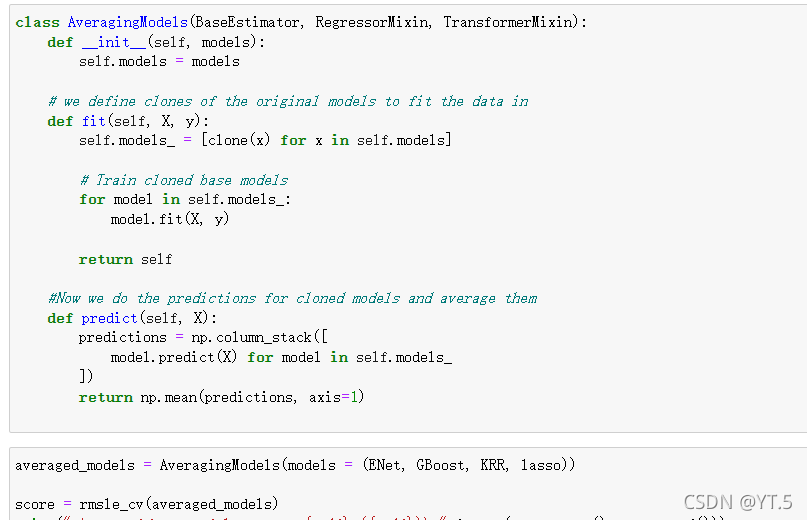
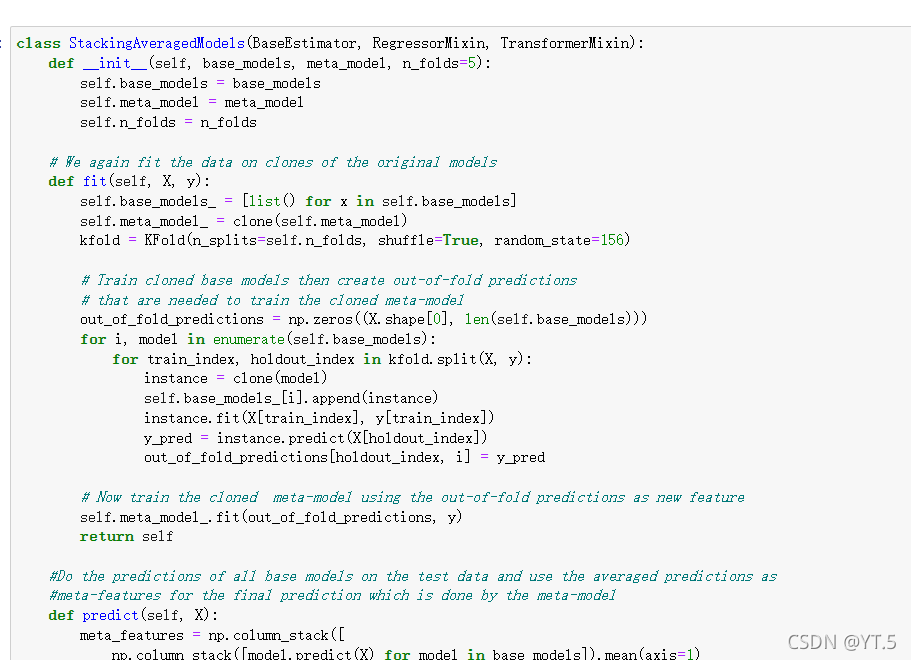
案例:探索性数据分析,房价预测
文章目录
- 探索性数据分析
-
- 查看数据量和简单信息
-
- 加载数据
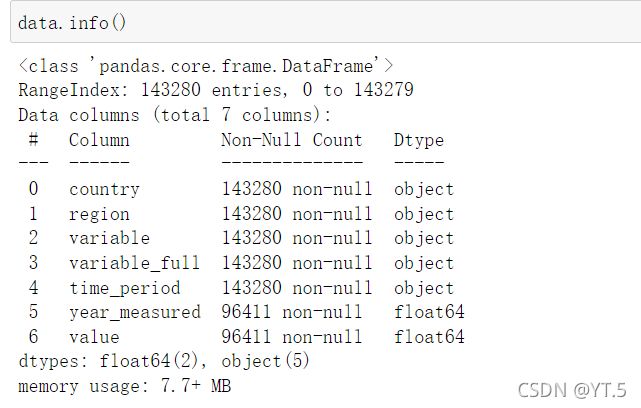
- 数据大致信息
- 数据切片分析
- 单变量分析
- 峰度和偏度
- 数据维度的分析
-
- 水资源分布情况
- 变量关系可视化展示
- 房价预测
探索性数据分析
数据集:粮农组织数据集
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cmawer/pycon-2017-eda-tutorial/master/data/aquastat/aquastat.csv.gzip
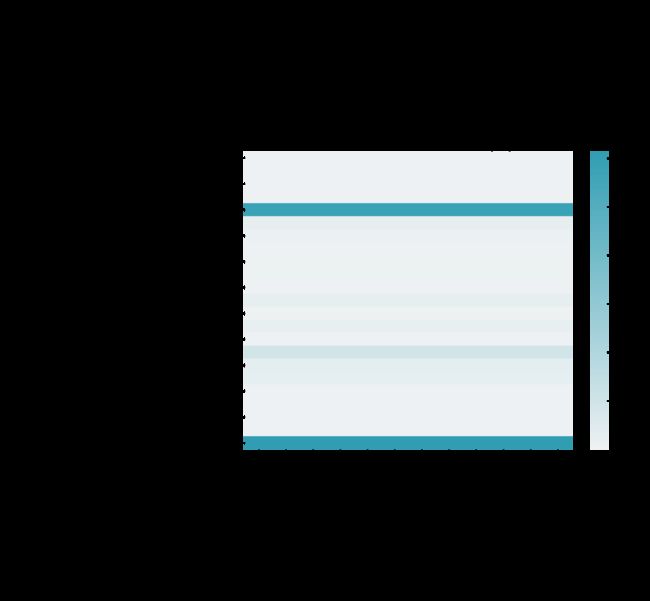
探索性数据分析是指对已有的数据(特别是调查或观察得来的原始数据)在尽量少的先验假定下进行探索,通过作图、制表、方程拟合、计算特征量等手段探索数据的结构和规律的一种数据分析方法,特别是当我们面对大数据时代到来的时候,各种杂乱的“脏数据”,往往不知所措,不知道从哪里开始了解目前拿到手上的数据时候,探索性数据分析就非常有效。
查看数据量和简单信息
加载数据
data = pd.read_csv(path,compression='gzip')
data.head()
数据大致信息
data.shape
数据切片分析
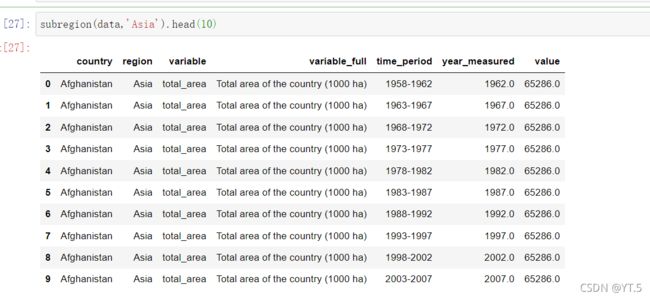
我们先来看一下variable,variable_full这两列的信息,

看一下统计了多少国家,
data.country.nunique()
#输出:199
看一下有多少个时间周期,
data.time_period.nunique()
#结果:12
看一下时间周期有哪些,
time_periods = data.time_period.unique()
我们看一下某一列某个指标的缺失值的个数,比如variable是total_area时缺失值的个数,
data[data.variable=='total_area'].value.isnull().sum()#缺失值个数
#输出结果:220
我们通过几个维度来进行数据的分析:
- 横截面:一个时期内所有国家
- 时间序列:一个国家随着时间的推移
- 面板数据:所有国家随着时间的推移(作为数据给出)
- 地理空间:所有地理上相互联系的国家
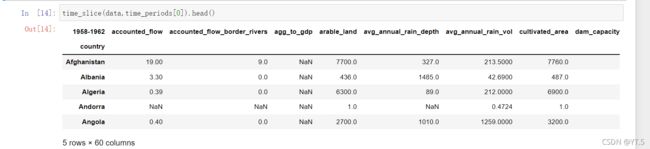
我们按照上面的处理继续,现在我们想统计一下对于一个时间周期来说,不同国家在这个周期内的变化情况,
# 数据切片分析
def time_slice(df,time_period):
df = df[df.time_period==time_period]
df = df.pivot(index='country',columns='variable',values='value') # 透视表 index是country 列索引是variable和value
df.columns.name = time_period
return df
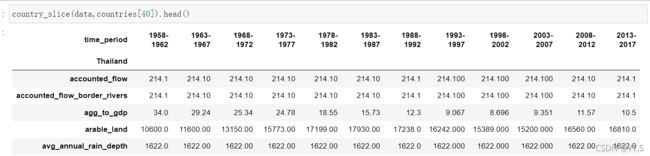
# 国家在不同的时间上分布的规则
def country_slice(df,country):
df = df[df.country==country]
df = df.pivot(index = 'variable',columns = 'time_period',values = 'value')
df.index.name = country
return df
# 所有国家随着时间的变化在指定属性下的变化情况
def variables_slice(df,variable):
df = df[df.variable == variable]
df = df.pivot(index = 'country',columns = 'time_period',values = 'value')
return df

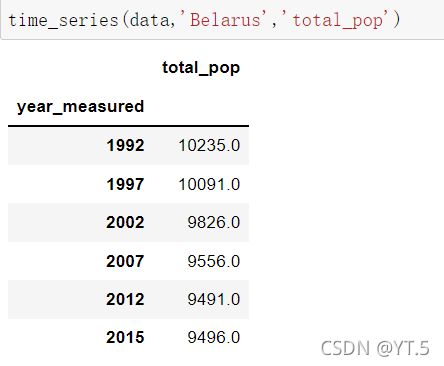
我们还可以给定国家和指标,查看这个国家在这个指标上的变化情况,
# 给定国家在指标的情况
def time_series(df,country,variable):
series = df[(df.country==country)&(df.variable==variable)]
series = series.dropna()[['year_measured','value']]
series.year_measured = series.year_measured.astype(int)
series.set_index('year_measured',inplace = True)
series.columns = [variable]
return series
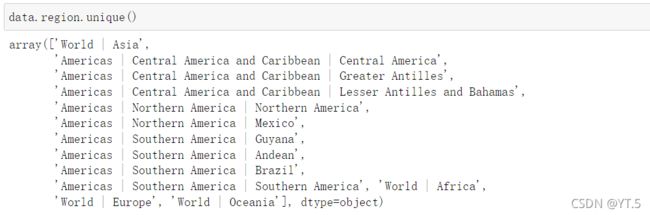
我们可能需要查看某些评估数据的子集。区域是一种直观的数据细分方式。
在这里插入代码片
通过上图可以看出,区域太多,不便于观察,我们可以将一些区域进行合并。减少区域数量有助于模型评估,可以创建一个字典来查找新的,更简单的区域(亚洲,北美洲,南美洲,大洋洲)
![]()
![]()
单变量分析
通过画图来分析,导入一些库
地图矢量数据可以自己网上搜
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBacked.figure_format = 'retina'
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_context('poster',font_scale=1.3)
import folium # 世界地图
import os,sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pivottablejs
import missingno as msno# 缺失值可视化
import pandas_profiling#可以以网页的形式展现给你数据总体概况
import ipynb
sys.path.append(r"F:\jpyter file\learn")
from demo1 import time_slice,country_slice,time_series,simple_regions,subregion,variables_slice
msno.matrix(recent,labels=True)#缺失值可视化
# 查看其中水资源总量缺失值
msno.matrix(variables_slice(data,'exploitable_total'),inline =False,sort = 'descending')
plt.xlabel('Time_period');
plt.ylabel('Country');
plt.title('Missing total exploitable water resources data across countries and time periods \n\n\n')
# 去掉无法使用的数据
data = data.loc[~data.variable.str.contains('exploitable'),:]
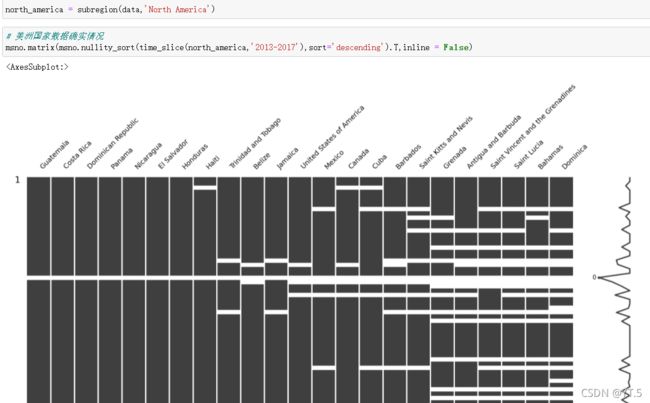
通过上图发现,南美洲各国缺失得的数据并不是很多,前几个国家是不缺数据的,我们抽查一下巴哈马(图中倒数第二),看一下它缺少了哪些数据,
msno.nullity_filter(country_slice(data,'Bahamas').T,filter='bottom',p=0.1)
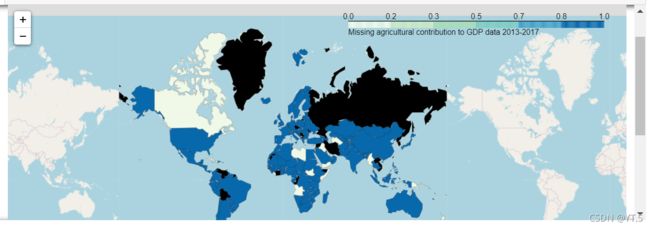
接下来我们探索一下区域之间的关系,看一下缺失值的出现,是不是跟国家之间有关系,我们画一下世界地图,选择区域,然后在这个区域选择某一个指标,看一下它的缺失值的分布情况,颜色越深,缺失值越严重,我们以农业对GDPagg_to_gdp,为指标看一下分布情况,
geo = r"D:\谷歌下载\世界国家geojson大全,各国地图json数据下载\countries.geo.json"
null_data = recent['agg_to_gdp'].notnull()*1
map = folium.Map(location = [48,-102],zoom_start=2)
map.choropleth(geo_data=geo,
data=null_data,
columns=['country','agg_to_gdp'],
key_on='feature.properties.name',reset=True,
fill_color='GnBu',fill_opacity=1,line_opacity=0.2,
legend_name='Missing agricultural contribution to GDP data 2013-2017')
map
def plot_null_map(df,time_period,variable,legend_name=None):
ts=time_slice(df,time_period).reset_index().copy()#不指明,从0开始
ts[variable]=ts[variable].notnull()*1
map = folium.Map(location=[48,-102],zoom_start=2)
map.choropleth(geo_data=geo,
data=ts,
columns=['country',variable],
key_on='feature.properties.name',reset=True,
fill_color='GnBu',fill_opacity=1,line_opacity=0.2,
legend_name=legend_name if legend_name else variable)
return map

接下来我们用热力图展示一下,不同指标随着时间的变化情况,颜色越深说明在这个指标上收集到的国家数据越少,反之则越多。
# 不同国家对不同变量随着时间推移的重视程度
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,16))
sns.heatmap(data.groupby(['time_period','variable']).value.count().unstack().T,ax=ax)
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.xlabel('Time period')
plt.ylabel('Variable')
plt.title('Number of countries with data reported for each variable over time')
# 单变量的分布规则和不同变量之间的关系
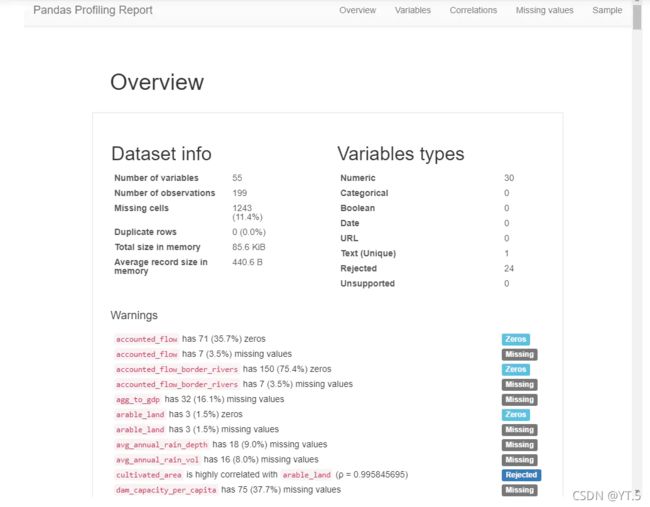
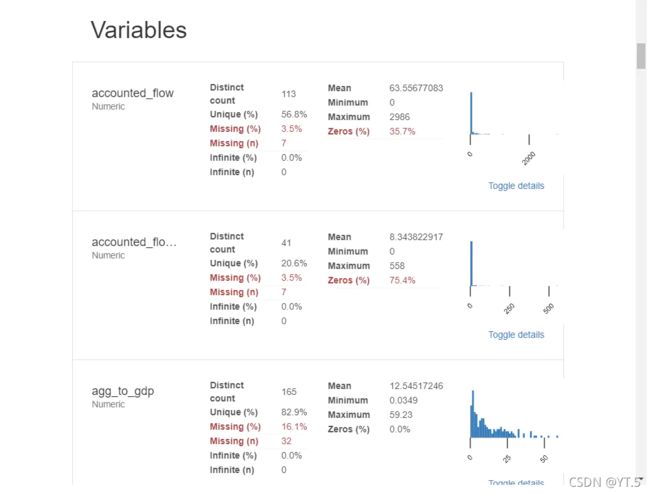
pandas_profiling.ProfileReport(time_slice(data,'2013-2017'))
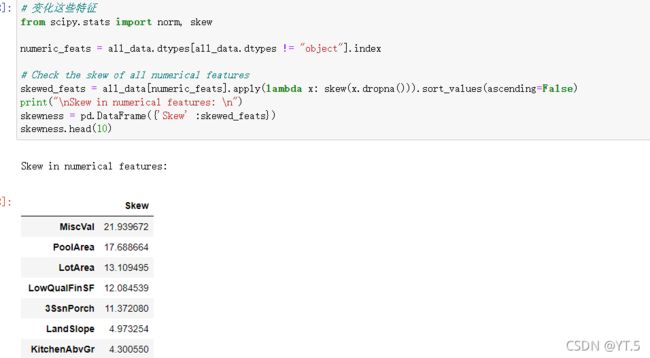
峰度和偏度

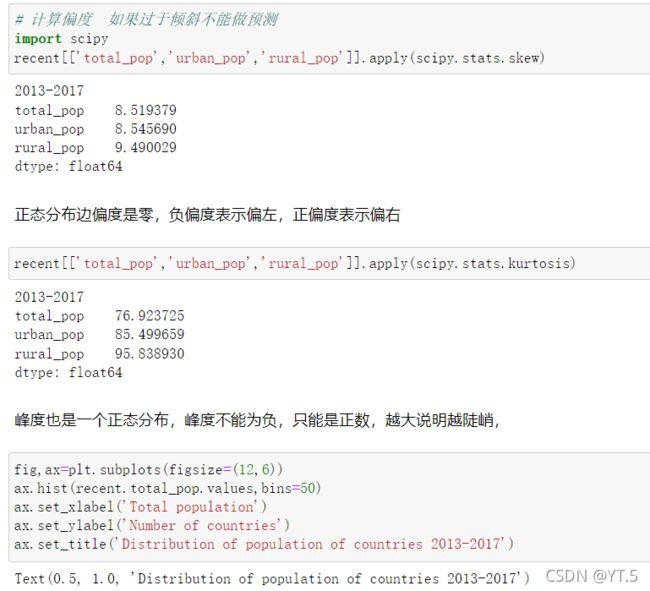

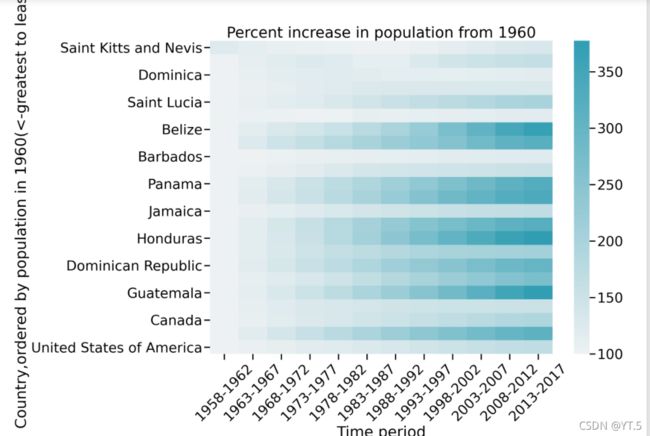
上图是2013-2017年国家总人数的分布,通过上图我们发现,人口量少于200000(不考虑单位)的国家非常多,人口大于1200000的国家非常少,如果我们需要建模的话,这种数据我们是不能要的。这个时候我们应该怎么办呢?
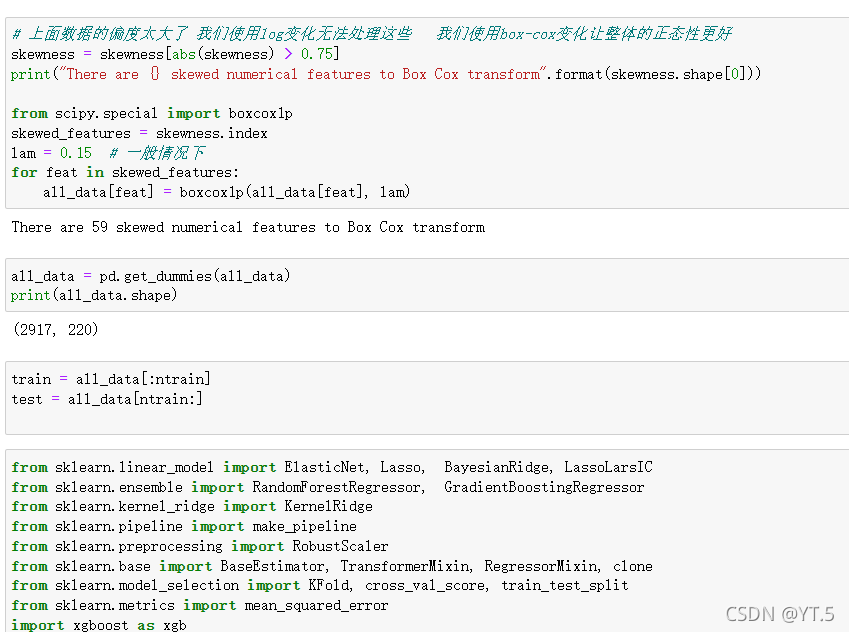
通常,遇到这种情况,使用log变换将其变为正常。对数变换是数据变换的一种常用方式,数据变换的目的在于使数据的呈现方式接近我们所希望的前提假设,从而更好的进行统计推断。
def plot_hist(df,variable,bins=20,xlabel=None,by=None,ylabel=None,title=None,logx=False,ax=None):
if not ax:
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
if logx:
if df[variable].min()<=0:
df[variable] = df[variable] -df[variable].min()+1
print('Warning:data<=0 exists,data transformed by %0.2g before plotting' % (-df[variable].min()))
bins = np.logspace(np.log10(df[variable].min()),np.log10(df[variable].max()),bins)
ax.set_xscale("log")
ax.hist(df[variable].dropna().values,bins=bins)
if xlabel:
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel)
if ylabel:
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
if title:
ax.set_title(title)
return ax
画图展示
plot_hist(recent,'total_pop',bins=25,logx=True,xlabel='Log of total population',ylabel='Number of countries',
title='Distribution of total population of countries 2013-2017')
数据维度的分析
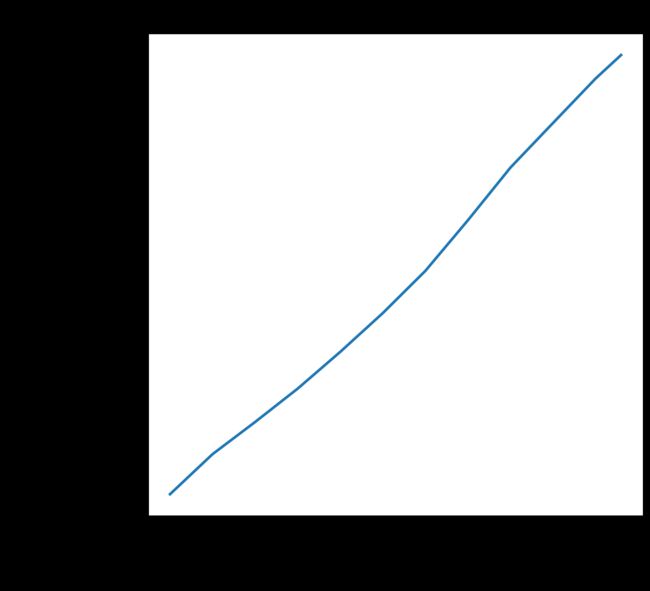
首先我们先来看一下美国的人口总数随时间的变化,
# 首先我们先来看一下美国的人口总数随时间的变化,
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.plot(time_series(data,'United States of America','total_pop'))
plt.xlabel('Year')
plt.ylabel('Population')
plt.title('United States population over time')
#查看北美洲每个国家人口总数随着时间的变化
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
with sns.color_palette(sns.diverging_palette(220,280,s=85,l=25,n=23)):
north_america = time_slice(subregion(data,'North America'),'1958-1962').sort_values('total_pop').index.tolist()
for country in north_america:
plt.plot(time_series(data,country,'total_pop'),label=country)
plt.xlabel('Year')
plt.ylabel('Population')
plt.title('North American populations over time')
plt.legend(loc=2,prop={'size':10})
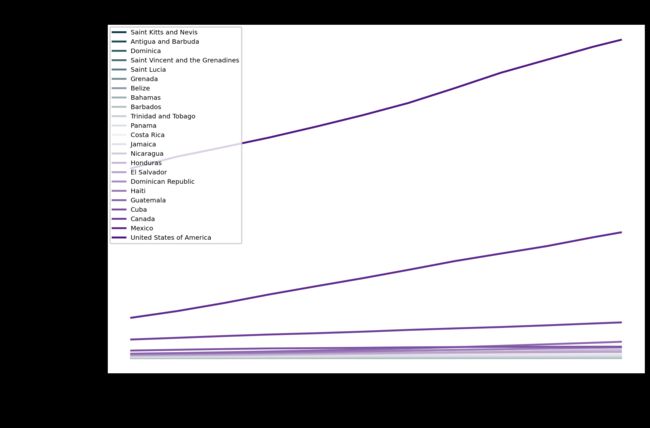
这个时候我们发现,一些国家由于人口数量本身就少,所以整个图像显示的不明显,我们可以改变一下参照指标,那我们通过什么标准化?我们可以选择一个国家的最小、平均、中位数、最大值…或任何其他位置。那我们选择最小值,这样我们就能看到每个国家的起始人口上的增长。
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
with sns.color_palette(sns.diverging_palette(220,280,s=85,l=25,n=23)):
for country in north_america:
ts=time_series(data,country,'total_pop')
ts['norm_pop']=ts.total_pop/ts.total_pop.min()*100
plt.plot(ts['norm_pop'],label=country)
plt.xlabel('Year')
plt.ylabel('Percent increase in population')
plt.title('Percent increase in population from 1960 in North American countries')
plt.legend(loc=2,prop={'size':10})
水资源分布情况
def plot_hist(df,variable,bins=20,xlabel=None,by=None,ylabel=None,title=None,logx=False,ax=None):
if not ax:
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
if logx:
if df[variable].min()<=0:
df[variable] = df[variable] -df[variable].min()+1
print('Warning:data<=0 exists,data transformed by %0.2g before plotting' % (-df[variable].min()))
bins = np.logspace(np.log10(df[variable].min()),np.log10(df[variable].max()),bins)
ax.set_xscale("log")
ax.hist(df[variable].dropna().values,bins=bins)
if xlabel:
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel)
if ylabel:
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
if title:
ax.set_title(title)
return ax
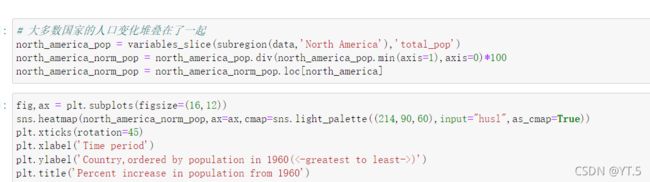
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,12))
sns.heatmap(north_america_renew,ax=ax,cmap=sns.light_palette((214,90,60),input="husl",as_cmap=True))
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.xlabel('Time period')
plt.ylabel('Country,ordered by Total renewable water resources in 1960(<-greatest to least->)')
plt.title('Total renewable water resources increase in population from 1960')
变量关系可视化展示
人均GDP变化与季节之间的关系
data=data.loc[~data.variable.str.contains('exploitable')]
data=data.loc[~(data.variable=='national_rainfall_index')]
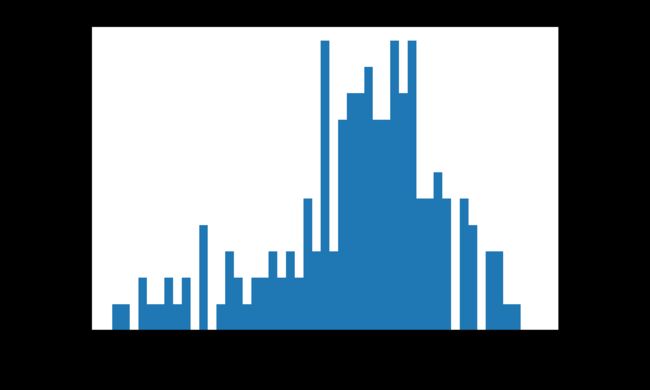
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.scatter(recent.seasonal_variability,recent.gdp_per_capita)
plt.xlabel('Seasonal variability')
plt.ylabel('GDP per capita ($USD/person)')
def plot_scatter(df,x,y,bins=20,xlabel=None,ylabel=None,title=None,ax=None,logx=False,logy=False):
if not ax:
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
colors = mpl.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'].by_key()['color']
if by:
groups = df.groupby(by)
for j,(name,group) in enumerate(groups):
ax.scatter(group[x],group[y],color=colors[j],label=name)
ax.legend()
else:
ax.scatter(df[x],df[y],color=colors[0])
if logx:
ax.set_xscale('log')
if logy:
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel if xlabel else x)
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel if ylabel else y)
if title:
ax.set_title(title)
return ax
svr = [recent.seasonal_variability.min(),recent.seasonal_variability.max()]
gdpr = [recent.gdp_per_capita.min(),recent.gdp_per_capita.max()]
gdpbins = np.logspace(*np.log10(gdpr),25)
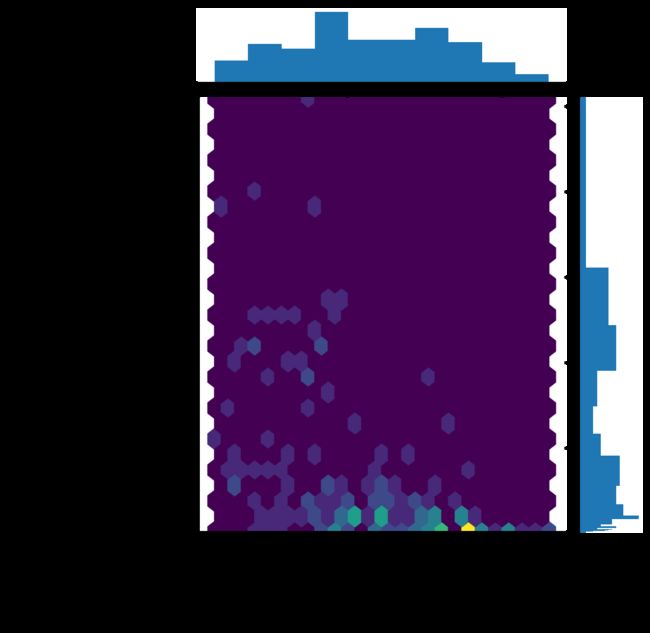
g = sns.JointGrid(x="seasonal_variability",y="gdp_per_capita",data=recent,ylim=gdpr)
g.ax_marg_x.hist(recent.seasonal_variability,range=svr)
g.ax_marg_y.hist(recent.gdp_per_capita,range=gdpr,bins=gdpbins,orientation="horizontal")
g.plot_joint(plt.hexbin,gridsize=25)
ax = g.ax_joint
g.fig.set_figheight(8)
g.fig.set_figwidth(9)
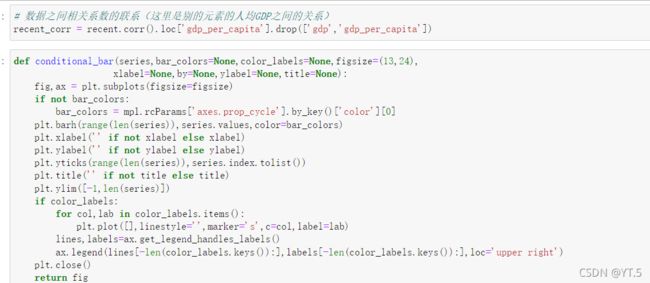
bar_colors = ['#0055A7' if x else '#2C3E4F' for x in list(recent_corr.values<0)]
color_labels = {'#0055A7':'Negative correlation','#2C3E4F':'Positive correlation'}
conditional_bar(recent_corr.apply(np.abs),bar_colors,color_labels,
title='Magnitude of correlation with GDP per capita,2013-2017',
xlabel='|Correlation|')
蓝色代表负相关,黑色是正相关
plot_hist(recent,'gdp_per_capita',xlabel='GDP per capita($)',
ylabel='Number of countries',
title='Distribution of GDP per capita,2013-2017')
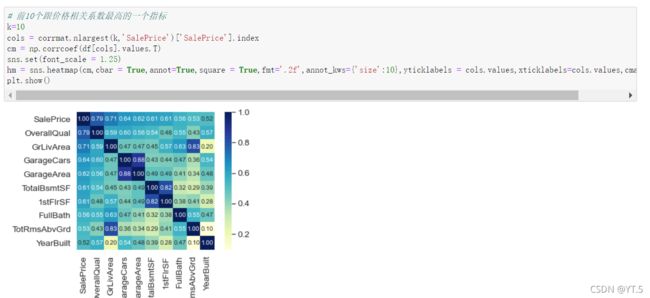
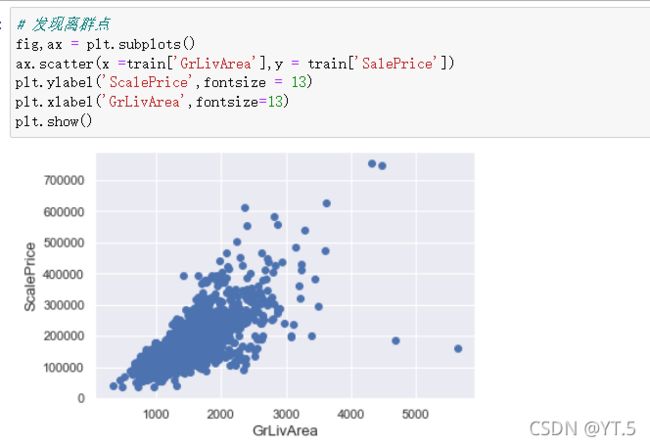
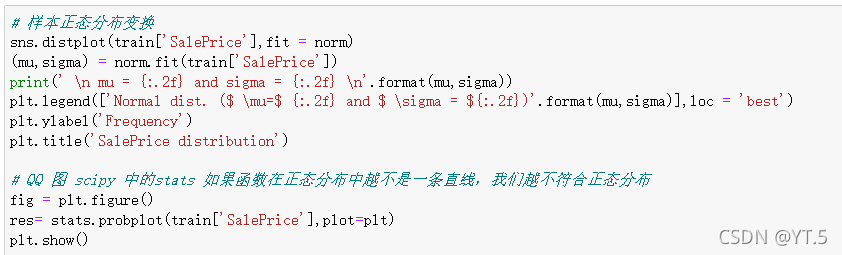
房价预测
数据集:https://www.kaggle.com/c/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/data?select=train.csv
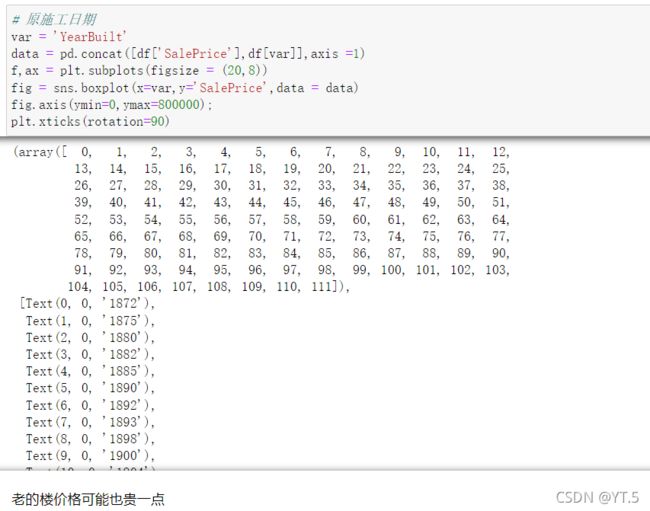
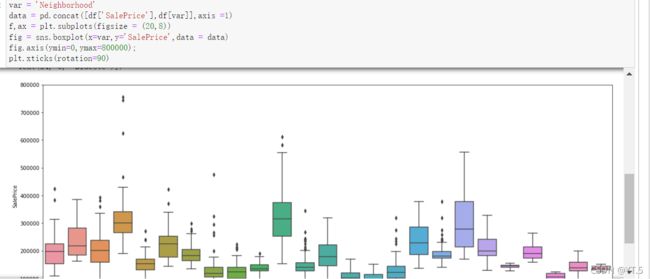
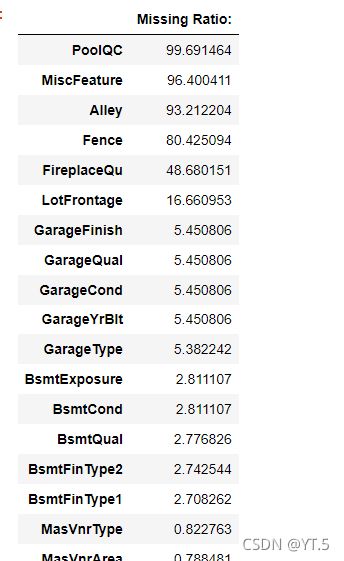
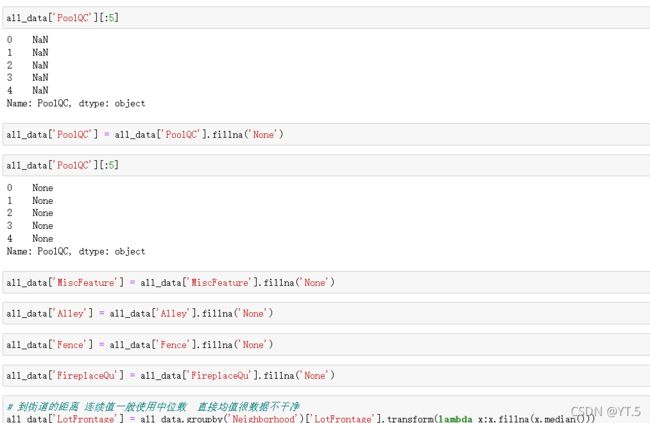
# 看完数据基本情况之后,查看处理缺失值了 cancat重塑(简单连接):0行1列
total = df.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending=False)
percent = (df.isnull().sum()/df.isnull().count()).sort_values(ascending=False)
missing_data = pd.concat([total,percent],axis=1,keys=['Total','Percent'])
missing_data.head(20)