列表的基本操作
直接创建一个列表
可以用中括号
lst = ["Hello","word",98,"word"]索取列表单个元素
正向索引:从0开始都N-1,例如lst[0]="Hello"
反向索引:从-N开始到-1,例如lst[-1]=98
print(lst[0])
print(lst[-1])输出为:
Hello
98切片:获取列表的多个元素
语法结构 列表名[start:end:step],step默认为1
python的括号范围都是左闭右开的。
获取列表1到2的元素
print(lst[1:3:1])输出为
['word', 98]获取列表中指定元素的索引
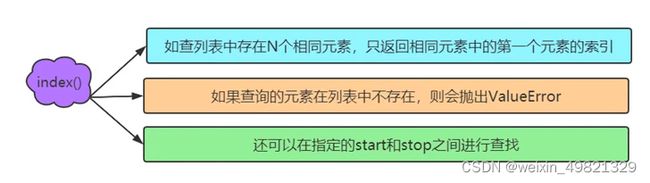
使用函数inde()
获取元素Hello的索引
print(lst.index("Hello"))输出为
0获取元素97的索引
print(lst.index(97))很明显列表lst中没有这个元素
区间索引单个元素
从0到3(但是不包含3)的位置索引Hello这个元素
print(lst.index("Hello",0,3))输出为:
0遍历列表
首先我们利用range创建一个0~9的列表lsts,然后用for循环遍历列表:
lsts = list(range(0, 10))
for lst in lsts:
print(lst)输出为:
上述for循环中,我们把列表lsts中的元素依次赋值给lst,利用print进行输出。