AS5600磁编码器的使用以及简单的滤波算法(arduino)
目录
前言
实践
示例一:发现IIC设备
示例二:读取AS5600原始数据
示例三:对读取到的AS5600原始数据进行低通滤波
1. 一阶滤波算法的原理
2.编程实现
前言
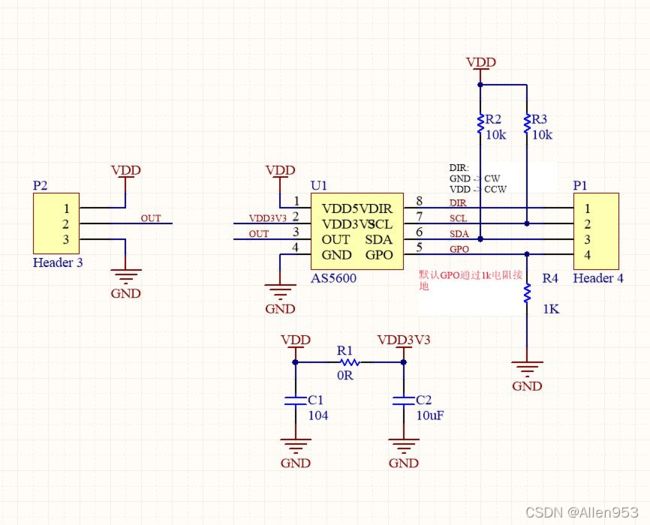
AS5600磁编码器常用于电机的角位移测量,如下图为使用AS5600芯片的一款编码器。
该磁编码器支持IIC,SPI和模拟输出三种方式,具体的引脚定义如下:
这款编码器的原理图如下:
AS5600的iic地址为0X36,数据所在寄存器地址如下
![]()
实践
示例一:发现IIC设备
#include
TwoWire I2Cone = TwoWire(0);
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
I2Cone.begin(18, 5, 100000);
for(int i=0;i<127;i++)
{
I2Cone.beginTransmission(i);
if(I2Cone.endTransmission()==0)
{
Serial.print("0x");
Serial.println(i,HEX);
}
}
}
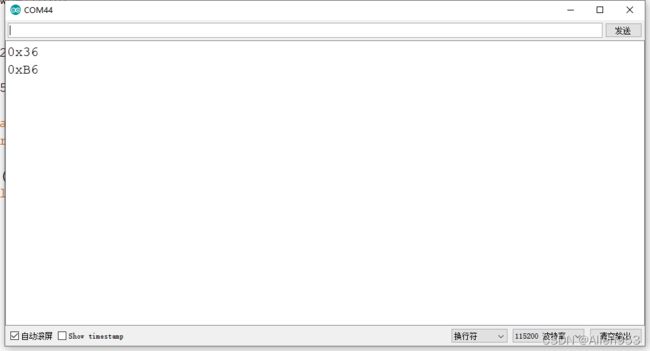
void loop(){} 可以查看串口看效果:
可以发现,单片机已经发现了其他的iic设备
示例二:读取AS5600原始数据
#include
TwoWire I2Cone = TwoWire(0);
uint16_t readValue = 0;
byte readArray[2];
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
I2Cone.begin(18, 5, 400000);
// notify the device that is aboout to be read
I2Cone.beginTransmission(0X36);
I2Cone.write(0X0C);
I2Cone.endTransmission(false);
}
void loop(){
// read the data msb and lsb
I2Cone.requestFrom(0X36, (uint8_t)2);
for (byte i=0; i < 2; i++) {
readArray[i] = I2Cone.read();
}
// depending on the sensor architecture there are different combinations of
// LSB and MSB register used bits
// AS5600 uses 0..7 LSB and 8..11 MSB
// AS5048 uses 0..5 LSB and 6..13 MSB
//readValue = ( readArray[1] & lsb_mask );
//readValue += ( ( readArray[0] & msb_mask ) << lsb_used );
readValue=readArray[0]*256+readArray[1];
Serial.println(readValue);
delay(100);
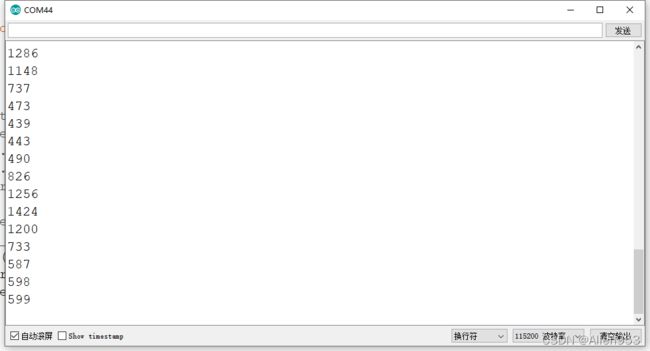
} 可以从串口查看效果:
可以看到,当我用手旋转电机一圈的过程中,这个数字从0增加到了4095
以下示例也可以:
主要删掉了setup函数中的begintransmission()等函数。
这个函数主要用于开启传输,但是requestFrom函数本身就会向从机发送数据请求信号,
#include
TwoWire I2Cone = TwoWire(0);
uint16_t readValue = 0;
byte readArray[2];
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
I2Cone.begin(18, 5, 400000);
}
void loop(){
// read the data msb and lsb
I2Cone.requestFrom(0X36, (uint8_t)2);
for (byte i=0; i < 2; i++) {
readArray[i] = I2Cone.read();
}
// depending on the sensor architecture there are different combinations of
// LSB and MSB register used bits
// AS5600 uses 0..7 LSB and 8..11 MSB
// AS5048 uses 0..5 LSB and 6..13 MSB
//readValue = ( readArray[1] & lsb_mask );
//readValue += ( ( readArray[0] & msb_mask ) << lsb_used );
readValue=readArray[0]*256+readArray[1];
Serial.println(readValue);
delay(100);
}
示例三:对读取到的AS5600原始数据进行低通滤波
这里我们把读取到的数据,进行一个低通滤波处理。
1. 一阶滤波算法的原理
一阶滤波,又叫一阶惯性滤波,或一阶低通滤波。是使用软件编程实现普通硬件RC低通滤波器的功能。
一阶低通滤波的算法公式为:
Y(n)=αX(n) + (1-α)Y(n-1)
式中:α=滤波系数;X(n)=本次采样值;Y(n-1)=上次滤波输出值;Y(n)=本次滤波输出值。
一阶低通滤波法采用本次采样值与上次滤波输出值进行加权,得到有效滤波值,使得输出对输入有反馈作用。
滤波系数越大,则更快达到目标开度,灵敏度越高,但曲线平滑性较差,滤波结果越不稳定;同样的滤波系数越小,则更慢达到目标开度,但曲线更加平滑,且稳定,但灵敏度较低。
因此在实际标定过程中,我们需要根据实际情况,平衡灵敏度和稳定性,来确定最终的滤波系数。
2.编程实现
#include
class LowPassFilte{
public:
LowPassFilte(float Tf);//低通滤波器时间常量
~LowPassFilte() = default;
float operator() (float x);
float Tf; //!< 低通滤波器时间常量
protected:
unsigned long timestamp_prev; //!< 上次执行时间戳
float y_prev; //!< 经过上次执行后过滤到的值
};
LowPassFilte::LowPassFilte(float time_constant)
: Tf(time_constant)
, y_prev(0.0f)
{
timestamp_prev = micros();
}
float LowPassFilte::operator() (float x)
{
unsigned long timestamp = micros();
float dt = (timestamp - timestamp_prev)*1e-6f;
if (dt < 0.0f || dt > 0.5f)
dt = 1e-3f;
float alpha = Tf/(Tf + dt);
float y = alpha*y_prev + (1.0f - alpha)*x;
y_prev = y;
timestamp_prev = timestamp;
return y;
}
TwoWire I2Cone = TwoWire(0);
LowPassFilte as5600_filter(0.001);
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
I2Cone.begin(18, 5, 400000);
I2Cone.beginTransmission(0X36);
I2Cone.write(0X0C);
I2Cone.endTransmission(false);
}
void loop(){
// read the data msb and lsb
I2Cone.requestFrom(0X36, (uint8_t)2);
byte readArray[2];
for (byte i=0; i < 2; i++) {
readArray[i] = I2Cone.read();
}
uint16_t readValue = 0;
readValue=readArray[0]*256+readArray[1];
// Serial.print(readValue);
// Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(as5600_filter(readValue));
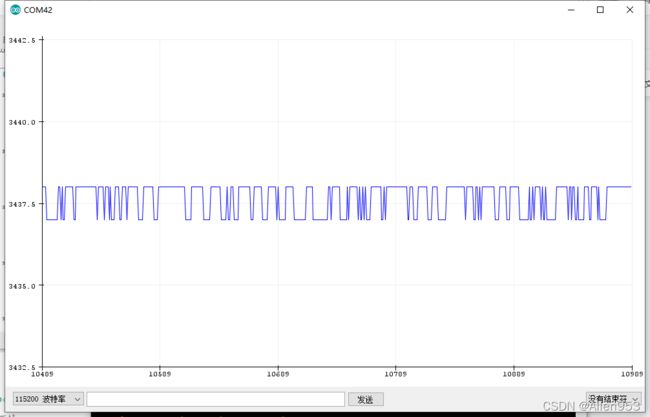
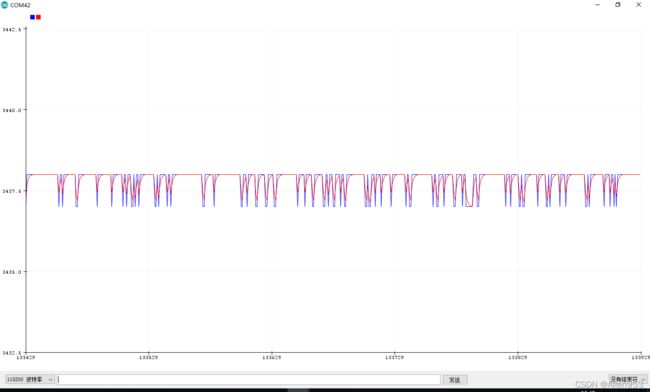
} 通过arduino的串口监视器,我们可以看到滤波后的数据跳动范围更小,变化更加平缓。
原数值
滤波后数值
放在一起对比(蓝色为原数值,红色为滤波后数值)
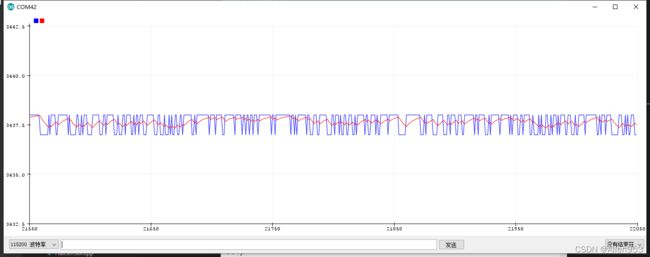
我们把时间常数从0.001改成0.01,可以看到输出数据更加稳定了。
参考链接:
1.算法学习笔记之一阶低通滤波算法_一颗偏执的心-CSDN博客_低通滤波算法