异常检测算法:孤立森林(isolation forest)的python代码实现
文章目录
-
- 孤立森林
-
- 算法简介
- 代码实现
- 可视化
孤立森林
算法简介
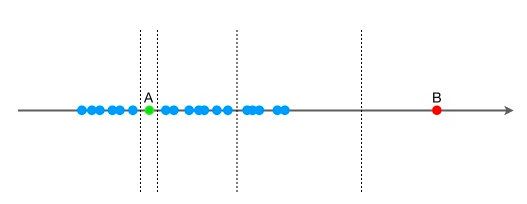
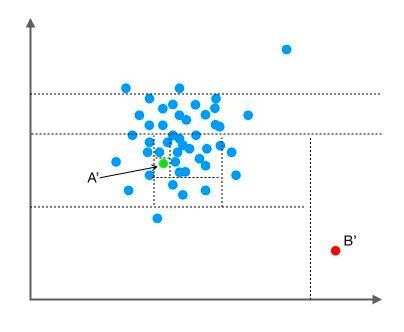
孤立森林是一种无监督学习算法,可以用来做anomaly detection。在孤立森林中,递归地随机分割数据集,直到所有的样本点都是孤立的。在这种随机分割的策略下,通常只需要极少的分割次数就可以使得异常点被孤立。换句话说,那些密度很高的簇是需要被切割很多次才能被孤立,但是那些密度很低的点很容易就可以被孤立。
将一维空间拓展到二维空间也是如此,异常点可以很快地被切割成孤立点。
代码实现
使用sklearn中的相关包来实现孤立森林算法,举一个很简单的小demo:
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
X = [[-1.1], [0.2], [10.1], [0.3], [2.5], [1.7], [2.2], [1.7]]
clf = IsolationForest()
clf.fit(X)
# 输出decision_function的结果:大于0表示正样本的可信度大于负样本,否则可信度小于负样本。
# 在这个demo中,第三个数字是异常点的可能性最大,其次是第一个数字
scores = clf.decision_function(X)
"""
输出的结果是:
[-0.10780172 0.08482445 -0.2449808 0.08846511 0.04413297 0.11703052
0.0870313 0.11703052]
"""
print(scores)
其他的内置函数以及介绍在:scikit-learn
可视化
sklearn上的可视化案例,链接为scikit-learn-iForest-demo
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
# Generate train data
X = 0.3 * rng.randn(100, 2)
X_train = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# Generate some regular novel observations
X = 0.3 * rng.randn(20, 2)
X_test = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# Generate some abnormal novel observations
X_outliers = rng.uniform(low=-4, high=4, size=(20, 2))
# fit the model
clf = IsolationForest(max_samples=100, random_state=rng)
clf.fit(X_train)
y_pred_train = clf.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = clf.predict(X_test)
y_pred_outliers = clf.predict(X_outliers)
# plot the line, the samples, and the nearest vectors to the plane
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5, 5, 50), np.linspace(-5, 5, 50))
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.title("IsolationForest")
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r)
b1 = plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c='white',
s=20, edgecolor='k')
b2 = plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c='green',
s=20, edgecolor='k')
c = plt.scatter(X_outliers[:, 0], X_outliers[:, 1], c='red',
s=20, edgecolor='k')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlim((-5, 5))
plt.ylim((-5, 5))
plt.legend([b1, b2, c],
["training observations",
"new regular observations", "new abnormal observations"],
loc="upper left")
plt.show()
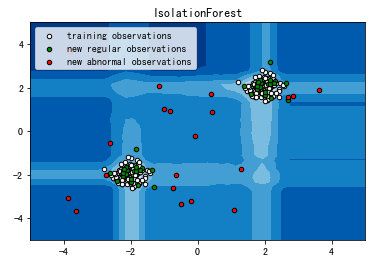
最终的结果是:
其中,红色即为异常点,白色是训练集,绿色是测试数据。