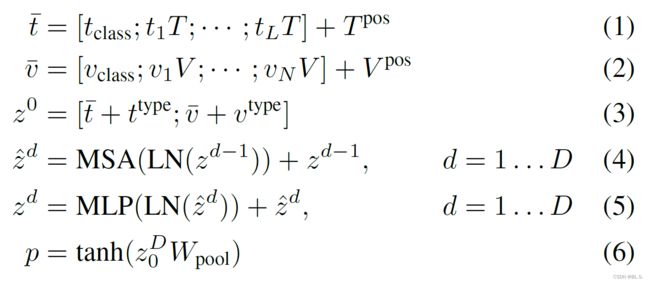ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision
ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision
Tags: Transformer, VLP, multimodal
发表日期: 2021
星级 : ★★★★★
模型简写: ViLT
简介: 使用统一tranformer架构的Vision-and-Lanuage多模态模型
精读: Yes
1. Abstract
当前VLP模型严重依赖于图像的特征抽取过程,而大多数的图像特征抽取往往包含region supervision (object detection)和convolution architecture (ResNet),这往往导致两个严重的问题:
- efficiency/speed: 特征抽取过程往往需要比多模态融合过程更大很多的计算资源
- expressive power: 图像特征提取器和预定义的视觉数据集绝对了模型的表达能力上限
本文中提出一种minimal VLP model (lightweight and fast embedding of visual inputs),完全移除region supervision和convolution过程,使得图像特征抽取过程大大缩短。
This paper
Keyword: VLP, multimodal
2. Introduction
术语:Vision-and-Language Pre-training (VLP)
The transformer module — used for modality interaction in VLP models — can also manage to process visual features in place of convolutional visual embedder, just as it process textual features.
Transformer module作用:1. modality interaction, 2. process textual features, 3. process visual features.
This paper proposes the Vision-and-Language Transformer (ViLT) that handles two modalities in a single unified manner. It mainly differs form previous VLP models in its shallow, convolution-free embedding of pixel-level inputs.
本文的主要贡献有3点:
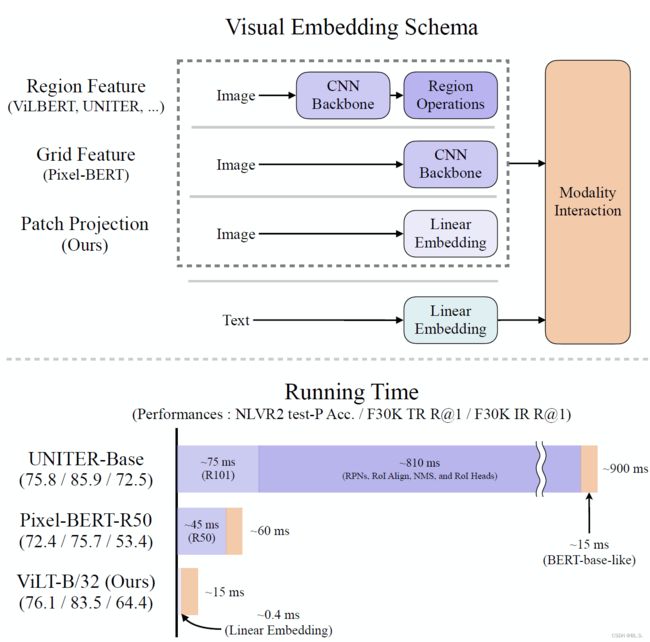
- ViLT是在论文提出时最轻量化的VLP模型,用transformer模块替代separate deep visual embedder,以用来抽取视觉特征,极大的节省了运行时间和参数效率。
- 第一个VLP模型,不使用region feature和deep convolutional visual embedder。
- Whole word masking和image augmentation可在VLP模型中用于提升下游任务性能。
Taxonomy of Vision-and-Language Models
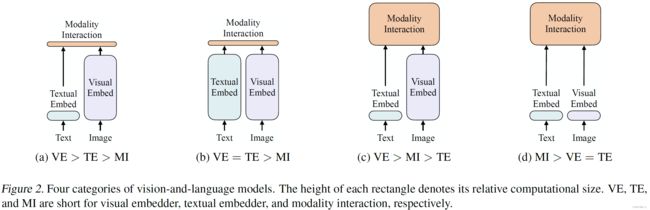
本文还对目前的 Vision-and-Language Model (VLP)做了简要的综述,首先对目前的模型做了分类 (依据两种模态的参数量和计算量,两种模态在网络中是如何融合的):
(a) visual semantic embedding: 视觉语义嵌入embedder比文本模型大很多
(b) CLIP, use separate but equally expensive transformer embedders for each modality. Interaction between the pooled image vector and text vector is still shallow (dot product), [简单融合多模态的特征表示的模型性能差]
© 使用deep transformer模型去学习image和text模态的融合
(d) 本文提出的架构
Modality Interaction Schema
一般多模态的融合框架分文
- single-stream approaches,例如UNITER,对图像和文本两种模态做拼接后再进行统一的操作
- dual-stream approaches,例如ViLBERT,LXMERT,对图像和文本先做单独的处理
本文采用single-stream approach,减少计算量。
Textual Embedding Schema
几乎所有的preformant VLP models share the same textual embedder: tokenizer from pre-trained BERT
Visual Embedding Schema
传统VLP模型:Region Feature / Grid Feature
本文所使用的方法(从ViT借鉴过来):Patch Projection: linear projection that operates on image patches
3. Method (Vision-and-Language Transformer)
A VLP model with a minimal visual embedding pipeline and following the single-stream approach.
模型主干结构是ViT,使用imagenet上预训练的ViT-B/32参数进行初始化。Hidden size H为768,layer depth D为12,patch size p为32. MLP size 为3072,注意力头为12.
输入的每个图像和文本embedding包含word/image embedding、token position embedding、patch position embedding modal-type embedding。
图像和文本embedding和相对应的positon embedding,modal-type embedding相加后输入Transfomer Encoder.
预训练目标函数
- Image Text Matching (ITM los)
以0.5的概率随机替换输入的真实图像。
- Word Patch Alignment (来源于几何最优化理论,approximate wasserstein distance)
- Mask Language Modeling
受启发于BERT,以0.15的概率随机mask输入text tokens
This paper use a two-layer MLP MLM head that inputs a m a s k e d D ∣ t a_{masked}^D|t amaskedD∣t and output logits over vocabulary, just as the MLP objective of BERT. The MLM loss is then computed as the negative log likehood loss for the masked tokens
训练技巧:
- Whole word masking
- Image Augmentation
RandAugment,但是不使用color inversion和cutout
论文展望
- Scalability
- Masked Modeling for Visual Inputs
- Augmentation Strategies
Author
Wonjae Kim