GoogLeNet的pytorch实现和调参
GoogLeNet
动手学深度学习代码开源 github
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import d2l.torch as d2l
I n c e p t i o n Inception Inception 块
相当于使用了不同的滤波器的 s i z e size size 来探索图像的细节
I n c e p t i o n Inception Inception 块相比于 3 × 3 3\times 3 3×3 或者 5 × 5 5\times 5 5×5 的卷积层来说, 有更少的参数个数和计算复杂度
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, c1, c2, c3, c4, **kwargs):
super(Inception, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.p1_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c1, kernel_size=1)
self.p2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c2[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p2_2 = nn.Conv2d(c2[0], c2[1], kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.p3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c3[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p3_2 = nn.Conv2d(c3[0], c3[1], kernel_size=5, padding=2)
self.p4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.p4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c4, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, X):
p1 = F.relu(self.p1_1(X))
p2 = F.relu(self.p2_2(F.relu(self.p2_1(X))))
p3 = F.relu(self.p3_2(F.relu(self.p3_1(X))))
p4 = F.relu(self.p4_2(self.p4_1(X))) # 汇聚层不需要 ReLU
return torch.cat((p1, p2, p3, p4), dim=1) # 在 output_channel 上堆叠
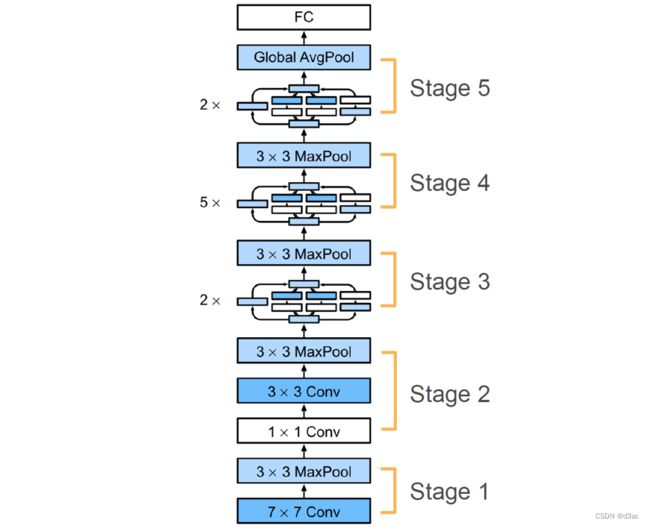
逐步实现 GoogLeNet
stage 1 & 2
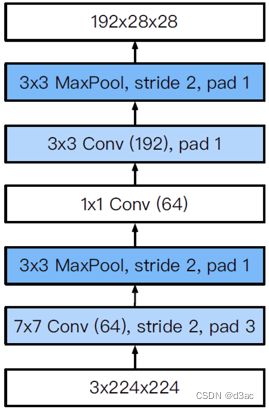
s t a g e stage stage 1 1 1 当中的两个层分别对输入图像进行了一个高宽减半的操作, 所以就是高宽缩小了 4 4 4 倍, 在这里先进行 p a d d i n g padding padding 然后设置 s t r i d e = 2 stride=2 stride=2 高宽就减半了
s t a g e stage stage 2 2 2 中, 先是用一个 1 × 1 1\times 1 1×1 的 k e r n e l kernel kernel 进行全连接, 再使用一个 3 × 3 3\times 3 3×3 的卷积层增大通道数, 这两个层都不改变图像的 s i z e size size, 最后用一个最大池化层来完成高宽减半
b1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
b2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
stage 3
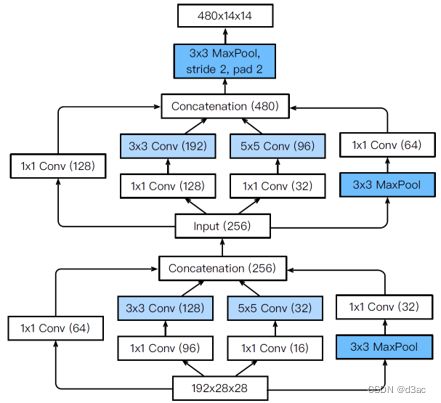
s t a g e stage stage 3 3 3 中, 使用了两个 I n c e p t i o n Inception Inception 块, I n c e p t i o n Inception Inception 块不改变图像的 s i z e size size , 最后还是由池化层来压缩图像的 s i z e size size
这幅图展示了输入的参数 , 最后一组数据加起来就是输出的 c h a n n e l channel channel , 64 + 128 + 32 + 32 = 256 64+128+32+32=256 64+128+32+32=256
b3 = nn.Sequential(
Inception(192, 64, (96, 128), (16, 32), 32),
Inception(256, 128, (128, 192), (32, 96), 64),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
stage 4 & 5
I n c e p t i o n Inception Inception 参数变化看 s t a g e stage stage 3 3 3 , s t a g e stage stage 4 4 4 和 5 5 5 是一堆 I n c e p t i o n Inception Inception 堆叠 , 最后通过一个全局池化层输出
b4 = nn.Sequential(
Inception(480, 192, (96, 208), (16, 48), 64),
Inception(512, 160, (112, 224), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 128, (128, 256), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 112, (144, 288), (32, 64), 64),
Inception(528, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
b5 = nn.Sequential(
Inception(832, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
Inception(832, 384, (192, 384), (48, 128), 128),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)),
nn.Flatten()
)
net = nn.Sequential(b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, nn.Linear(1024, 10))
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 96, 96))
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__, 'output shape : \t', X.shape)
Sequential output shape : torch.Size([1, 64, 24, 24])
Sequential output shape : torch.Size([1, 192, 12, 12])
Sequential output shape : torch.Size([1, 480, 6, 6])
Sequential output shape : torch.Size([1, 832, 3, 3])
Sequential output shape : torch.Size([1, 1024])
Linear output shape : torch.Size([1, 10])
learning_rate, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.05, 25, 64
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
c o s t cost cost 14 m 57.2 s 14m57.2s 14m57.2s
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, learning_rate, d2l.try_gpu(), ylim=[0.0, 1.0])
loss 0.101, train acc 0.961, test acc 0.913
1961.3 examples/sec on cuda:0
c o s t cost cost 8 m 51.8 s 8m51.8s 8m51.8s
learning_rate, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.02, 20, 512
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, learning_rate, d2l.try_gpu(), ylim=[0.0, 1.0])
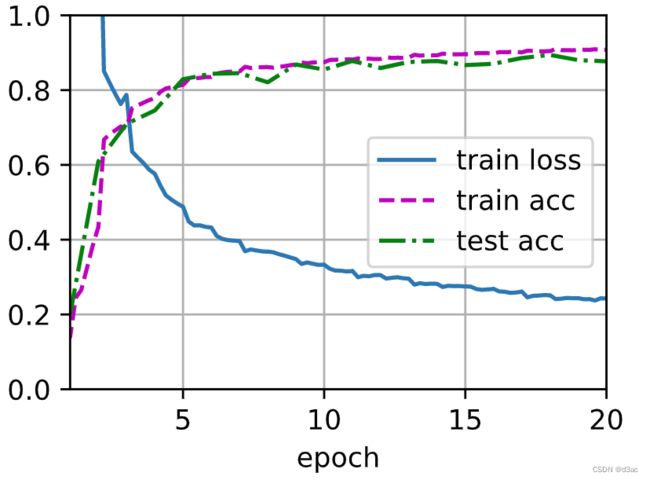
loss 0.431, train acc 0.838, test acc 0.722
2766.8 examples/sec on cuda:0
c o s t cost cost 10 m 56.7 s 10m56.7s 10m56.7s
learning_rate, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.02, 20, 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, learning_rate, d2l.try_gpu(), ylim=[0.0, 1.0])
loss 0.243, train acc 0.908, test acc 0.877
2169.8 examples/sec on cuda:0
c o s t cost cost 33 m 23.3 s 33m23.3s 33m23.3s
learning_rate, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.02, 10, 8
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, learning_rate, d2l.try_gpu(), ylim=[0.0, 1.0])
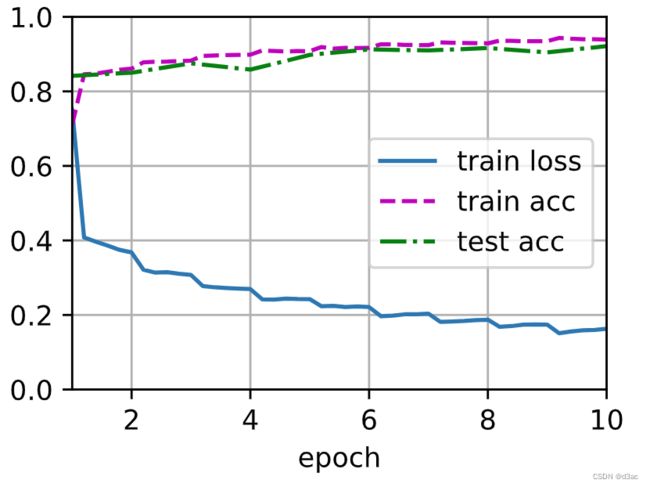
loss 0.163, train acc 0.939, test acc 0.921
325.1 examples/sec on cuda:0
c o s t cost cost 21 m 59.2 s 21m59.2s 21m59.2s
learning_rate, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.05, 50, 1000
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, learning_rate, d2l.try_gpu(), ylim=[0.0, 1.0])
loss 0.269, train acc 0.897, test acc 0.882
2897.8 examples/sec on cuda:0
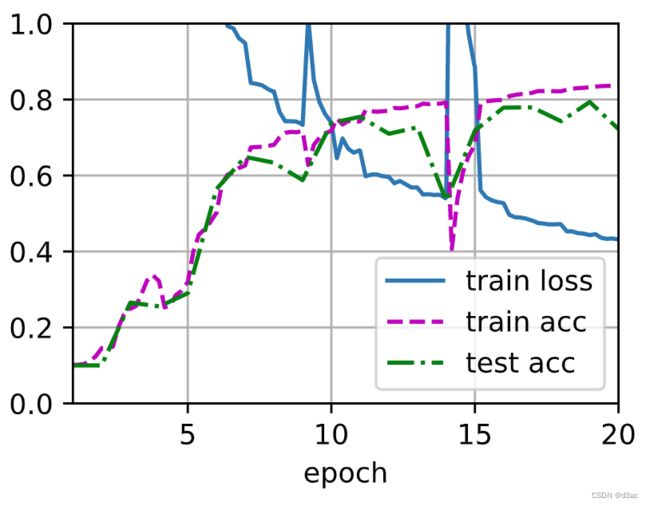
低的 b a t c h _ s i z e batch\_size batch_size 会导致 G P U GPU GPU 的并行度变差, 也就是运行速度会变得非常的慢
b a t c h _ s i z e batch\_size batch_size 变低的时候, 会进行更多次的更新, 所以在曲线上来看下降的更快, 因为每一个 m i n i mini mini b a t c h batch batch 都会对所有的参数进行一次更新, 更新了很多次, 虽然可能走了很多的弯路, 但是由于走了很多步, 所以最后的图像看起来比较规整, 都是呈下降趋势, 而 b a t c h _ s i z e batch\_size batch_size 很大的时候看起来曲线很抖是因为更新的次数少了, 弯弯曲曲走的都在 e p o c h epoch epoch - l o s s loss loss 曲线中体现出来了
b a t c h _ s i z e batch\_size batch_size 小不是一件坏事, 这样使用的显存更小, 小的 b a t c h _ s i z e batch\_size batch_size 会对网络产生更多的噪声, 这对神经网络来说是一件好事