dijkstra算法C++实现
目录
- 1 acwing模板
-
- 1.1 稠密图-用邻接矩阵
- 1.2 稀疏图-用邻接表
- 2 leetcode模板
1 acwing模板
1.1 稠密图-用邻接矩阵
//dijkstra() 迪杰斯特拉算法
//输入
const int N = 510;
int dist[N];//dist[i]表示结点i到起点的距离
int g[N][N];//g[i][j]表示结点i到结点j的边的长度,稠密图用邻接矩阵来存储
bool st[N];//st[i]表示该结点是否确定了最小距离,1是确定,0是未确定
int n, m;//n个点,m条边
//输出
dist[];//每个结点到起点的最短距离
//适用情况
边权非负
第1步:初始化dist数组为正无穷,起点距离dist[1]为0
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof d);
d[1] = 0;
第2步:循环n次
第2.1步:找到某个结点,它属于没有确定最短路的点集,它距离起点最近
int t = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(st[i] == 0 && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[i]))
t = i;
第2.2步:设置st[t] = 1,用这个结点的dist去更新剩余结点的dist
st[t] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(st[i] == 0)
dist[i] = min(dist[i], dist[t] + g[t][i]);
结束!
示例代码如下,
#include 输入为,
3 3
1 2 2
2 3 1
1 3 4
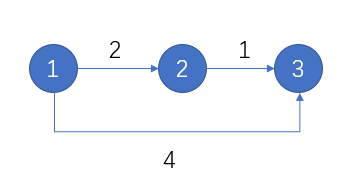
用图表示为,
输出为起点到终点的最短距离,
3
1.2 稀疏图-用邻接表
//dijkstra()算法
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int head[N];
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int e[N], ne[N], w[N], idx;
//head,dist和st用来存图结点,e,ne,和w用来存边
第1步:初始化
memset(head, -1, sizeof head);//邻接表初始化
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);//dist初始化
dist[1] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
heap.push({0, 1});//first存距离,second存图结点
第2步:遍历图
第2.1步:取出当前距离最小的结点
PII t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.second, d = t.first;
第2.2步:已知a->b中,结点a的距离d,用它去更新b
for(int i = head[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > d + w[i])
{
dist[j] = d + w[i];
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
结束!
示例代码为,
#include 示例输入,
3 3
1 2 2
2 3 1
1 3 4
示例输出,
3
2 leetcode模板
743.网络延迟时间
class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
const int inf = INT_MAX / 2;
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(n);
for (auto &t : times) {
int x = t[0] - 1, y = t[1] - 1;
g[x].emplace_back(y, t[2]);
}
vector<int> dist(n, inf);
dist[k - 1] = 0;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int,int>>, greater<>> q;
q.emplace(0, k - 1);
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.top();
q.pop();
int time = p.first, x = p.second;
if (dist[x] < time) {
continue;
}
for (auto &e : g[x]) {
int y = e.first, d = dist[x] + e.second;
if (d < dist[y]) {
dist[y] = d;
q.emplace(d, y);
}
}
}
int ans = *max_element(dist.begin(), dist.end());
return ans == inf ? -1 : ans;
}
};