人工智能之机器学习-逻辑回归、回归(Regression)-Pytorch快速实现
文章目录
- 概述
- 直接上pytorch
-
- 网络搭建
- 设置优化器
- 选择损失函数
- 开始训练(炼丹)
- 测试模式(nograd)
- 进阶指南
听说点进蝈仔帖子的都喜欢点赞加关注~~
老规矩,先送上官网,建议不知道优化器,损失函数,网络模型的朋友们看看官网
https://pytorch.org/
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html
基本都在torch.nn下

鸣谢:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74874291?utm_source=com.youdao.note
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/86982616
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/127972563
概述
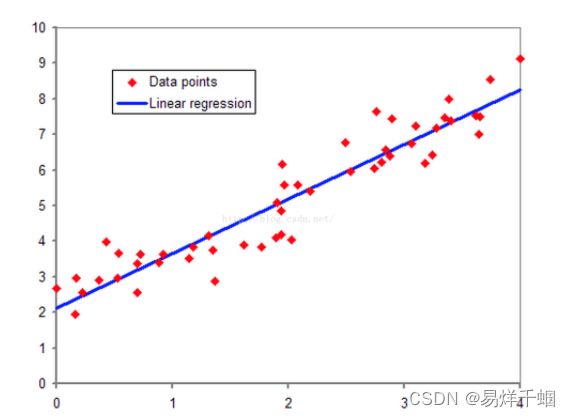
回归问题是机器学习三大基本模型中很重要的一环,其功能是建模和分析变量之间的关系。
回归问题多用来预测一个具体的数值,如预测房价、未来的天气情况等等。例如我们根据一个地区的若干年的PM2.5数值变化来估计某一天该地区的PM2.5值大小,预测值与当天实际数值大小越接近,回归分析算法的可信度越高。
面对一个回归问题,我们可简要描述其求解流程:
选定训练模型,即我们为程序选定一个求解框架,如线性回归模型(Linear Regression)等。
导入训练集 train_set,即给模型提供大量可供学习参考的正确数据。
选择合适的学习算法,通过训练集中大量输入输出结果让程序不断优化输入数据与输出数据间的关联性,从而提升模型的预测准确度。
在训练结束后即可让模型预测结果,我们为程序提供一组新的输入数据,模型根据训练集的学习成果来预测这组输入对应的输出值。
直接上pytorch
注意:这里使用cpu模式,可以增加todevice的cuda判断使用cuda加速运算。
网络搭建
class LinearRegression(torch.nn.Module):
"""
Linear Regressoin Module, the input features and output
features are defaults both 1
"""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1,1)
def forward(self,x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
设置优化器
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.model.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate)
torch.optim.Adam(params,lr,betas, eps=,weight_decay,amsgrad)
选择损失函数
这里使用最为常用的mseloss方法
self.loss_function = torch.nn.MSELoss()
开始训练(炼丹)
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def create_linear_data(nums_data, if_plot= False):
"""
Create data for linear model
Args:
nums_data: how many data points that wanted
Returns:
x with shape (nums_data, 1)
"""
x = torch.linspace(0,1,nums_data)
x = torch.unsqueeze(x,dim=1)
k = 2
y = k * x + torch.rand(x.size())
if if_plot:
plt.scatter(x.numpy(),y.numpy(),c=x.numpy())
plt.show()
data = {"x":x, "y":y}
return data
data = create_linear_data(300, if_plot=True)
print(data["x"].size())
def train(self, data, model_save_path="model.pth"):
"""
Train the model and save the parameters
Args:
model_save_path: saved name of model
data: (x, y) = data, and y = kx + b
Returns:
None
"""
x = data["x"]
y = data["y"]
for epoch in range(self.epoches):
prediction = self.model(x)
loss = self.loss_function(prediction, y)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
if epoch % 500 == 0:
print("epoch: {}, loss is: {}".format(epoch, loss.item()))
torch.save(self.model.state_dict(), "linear.pth")
测试模式(nograd)
def test(self, x, model_path="linear.pth"):
"""
Reload and test the model, plot the prediction
Args:
model_path: the model's path and name
data: (x, y) = data, and y = kx + b
Returns:
None
"""
x = data["x"]
y = data["y"]
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
prediction = self.model(x)
plt.scatter(x.numpy(), y.numpy(), c=x.numpy())
plt.plot(x.numpy(), prediction.detach().numpy(), color="r")
plt.show()
进阶指南
这块想要进阶只能在dataloader和batch上下文章了,加快训练速度并且提升模型泛化能力,其他的好像没有什么可以做的了。