NormalEstimation法向量估计理论和代码---PCL源码笔记
NormalEstimation
确定表面一点法线的问题近似于估计临近点所拟合表面的一个相切面法线的问题,因此转换过来以后就变成了一个最小二乘法平面拟合的问题。因此估计表面法线的解决方案就变成了分析一个协方差矩阵的特征向量和特征值(或者PCA-主成分分析),这个协方差矩阵从查询点的近邻元素中创建。最大主成分为投影到某方向后方差最大的方向(信息量最大的方向);而法向量为投影到某方向后,信息量最小的方向,因此需要PCA变换,将点云投影到特征值最小的方向。
上面这里有几个概念:
- 平面的定义和点到直线的距离
- 最小二乘法和主成分分析(PCA)
- 协方差矩阵,及其特征向量和特征值
法向量求解步骤
目标平面可以由一个点 x x x和一个法向量 n ⃗ \vec{n} n来表示,且一个点 p i ∈ P k p_i \in P^k pi∈Pk 到平面的距离为:
d i = ( p i − x ) ⋅ n ⃗ d_i = (p_i - x) \cdot \vec{n} di=(pi−x)⋅n
即取平面上一点,平面外一点的到平面的距离,就是这两点组成的向量在法向量上面的投影。
如果点到平面的距离为0,即 d i = 0 d_i = 0 di=0,我们就可以求出平面的法向量了。因此通过以下步骤:
-
求所有点的质心 p k p^k pk
x = p ˉ = 1 k ⋅ ∑ i = 1 k p i x = \bar{p} = \frac{1}{k} \cdot \sum_{i=1}^k p_i x=pˉ=k1⋅i=1∑kpi -
计算质心 p k p^k pk的协方差矩阵 C ∈ R 3 × 3 C \in \R^{3 \times 3} C∈R3×3,及其特征向量和特征值
C = 1 k ∑ i = 1 k ϵ ⋅ ( p i − p ˉ ) ⋅ ( p i − p ˉ ) T , C ⋅ v j ⃗ = λ j ⋅ v j ⃗ , j ∈ { 0 , 1 , 2 } C = \frac{1}{k} \sum_{i=1}^k \epsilon \cdot (p_i - \bar{p}) \cdot (p_i - \bar{p})^T, C\cdot \vec{v_j} = \lambda_j \cdot \vec{v_j}, j\in \{0, 1, 2\} C=k1i=1∑kϵ⋅(pi−pˉ)⋅(pi−pˉ)T,C⋅vj=λj⋅vj,j∈{0,1,2}其中 ϵ \epsilon ϵ通常为1。 C C C是对称和半正定矩阵且它的特征值是实数 λ j ∈ R \lambda_j \in \R λj∈R。特征向量 v j ⃗ \vec{v_j} vj形成了orthogonal frame, 相对应于质心 p k p^k pk的主成分(principal components)。 如果 0 ≤ λ 0 ≤ λ 1 ≤ λ 2 0 \leq \lambda_0 \leq \lambda_1 \leq \lambda_2 0≤λ0≤λ1≤λ2,最小特征值 λ 0 \lambda_0 λ0的特征向量 v 0 ⃗ \vec{v_0} v0就是法向量 + n ⃗ = { n x , n y , n z } + \vec{n} = \{n_x, n_y, n_z\} +n={nx,ny,nz}或者 − n ⃗ - \vec{n} −n的近似。 或者, n ⃗ \vec{n} n可以在球坐标系下用 ϕ , θ \phi, \theta ϕ,θ表示:
ϕ = arctan ( n z n y ) , θ = arctan ( n y 2 + n z 2 ) n x \phi = \arctan (\frac{n_z}{n_y}) , \theta = \arctan \frac{\sqrt{(n_y^2+n_z^2)}}{n_x} ϕ=arctan(nynz),θ=arctannx(ny2+nz2)可以看到,通过主成分分析法(PCA)来计算它的方向具有二异性,无法对整个点云数据集的法向方向进行一致性定向。 如下图所示:
-
计算法向与视点
解决这个问题的办法就是使用视点 V p V_p Vp。对所有法线 n i ⃗ \vec{n_i} ni定向只需要使它们一致朝向视点的方向,满足下面的方程式:
n i ⃗ ⋅ ( V p − p i ) > 0 \vec{n_i} \cdot (V_p - p_i) > 0 ni⋅(Vp−pi)>0
PCL法向量估计
先来看看PCL法向量估计的模板。通常包含以下步骤:
- 设置输入点云,及其索引方法
- 设置临近点的半径
- 计算法向量
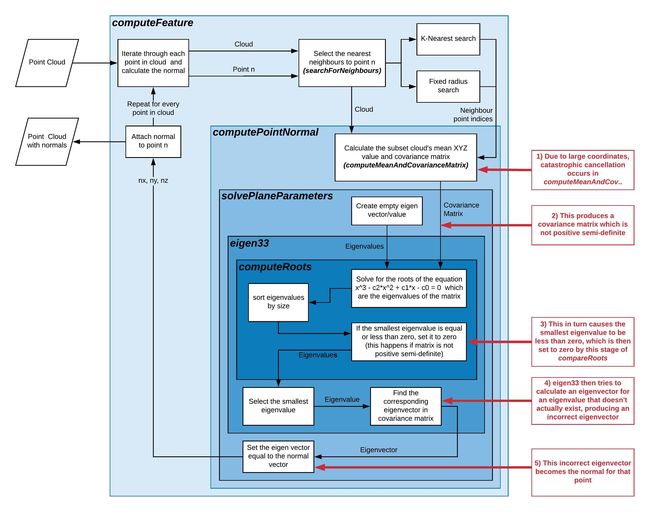
#include 上面的主要函数在于compute模板函数。compute模板函数关键在于computeFeature函数,我们深入看看,在PCL源码 normal_3d.hpp文件内。
1. computeFeature 函数
template <typename PointInT, typename PointOutT> void
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointInT, PointOutT>::computeFeature (PointCloudOut &output)
{
// Allocate enough space to hold the results
// \note This resize is irrelevant for a radiusSearch ().
pcl::Indices nn_indices (k_);
std::vector<float> nn_dists (k_);
output.is_dense = true;
// Iterating over the entire index vector
for (std::size_t idx = 0; idx < indices_->size (); ++idx)
{
if (this->searchForNeighbors ((*indices_)[idx], search_parameter_, nn_indices, nn_dists) == 0 ||
!computePointNormal (*surface_, nn_indices, output[idx].normal[0], output[idx].normal[1], output[idx].normal[2], output[idx].curvature))
{
output[idx].normal[0] = output[idx].normal[1] = output[idx].normal[2] = output[idx].curvature = std::numeric_limits<float>::quiet_NaN ();
output.is_dense = false;
continue;
}
flipNormalTowardsViewpoint ((*input_)[(*indices_)[idx]], vpx_, vpy_, vpz_,
output[idx].normal[0], output[idx].normal[1], output[idx].normal[2]);
}
}
computeFeature模板函数就有两个对应的函数API是我们上面理论部分,computePointNormal和flipNormalTowardsViewpoint,也就是对应于上面的第二第三步骤。 接着深入看看。
2. computePointNormal模板函数
template <typename PointT> inline bool
computePointNormal (const pcl::PointCloud<PointT> &cloud, const pcl::Indices &indices,
Eigen::Vector4f &plane_parameters, float &curvature)
{
// Placeholder for the 3x3 covariance matrix at each surface patch
EIGEN_ALIGN16 Eigen::Matrix3f covariance_matrix;
// 16-bytes aligned placeholder for the XYZ centroid of a surface patch
Eigen::Vector4f xyz_centroid;
if (indices.size () < 3 ||
computeMeanAndCovarianceMatrix (cloud, indices, covariance_matrix, xyz_centroid) == 0)
{
plane_parameters.setConstant (std::numeric_limits<float>::quiet_NaN ());
curvature = std::numeric_limits<float>::quiet_NaN ();
return false;
}
// Get the plane normal and surface curvature
solvePlaneParameters (covariance_matrix, xyz_centroid, plane_parameters, curvature);
return true;
}
这个模板函数,首先计算点云的协方差矩阵,通过computeMeanAndCovarianceMatrix模板函数,然后计算平面参数。
3. computeMeanAndCovarianceMatrix模板函数
template <typename PointT, typename Scalar> inline unsigned int
computeMeanAndCovarianceMatrix (const pcl::PointCloud<PointT> &cloud,
const Indices &indices,
Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 3> &covariance_matrix,
Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 4, 1> ¢roid)
{
// Shifted data/with estimate of mean. This gives very good accuracy and good performance.
// create the buffer on the stack which is much faster than using cloud[indices[i]] and centroid as a buffer
Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 1, 9, Eigen::RowMajor> accu = Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 1, 9, Eigen::RowMajor>::Zero ();
Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 1> K(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for(const auto& index : indices)
if(isFinite(cloud[index])) {
K.x() = cloud[index].x; K.y() = cloud[index].y; K.z() = cloud[index].z; break;
}
std::size_t point_count;
point_count = indices.size ();
for (const auto &index : indices)
{
Scalar x = cloud[index].x - K.x(), y = cloud[index].y - K.y(), z = cloud[index].z - K.z();
accu [0] += x * x;
accu [1] += x * y;
accu [2] += x * z;
accu [3] += y * y;
accu [4] += y * z;
accu [5] += z * z;
accu [6] += x;
accu [7] += y;
accu [8] += z;
}
if (point_count != 0)
{
accu /= static_cast<Scalar> (point_count);
centroid[0] = accu[6] + K.x(); centroid[1] = accu[7] + K.y(); centroid[2] = accu[8] + K.z();
centroid[3] = 1;
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (0) = accu [0] - accu [6] * accu [6];
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (1) = accu [1] - accu [6] * accu [7];
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (2) = accu [2] - accu [6] * accu [8];
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (4) = accu [3] - accu [7] * accu [7];
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (5) = accu [4] - accu [7] * accu [8];
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (8) = accu [5] - accu [8] * accu [8];
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (3) = covariance_matrix.coeff (1);
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (6) = covariance_matrix.coeff (2);
covariance_matrix.coeffRef (7) = covariance_matrix.coeff (5);
}
return (static_cast<unsigned int> (point_count));
}
这里有 Shifted data/with estimate of mean. This gives very good accuracy and good performance. 在参考2中作出了详细的解释。
4. solvePlaneParameters模板函数
inline void
solvePlaneParameters (const Eigen::Matrix3f &covariance_matrix,
const Eigen::Vector4f &point,
Eigen::Vector4f &plane_parameters, float &curvature)
{
solvePlaneParameters (covariance_matrix, plane_parameters [0], plane_parameters [1], plane_parameters [2], curvature);
plane_parameters[3] = 0;
// Hessian form (D = nc . p_plane (centroid here) + p)
plane_parameters[3] = -1 * plane_parameters.dot (point);
}
inline void
solvePlaneParameters (const Eigen::Matrix3f &covariance_matrix,
float &nx, float &ny, float &nz, float &curvature)
{
// Avoid getting hung on Eigen's optimizers
// for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i)
// if (!std::isfinite (covariance_matrix.coeff (i)))
// {
// //PCL_WARN ("[pcl::solvePlaneParameters] Covariance matrix has NaN/Inf values!\n");
// nx = ny = nz = curvature = std::numeric_limits::quiet_NaN ();
// return;
// }
// Extract the smallest eigenvalue and its eigenvector
EIGEN_ALIGN16 Eigen::Vector3f::Scalar eigen_value;
EIGEN_ALIGN16 Eigen::Vector3f eigen_vector;
pcl::eigen33 (covariance_matrix, eigen_value, eigen_vector);
nx = eigen_vector [0];
ny = eigen_vector [1];
nz = eigen_vector [2];
// Compute the curvature surface change
float eig_sum = covariance_matrix.coeff (0) + covariance_matrix.coeff (4) + covariance_matrix.coeff (8);
if (eig_sum != 0)
curvature = std::abs (eigen_value / eig_sum);
else
curvature = 0;
}
求出特征向量和特征值。
5. flipNormalTowardsViewpoint模板函数
template <typename PointT> inline void
flipNormalTowardsViewpoint (const PointT &point, float vp_x, float vp_y, float vp_z,
float &nx, float &ny, float &nz)
{
// See if we need to flip any plane normals
vp_x -= point.x;
vp_y -= point.y;
vp_z -= point.z;
// Dot product between the (viewpoint - point) and the plane normal
float cos_theta = (vp_x * nx + vp_y * ny + vp_z * nz);
// Flip the plane normal
if (cos_theta < 0)
{
nx *= -1;
ny *= -1;
nz *= -1;
}
}
Reference
- pcl::NormalRobustEstimation - computing robust normals at the origin, https://github.com/PointCloudLibrary/pcl/issues/4965
- Algorithms for calculating variancek, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithms_for_calculating_variance
- Regression asymetry and PCA (Principal Component Analysis), http://zoonek2.free.fr/UNIX/48_R/09.html#7