_models)
self.pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(self.upscale)
elif self.upscale == 4:
self.upconv1 = Dynamic_conv2d(num_feat, num_feat * 4, 3, groups=1, if_bias=True, K=num_models)
self.upconv2 = Dynamic_conv2d(num_feat, num_feat * 4, 3, groups=1, if_bias=True, K=num_models)
self.pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(2)
self.conv_hr = Dynamic_conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, groups=1, if_bias=True, K=num_models)
self.conv_last = Dynamic_conv2d(num_feat, num_out_ch, 3, groups=1, if_bias=True, K=num_models)
# activation function
self.lrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1, inplace=True)
def forward(self, x, weights):
out = self.lrelu(self.conv_first({'x': x, 'weights': weights}))
out = self.body({'x': out, 'weights': weights})['x']
if self.upscale == 4:
out = self.lrelu(self.pixel_shuffle(self.upconv1({'x': out, 'weights': weights})))
out = self.lrelu(self.pixel_shuffle(self.upconv2({'x': out, 'weights': weights})))
elif self.upscale in [2, 3]:
out = self.lrelu(self.pixel_shuffle(self.upconv1({'x': out, 'weights': weights})))
out = self.lrelu(self.conv_hr({'x': out, 'weights': weights}))
out = self.conv_last({'x': out, 'weights': weights})
base = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=self.upscale, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
out += base
return out
3. 数据集
1. 训练数据集
div2k
flickr2k
ost
下载地址:kaggle
参考 resl-esrgan
对下载的三个数据集 rescale , crop and generate meta info
得到DF2K_multiscale_sub 数据集
2. 测试数据集
div2k test 和 RealWorld38 : 下载地址
常用的bsds100, set5, set14, urban100等: 下载地址
4. degradation strategy
退化步骤和文中介绍是一致的。主要分为3个强度的退化空间,在处理数据集的时候,应用的概率分别是
degree_list: ['weak_degrade_one_stage', 'standard_degrade_one_stage', 'severe_degrade_two_stage']
degree_prob: [0.3, 0.3, 0.4]
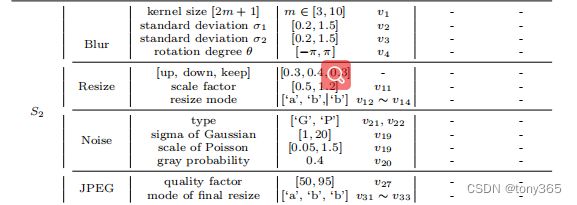
这里以standard_degrade_one_stage 退化空间为例,在paper中是S2
具体实现
blur的kernel是在DASRDataset 中计算
对于standard_degrade_one_stage
返回的是:
{‘gt’: img_gt, ‘kernel1’: kernel_info,‘gt_path’: gt_path}
在DASRDataset只是计算blur kernel, 而 blur退化的执行, 以及 resize, noise, jpeg compress等退化的执行是在 DASRModel 类中的 feed_data 函数中
elif self.degradation_degree == 'standard_degrade_one_stage':
# 第一步是blur, 要根据参数对图像执行blur, 同时得到degradation_params[0:4], 对应论文 v1-v4
self.degradation_params = torch.zeros(self.opt_train['batch_size_per_gpu'],
self.num_degradation_params) # [B, 33]
self.kernel1 = data['kernel1']['kernel'].to(self.device)
kernel_size_range1 = [self.opt_train['blur_kernel_size_minimum_standard1'],
self.opt_train['blur_kernel_size_standard1']]
rotation_range = [-math.pi, math.pi]
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[0]:self.road_map[0] + 1] = (data['kernel1'][
'kernel_size'].unsqueeze(1) -
kernel_size_range1[0]) / (
kernel_size_range1[1] -
kernel_size_range1[0])
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[0] + 1:self.road_map[0] + 2] = (data['kernel1'][
'sigma_x'].unsqueeze(1) -
self.opt_train[
'blur_sigma_standard1'][
0]) / (self.opt_train[
'blur_sigma_standard1'][
1] -
self.opt_train[
'blur_sigma_standard1'][
0])
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[0] + 2:self.road_map[0] + 3] = (data['kernel1'][
'sigma_y'].unsqueeze(1) -
self.opt_train[
'blur_sigma_standard1'][
0]) / (self.opt_train[
'blur_sigma_standard1'][
1] -
self.opt_train[
'blur_sigma_standard1'][
0])
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[0] + 3:self.road_map[0] + 4] = (data['kernel1'][
'rotation'].unsqueeze(1) -
rotation_range[0]) / (
rotation_range[1] -
rotation_range[0])
ori_h, ori_w = self.gt.size()[2:4]
# blur
out = filter2D(self.gt, self.kernel1)
# 第二步, resize 参数:scale 和下采样方法。
# random resize
updown_type = random.choices(['up', 'down', 'keep'], self.opt['resize_prob_standard1'])[0]
if updown_type == 'up':
scale = np.random.uniform(1, self.opt['resize_range_standard1'][1])
elif updown_type == 'down':
scale = np.random.uniform(self.opt['resize_range_standard1'][0], 1)
else:
scale = 1
mode = random.choice(self.resize_mode_list)
out = F.interpolate(out, scale_factor=scale, mode=mode)
normalized_scale = (scale - self.opt['resize_range_standard1'][0]) / (
self.opt['resize_range_standard1'][1] - self.opt['resize_range_standard1'][0])
onehot_mode = torch.zeros(len(self.resize_mode_list))
for index, mode_current in enumerate(self.resize_mode_list):
if mode_current == mode:
onehot_mode[index] = 1
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[1]:self.road_map[1] + 1] = torch.tensor(
normalized_scale).expand(self.gt.size(0), 1) # scale
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[1] + 1:self.road_map[1] + 4] = onehot_mode.expand(
self.gt.size(0), len(self.resize_mode_list)) # resize mode
# 第三步,添加噪声
# noise # noise_range: [1, 30] poisson_scale_range: [0.05, 3]
gray_noise_prob = self.opt['gray_noise_prob_standard1']
if np.random.uniform() < self.opt['gaussian_noise_prob_standard1']:
sigma, gray_noise, out, self.noise_g_first = random_add_gaussian_noise_pt(
out, sigma_range=self.opt['noise_range_standard1'], clip=True, rounds=False,
gray_prob=gray_noise_prob)
normalized_sigma = (sigma - self.opt['noise_range_standard1'][0]) / (
self.opt['noise_range_standard1'][1] - self.opt['noise_range_standard1'][0])
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[2]:self.road_map[2] + 1] = normalized_sigma.unsqueeze(1)
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[2] + 1:self.road_map[2] + 2] = gray_noise.unsqueeze(1)
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[2] + 2:self.road_map[2] + 4] = torch.tensor([1, 0]).expand(
self.gt.size(0), 2)
self.noise_p_first = only_generate_poisson_noise_pt(out, scale_range=self.opt[
'poisson_scale_range_standard1'], gray_prob=gray_noise_prob)
else:
scale, gray_noise, out, self.noise_p_first = random_add_poisson_noise_pt(
out, scale_range=self.opt['poisson_scale_range_standard1'], gray_prob=gray_noise_prob,
clip=True, rounds=False)
normalized_scale = (scale - self.opt['poisson_scale_range_standard1'][0]) / (
self.opt['poisson_scale_range_standard1'][1] -
self.opt['poisson_scale_range_standard1'][0])
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[2]:self.road_map[2] + 1] = normalized_scale.unsqueeze(1)
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[2] + 1:self.road_map[2] + 2] = gray_noise.unsqueeze(1)
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[2] + 2:self.road_map[2] + 4] = torch.tensor([0, 1]).expand(
self.gt.size(0), 2)
self.noise_g_first = only_generate_gaussian_noise_pt(out,
sigma_range=self.opt['noise_range_standard1'],
gray_prob=gray_noise_prob)
# 第四步, jpeg 处理,参数只有一个图像质量。另外3个是图像resize 方法(one-hot表示)
# JPEG compression
jpeg_p = out.new_zeros(out.size(0)).uniform_(
*self.opt['jpeg_range_standard1']) # tensor([61.6463, 94.2723, 37.1205, 34.9564], device='cuda:0')]
normalized_jpeg_p = (jpeg_p - self.opt['jpeg_range_standard1'][0]) / (
self.opt['jpeg_range_standard1'][1] - self.opt['jpeg_range_standard1'][0])
out = torch.clamp(out, 0, 1)
out = self.jpeger(out, quality=jpeg_p)
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[3]:self.road_map[3] + 1] = normalized_jpeg_p.unsqueeze(1)
# resize back
mode = random.choice(self.resize_mode_list)
onehot_mode = torch.zeros(len(self.resize_mode_list))
for index, mode_current in enumerate(self.resize_mode_list):
if mode_current == mode:
onehot_mode[index] = 1
out = F.interpolate(out, size=(ori_h // self.opt['scale'], ori_w // self.opt['scale']), mode=mode)
self.degradation_params[:, self.road_map[3] + 4:] = onehot_mode.expand(self.gt.size(0),
len(self.resize_mode_list))
self.degradation_params = self.degradation_params.to(self.device)
# clamp and round
self.lq = torch.clamp((out * 255.0).round(), 0, 255) / 255.
# random crop
gt_size = self.opt['gt_size']
self.gt, self.lq, self.top, self.left = paired_random_crop_return_indexes(self.gt, self.lq, gt_size,
self.opt['scale'])
degradation_params 是一个33dim的向量,也是退化预测网络中回归损失函数的 gt.
5. 损失函数
1. pixel 重建损失L1 loss:
def l1_loss(pred, target):
return F.l1_loss(pred, target, reduction='none')
2. degradation regression 损失函数也是 L1 loss
3. 感知损失的配置如下:
perceptual_opt:
type: PerceptualLoss
layer_weights:
# before relu
'conv1_2': 0.1
'conv2_2': 0.1
'conv3_4': 1
'conv4_4': 1
'conv5_4': 1
vgg_type: vgg19
use_input_norm: true
perceptual_weight: !!float 1
style_weight: 0
range_norm: false
criterion: l1
实现如下:
指定vgg net 的 一些 layer 和 对应的weights
输入预测 和 gt, 计算 layer feature 间的 感知损失和style 损失。
class PerceptualLoss(nn.Module):
"""Perceptual loss with commonly used style loss.
Args:
layer_weights (dict): The weight for each layer of vgg feature.
Here is an example: {'conv5_4': 1.}, which means the conv5_4
feature layer (before relu5_4) will be extracted with weight
1.0 in calculting losses.
vgg_type (str): The type of vgg network used as feature extractor.
Default: 'vgg19'.
use_input_norm (bool): If True, normalize the input image in vgg.
Default: True.
range_norm (bool): If True, norm images with range [-1, 1] to [0, 1].
Default: False.
perceptual_weight (float): If `perceptual_weight > 0`, the perceptual
loss will be calculated and the loss will multiplied by the
weight. Default: 1.0.
style_weight (float): If `style_weight > 0`, the style loss will be
calculated and the loss will multiplied by the weight.
Default: 0.
criterion (str): Criterion used for perceptual loss. Default: 'l1'.
"""
def __init__(self,
layer_weights,
vgg_type='vgg19',
use_input_norm=True,
range_norm=False,
perceptual_weight=1.0,
style_weight=0.,
criterion='l1'):
super(PerceptualLoss, self).__init__()
self.perceptual_weight = perceptual_weight
self.style_weight = style_weight
self.layer_weights = layer_weights
self.vgg = VGGFeatureExtractor(
layer_name_list=list(layer_weights.keys()),
vgg_type=vgg_type,
use_input_norm=use_input_norm,
range_norm=range_norm)
self.criterion_type = criterion
if self.criterion_type == 'l1':
self.criterion = torch.nn.L1Loss()
elif self.criterion_type == 'l2':
self.criterion = torch.nn.L2loss()
elif self.criterion_type == 'fro':
self.criterion = None
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f'{criterion} criterion has not been supported.')
def forward(self, x, gt):
"""Forward function.
Args:
x (Tensor): Input tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
gt (Tensor): Ground-truth tensor with shape (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
Tensor: Forward results.
"""
# extract vgg features
x_features = self.vgg(x)
gt_features = self.vgg(gt.detach())
# calculate perceptual loss
if self.perceptual_weight > 0:
percep_loss = 0
for k in x_features.keys():
if self.criterion_type == 'fro':
percep_loss += torch.norm(x_features[k] - gt_features[k], p='fro') * self.layer_weights[k]
else:
percep_loss += self.criterion(x_features[k], gt_features[k]) * self.layer_weights[k]
percep_loss *= self.perceptual_weight
else:
percep_loss = None
# calculate style loss
if self.style_weight > 0:
style_loss = 0
for k in x_features.keys():
if self.criterion_type == 'fro':
style_loss += torch.norm(
self._gram_mat(x_features[k]) - self._gram_mat(gt_features[k]), p='fro') * self.layer_weights[k]
else:
style_loss += self.criterion(self._gram_mat(x_features[k]), self._gram_mat(gt_features[k])) * self.layer_weights[k]
style_loss *= self.style_weight
else:
style_loss = None
return percep_loss, style_loss
def _gram_mat(self, x):
"""Calculate Gram matrix.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): Tensor with shape of (n, c, h, w).
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Gram matrix.
"""
n, c, h, w = x.size()
features = x.view(n, c, w * h)
features_t = features.transpose(1, 2)
gram = features.bmm(features_t) / (c * h * w)
return gram
4. gan 损失函数
```bash
gan_opt:
type: GANLoss
gan_type: vanilla
real_label_val: 1.0
fake_label_val: 0.0
loss_weight: !!float 1e-1
```
对于本文其实就是一个二分类损失nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
class GANLoss(nn.Module):
"""Define GAN loss.
Args:
gan_type (str): Support 'vanilla', 'lsgan', 'wgan', 'hinge'.
real_label_val (float): The value for real label. Default: 1.0.
fake_label_val (float): The value for fake label. Default: 0.0.
loss_weight (float): Loss weight. Default: 1.0.
Note that loss_weight is only for generators; and it is always 1.0
for discriminators.
"""
def __init__(self, gan_type, real_label_val=1.0, fake_label_val=0.0, loss_weight=1.0):
super(GANLoss, self).__init__()
self.gan_type = gan_type
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.real_label_val = real_label_val
self.fake_label_val = fake_label_val
if self.gan_type == 'vanilla':
self.loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
elif self.gan_type == 'lsgan':
self.loss = nn.MSELoss()
elif self.gan_type == 'wgan':
self.loss = self._wgan_loss
elif self.gan_type == 'wgan_softplus':
self.loss = self._wgan_softplus_loss
elif self.gan_type == 'hinge':
self.loss = nn.ReLU()
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f'GAN type {self.gan_type} is not implemented.')
def _wgan_loss(self, input, target):
"""wgan loss.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target (bool): Target label.
Returns:
Tensor: wgan loss.
"""
return -input.mean() if target else input.mean()
def _wgan_softplus_loss(self, input, target):
"""wgan loss with soft plus. softplus is a smooth approximation to the
ReLU function.
In StyleGAN2, it is called:
Logistic loss for discriminator;
Non-saturating loss for generator.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target (bool): Target label.
Returns:
Tensor: wgan loss.
"""
return F.softplus(-input).mean() if target else F.softplus(input).mean()
def get_target_label(self, input, target_is_real):
"""Get target label.
Args:
input (Tensor): Input tensor.
target_is_real (bool): Whether the target is real or fake.
Returns:
(bool | Tensor): Target tensor. Return bool for wgan, otherwise,
return Tensor.
"""
if self.gan_type in ['wgan', 'wgan_softplus']:
return target_is_real
target_val = (self.real_label_val if target_is_real else self.fake_label_val)
return input.new_ones(input.size()) * target_val # target 全为1
def forward(self, input, target_is_real, is_disc=False):
"""
Args:
input (Tensor): The input for the loss module, i.e., the network
prediction.
target_is_real (bool): Whether the targe is real or fake.
is_disc (bool): Whether the loss for discriminators or not.
Default: False.
Returns:
Tensor: GAN loss value.
"""
target_label = self.get_target_label(input, target_is_real) #
if self.gan_type == 'hinge':
if is_disc: # for discriminators in hinge-gan
input = -input if target_is_real else input
loss = self.loss(1 + input).mean()
else: # for generators in hinge-gan
loss = -input.mean()
else: # other gan types
loss = self.loss(input, target_label)
# loss_weight is always 1.0 for discriminators
return loss if is_disc else loss * self.loss_weight
6. 判别器
在测试的时候没有判别器,训练的时候有判别器。
判别器是一个常规的U-net网络
class UNetDiscriminatorSN(nn.Module):
"""Defines a U-Net discriminator with spectral normalization (SN)"""
def __init__(self, num_in_ch, num_feat=64, skip_connection=True):
super(UNetDiscriminatorSN, self).__init__()
self.skip_connection = skip_connection
norm = spectral_norm
self.conv0 = nn.Conv2d(num_in_ch, num_feat, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv1 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False))
self.conv2 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 2, num_feat * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False))
self.conv3 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 4, num_feat * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False))
# upsample
self.conv4 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 8, num_feat * 4, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))
self.conv5 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 4, num_feat * 2, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))
self.conv6 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 2, num_feat, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))
# extra
self.conv7 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))
self.conv8 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))
self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, 1, 3, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x0 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv0(x), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
x1 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv1(x0), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
x2 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv2(x1), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
x3 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv3(x2), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
# upsample
x3 = F.interpolate(x3, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
x4 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv4(x3), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
if self.skip_connection:
x4 = x4 + x2
x4 = F.interpolate(x4, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
x5 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv5(x4), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
if self.skip_connection:
x5 = x5 + x1
x5 = F.interpolate(x5, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
x6 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv6(x5), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
if self.skip_connection:
x6 = x6 + x0
# extra
out = F.leaky_relu(self.conv7(x6), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
out = F.leaky_relu(self.conv8(out), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
out = self.conv9(out)
return out
U-net主要包括10个卷积层(spectral norm, leaky_relu)
输入为 [2,3,512,512] 时,output shape 如下
对判别器有个大概的了解,输入的是3通道图像,输出的是单通道等尺寸map
7. 训练步骤
生成器的部分网络是加载的预训练模型msrresnet. 如果从头训练可能会不收敛。当然也可以先用pixel loss训练一个 pretrained weight.
代码注解加在下面注释里
def optimize_parameters(self, current_iter):
# 一次迭代步骤的优化。优化一次生成器,接着优化一次判别器。
# optimize net_g
# 1. 首先优化 生成网络net_g, net_d判别网络不更新weight
for p in self.net_d.parameters():
p.requires_grad = False
# 2. 梯度归0
self.optimizer_g.zero_grad()
# 3. 前向生成网络,输入的是一个低质低分辨率图像
# predicted_params, weights分别是33dim的退化类型参数,net_g的动态卷积参数
# 图像先经过退化网络预测退化,并融入超分生成网络,生成超分图像output
predicted_params, weights = self.net_p(self.lq)
self.output = self.net_g(self.lq.contiguous(), weights)
# 4. 计算训练生成网络的损失
# 主要包括 pixel loss 重建损失 self.cri_pix(self.output, self.gt)
# 主要包括 退化预测回归损失 self.cri_regress(predicted_params, self.degradation_params)
# 图像内容和风格感知损失 self.cri_perceptual(self.output, self.gt)
# gan损失,使预测迷惑判别器 self.cri_gan(fake_g_pred, True, is_disc=False)
l_g_total = 0
loss_dict = OrderedDict()
if (current_iter % self.net_d_iters == 0 and current_iter > self.net_d_init_iters):
# pixel loss
if self.cri_pix:
l_pix = self.cri_pix(self.output, self.gt)
l_g_total += l_pix
loss_dict['l_pix'] = l_pix
if self.cri_regress:
l_regression = self.cri_regress(predicted_params, self.degradation_params)
l_g_total += l_regression
loss_dict['l_regression'] = l_regression
# perceptual loss
if self.cri_perceptual:
l_percep, l_style = self.cri_perceptual(self.output, self.gt)
if l_percep is not None:
l_g_total += l_percep
loss_dict['l_percep'] = l_percep
if l_style is not None:
l_g_total += l_style
loss_dict['l_style'] = l_style
# gan loss
fake_g_pred = self.net_d(self.output)
l_g_gan = self.cri_gan(fake_g_pred, True, is_disc=False)
l_g_total += l_g_gan
loss_dict['l_g_gan'] = l_g_gan
# 5. 计算梯度和优化
l_g_total.backward()
self.optimizer_g.step()
# optimize net_d
# 6. 优化判别器网络,首先requires_grad设为ture,可训练
for p in self.net_d.parameters():
p.requires_grad = True
# 7. 梯度归0
self.optimizer_d.zero_grad()
# real
# 8. 计算gt进入判别器的损失,使gt 尽量为 1
real_d_pred = self.net_d(self.gt)
l_d_real = self.cri_gan(real_d_pred, True, is_disc=True)
loss_dict['l_d_real'] = l_d_real
loss_dict['out_d_real'] = torch.mean(real_d_pred.detach())
l_d_real.backward()
# fake
# 9. 计算gt进入判别器的损失,使predict output 尽量为 0
fake_d_pred = self.net_d(self.output.detach())
l_d_fake = self.cri_gan(fake_d_pred, False, is_disc=True)
loss_dict['l_d_fake'] = l_d_fake
loss_dict['out_d_fake'] = torch.mean(fake_d_pred.detach())
# 10. 梯度计算和优化
l_d_fake.backward()
self.optimizer_d.step()
self.log_dict = self.reduce_loss_dict(loss_dict)
if self.ema_decay > 0:
self.model_ema(decay=self.ema_decay)