transformer中
前馈全连接层
什么是前馈全连接层
在transformer中前馈全连接层就是具有两层线性层的全连接网络
前馈全连接层的作用
考虑注意力机制可能对复杂过程的拟合程度不够,通过增加两层网络来增强模拟的能力
# 前馈全连接层的代码分析
# 通过类PositionwiseFeedForward来实现前馈全连接层
class PositionwiseFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,d_model,d_ff,dropout=0.1):
"""初始化函数有三个输入函数分别是d_model 线性层的输入维度,第一个线性层输入的维度就是第二线性层输出的维度
因此我们希望输入通过前馈全连接层输入和输出的维度不变,第二个参数d_Ff就是第二个线性层
最后一个是置零比率
"""
super(PositionwiseFeedForward,self).__init__()
# 首先按照我们预期使用nn实例化了两个线性层对象,self.w1,self.w2
# 它们的参数分别是d_model,d_ff,d_model
self.w1 = nn.Linear(d_model,d_ff)
self.w2 = nn.Linear(d_ff,d_model)
# 然后使用nn的Dropout实例化了对象self.dropout
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
def forward(self,x):
"""输入参数为x,代表来自上一层的输出"""
# 首先经过第一个线性层,然后使用Functional中relu函数进行激活
# 之后再使用dropout进行随机置0,最后通过第二个线性层w2,返回最终结果
return self.w2(self.dropout(F.relu(self.w1(x))))
# 实例化参数
d_model = 512
# 线性变化的维度
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
# 输入参数x可以是多头注意力机制的输出
x = mha_result
print(x)
print(x.shape)
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model,d_ff,dropout)
ff_result = ff(x)
print(ff_result)
print(ff_result.shape)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
torch.Size([2, 4, 4])
tensor([[[-5.5992, 1.0742, -0.1025, ..., -0.8787, -1.9476, 0.3934],
[-6.8009, -1.6855, 0.1202, ..., -2.6405, 3.3057, 0.9944],
[-6.3014, -3.2064, -1.9752, ..., 2.0258, 6.4564, -0.9483],
[-4.7112, -2.1608, -4.7235, ..., 1.1519, 5.1089, -0.7141]],
[[-0.2383, -1.7213, -4.8471, ..., -4.1019, 1.3218, 2.8073],
[ 3.9948, -2.8342, -4.2963, ..., -3.1237, 2.7896, 4.8488],
[ 6.5958, -1.0913, -2.0725, ..., -5.0694, 5.3710, 4.3295],
[ 5.2731, -2.9556, -5.2626, ..., -6.8202, 3.8721, 2.1508]]],
grad_fn=<ViewBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
tensor([[[-0.5221, -0.9886, 0.3141, ..., 1.5486, -0.8625, -0.5573],
[ 1.1142, -1.0538, 1.1341, ..., 0.8071, 0.2595, -1.3223],
[-0.0189, -0.9423, 1.0818, ..., 0.5622, 0.1552, -0.7604],
[-0.3909, 1.2397, 0.6896, ..., 1.9819, 0.3029, -0.1886]],
[[-1.9421, -0.4179, -0.4647, ..., 0.7023, 1.6178, 0.2486],
[-1.8467, 0.2703, -1.6761, ..., -0.0637, 2.0552, 1.3232],
[-2.4583, -1.2925, -1.7345, ..., -0.9665, 0.7732, 0.1152],
[-2.6982, -1.6213, 0.7726, ..., 0.8863, 1.7218, 0.6042]]],
grad_fn=<ViewBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
进程已结束,退出代码0
前馈全连接层总结
学习了什么是前馈全连接层
在transformer中前馈全连接层就是具有两层线性层的全连接网络
学习了前馈全连接层的作用:
考虑注意力机制可能对复杂过程的拟合程度不够,通过增加两层网络来增强模型的能力
学习并实现了前馈全连接层的类:PositionwiseFeedForward
它的实例化参数为d_model,d_ff,dropout分别代表词嵌入维度,线性变换维度,和置零比率
它的输入参数x,表示上层的输出
它的输出是经过2层线性网络变换的特征表现。
规范化层
规范化层的作用:
它是所有深层网络模型都需要的标准网格层,因为随着网络层数的增加,通过多层的计算后参数可能开始出现过大或过小的情况,这样可能会导致学习过程出现异常,模型可能收敛非常的慢,因此都会在一定层数后规范化层进行数值的规范化,使其特征数值在合理范围内。
# 规范化层的代码实现
# 通过LayerNorm实现规范化层的类
class LayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,features,eps=1e-6):
"""初始化函数有两个参数,一个是features,表示词嵌入的维度
另一个是eps它是一个足够小的数,在规范化公式的分母中出现
防止分母为0,默认是1e-6"""
super(LayerNorm, self).__init__()
# 根据feature的形状初始化两个参数张量a2,和b2,第一个初始化为1张量
# 也就是里面的元素都是1,第二个初始化为0张量,也就是也就是里面的元素都是0,这两个张量就是规范化层的参数
# 因为直接对上一层得到的结果做规范化公式计算,将改变结果的正常表征,因此就需要有参数作为调节银子
# 使其既能满足规范化要求,又不能改变针对目标的表征,最后使用nn.parameter封装,代表它们是模型的参数
self.a2 = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(features))
self.b2 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(features))
# 把eps传到类中
self.eps = eps
def forward(self,x):
"""输入参数x代表来自上一层的输出"""
# 在函数中,首先对输入变量x求其最后一个维度的均值,并保持输出维度与输入维度一致
# 接着再求最后一个维度的标准差,然后就是根据规范化公式,用x减去均值除以标准差获得规范化的
# 最后对结果乘以我们的缩放参数,即a2,*号代表同型点乘,即对应位置进行乘法操作,加上位移参数b2,返回即可
mean = x.mean(-1,keepdim=True)
std = x.std(-1,keepdim=True)
return self.a2 * (x-mean) / (std+self.eps) + self.b2
# 全1的标准差乘以 标准差(为了防止为0,所以加上eps),之后都为0之后,就会加上了全一的b2
# 实例化参数
feature = d_model = 512
eps = 1e-6
# 输入参数
x = ff_result
# 输入的x来自前馈全连接层的输出
# 调用
ln = LayerNorm(feature,eps)
ln_result = ln(x)
print(ln_result)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
torch.Size([2, 4, 4])
tensor([[[-3.8593, -2.6937, 2.0049, ..., -1.7184, 10.0169, 3.4599],
[-1.6628, -0.1407, 3.7844, ..., -6.1630, 7.3321, 6.2921],
[-3.0315, 0.3443, 0.9926, ..., -2.2832, 8.6451, 4.6603],
[-6.1410, -0.6480, 1.4155, ..., 1.0516, 6.4925, 6.3924]],
[[-7.0660, -0.2978, 1.4820, ..., -0.3551, 5.8069, -4.3561],
[-7.5021, 0.7103, -0.0512, ..., -0.8669, 2.0102, -6.3286],
[-3.6880, -2.3512, 0.3315, ..., 2.6193, 5.5376, -2.0390],
[-6.3465, -1.1218, 1.1665, ..., 1.0985, 6.9518, -4.3248]]],
grad_fn=<ViewBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
tensor([[[-0.6525, -0.3327, -1.5058, ..., -0.4854, 0.6746, 0.0533],
[ 1.3234, -1.6772, 0.7271, ..., -0.4401, 1.8648, -0.4798],
[-0.0266, -0.8159, -0.2665, ..., -0.1831, 0.5600, -0.4437],
[-1.0283, -0.1501, -0.8698, ..., -1.8278, -0.1497, 0.4778]],
[[ 1.7016, 0.3336, 0.3490, ..., -1.1415, 0.1094, -0.5996],
[ 0.0894, -0.8116, -0.3802, ..., -1.5428, -0.6081, 0.2940],
[ 1.6869, -0.4314, -0.2462, ..., -2.4920, -1.7258, -0.1710],
[ 0.4620, 0.2076, 0.0044, ..., -1.1373, -0.9668, -0.8344]]],
grad_fn=<ViewBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
tensor([[[-0.5649, -0.2767, -1.3341, ..., -0.4143, 0.6312, 0.0712],
[ 1.0456, -1.2721, 0.5850, ..., -0.3166, 1.4638, -0.3472],
[-0.0331, -0.8198, -0.2722, ..., -0.1891, 0.5516, -0.4488],
[-1.0480, -0.1295, -0.8822, ..., -1.8842, -0.1291, 0.5272]],
[[ 1.2066, 0.2518, 0.2626, ..., -0.7777, 0.0954, -0.3995],
[ 0.1082, -0.5630, -0.2416, ..., -1.1077, -0.4114, 0.2606],
[ 1.4276, -0.3503, -0.1949, ..., -2.0798, -1.4367, -0.1317],
[ 0.3958, 0.1913, 0.0278, ..., -0.8904, -0.7533, -0.6468]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
进程已结束,退出代码0
规范化层总结
学习了规范化层的作用:
它是所有深层网络模型都需要的标准网络层,因为随着网络层数的增加,通过多层的计算后参数可能开始出现过大或过小的情况,这样可能会导致学习过程出现异常,模型可能收敛非常的慢,因此都会在一定层数后接规范化层进行数值的规范化,使其特征数值在合理范围内。
学习并实现了规范化层的类:LayerNorm
它的实例化参数有两个,feature和eps,分别代表词嵌入特征大小,和一个足够小的数
它的输入参数x代表来自上一层的输出
它的输出就是经过规范化的特征表示
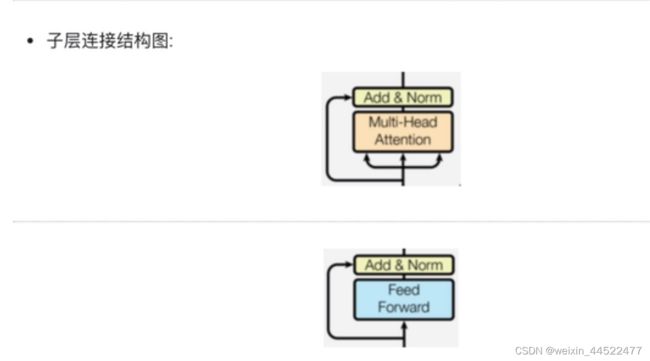
子层连接结构
如图所示,输入到每个子层以及规范化层的过程中,还使用了残差连接(跳跃连接),因此我们把这一部分结构整体叫做子层连接(代表子层及其链接结构),在每个编码器层中,都有两个子层,这两个子层加上周围的链接结构就形成了两个子层连接结构。
# 子层连接结构的代码分析
# 使用SublayerConnection来实现子层连接结构的类
class SublayerConnection(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,size,dropout=0.1):
"""size:词嵌入维度的大小
dropout本身对模型结构中的节点数进行随机抑制的比率:
又因为节点被抑制等效就是该节点的输出都是0,因此也可以把dropout看作是对输出矩阵的随机
"""
super(SublayerConnection, self).__init__()
#实例化规范化对象self.norm
self.norm = LayerNorm(size)
# 又使用nn中预定义的dropout实例化一个self.dropout对象
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
self.size = size
def forward(self,x,sublayer):
"""前向逻辑函数中,接收上一层或者子层的输入作为第一个参数,将该子层连接中的子层函数作为第二个参数"""
# 我们首先对输出进行规范化,然后将结果传给子层处理,之后再对子层进行dropout操作
# 随机停止一些网络中神经元的作用,来防止过拟合,最后还有一个add操作
# 因为存在跳跃连接,所以是将输入x与dropout后的子层输出结果相加作为最终的子层连接输出
return x + self.dropout(sublayer(self.norm(x)))
# 实例化参数
size = 512
dropout=0.2
head = 8
d_model = 512
# 令x为位置编码器的输出
x = pe_result
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2,4,4))
# 假设子层中装的多头注意力层,实例化这个类
self_attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head,d_model)
# 使用lambda获得一个函数类型的子层
# sublayer要传一个子层函数
# 这三个参数相同,相当于自注意力
sublayer = lambda x:self_attn(x,x,x,mask)
# 调用
sc = SublayerConnection(size,dropout)
sc_result = sc(x,sublayer)
print(sc_result)
print(sc_result.shape)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
torch.Size([2, 4, 4])
tensor([[[ 12.6191, 3.8772, -16.2525, ..., 48.7128, 22.0340, -3.1954],
[ 56.8472, -31.3871, 17.6264, ..., 0.1026, 53.5558, 1.6699],
[ 0.0722, -22.1353, -14.6820, ..., 9.8679, 34.0564, -42.3564],
[-14.9600, 4.3225, 17.0936, ..., -8.4868, -0.2952, -10.5150]],
[[-21.0714, -30.6257, 36.8571, ..., 1.0697, -21.3823, -26.4516],
[ 20.2159, -3.8735, -37.3821, ..., 9.3443, -50.2942, 15.9988],
[ 2.7210, -0.1320, -12.0791, ..., -42.7716, 10.1888, 6.0287],
[ -2.1989, 0.2898, 0.1916, ..., -8.9639, 24.7675, 13.1533]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
进程已结束,退出代码0
子层连接结构总结
什么是子层连接结构
输入到每个子层以及规范化层的过程中,还是用了残差连接,因此我们把这一部分结构整体叫做子层连接,在每个编码器中,都有两个子层,这两子层是加上周围的连接结构就形成了两个子层连接结构。
学习并实现了子层连接结构的类:SublayerConnection
类的初始化函数输入参数是size,dropout分别代表词嵌入大小和置零比率
它的实例化对象输入参数是x,sublayer,上一层的输出以及子层的函数表示
它的输出就是通过子层连接结构处理的输出
编码器层
编码器层的作用
作为编码器的组成单元,每个编码器层完成一次对输入的特征提取过程,即编码过程
# 编码器层
# 使用EncoderLayer类实现编码层
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,size,self_attn,feed_forward,dropout):
"""
:param size: 词嵌入维度的大小,
:param self_attn: 传入多头自注意力子层实例化对象,并且是自注意力机制
:param feed_forward: 传入前馈全连接层实例化对象
:param dropout: 置零比率
"""
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
# 首先将self_attn 和feed_forward传入其中
self.self_attn = self_attn
self.feed_forward = feed_forward
# 编码器层有两个子层连接结构,所以使用clones函数进行克隆
self.sublayer = clones(SublayerConnection(size,dropout),2)
# 把size 传入其中
self.size = size
def forward(self,x,mask):
"""
:param x: 上一层的输出
:param mask: 掩码张量
:return:
"""
# 第一个子层连接结构,包含多头自主里子层
# 第二个子层连接结构,前馈全连接子层,最终返回结果
x = self.sublayer[0](x,lambda x: self.self_attn(x,x,x,mask))
return self.sublayer[1](x,self.feed_forward)
# 实例化参数
size = 512
head = 8
d_model = 512
x = pe_result
dropout = 0.2
self_attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head,d_model)
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model,d_ff,dropout)
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2,4,4))
e1 = EncoderLayer(size,self_attn,ff,dropout)
e1_result = e1(x,mask)
print(e1_result)
print(e1_result.shape)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
torch.Size([2, 4, 4])
tensor([[[ 3.5775e+01, -1.8941e+01, -2.0456e+01, ..., -1.5323e+01,
-3.1003e+00, 2.8386e+01],
[-1.4315e+01, -1.6286e+01, -2.7690e+01, ..., -3.6282e-02,
-2.6855e+01, 3.3641e+00],
[-1.5930e+01, 9.3267e+00, 3.0532e+01, ..., 1.5100e+01,
2.7193e+01, -1.9352e+01],
[ 1.2735e+01, -3.0368e+01, 1.2358e+01, ..., -3.3809e+01,
-5.9452e-01, 1.8711e+01]],
[[-3.0133e+01, 1.9472e+01, -3.3228e+01, ..., -3.4911e+01,
1.3713e+01, -1.0666e+01],
[ 5.1824e+00, 1.5201e+01, -8.5935e+01, ..., -1.6287e+01,
-8.5141e+00, -5.2643e+01],
[-5.7583e+01, -3.8192e+01, -2.0143e-01, ..., -2.8396e+01,
1.2020e-01, -1.0064e-01],
[ 1.6422e+01, 1.0526e+00, 2.7490e+01, ..., 6.2439e+01,
-4.4403e+01, 1.5383e-01]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
进程已结束,退出代码0
编码器层总结:
编码器层的作用
作为编码器的组成单元,每个编码器层完成一次对输入的特征提取过程,即编码过程
学习并实现了编码器层的类:EncoderLayer
类的初始化函数共有4个,分别是size,self_attn,feed_forward,dropout
实例化对象的输入参数有两个,x代表上一层的输出,mask掩码张量
输出代表经过整个编码层的特征表示
编码器
编码器的作用:编码器用于对输入进行指定的特征提取过程,也称为编码,由N个编码器层堆叠而成
编码器的结构图
# 编码器
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,layer,N):
"""
:param layer: 编码器层
:param N: 编码器层的个数
"""
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
# 首先使用clones函数克隆N个编码器层放在self.layers中
self.layers = clones(layer,N)
# 再初始化一个规范化层,它将用来编码器的最后面
self.norm = LayerNorm(layer.size)
def forward(self,x,mask):
# 首先就是对我们克隆的循环器层进行循环,每次都会得到一个新的x
# 这个循环的过程,就相当于输出的x经过N个编码器层的处理
# 最后再通过规范化层的对象self.norm进行处理,最后返回结果
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x,mask)
return self.norm(x)
# 实例化参数
# 第一个实例化参数layer,它是一个编码器层的实例化对象,因此需要传入编码器层的参数
# 又因为编码器层的子层是不共享的,因此需要使用深度拷贝各个对象
size = 512
head = 8
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
c = copy.deepcopy()
attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head,d_model)
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model,dropout)
dropout = 0.2
layer = EncoderLayer(size,c(attn),c(ff),dropout)
# 编码器的层数
N = 8
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2,4,4))
# 调用
en = Encoder(layer,N)
en_result = en(x,mask)
print(en_result)
print(en_result.shape)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
torch.Size([2, 4, 4])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 639, in <module>
c = copy.deepcopy()
TypeError: deepcopy() missing 1 required positional argument: 'x'
tensor([[[-2.4088e+01, -4.7052e+01, -1.0659e-01, ..., 2.5291e+01,
-5.0517e+01, 1.5095e+01],
[ 2.9400e+01, -1.1476e+01, 2.5877e+01, ..., 2.7515e+01,
-2.7167e+01, 2.1456e+01],
[-6.2381e+00, -7.5147e+00, -4.9948e+00, ..., -2.0679e+00,
-8.2479e+00, 1.7333e+01],
[ 8.2518e+00, -6.0388e+00, -6.7308e+00, ..., 5.5313e+00,
-1.1943e+01, 1.7019e+01]],
[[ 5.2740e+00, -4.9948e+01, -3.2455e+01, ..., -2.7291e+01,
-1.9919e+01, -1.1546e+01],
[-1.2694e+01, -6.6146e-02, 1.5243e+01, ..., -4.7019e+01,
6.3593e-01, -3.3604e+01],
[-3.7788e+00, 6.3428e+00, 4.2921e-02, ..., -2.0845e-01,
1.4364e+00, -3.7012e+01],
[-2.4661e+01, -1.0729e+01, 1.1131e+01, ..., 6.2810e+00,
2.8209e-01, 6.4647e+00]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
进程已结束,退出代码1
编码器的总结
编码器的作用:编码器用于对输入进行指定的特征提取过程,也称为编码,由N个编码器层堆叠而成
学习并实现了编码器的类:Encoder
类的初始化函数参数有两个,分别是layer和N
forward函数的输入参数也有两个,和编码器层的forward相同,x 和mask
编码器类的输出就是Transformer中编码器的特征提取表示,它将称为编码器的输入的一部分
解码器部分实现
解码器部分
由N个解码器层堆叠而成
每个编码器由三个子层连接结构组成
第一层包括一个Multiheadattention和forward和一个残差连接
第二层multiheadattention和forward以及一个残差连接
第三层包括一个前馈全连接子层和规范化层以及一个残差连接
说明:
解码器层中的各个部分,与编码器中实现相同,这里就可以直接用来解码器层
解码器层的作用
作为解码器的组成单元,每个解码器层根据给定的输入向目标方向进行特征提取操作,即解码过程
# 解码器层的代码实现
# 使用DecoderLayer的类实现解码器层
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,size,self_attn,src_attn,feed_forward,dropout):
"""
:param size: 词嵌入维度的大小,同时也代表解码层的尺寸
:param self_attn: 多头自注意力对象,Q=K=V
:param src_attn: 多头注意力对象 Q !=k = V
:param feed_forward: 前馈全连接层对象
:param dropout:置0率
"""
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
# 在初始化函数中,主要就是将这些输入传到类中
self.size = size
self.self_attn = self_attn
self.src_attn = src_attn
self.feed_forward = feed_forward
self.dropout = dropout
# 按照结构图使用clones函数克隆三个子层连接对象
self.sublayer = clones(SublayerConnection(size,dropout),3)
def forward(self,x,memory,source_mask,target_mask):
"""
:param x: 上一层的输入x
:param memory: 编码层的语义存储变量memory,最后有一个张量就是2,4,512,语义文本的抽取
:param source_mask: 源数据掩码张量
:param target_mask: 目标数据掩码张量
:return:
"""
# 将memory表示m方便使用
m = memory
# 将x传入第一个子层结构,第一个子层结构的输入分别是x和self_attn函数,因为是自注意力机制
# 最后一个参数是目标数据掩码张量,这时要对目标数据进行遮掩,因此此时模型可能还没有生成任何目标数据
# 解码器准备生成第一个字符或词汇时,我们其实已经传入了第一个字符以便计算损失
# 但是我们不希望在生成第一个字符时模型能利用这个信息,因此我们会将其遮掩,同样生成第二个字符或者词汇时也进行遮掩
# 模型只能使用第一个字符或者词汇信息,第二个字符以后之后的信息都不允许被模型使用
x = self.sublayer[0](x,lambda x: self.self_attn(x,x,x,target_mask))
# 接着进入第二个子层,注意力机制,q时输入x, k,v都是编码层输出memory
# 同样也传入source_mask,但是进行源数据遮掩的原因并非是一致信息泄露,而是遮掩掉对结果没有意义的字符而产生的注意力的值
# 以此提升模型效果和训练速度,这样就完成了第二个子层的处理
x = self.sublayer[1](x,lambda x:self.src_attn(x,m,m,source_mask))
# 最后一个子层就是前馈全连接子层,经过它的处理后就可以返回结果,这就是我们的解码器层结构
return self.sublayer[2](x,self.feed_forward)
# 实例化参数
head = 8
size = 512
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
self_attn = src_attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head,d_model,dropout)
# 前馈全连接层也和之前相同
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model,d_ff,dropout)
# 输入参数
# x是来自目标数据的词嵌入表示,但形式和元数据的词嵌入表示相同,这里使用per充当
x = pe_result
# memory是来自编码器的输出
memory = pe_result
# 实际中source_mask和target_mask并不相同,这里为了方便计算使他们都为mask
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2,4,4))
source_mask = target_mask = mask
# 调用
dl = DecoderLayer(size,self_attn,src_attn,ff,dropout)
dl_result=dl(x,memory,source_mask,target_mask)
print(dl_result)
print(dl_result.shape)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
torch.Size([2, 4, 4])
tensor([[[ -1.9369, -3.3912, 44.8981, ..., 7.7902, -38.9288, 21.8915],
[ 19.8032, -28.1045, 42.7394, ..., -22.9733, 4.9915, -18.9890],
[-20.0487, 4.5310, -26.0176, ..., 38.8181, -12.5031, 23.9239],
[-15.4446, 0.5000, 15.4785, ..., -1.9862, 0.3196, -17.0533]],
[[ 46.1806, -33.8526, 10.8418, ..., -32.5074, -2.6210, -26.3825],
[ 12.5362, 19.1355, -51.1015, ..., 4.1746, -12.1397, 20.4997],
[-35.0968, -50.6318, -15.8238, ..., 30.0835, -38.9728, 27.2341],
[-18.0310, 9.5662, -43.0816, ..., 6.9575, -1.5159, 3.7326]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
进程已结束,退出代码0
编码器层的总结
解码器层的作用
作为解码器的组成单元,每个解码器层根据给定的输入向目标方向进行特征提取操作,即解码过程
学习并实现了解码器层的类:DecoderLayer
类的初始化函数的参数有5个
:param size: 词嵌入维度的大小,同时也代表解码层的尺寸
:param self_attn: 多头自注意力对象,Q=K=V
:param src_attn: 多头注意力对象 Q !=k = V
:param feed_forward: 前馈全连接层对象
:param dropout:置0率
forward函数的参数有四个,x,memory,源数据掩码张量,目标数据掩码张量
最终输出了由编码器输入和目标数据一同作用的特征提取结果
pycharm快捷键
Shift + Enter 任意位置换行
双击Shift 快速查找
Ctrl + Alt + L 代码格式化
Ctrl + D 复制选定的区域(一行或多行)
Ctrl + Y 删除当前行
解码器
解码器的作用
根据解码器的结果以及上一次预测的结果,对下一个可能出现的值进行特征表示
解码器的代码分析
# 解码器层的代码实现
# 使用DecoderLayer的类实现解码器层
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, size, self_attn, src_attn, feed_forward, dropout):
"""
:param size: 词嵌入维度的大小,同时也代表解码层的尺寸
:param self_attn: 多头自注意力对象,Q=K=V
:param src_attn: 多头注意力对象 Q !=k = V
:param feed_forward: 前馈全连接层对象
:param dropout:置0率
"""
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
# 在初始化函数中,主要就是将这些输入传到类中
self.size = size
self.self_attn = self_attn
self.src_attn = src_attn
self.feed_forward = feed_forward
self.dropout = dropout
# 按照结构图使用clones函数克隆三个子层连接对象
self.sublayer = clones(SublayerConnection(size, dropout), 3)
def forward(self, x, memory, source_mask, target_mask):
"""
:param x: 上一层的输入x
:param memory: 编码层的语义存储变量memory,最后有一个张量就是2,4,512,语义文本的抽取
:param source_mask: 源数据掩码张量
:param target_mask: 目标数据掩码张量
:return:
"""
# 将memory表示m方便使用
m = memory
# 将x传入第一个子层结构,第一个子层结构的输入分别是x和self_attn函数,因为是自注意力机制
# 最后一个参数是目标数据掩码张量,这时要对目标数据进行遮掩,因此此时模型可能还没有生成任何目标数据
# 解码器准备生成第一个字符或词汇时,我们其实已经传入了第一个字符以便计算损失
# 但是我们不希望在生成第一个字符时模型能利用这个信息,因此我们会将其遮掩,同样生成第二个字符或者词汇时也进行遮掩
# 模型只能使用第一个字符或者词汇信息,第二个字符以后之后的信息都不允许被模型使用
x = self.sublayer[0](x, lambda x: self.self_attn(x, x, x, target_mask))
# 接着进入第二个子层,注意力机制,q时输入x, k,v都是编码层输出memory
# 同样也传入source_mask,但是进行源数据遮掩的原因并非是一致信息泄露,而是遮掩掉对结果没有意义的字符而产生的注意力的值
# 以此提升模型效果和训练速度,这样就完成了第二个子层的处理
x = self.sublayer[1](x, lambda x: self.src_attn(x, m, m, source_mask))
# 最后一个子层就是前馈全连接子层,经过它的处理后就可以返回结果,这就是我们的解码器层结构
return self.sublayer[2](x, self.feed_forward)
# 实例化参数
head = 8
size = 512
d_model = 512
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
self_attn = src_attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model, dropout)
# 前馈全连接层也和之前相同
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff, dropout)
# 输入参数
# x是来自目标数据的词嵌入表示,但形式和元数据的词嵌入表示相同,这里使用per充当
x = pe_result
# memory是来自编码器的输出
memory = en_result
# 实际中source_mask和target_mask并不相同,这里为了方便计算使他们都为mask
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
source_mask = target_mask = mask
# 调用
dl = DecoderLayer(size, self_attn, src_attn, ff, dropout)
dl_result = dl(x, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
# print(dl_result)
# print(dl_result.shape)
# 解码器层的代码分析
# 使用类Decoder来实现解码器
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer, N):
"""
:param layer: 解码器层
:param N: 解码器的个数
"""
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
# 首先使用clones方法克隆了N个layer,然后实例化了一个规范化层
# 因为数据走过了所有的解码器层后最后要做规范化处理
self.layers = clones(layer, N)
self.norm = LayerNorm(layer.size)
def forward(self, x, memory, source_mask, target_mask):
"""
:param x: 目标数据的嵌入表示
:param memory: 编码层的输出
:param source_mask: 源数据的掩码张量
:param target_mask: 目标数据的掩码张量
:return: 解码器层
"""
# 然后就是对每个层进行循环,当然这个循环就是变量x通过每一个层的处理
# 得到最后的结果,再进行一次规范化返回即可
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
return self.norm(x)
# 实例化参数
size = 512
d_model = 512
head = 8
d_ff = 64
dropout = 0.2
c = copy.deepcopy
attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head, d_model)
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff, dropout)
layer = DecoderLayer(d_model, c(attn), c(attn), c(ff), dropout)
N = 8
# 输入参数
# 输入参数与解码器层的输入参数相同
x = pe_result
memory = en_result
mask = Variable(torch.zeros(2, 4, 4))
source_mask = target_mask = mask
de = Decoder(layer, N)
de_result = de(x, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
print(de_result)
print(de_result.shape)
"""错误
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 663, in
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, dropout)
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 449, in __init__
self.w1 = nn.Linear(d_model, d_ff)
File "D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\lib\site-packages\torch\nn\modules\linear.py", line 96, in __init__
self.weight = Parameter(torch.empty((out_features, in_features), **factory_kwargs))
TypeError: empty() received an invalid combination of arguments - got (tuple, dtype=NoneType, device=NoneType), but expected one of:
* (tuple of ints size, *, tuple of names names, torch.memory_format memory_format, torch.dtype dtype, torch.layout layout, torch.device device, bool pin_memory, bool requires_grad)
* (tuple of ints size, *, torch.memory_format memory_format, Tensor out, torch.dtype dtype, torch.layout layout, torch.device device, bool pin_memory, bool requires_grad)
进程已结束,退出代码1
ff掉了一个d_ff 没有传进去
"""
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
tensor([[[ 0.0349, -0.6634, -0.7218, ..., 1.2931, -0.1682, -0.9778],
[-0.3160, -1.4353, -0.1782, ..., -0.1218, 0.9247, -0.2183],
[ 0.2027, 1.6564, -0.0257, ..., -2.0023, -0.2028, 0.5717],
[-1.6855, -0.7104, -1.2941, ..., 0.9374, -0.2138, -1.4794]],
[[-0.0133, 0.4142, -0.2952, ..., 0.1107, 0.1560, -0.3563],
[-0.3103, 0.5886, 0.1842, ..., -0.9812, 0.6723, -0.2766],
[ 0.7875, 1.2223, 0.9733, ..., -0.3033, -0.9513, 1.3531],
[ 0.8965, 0.8563, -2.4974, ..., 0.8172, -0.1071, 0.6657]]],
grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 512])
进程已结束,退出代码0
解码器总结
学习了解码器的作用
根据编码器的结果以及上一次预测的结果,对下一次可能出现的值进行特征表示
学习并实现了解码器的类:Decoder
类的初始化函数的参数由两个,第一个是解码器层layer,第二个是解码器层的个数N
forward函数中的参数有4个,x代表目标数据的嵌入表示,memory编码器层的输出,src_mask,tgt_mask
输出解码过程的最终特征表示
输出部分实现
输出部分包含
线性层
softmax层
线性层的作用
通过对上一步的线性变化得到指定维度的输出,也就是转换维度的作用
softmax层的作用
使最后一维的向量中的数字缩放到0-1的概率值域内,并满足它们的和为1
# 线性层和softmax层的代码分析
# nn.functional工具包装载了网络层中哪些只进行计算,而没有参数的层
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 将线性层和softmax计算层一起实现,因为二者的共同目标使生成最后的结构
# 因此把类的名字叫做Generator,生成器类
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,d_model,vocab_size):
"""
:param d_model: 词嵌入维度
:param vocab_size: 词表大小
"""
super(Generator, self).__init__()
# 首先就是使用nn中的预定义线性层进行实例化,得到一个对象self.project等待使用
# 这个线性层的参数有两个,就是初始化函数传进来的两个参数,d_model,vocab_size
self.project = nn.Linear(d_model,vocab_size)
def forward(self,x):
"""
:param x:
:return:
"""
# 首先使用上一层得到的self.project对x进行线性变换
# 使用F中已经实现的log_softmax进行softmax处理
# 使用log_softmax使因为和我们这个pytorch版本的损失函数实现有关
# log+softmax就是对softmax的结果又取了对数,因为对数函数使单调递增函数
# 因此对最终我们取最大的概率值没有影响,最后返回结果即可
return F.log_softmax(self.project(x),dim=-1)
# # nn.Linear演示
# m = nn.Linear(20,30)
# input = torch.randn(128,20)
# output = m(input)
# print(output.size())
# 实例化参数
d_model = 512
# 词表大小使1000
vocab_size = 1000
# 输入参数
x = de_result
# 调用
gen = Generator(d_model,vocab_size)
gen_result = gen(x)
print(gen_result)
print(gen_result.shape)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
tensor([[[-8.0748, -7.1752, -7.5282, ..., -8.2559, -7.8693, -7.5256],
[-7.2366, -7.6346, -7.0886, ..., -6.9814, -8.0830, -6.1256],
[-6.5867, -7.4181, -6.9777, ..., -7.6399, -7.1493, -6.3277],
[-7.6567, -6.1960, -6.9909, ..., -7.0748, -7.4520, -7.2986]],
[[-7.6927, -6.8764, -7.6808, ..., -7.0979, -6.5261, -7.3172],
[-6.7495, -6.0198, -6.9135, ..., -6.8014, -7.7436, -6.8036],
[-7.1508, -6.0661, -7.5009, ..., -6.7963, -7.2601, -6.9016],
[-7.7333, -6.2288, -7.5624, ..., -7.4179, -6.0605, -6.7856]]],
grad_fn=<LogSoftmaxBackward0>)
torch.Size([2, 4, 1000])
进程已结束,退出代码0
小结
学习了输出部分包含
线性层、softmax层
线性层的作用
通过对上一步的线性变化得到指定维度的输出,也就是zhua能换维度的作用
softmax层的作用
使最后一维的向量中的数字缩放到0-1的概率值域内,并满足它们的和为1
学习并实现了线性层和softmax层的类:Generator
初始化函数的输入参数有两个:d_model代表词嵌入维度,vocab_size代表词表大小
forward函数接受上一层的输出
最终获得经过线性层和softmax层处理的结果
模型的构建
transformer总体架构图
编码器-解码器结构的代码实现
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 948, in <module>
ed_result = ed(source,target,source_mask,target_mask)
File "D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\lib\site-packages\torch\nn\modules\module.py", line 1130, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 922, in forward
return self.decode(self.encoder(source,source_mask),source_mask,target,target_mask)
File "D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\lib\site-packages\torch\nn\modules\module.py", line 1130, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 649, in forward
x = layer(x, mask)
File "D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\lib\site-packages\torch\nn\modules\module.py", line 1130, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 611, in forward
x = self.sublayer[0](x, lambda x: self.self_attn(x, x, x, mask))
File "D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\lib\site-packages\torch\nn\modules\module.py", line 1130, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 551, in forward
return x + self.dropout(sublayer(self.norm(x)))
File "D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\lib\site-packages\torch\nn\modules\module.py", line 1130, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*input, **kwargs)
File "D:\soft\pycharm\pythonProject2\main.py", line 510, in forward
mean = x.mean(-1, keepdim=True)
RuntimeError: mean(): could not infer output dtype. Input dtype must be either a floating point or complex dtype. Got: Long
进程已结束,退出代码1
还是并没有解决
模型构造函数make_moel
def make_model(source_vocab,target_vocab,N=6,d_model=512,d_ff=2048,head = 8, dropout = 0.1):
"""
:param source_vocab: 源数据的总数:比如英译法,英文词汇的总数
:param target_vocab: 法文的词汇总数
:param N: 编码器和解码器堆叠的数
:param d_model: 词向量映射维度
:param d_ff: 前馈全连接网络中变换矩阵的维度
:param head: 多头注意力结构中的多头数
:param dropout: 置零率
:return:
"""
# 首先得到一个深度拷贝命令
c = copy.deepcopy
# 实例化多头注意力类,得到对象attn
attn = MultiHeadedAttention(head,d_model)
# 前馈全连接层,ff
ff = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model,d_ff,dropout)
# 实例化位置编码类
position = PositionalEncoding(d_model,dropout)
# 最外层使EncoderDecoder
model = EncoderDecoder(
# 编码器子层
Encoder(EncoderLayer(d_model,c(attn),c(ff),dropout),N),
Decoder(DecoderLayer(d_model,c(attn),c(attn),c(ff),dropout),N),
# 目标数据经过embedding处理之后和位置编码构成的有序结构
nn.Sequential(Embeddings(d_model,source_vocab),c(position)),
nn.Sequential(Embeddings(d_model,source_vocab),c(position)),
Generator(d_model,target_vocab)
)
# 模型构造玩之后,初始化模型中的参数,比如线性层中的矩阵变换
# 这里一旦判断参数的维度大于1,则会将其初始化成一个服从均匀分布的矩阵
# 显示的更新参数
for p in model.parameters():
if p.dim()>1:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(p)
return model
# # nn.init.xavier_uniform演示
# # 结果服从均匀分布U(-a,a)
# w = torch.empty(3,5)
# w = nn.init.xavier_uniform_(w,gain=nn.init.calculate_gain('relu'))
# print(w)
# 输入参数
source_vocab = 11
target_vocab = 11
N = 6
# 其他使用默认
if __name__ == '__main__':
res = make_model(source_vocab,target_vocab,N)
print(res)
D:\soft\Anaconda\envs\py3.9\python.exe D:/soft/pycharm/pythonProject2/main.py
EncoderDecoder(
(encoder): Encoder(
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(1): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(2): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(3): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(4): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(5): EncoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
(norm): LayerNorm()
)
(decoder): Decoder(
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(1): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(2): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(3): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(4): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
(5): DecoderLayer(
(self_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(src_attn): MultiHeadedAttention(
(linears): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(feed_forward): PositionwiseFeedForward(
(w1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=2048, bias=True)
(w2): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=512, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(sublayer): ModuleList(
(0): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(2): SublayerConnection(
(norm): LayerNorm()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
(norm): LayerNorm()
)
(src_embed): Sequential(
(0): Embeddings(
(lut): Embedding(11, 512)
)
(1): PositionalEncoding(
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(tgt_embed): Sequential(
(0): Embeddings(
(lut): Embedding(11, 512)
)
(1): PositionalEncoding(
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(generator): Generator(
(project): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=11, bias=True)
)
)
进程已结束,退出代码0
小结
学习并实现了编码器-解码器结构的类:EncoderDecoder