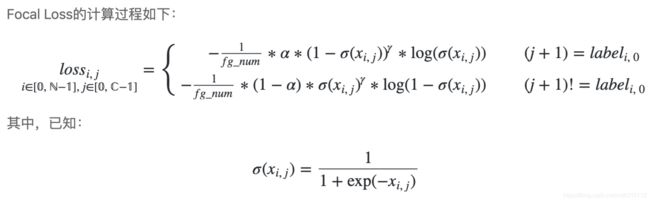paddle 基础函数 loss 函数
(1)bpr_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/bpr_loss_cn.html
(2)center_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/center_loss_cn.html
(3)dice_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/dice_loss_cn.html
(4)huber_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/huber_loss_cn.html
(5)kldiv_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/kldiv_loss_cn.html
(6)log_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/log_loss_cn.html
(7)margin_rank_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/margin_rank_loss_cn.html
(8)mse_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/mse_loss_cn.html
(9)npair_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/npair_loss_cn.html
(10)rank_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/rank_loss_cn.html
(11)sigmoid_facal_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/sigmoid_focal_loss_cn.html
(12)ssd_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/ssd_loss_cn.html
(13)teacher_student_sigmoid_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/teacher_student_sigmoid_loss_cn.html
(14)yolov3_loss:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/yolov3_loss_cn.html
(15)nce:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/nce_cn.html
(16)smooth_l1:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/layers_cn/smooth_l1_cn.html
(1)bpr_loss:贝叶斯个性化排序损失函数(Bayesian Personalized Ranking Loss Operator )
paddle.fluid.layers.bpr_loss(input, label, name=None)
属于pairwise类型的损失函数。损失值由下式计算而得:
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
neg_size = 3
# label=[0]
label = fluid.data(name="label", shape=[-1, 1], dtype="int64")
# predict = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]
predict = fluid.layers.data(
name="predict", shape=[-1, neg_size + 1], dtype="float32")
# bpr_Loss : label [0] 表示predict中下标0表示正例,即为0.1, 负例有3个为0.2,0.3,0.4
cost = fluid.layers.bpr_loss(input=predict, label=label)
use_cuda = False
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
x = np.random.randint(0, high=4, size=(3, 1))
y = np.random.random(size=(3, 4)).astype("float32")
output= exe.run(feed={"label":x, "predict":y},
fetch_list=[cost])
print(x)
print(y)
print(output)(2)center_loss:接收一个来自于最后一个隐藏层的输出和目标标签作为输入,返回损失值。为每一个类别提供一个类别中心,计算mini-batch中每个样本与对应类别中心的距离的平均值作为center loss。
paddle.fluid.layers.center_loss(input, label, num_classes, alpha, param_attr, update_center=True)
计算公式为:
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
input = fluid.data(name='x',shape=[-1, 7],dtype='float32')
label = fluid.data(name='y',shape=[-1, 1],dtype='int64')
num_classes = 1000
alpha = 0.01
center_loss=fluid.layers.center_loss(input=input,
label=label,
num_classes=1000,
alpha=alpha,
param_attr=fluid.initializer.Xavier(uniform=False),
update_center=True)
use_cuda = False
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
x = np.random.random(size=(3, 7)).astype("float32")
y = np.random.randint(0, high=4, size=(3, 1))
output= exe.run(feed={"x":x, "y":y},
fetch_list=[center_loss])
print(x)
print(y)
print(output)(3)dice_loss:用来比较预测结果跟标签之间的相似度,通常用于二值图像分割,即标签为二值,也可以做多标签的分割。
paddle.fluid.layers.dice_loss(input, label, epsilon=1e-05)
计算公式为:
(4)huber_loss:计算输入(input)与标签(label)之间的Huber损失。Huber损失是常用的回归损失之一,相较于平方误差损失,Huber损失减小了对异常点的敏感度,更具鲁棒性。
paddle.fluid.layers.huber_loss(input, label, delta)
当输入与标签之差的绝对值大于delta时,计算线性误差:
![]()
当输入与标签之差的绝对值小于delta时,计算平方误差:
![]()
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
DATATYPE='float32'
input_data = np.array([[1.],[2.],[3.],[4.]]).astype(DATATYPE)
label_data = np.array([[3.],[3.],[4.],[4.]]).astype(DATATYPE)
x = fluid.data(name='input', shape=[-1, 1], dtype=DATATYPE)
y = fluid.data(name='label', shape=[-1, 1], dtype=DATATYPE)
loss = fluid.layers.huber_loss(input=x, label=y, delta=1.0)
place = fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
HuberLoss, = exe.run(feed={'input':input_data ,'label':label_data},
fetch_list=[loss.name])
print(HuberLoss) #[[1.5], [0.5], [0.5], [0. ]], dtype=float32
(5)kldiv_loss:计算输入(X)和输入(Target)之间的Kullback-Leibler散度损失。注意其中输入(X)应为对数概率值,输入(Target)应为概率值。
paddle.fluid.layers.kldiv_loss(x, target, reduction='mean', name=None)
kL发散损失计算如下:
![]()
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
# 'batchmean' reduction, loss shape 为[N]
x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32') # shape=[-1, 4, 2, 2]
target = fluid.data(name='target', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32')
loss = fluid.layers.kldiv_loss(x=x, target=target, reduction='batchmean') # shape=[-1]
# 'mean' reduction, loss shape 为[1]
x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32') # shape=[-1, 4, 2, 2]
target = fluid.data(name='target', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32')
loss = fluid.layers.kldiv_loss(x=x, target=target, reduction='mean') # shape=[1]
# 'sum' reduction, loss shape 为[1]
x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32') # shape=[-1, 4, 2, 2]
target = fluid.data(name='target', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32')
loss = fluid.layers.kldiv_loss(x=x, target=target, reduction='sum') # shape=[1]
# 'none' reduction, loss shape 与X相同
x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32') # shape=[-1, 4, 2, 2]
target = fluid.data(name='target', shape=[-1,4,2,2], dtype='float32')
loss = fluid.layers.kldiv_loss(x=x, target=target, reduction='none') # shape=[-1, 4, 2, 2]
(6) log_loss:对输入的预测结果和目标标签进行计算,返回负对数损失值。分类任务常用损失函数。
paddle.fluid.layers.log_loss(input, label, epsilon=0.0001, name=None)
计算公式:
![]()
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
label = fluid.data(name='label', shape=[-1, 1], dtype='float32')
prob = fluid.data(name='prob', shape=[-1, 1], dtype='float32')
cost = fluid.layers.log_loss(input=prob, label=label)
use_cuda = False
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
x = np.random.randint(0, high=2, size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
y = np.random.random(size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
output= exe.run(feed={"label":x, "prob":y},
fetch_list=[cost])
print(x)
print(y)
print(output)
(7)margin_rank_loss:间隔排序损失。在排序问题中,它可以比较来自排序网络的输入 left 和输入 right 的得分。
paddle.fluid.layers.margin_rank_loss(label, left, right, margin=0.1, name=None)
计算公式:
![]()
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
label = fluid.data(name="label", shape=[-1, 1], dtype="float32")
left = fluid.data(name="left", shape=[-1, 1], dtype="float32")
right = fluid.data(name="right", shape=[-1, 1], dtype="float32")
out = fluid.layers.margin_rank_loss(label, left, right)
use_cuda = False
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
x = np.random.randint(0, high=2, size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
y = np.random.random(size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
z = np.random.random(size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
output= exe.run(feed={"label":x, "left":y, "right":z},
fetch_list=[out])
print(x)
print(y)
print(z)
print(output)
(8)mse_loss:计算预测值和目标值的均方差误差。
paddle.fluid.layers.mse_loss(input, label)
对于预测值input和目标值label,公式为:
![]()
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
y = fluid.data(name='y', shape=[-1, 1], dtype='float32')
y_predict = fluid.data(name='y_predict', shape=[-1, 1], dtype='float32')
cost = fluid.layers.mse_loss(input=y_predict, label=y)
use_cuda = False
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
x = np.random.randint(0, high=2, size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
y = np.random.random(size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
output= exe.run(feed={"y":x, "y_predict":y},
fetch_list=[cost])
print(x)
print(y)
print(output)
(9)npair_loss:NPair损失需要成对的数据。NPair损失分为两部分:第一部分是对嵌入向量进行L2正则化;第二部分是每一对数据的相似性矩阵的每一行和映射到ont-hot之后的标签的交叉熵损失的和。
paddle.fluid.layers.npair_loss(anchor, positive, labels, l2_reg=0.002)
(10)rank_loss:实现了RankNet模型中的排序损失层。RankNet是一种文档对(pairwise)排序模型,训练样本由一对文档(假设用A、B来表示)组成。标签(假设用P来表示)表示A的排名是否高于B。
paddle.fluid.layers.rank_loss(label, left, right, name=None)
示例:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy as np
label = fluid.layers.data(name="label", shape=[-1, 1], dtype="float32")
left = fluid.layers.data(name="left", shape=[-1, 1], dtype="float32")
right = fluid.layers.data(name="right", shape=[-1, 1], dtype="float32")
out = fluid.layers.rank_loss(label, left, right)
use_cuda = False
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
x = np.random.randint(0, high=2, size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
y = np.random.random(size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
z = np.random.random(size=(3, 1)).astype("float32")
output= exe.run(feed={"label":x, "left":y, "right":z},
fetch_list=[out])
print(x)
print(y)
print(z)
print(output)
(11)sigmoid_focal_loss:用于解决计算机视觉任务中前景-背景不平衡的问题。该OP先计算输入x中每个元素的sigmoid值,然后计算sigmoid值与类别目标值label之间的Focal Loss。
paddle.fluid.layers.sigmoid_focal_loss(x, label, fg_num, gamma=2.0, alpha=0.25)
(12)ssd_loss:用于SSD物体检测算法的多窗口损失层。该层用于计算SSD的损失,给定位置偏移预测,置信度预测,候选框和真实框标签,以及难样本挖掘的类型。通过执行以下步骤,返回的损失是本地化损失(或回归损失)和置信度损失(或分类损失)的加权和。
paddle.fluid.layers.ssd_loss(location, confidence, gt_box, gt_label, prior_box, prior_box_var=None, background_label=0, overlap_threshold=0.5, neg_pos_ratio=3.0, neg_overlap=0.5, loc_loss_weight=1.0, conf_loss_weight=1.0, match_type='per_prediction', mining_type='max_negative', normalize=True, sample_size=None)
1、通过二分匹配算法查找匹配的边界框。
1.1、计算真实框与先验框之间的IOU相似度。
1.2、通过二分匹配算法计算匹配的边界框。
2、计算难分样本的置信度
2.1、根据匹配的索引获取目标标签。
2.2、计算置信度损失。
3、应用难样本挖掘算法来获取负样本索引并更新匹配的索引。
4、分配分类和回归目标
4.1、根据生成的候选框bbox进行编码。
4.2、分配回归目标。
4.3、分配分类目标。
5、计算总体的物体损失。
5.1计算置信度(confidence)损失。
5.2计算回归(location)损失。
5.3计算总体加权损失。
(13)teacher_student_sigmoid_loss:定制化需求,用于student萃取teacher的值。此图层接受输入预测和目标标签,并返回teacher_student损失。 z表示是否点击,z'表示teacher q值。label取值范围{-2,-1,[0, 2]} teacher q值不存在时,点击时label为-1,否则为-2。 teacher q值存在时,点击时label为z',否则为1 + z'。
paddle.fluid.layers.teacher_student_sigmoid_loss(input, label, soft_max_up_bound=15.0, soft_max_lower_bound=-15.0)
公式:
(14)yolov3_loss:通过给定的预测结果和真实框计算yolov3损失。
paddle.fluid.layers.yolov3_loss(x, gt_box, gt_label, anchors, anchor_mask, class_num, ignore_thresh, downsample_ratio, gt_score=None, use_label_smooth=True, name=None)