PyTorch——DenseNet
参考链接
- https://tangshusen.me/Dive-into-DL-PyTorch/#/chapter05_CNN/5.12_densenet
DenseNet vs ResNet
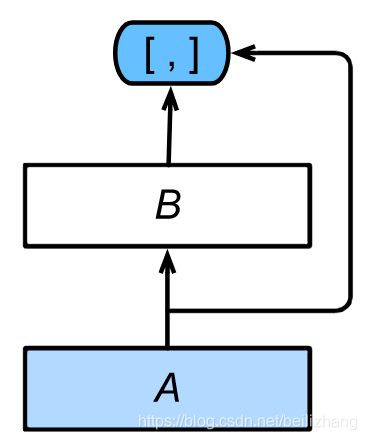
与ResNet的主要区别在于,DenseNet里模块B的输出不是像ResNet那样和模块A的输出相加,而是在通道维上连结。这样模块A的输出可以直接传入模块B后面的层。在这个设计里,模块A直接跟模块B后面的所有层连接在了一起。这也是它被称为“稠密连接”的原因。
DenseNet的主要构建模块是稠密块(dense block)和过渡层(transition layer)。前者定义了输入和输出是如何连结的,后者则用来控制通道数,使之不过大。
稠密块
稠密块由多个conv_block组成,每块使用相同的输出通道数。但在前向计算时,我们将每块的输入和输出在通道维上连结。conv_block使用了ResNet改良版的“批量归一化、激活和卷积”结构。
def conv_block(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
return blk
class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
net = []
for i in range(num_convs):
in_c = in_channels + i * out_channels
net.append(conv_block(in_c, out_channels))
self.net = nn.ModuleList(net)
self.out_channels = in_channels + num_convs * out_channels # 计算输出通道数
def forward(self, X):
for blk in self.net:
Y = blk(X)
X = torch.cat((X, Y), dim=1) # 在通道维上将输入和输出连结
return X
过渡层
过渡层用来控制模型复杂度。它通过1×1卷积层来减小通道数,并使用步幅为2的平均池化层减半高和宽,从而进一步降低模型复杂度。
def transition_block(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
return blk
DenseNet模型
DenseNet首先使用同ResNet一样的单卷积层和最大池化层。
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
接下来使用的是4个稠密块。我们可以设置每个稠密块使用多少个卷积层。这里我们设成4。稠密块里的卷积层通道数(即增长率)设为32,所以每个稠密块将增加128个通道。同时使用过渡层来减半高和宽,并减半通道数。
num_channels, growth_rate = 64, 32 # num_channels为当前的通道数
num_convs_in_dense_blocks = [4, 4, 4, 4]
for i, num_convs in enumerate(num_convs_in_dense_blocks):
DB = DenseBlock(num_convs, num_channels, growth_rate)
net.add_module("DenseBlosk_%d" % i, DB)
# 上一个稠密块的输出通道数
num_channels = DB.out_channels
# 在稠密块之间加入通道数减半的过渡层
if i != len(num_convs_in_dense_blocks) - 1:
net.add_module("transition_block_%d" % i, transition_block(num_channels, num_channels // 2))
num_channels = num_channels // 2
最后接上全局池化层和全连接层来输出。
net.add_module("BN", nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels))
net.add_module("relu", nn.ReLU())
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", d2l.GlobalAvgPool2d()) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, num_channels, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(d2l.FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(num_channels, 10)))
完整代码
import time
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
import sys
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=None, root='~/Datasets/FashionMNIST'):
if sys.platform.startswith('win'):
num_workers = 0
else:
num_workers = 4
trans = []
if resize:
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=resize))
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(trans)
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_workers)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=num_workers)
return train_iter, test_iter
batch_size = 128
train_iter, test_iter = load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
def conv_block(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
return blk
class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
net = []
for i in range(num_convs):
in_c = in_channels + i * out_channels
net.append(conv_block(in_c, out_channels))
self.net = nn.ModuleList(net)
self.out_channels = in_channels + num_convs * out_channels # 计算输出通道数
def forward(self, X):
for blk in self.net:
Y = blk(X)
X = torch.cat((X, Y), dim=1) # 在通道维上将输入和输出连结
return X
def transition_block(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
return blk
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
num_channels, growth_rate = 64, 32 # num_channels为当前的通道数
num_convs_in_dense_blocks = [4, 4, 4, 4]
for i, num_convs in enumerate(num_convs_in_dense_blocks):
DB = DenseBlock(num_convs, num_channels, growth_rate)
net.add_module("DenseBlosk_%d" % i, DB)
# 上一个稠密块的输出通道数
num_channels = DB.out_channels
# 在稠密块之间加入通道数减半的过渡层
if i != len(num_convs_in_dense_blocks) - 1:
net.add_module("transition_block_%d" % i, transition_block(num_channels, num_channels // 2))
num_channels = num_channels // 2
net.add_module("BN", nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels))
net.add_module("relu", nn.ReLU())
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", d2l.GlobalAvgPool2d()) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, num_channels, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(d2l.FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(num_channels, 10)))
def evaluate_accuracy(data_iter, net, device=None):
if device is None and isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
# 如果没指定device就使用net的device
device = list(net.parameters())[0].device
acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
net.eval() # 评估模式, 这会关闭dropout
acc_sum += (net(X.to(device)).argmax(dim=1) == y.to(device)).float().sum().cpu().item()
net.train() # 改回训练模式
n += y.shape[0]
return acc_sum / n
def train(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs):
net = net.to(device)
print("training on ", device)
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum, train_acc_sum, n, batch_count, start = 0.0, 0.0, 0, 0, time.time()
for X, y in train_iter:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_l_sum += l.cpu().item()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
batch_count += 1
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, time %.1f sec'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum / batch_count, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc, time.time() - start))
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 5
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
train(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs)