优化 | Operations Research文章精选:品类优化问题中的Logit模型
编者按:
在“Operations Research近期论文精选”中,我们有主题、有针对性地选择了Operations Research中一些有趣的文章,不仅对文章的内容进行了概括与点评,而且也对文章的结构进行了梳理,旨在激发广大读者的阅读兴趣与探索热情。在本期“论文精选”中,我们以“品类优化问题中的Logit模型”为主题,对Logit模型进行了简单介绍,主要探究了当客户在多元Logit模型下进行购物选择时的品类优化问题,商家怎样才能使用户在选择组合商品和替代商品时实现自己利益的最大化呢?下文推荐的三篇文章为我们提供了三种不同的思路和方法。
Logit模型简要介绍
1. Logit模型产生的原因
我们在日常生活和工作学习中所能见到的数据主要分为两大类:数值型的和分类型的。数值型的数据主要指身高、体重这一类可以表现为具体数字的数据,而分类型的数据是一种衡量标准,比如“是或否”,“对或错”,“高中低”。当这些数据作为自变量时,我们可以用虚拟化的手段把他们转化成为数值型的变量(如0-1整数规划);可是当他们作为因变量时,我们却无从下手,为此,科学家们研究出了一系列的二值选择模型。
对于二值选择问题,我们当然可以选择使用原来的思路,使用OLS(普通最小二乘)做一个拟合,那我们就会得到一个线性概率模型(LPM)。可是这样的线性概率模型是有一定缺陷的。首先,在二值选择中y没有连续的变化, y i y_i yi要么为0,要么为1,可是对于线性概率模型而言,当我们用一条线去拟合的时候,我们会发现会出现 y i < 0 y_i<0 yi<0或者 y i > 1 y_i>1 yi>1的情况。不仅如此,LPM中的违背了高斯-马尔可夫定理(Gauss–Markov theory)的假定,即对于二值选择的 y i = a x i + b y_i=ax_i+b yi=axi+b而言,b本应该服从正态分布,可是在LPM模型中b却服从两点分布。同时,当y是一个二值变量时, V a r ( b ) Var(b) Var(b)与x相关,所以会出现异方差问题,这会使得我们估计量的方差偏大,所以线性概率模型虽然简单易懂,但也存在着一些问题,所以为了修复线性概率模型的问题,科学家们又研究出了Probit和Logit模型。
2. Logit模型与Probit模型
首先,这两个模型的基本思路其实都是:找到一条拟合的线,当x无限小时,函数值无限趋近于0,当x无限大时,函数值无限趋向于1。接下来我们对这条曲线的累积分布函数(CDF)做一些特殊的假设,若他服从标准正态分布,那么他就是一个Probit模型,若他服从Logistic分布,那么他就是一个Logit模型。而因为Logit模型的CDF有明确的表达式,为了方便计算,大多数时候我们选择应用Logit模型。
3. Logistic回归分类与Logit模型应用场景
对于Logistic回归分析,我们主要把他分成三类。第一类是二元Logistic回归分析。如果因变量只有两个选项(有和无)、(是和否)、(愿意和不愿意),那么我们选择二元Logistic回归分析;第二类是多元无序Logistic回归分析。如果因变量有多个选项,而且选项之间是平等的,即没有大小比对关系和比对意义(一线城市、二线城市和三线城市),则我们选择多元无序Logistic无序分析;第三类是多元有序Logistic回归分析。他所对应的情况是:因变量有多个选项,而各个选项之间是有比较意义的。综上,这三种Logistic回归分类模型也逐一对应着我们不同的Logit模型。
Logit模型是社会学、计量经济学、临床医学等多个领域实证分析的常用方法,应用场景极其广泛。下面让我们以发表在《Operations Research》上的三篇文章为例,以品类优化问题为切入点,深入了解Logit模型的变体与应用。
推荐文章1
题目:
Revenue Management Under a Mixture of Independent Demand and Multinomial Logit Models
独立需求和多元Logit模型混合作用下的收益管理
期刊:
Operations Research
发表时间:
2022.9.2
原文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.2022.2333
作者:
Yufeng Cao, Paat Rusmevichientong, Huseyin Topaloglu
关键词:
assortment optimization(品类优化) • choice model(选择模型) • multinomial logit(多元Logit)
摘要:
We consider assortment optimization problems when customers choose under a mixture of independent demand and multinomial logit models. In the assortment optimization setting, each product has a fixed revenue associated with it. The customers choose among the products according to our mixture choice model. The goal is to find an assortment that maximizes the expected revenue from a customer. We show that we can find the optimal assortment by solving a linear program. We establish that the optimal assortment becomes larger as the relative size of the customer segment with the independent demand model increases. Moreover, we show that the Pareto-efficient assortments that maximize a weighted average of the expected revenue and the total purchase probability are nested, in the sense that the Pareto-efficient assortments become larger as the weight on the total purchase probability increases. Considering the assortment optimization problem with a capacity constraint on the offered assortment, we show that the problem is NP-hard, even when each product consumes unit capacity, so that we have a constraint on the number of offered products. We give a fully polynomial-time approximation scheme. In the assortment-based network revenue-management problem, we have resources with limited capacities, and each product consumes a combination of resources. The goal is to find a policy for deciding which assortment of products to offer to each arriving customer to maximize the total expected revenue over a finite selling horizon. A standard linear-programming approximation for this problem includes one decision variable for each subset of products. We show that this linear program can be reduced to an equivalent one of substantially smaller size. We give an expectation-maximization algorithm to estimate the parameters of our mixture model. Our computational experiments indicate that our mixture model can provide improvements in predicting customer purchases and identifying profitable assortments.
我们考虑当客户在有独立需求和多元Logit模型混合下进行选择时的品类优化问题。在品类优化设置中,每个产品都有一个与之相关的固定收益。顾客根据我们的混合选择模型在产品中进行选择。我们的目标是找到一个能从顾客中得到最大预期收益的组合。我们表明,我们可以通过解决一个LP问题来找到最佳组合。我们发现,随着有独立需求的客户群体相对规模的增加,最优组合也会变多。此外,我们表明,可以使预期收入和总购买概率的加权平均值最大化的帕累托有效组合是嵌套式的,即帕累托有效组合也随着总购买概率权重的增加而变大。对于有约束的品类优化问题,我们的研究表明这类问题是NP-hard的(所有NP问题都能在多项式时间复杂度内归约到的问题)。我们给出了一个有多项式时间复杂度的近似方案。在基于分类的网络收益管理问题中,我们的资源有限,但每个产品都要消耗一个资源组合。我们的目标是找到一个策略,通过决定向每个到达的顾客提供哪种产品,使得在销售范围有限的情况下总预期收入达到最大值。这个问题的线性近似值会包括代表每个产品子集的决策变量。我们表明,这个LP问题可以被简化为一个规模小得多的等效的LP问题。我们给出了一个可使期望最大的算法来估计我们的混合模型的参数。我们的计算实验表明,我们的混合模型可以在预测顾客购买量和识别盈利商品组合方面提供改进。
点评:
本文对客户在有独立需求和多元Logit模型混合下进行选择时的品类优化问题进行了研究,作者站在前人的肩膀上,在吸取收益管理领域蓬勃发展成果的同时大胆创新,提出了自己的混合选择模型。这种模型既提高了独立需求模型和多元Logit模型的灵活性,又确保了对应品类优化问题的可行性,有替代指数选择模型和马尔可夫选择模型的潜力。如果你对本领域最新的发展感兴趣,欢迎阅读这篇文章,如果你想要了解过去学者对Logit离散选择模型和品类优化问题的研究成果了研究脉络,清华大学工业工程系陈瑞教授和姜海教授所著的文章《基于Logit离散选择模型的品类优化问题综述》( DOI: 10.15960/j.cnki.issn.1007-6093.2017.04.008 )也值得一读。
推荐文章2
题目:
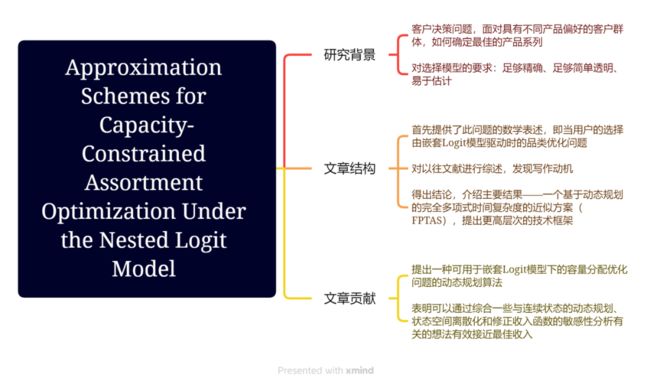
Approximation Schemes for Capacity-Constrained Assortment Optimization Under the Nested Logit Model
嵌套Logit模型下能力受限品类优化问题的近似方案
期刊:
Operations Research
发表时间:
2022.8.17
原文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.2022.2336
作者:
Danny Segev
关键词:
assortment optimization(品类优化) • approximation scheme(近似方案) • dynamic programming(动态规划)
摘要:
The main contribution of this paper resides in proposing a carefully crafted dynamic programming approach for capacitated assortment optimization under the nested logit model in its utmost generality. Specifically, we show that the optimal revenue can be efficiently approached within any degree of accuracy by synthesizing ideas related to continuous-state dynamic programming, state space discretization, and sensitivity analysis of modified revenue functions. These developments allow us to devise the first fully polynomial-time approximation scheme in this context, thus resolving fundamental open questions posed in previous papers.
本文的主要贡献在于提出了一种精心设计的动态规划方法,这种方法可用于嵌套Logit模型下的容量分配优化问题并具有最大的通用性。具体来说,我们表明,如果综合一些与连续状态的动态规划、状态空间离散化和修正收入函数的敏感性分析有关的想法,那么在任何精度范围内我们都能有效地接近最佳收入。这些发现使我们能够在这种情况下设计出第一个具有多项式时间复杂度的近似方案,从而解决了以前论文中提出的基本的开放问题。
点评:
本文与我们推荐的第一篇文章关注了同一个问题,都是“客户在商品选择和寻找可替代产品时,商家应该如何设置产品组合才能使得收益最大化”这一问题。不过这两篇文章都提供了不同的解决方法。本文基于动态规划的思想对上述问题进行了分析和解决,也提出了可靠的近似方案。将这些文章对比阅读也有利于我们对收益管理领域当前学术成果有全局的掌握。
推荐文章3
题目:
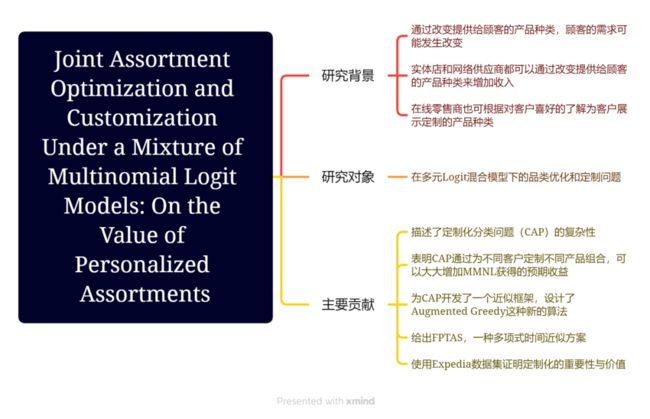
Joint Assortment Optimization and Customization Under a Mixture of Multinomial Logit Models: On the Value of Personalized Assortments
混合多元Logit模型下的品类优化和定制化问题:论个性化组合的价值
期刊:
Operations Research
发表时间:
2022.10.26
原文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.2022.2384
作者:
Omar El Housni, Huseyin Topaloglu
关键词:
assortment optimization(品类优化) • customization(个性化) • mixture of multinomial logit models(多元混合Logit模型)
摘要:
We consider a joint assortment optimization and customization problem under a mixture of multinomial logit models. In this problem, a firm faces customers of different types, each making a choice within an offered assortment according to the multinomial logit model with different parameters. The problem takes place in two stages. In the first stage, the firm picks an assortment of products to carry the subject to a cardinality constraint. In the second stage, a customer of a certain type arrives into the system. Observing the type of the customer, the firm customizes the assortment that it carries by, possibly, dropping products from the assortment.
The goal of the firm is to find an assortment of products to carry and a customized assortment to offer to each customer type that can arrive in the second stage to maximize the expected revenue from a customer visit. The problem arises, for example, in online platforms, where retailers commit to a selection of products before the start of the selling season; but they can potentially customize the displayed assortment for each customer type. We refer to this problem as the Customized Assortment Problem (CAP). Letting m be the number of customer types, we show that the optimal expected revenue of (CAP) can be Ω(m) times greater than the optimal expected revenue of the corresponding model without customization and this bound is tight. We establish that (CAP) is NP-hard to approximate within a factor better than 1 − 1 / e 1-1/e 1−1/e, so we focus on providing an approximation framework for (CAP). As our main technical contribution, we design a novel algorithm, which we refer to as Augmented Greedy; building on it, we give a Ω(1/logm)-approximation algorithm to (CAP). Also, we present a fully polynomial-time approximation scheme for (CAP) when the number of customer types is constant. Considering the case where we have a cardinally constraint on the assortment offered to each customer type in the second stage of (CAP), we give a Ω( 1 / ( m l o g m ) 1 / 2 1/(mlogm)^{1/2} 1/(mlogm)1/2)-approximation algorithm. In our computational experiments, we demonstrate the value of customization by using a data set from Expedia and check the practical performance of our approximation algorithm.
我们考虑的是在混合的多元Logit模型下的联合分类优化和定制问题。在这个问题中,公司面对不同类型的客户,每个客户都根据不同参数的多分类逻辑模型在提供给他们的品种中做出选择。该问题分两个阶段进行。在第一阶段,公司在基数限制的制约下选择产品种类。在第二阶段,特定类型的顾客进入我们已经设定好的系统中,通过观察顾客的类型,公司很可能会通过删除原有分类中的某些产品来实现对每一个顾客个性化定制的产品种类。
公司的目标是要找到一套固定的优化品类和一些定制品类的产品提供给用户,使自己得到的收益最大。例如,在线上,零售商通常在销售季节开始前致力于产品选择;他们有可能为每种客户类型定制不同的品种。我们把这个问题称为定制化分类问题(CAP)。假设m是客户类型的数量,我们表明在此模型下(CAP)的最佳预期收入可以是没有定制模型下最佳预期收入的Ω(m)倍,而且这个界限是严格的。我们确定(CAP)在优于1-1/e的系数内近似是NP-hard的(所有NP问题都能在多项式时间复杂度内归约到的问题),因此我们专注于为(CAP)提供一个近似框架。
说起我们的主要技术贡献,我们其实设计了一种新的算法——Augmented Greedy;在此基础上,我们给出了(CAP)的一个Ω(1/logm)的近似算法。另外,当客户类型的数量为常数时,我们为(CAP)提出了一个完全多项式时间复杂度的近似解决方案。考虑到在(CAP)的第二阶段,我们对提供给每个顾客类型的品种有基数限制,我们给出了一个Ω( 1 / ( m l o g m ) 1 / 2 1/(mlogm)^{1/2} 1/(mlogm)1/2 )的近似算法。在我们的计算实验中,我们通过使用Expedia的数据集来证明定制化的价值,并检查我们的近似算法的实际性能。
点评:
相较于前两篇文章而言,本文发表时间稍晚,但是其在内容上和方法上又产生了创新。相较于前两篇文章只考虑单纯的品类优化,本文在其基础上引入了“用户定制化”对收益提升的影响。除此之外,本文介绍的Augmented Greedy算法及其衍生也十分有价值。短短的三个月内,在《Operations Research》这样权威的期刊上已经至少发表了三篇同样主题的文章,我想,这也可以帮助我们一窥收益管理领域最新的学术动向与趋势。