SiamMask 测试程序分析
之前分析了 DaSiamRPN 的测试代码,侧重于执行细节。到了 SiamMask,似乎主题应该有所升华。故事的明线为跟踪器构成,暗线为训练流图。
相比于 DaSiamRPN,SiamMask 不仅网络结构是现代化的,系统设计也更具匠心。这便于我们一窥其轮廓。
SiamMask/models 文件夹下定义了网络的基本架构。
网络工作流为:
SiamMask/experiments/siammask 文件夹定义了实际网络。具体到 Custom,其多了一个 Refine 模块用于融合不同层次上的特征。
SiamMask/tools 文件夹中定义了测试和评估程序。
下面介绍其环境配置。编译 Cython 需要 python3-devel 库。
SiamMask/requirements.txt
项目推荐安装以下包:
- Cython 是 Python 及其扩展 Cython 编程语言(基于 Pyrex)的优化静态编译器。它使 Python 编写 C 扩展就像 Python 本身一样简单。
- Colorama 实现跨平台彩色终端文本。
- NumPy 是使用 Python 进行科学计算的基础包。
- Fire 用于自动生成命令行界面的库。(未见使用)
- torch 指定了0.4.1版本。
- torchvision 用于 Torch 深度学习的图像、视频数据集和模型。
- Numba 是一个开源 JIT 编译器,它将 Python 和 NumPy 代码的子集转换为快速机器码。(在 pysot 中使用)
- SciPy 是数学、科学和工程的开源软件。SciPy 库依赖于 NumPy,它提供方便快捷的 N 维数组操作。(未见使用)
- h5py 从 Python 读取和写入 HDF5文件。(未见使用)
- pandas 用于数据分析、时间序列和统计的强大的数据结构。(未见使用)
- tqdm Python 和 CLI 的快速、可扩展的进度条。
- opencv-python 用于 Python 的非官方预构建 OpenCV 包。
get_test_data.sh 脚本首先借助 jvlmdr/trackdat 下载 vot2016 vot2018 搭配作者相应的 json 文件。然后下载 DAVIS-2017-trainval-480p.zip。DAVIS 2017 在每个视频序列中标注了多个实例。
jvlmdr/trackdat 中解析 json 文件需要安装 jq。
test_mask_refine.sh
检查输入参数3是否存在。
if [ -z "$4" ]
then
echo "Need input parameter!"
echo "Usage: bash `basename "$0"` \$CONFIG \$MODEL \$DATASET \$GPUID"
exit
fi
git-rev-parse 挑选并管理参数。–show-toplevel 显示顶级目录的绝对路径。
将项目加入 Python 的环境变量中,创建“logs”文件夹。
ROOT=`git rev-parse --show-toplevel`
export PYTHONPATH=$ROOT:$PYTHONPATH
mkdir -p logs
导入参数后运行 test.py。
config=$1
model=$2
dataset=$3
gpu=$4
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$gpu python -u $ROOT/tools/test.py \
--config $config \
--resume $model \
--mask --refine \
--dataset $dataset 2>&1 | tee logs/test_$dataset.log
test.py
load_config 加载 JSON 配置文件并设置args.arch的值。
add_file_handler 创建一个记录器并绑定文件句柄。
global args, logger, v_id
args = parser.parse_args()
cfg = load_config(args)
init_log('global', logging.INFO)
if args.log != "":
add_file_handler('global', args.log, logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger('global')
logger.info(args)
Custom 为论文实现的网络。
如果不是“Custom”,加载 models 下指定的结构。
load_pretrain 能够处理网络之间的不一致。
# setup model
if args.arch == 'Custom':
from custom import Custom
model = Custom(anchors=cfg['anchors'])
else:
model = models.__dict__[args.arch](anchors=cfg['anchors'])
if args.resume:
assert isfile(args.resume), '{} is not a valid file'.format(args.resume)
model = load_pretrain(model, args.resume)
model.eval()
model = model.cuda()
load_dataset 能够加载 VOT、DAVIS、ytb_vos 三种数据集。
# setup dataset
dataset = load_dataset(args.dataset)
仅以上三种数据源支持掩膜输出。
调用 track_vos 或者 track_vot。
# VOS or VOT?
if args.dataset in ['DAVIS2016', 'DAVIS2017', 'ytb_vos'] and args.mask:
vos_enable = True # enable Mask output
else:
vos_enable = False
total_lost = 0 # VOT
iou_lists = [] # VOS
speed_list = []
for v_id, video in enumerate(dataset.keys(), start=1):
if vos_enable:
iou_list, speed = track_vos(model, dataset[video], cfg['hp'] if 'hp' in cfg.keys() else None,
args.mask, args.refine, args.dataset in ['DAVIS2017', 'ytb_vos'])
iou_lists.append(iou_list)
else:
lost, speed = track_vot(model, dataset[video], cfg['hp'] if 'hp' in cfg.keys() else None,
args.mask, args.refine)
total_lost += lost
speed_list.append(speed)
记录最终结果。
# report final result
if vos_enable:
for thr, iou in zip(thrs, np.mean(np.concatenate(iou_lists), axis=0)):
logger.info('Segmentation Threshold {:.2f} mIoU: {:.3f}'.format(thr, iou))
else:
logger.info('Total Lost: {:d}'.format(total_lost))
logger.info('Mean Speed: {:.2f} FPS'.format(np.mean(speed_list)))
track_vos
track_vos 函数中使用了 Image.open。分割数据的标注亦为图片。
image_files = video['image_files']
annos = [np.array(Image.open(x)) for x in video['anno_files']]
if 'anno_init_files' in video:
annos_init = [np.array(Image.open(x)) for x in video['anno_init_files']]
else:
annos_init = [annos[0]]
"DAVIS2017"和"ytb_vos"会开启多目标跟踪。
if not mot_enable:
annos = [(anno > 0).astype(np.uint8) for anno in annos]
annos_init = [(anno_init > 0).astype(np.uint8) for anno_init in annos_init]
if 'start_frame' in video:
object_ids = [int(id) for id in video['start_frame']]
else:
object_ids = [o_id for o_id in np.unique(annos[0]) if o_id != 0]
if len(object_ids) != len(annos_init):
annos_init = annos_init*len(object_ids)
object_num = len(object_ids)
每个目标都遍历图像,在起止帧之间执行跟踪。
pred_masks记录所有的 mask。
boundingRect() 计算点集或灰度图像的非零像素的垂直矩形。
toc = 0
pred_masks = np.zeros((object_num, len(image_files), annos[0].shape[0], annos[0].shape[1]))-1
for obj_id, o_id in enumerate(object_ids):
if 'start_frame' in video:
start_frame = video['start_frame'][str(o_id)]
end_frame = video['end_frame'][str(o_id)]
else:
start_frame, end_frame = 0, len(image_files)
for f, image_file in enumerate(image_files):
im = cv2.imread(image_file)
tic = cv2.getTickCount()
if f == start_frame: # init
mask = annos_init[obj_id] == o_id
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect((mask).astype(np.uint8))
cx, cy = x + w/2, y + h/2
target_pos = np.array([cx, cy])
target_sz = np.array([w, h])
state = siamese_init(im, target_pos, target_sz, model, hp) # init tracker
elif end_frame >= f > start_frame: # tracking
state = siamese_track(state, im, mask_enable, refine_enable) # track
mask = state['mask']
toc += cv2.getTickCount() - tic
if end_frame >= f >= start_frame:
pred_masks[obj_id, f, :, :] = mask
toc /= cv2.getTickFrequency()
MultiBatchIouMeter 批量计算 IoU。
if len(annos) == len(image_files):
multi_mean_iou = MultiBatchIouMeter(thrs, pred_masks, annos,
start=video['start_frame'] if 'start_frame' in video else None,
end=video['end_frame'] if 'end_frame' in video else None)
for i in range(object_num):
for j, thr in enumerate(thrs):
logger.info('Fusion Multi Object{:20s} IOU at {:.2f}: {:.4f}'.format(video['name'] + '_' + str(i + 1), thr,
multi_mean_iou[i, j]))
else:
multi_mean_iou = []
pred_mask_final合并图像上多个目标的模板索引,默认0通道为背景。索引直接保存为图片无法可视化。
if args.save_mask:
video_path = join('test', args.dataset, 'SiamMask', video['name'])
if not isdir(video_path): makedirs(video_path)
pred_mask_final = np.array(pred_masks)
pred_mask_final = (np.argmax(pred_mask_final, axis=0).astype('uint8') + 1) * (
np.max(pred_mask_final, axis=0) > state['p'].seg_thr).astype('uint8')
for i in range(pred_mask_final.shape[0]):
cv2.imwrite(join(video_path, image_files[i].split('/')[-1].split('.')[0] + '.png'), pred_mask_final[i].astype(np.uint8))
由于图像序列处理完才显示,所以有些卡顿。
if args.visualization:
pred_mask_final = np.array(pred_masks)
pred_mask_final = (np.argmax(pred_mask_final, axis=0).astype('uint8') + 1) * (
np.max(pred_mask_final, axis=0) > state['p'].seg_thr).astype('uint8')
COLORS = np.random.randint(128, 255, size=(object_num, 3), dtype="uint8")
COLORS = np.vstack([[0, 0, 0], COLORS]).astype("uint8")
mask = COLORS[pred_mask_final]
for f, image_file in enumerate(image_files):
output = ((0.4 * cv2.imread(image_file)) + (0.6 * mask[f,:,:,:])).astype("uint8")
cv2.imshow("mask", output)
cv2.waitKey(1)
logger.info('({:d}) Video: {:12s} Time: {:02.1f}s Speed: {:3.1f}fps'.format(
v_id, video['name'], toc, f*len(object_ids) / toc))
return multi_mean_iou, f*len(object_ids) / toc
track_vot
regions记录目标框以及状态。
regions = [] # result and states[1 init / 2 lost / 0 skip]
image_files, gt = video['image_files'], video['gt']
start_frame, end_frame, lost_times, toc = 0, len(image_files), 0, 0
get_axis_aligned_bbox 能够得到目标的最小外接矩形。
遍历图像序列,由目标出现的帧初始化。
for f, image_file in enumerate(image_files):
im = cv2.imread(image_file)
tic = cv2.getTickCount()
if f == start_frame: # init
cx, cy, w, h = get_axis_aligned_bbox(gt[f])
target_pos = np.array([cx, cy])
target_sz = np.array([w, h])
state = siamese_init(im, target_pos, target_sz, model, hp) # init tracker
location = cxy_wh_2_rect(state['target_pos'], state['target_sz'])
regions.append(1 if 'VOT' in args.dataset else gt[f])
在后续帧跟踪,由state获取目标框。
vot_overlap 计算两个多边形之间的重叠。
elif f > start_frame: # tracking
state = siamese_track(state, im, mask_enable, refine_enable) # track
if mask_enable:
location = state['ploygon'].flatten()
mask = state['mask']
else:
location = cxy_wh_2_rect(state['target_pos'], state['target_sz'])
mask = []
if 'VOT' in args.dataset:
gt_polygon = ((gt[f][0], gt[f][1]), (gt[f][2], gt[f][3]),
(gt[f][4], gt[f][5]), (gt[f][6], gt[f][7]))
if mask_enable:
pred_polygon = ((location[0], location[1]), (location[2], location[3]),
(location[4], location[5]), (location[6], location[7]))
else:
pred_polygon = ((location[0], location[1]),
(location[0] + location[2], location[1]),
(location[0] + location[2], location[1] + location[3]),
(location[0], location[1] + location[3]))
b_overlap = vot_overlap(gt_polygon, pred_polygon, (im.shape[1], im.shape[0]))
else:
b_overlap = 1
OTB 测试一跟到底,VOT 跟丢则隔几帧重置。
if b_overlap:
regions.append(location)
else: # lost
regions.append(2)
lost_times += 1
start_frame = f + 5 # skip 5 frames
else: # skip
regions.append(0)
toc += cv2.getTickCount() - tic
处理完一帧后进行显示。这里复制得到im_show似乎并无必要。
if args.visualization and f >= start_frame: # visualization (skip lost frame)
im_show = im.copy()
if f == 0: cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if gt.shape[0] > f:
if len(gt[f]) == 8:
cv2.polylines(im_show, [np.array(gt[f], np.int).reshape((-1, 1, 2))], True, (0, 255, 0), 3)
else:
cv2.rectangle(im_show, (gt[f, 0], gt[f, 1]), (gt[f, 0] + gt[f, 2], gt[f, 1] + gt[f, 3]), (0, 255, 0), 3)
if len(location) == 8:
if mask_enable:
mask = mask > state['p'].seg_thr
im_show[:, :, 2] = mask * 255 + (1 - mask) * im_show[:, :, 2]
location_int = np.int0(location)
cv2.polylines(im_show, [location_int.reshape((-1, 1, 2))], True, (0, 255, 255), 3)
else:
location = [int(l) for l in location]
cv2.rectangle(im_show, (location[0], location[1]),
(location[0] + location[2], location[1] + location[3]), (0, 255, 255), 3)
cv2.putText(im_show, str(f), (40, 40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(im_show, str(lost_times), (40, 80), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow(video['name'], im_show)
cv2.waitKey(1)
toc /= cv2.getTickFrequency()
跟踪完成,记录结果到文本文件。
# save result
name = args.arch.split('.')[0] + '_' + ('mask_' if mask_enable else '') + ('refine_' if refine_enable else '') +\
args.resume.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0]
if 'VOT' in args.dataset:
video_path = join('test', args.dataset, name,
'baseline', video['name'])
if not isdir(video_path): makedirs(video_path)
result_path = join(video_path, '{:s}_001.txt'.format(video['name']))
with open(result_path, "w") as fin:
for x in regions:
fin.write("{:d}\n".format(x)) if isinstance(x, int) else \
fin.write(','.join([vot_float2str("%.4f", i) for i in x]) + '\n')
else: # OTB
video_path = join('test', args.dataset, name)
if not isdir(video_path): makedirs(video_path)
result_path = join(video_path, '{:s}.txt'.format(video['name']))
with open(result_path, "w") as fin:
for x in regions:
fin.write(','.join([str(i) for i in x])+'\n')
logger.info('({:d}) Video: {:12s} Time: {:02.1f}s Speed: {:3.1f}fps Lost: {:d}'.format(
v_id, video['name'], toc, f / toc, lost_times))
return lost_times, f / toc
get_axis_aligned_bbox
numpy.linalg.norm 计算矩阵或矢量的范数。默认计算矩阵元素平方和再开根号。
求多边形中心(cx, cy),外接矩形[(x1, y1), (x2, y2)]。
A1是平行四边形拉伸为矩形后的面积,A2为外接矩形的面积。
nv = region.size
if nv == 8:
cx = np.mean(region[0::2])
cy = np.mean(region[1::2])
x1 = min(region[0::2])
x2 = max(region[0::2])
y1 = min(region[1::2])
y2 = max(region[1::2])
A1 = np.linalg.norm(region[0:2] - region[2:4]) * np.linalg.norm(region[2:4] - region[4:6])
A2 = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
s = np.sqrt(A1 / A2)
w = s * (x2 - x1) + 1
h = s * (y2 - y1) + 1
else:
x = region[0]
y = region[1]
w = region[2]
h = region[3]
cx = x+w/2
cy = y+h/2
return cx, cy, w, h
MultiBatchIouMeter
获得预测掩膜及标注的数量。构造预测结果的 id 列表object_ids。
targets = np.array(targets)
outputs = np.array(outputs)
num_frame = targets.shape[0]
if start is None:
object_ids = np.array(list(range(outputs.shape[0]))) + 1
else:
object_ids = [int(id) for id in start]
num_object = len(object_ids)
res = np.zeros((num_object, len(thrs)), dtype=np.float32)
output_max_id为每个像素位置预测的 id,0通道为背景。
outputs_max合并一张图上的预测。
thrs为全局变量。对于每个阈值,output_thr过滤结果,对于每个目标,target_j选中其表注像素位置。
output_max_id = np.argmax(outputs, axis=0).astype('uint8')+1
outputs_max = np.max(outputs, axis=0)
for k, thr in enumerate(thrs):
output_thr = outputs_max > thr
for j in range(num_object):
target_j = targets == object_ids[j]
对于每幅图像,pred为目标 j 的预测掩码。统计数量,计算与标注的交并比。
if start is None:
start_frame, end_frame = 1, num_frame - 1
else:
start_frame, end_frame = start[str(object_ids[j])] + 1, end[str(object_ids[j])] - 1
iou = []
for i in range(start_frame, end_frame):
pred = (output_thr[i] * output_max_id[i]) == (j+1)
mask_sum = (pred == 1).astype(np.uint8) + (target_j[i] > 0).astype(np.uint8)
intxn = np.sum(mask_sum == 2)
union = np.sum(mask_sum > 0)
if union > 0:
iou.append(intxn / union)
elif union == 0 and intxn == 0:
iou.append(1)
res[j, k] = np.mean(iou)
return res
siamese_init
siamese_init 构造state字典。
TrackerConfig 配置参数。
generate_anchor 生成锚点。
state = dict()
state['im_h'] = im.shape[0]
state['im_w'] = im.shape[1]
p = TrackerConfig()
p.update(hp, model.anchors)
p.renew()
net = model
p.scales = model.anchors['scales']
p.ratios = model.anchors['ratios']
p.anchor_num = len(p.ratios) * len(p.scales)
p.anchor = generate_anchor(model.anchors, p.score_size)
avg_chans = np.mean(im, axis=(0, 1))
wc_z = target_sz[0] + p.context_amount * sum(target_sz)
hc_z = target_sz[1] + p.context_amount * sum(target_sz)
s_z = round(np.sqrt(wc_z * hc_z))
# initialize the exemplar
z_crop = get_subwindow_tracking(im, target_pos, p.exemplar_size, s_z, avg_chans)
z = Variable(z_crop.unsqueeze(0))
net.template(z.cuda())
numpy.outer 计算两个向量的外积。
if p.windowing == 'cosine':
window = np.outer(np.hanning(p.score_size), np.hanning(p.score_size))
elif p.windowing == 'uniform':
window = np.ones((p.score_size, p.score_size))
window = np.tile(window.flatten(), p.anchor_num)
state['p'] = p
state['net'] = net
state['avg_chans'] = avg_chans
state['window'] = window
state['target_pos'] = target_pos
state['target_sz'] = target_sz
return state
generate_anchor
由 Anchors 类创建锚点,转译为[cx,cy,w,h]格式。
anchors = Anchors(cfg)
anchor = anchors.anchors
x1, y1, x2, y2 = anchor[:, 0], anchor[:, 1], anchor[:, 2], anchor[:, 3]
anchor = np.stack([(x1+x2)*0.5, (y1+y2)*0.5, x2-x1, y2-y1], 1)
total_stride = anchors.stride
anchor_num = anchor.shape[0]
按原来的方式广播得到所有的锚点。复制锚点,然后添加不同位置的偏移量。
anchor = np.tile(anchor, score_size * score_size).reshape((-1, 4))
ori = - (score_size // 2) * total_stride
xx, yy = np.meshgrid([ori + total_stride * dx for dx in range(score_size)],
[ori + total_stride * dy for dy in range(score_size)])
xx, yy = np.tile(xx.flatten(), (anchor_num, 1)).flatten(), \
np.tile(yy.flatten(), (anchor_num, 1)).flatten()
anchor[:, 0], anchor[:, 1] = xx.astype(np.float32), yy.astype(np.float32)
return anchor
siamese_track
p = state['p']
net = state['net']
avg_chans = state['avg_chans']
window = state['window']
target_pos = state['target_pos']
target_sz = state['target_sz']
由扩展后的宽高计算等效面积。使用与模板分支相同的缩放系数得到检测区域。
wc_x = target_sz[1] + p.context_amount * sum(target_sz)
hc_x = target_sz[0] + p.context_amount * sum(target_sz)
s_x = np.sqrt(wc_x * hc_x)
scale_x = p.exemplar_size / s_x
d_search = (p.instance_size - p.exemplar_size) / 2
pad = d_search / scale_x
s_x = s_x + 2 * pad
crop_box = [target_pos[0] - round(s_x) / 2, target_pos[1] - round(s_x) / 2, round(s_x), round(s_x)]
# extract scaled crops for search region x at previous target position
x_crop = Variable(get_subwindow_tracking(im, target_pos, p.instance_size, round(s_x), avg_chans).unsqueeze(0))
运行网络。
if mask_enable:
score, delta, mask = net.track_mask(x_crop.cuda())
else:
score, delta = net.track(x_crop.cuda())
解码出预测框,并根据位置、宽高比和位移量惩罚得分,挑选出最优预测。
delta = delta.permute(1, 2, 3, 0).contiguous().view(4, -1).data.cpu().numpy()
score = F.softmax(score.permute(1, 2, 3, 0).contiguous().view(2, -1).permute(1, 0), dim=1).data[:,
1].cpu().numpy()
delta[0, :] = delta[0, :] * p.anchor[:, 2] + p.anchor[:, 0]
delta[1, :] = delta[1, :] * p.anchor[:, 3] + p.anchor[:, 1]
delta[2, :] = np.exp(delta[2, :]) * p.anchor[:, 2]
delta[3, :] = np.exp(delta[3, :]) * p.anchor[:, 3]
def change(r):
return np.maximum(r, 1. / r)
def sz(w, h):
pad = (w + h) * 0.5
sz2 = (w + pad) * (h + pad)
return np.sqrt(sz2)
def sz_wh(wh):
pad = (wh[0] + wh[1]) * 0.5
sz2 = (wh[0] + pad) * (wh[1] + pad)
return np.sqrt(sz2)
# size penalty
target_sz_in_crop = target_sz*scale_x
s_c = change(sz(delta[2, :], delta[3, :]) / (sz_wh(target_sz_in_crop))) # scale penalty
r_c = change((target_sz_in_crop[0] / target_sz_in_crop[1]) / (delta[2, :] / delta[3, :])) # ratio penalty
penalty = np.exp(-(r_c * s_c - 1) * p.penalty_k)
pscore = penalty * score
# cos window (motion model)
pscore = pscore * (1 - p.window_influence) + window * p.window_influence
best_pscore_id = np.argmax(pscore)
pred_in_crop = delta[:, best_pscore_id] / scale_x
lr = penalty[best_pscore_id] * score[best_pscore_id] * p.lr # lr for OTB
res_x = pred_in_crop[0] + target_pos[0]
res_y = pred_in_crop[1] + target_pos[1]
res_w = target_sz[0] * (1 - lr) + pred_in_crop[2] * lr
res_h = target_sz[1] * (1 - lr) + pred_in_crop[3] * lr
target_pos = np.array([res_x, res_y])
target_sz = np.array([res_w, res_h])
numpy.unravel_index 将平面索引或平面索引数组转换为坐标数组的元组。
由best_pscore_id得到特征图上的位置。
track_refine 函数运行 Refine 模块,由相关特征图上 1 × 1 × 256 1\times 1\times 256 1×1×256 的特征向量与检测下采样前的特征图得到目标掩膜。
# for Mask Branch
if mask_enable:
best_pscore_id_mask = np.unravel_index(best_pscore_id, (5, p.score_size, p.score_size))
delta_x, delta_y = best_pscore_id_mask[2], best_pscore_id_mask[1]
if refine_enable:
mask = net.track_refine((delta_y, delta_x)).cuda().sigmoid().squeeze().view(
p.out_size, p.out_size).cpu().data.numpy()
else:
mask = mask[0, :, delta_y, delta_x].sigmoid(). \
squeeze().view(p.out_size, p.out_size).cpu().data.numpy()
warpAffine() 对图像应用仿射变换。
手动构造变换矩阵mapping,a和b为尺度系数,c和d为平移量。
def crop_back(image, bbox, out_sz, padding=-1):
a = (out_sz[0] - 1) / bbox[2]
b = (out_sz[1] - 1) / bbox[3]
c = -a * bbox[0]
d = -b * bbox[1]
mapping = np.array([[a, 0, c],
[0, b, d]]).astype(np.float)
crop = cv2.warpAffine(image, mapping, (out_sz[0], out_sz[1]),
flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR,
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,
borderValue=padding)
return crop
crop_box为检测截取框,格式为[x,y,width,height]。s为缩放系数。sub_box为预测的模板区域框。
p.out_size似乎与p.exemplar_size混用。
back_box为背景框。为什么back_box的左上角坐标为负?
s = crop_box[2] / p.instance_size
sub_box = [crop_box[0] + (delta_x - p.base_size / 2) * p.total_stride * s,
crop_box[1] + (delta_y - p.base_size / 2) * p.total_stride * s,
s * p.exemplar_size, s * p.exemplar_size]
s = p.out_size / sub_box[2]
back_box = [-sub_box[0] * s, -sub_box[1] * s, state['im_w'] * s, state['im_h'] * s]
mask_in_img = crop_back(mask, back_box, (state['im_w'], state['im_h']))
OpenCV4 的 findContours() 函数返回值数量少。
在二进制图像中查找轮廓。
minAreaRect() 寻找包围输入2D 点集的最小区域的旋转矩形。
boxPoints 查找旋转矩形的四个顶点。用于绘制旋转的矩形。
target_mask = (mask_in_img > p.seg_thr).astype(np.uint8)
if cv2.__version__[-5] == '4':
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(target_mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
else:
_, contours, _ = cv2.findContours(target_mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cnt_area = [cv2.contourArea(cnt) for cnt in contours]
if len(contours) != 0 and np.max(cnt_area) > 100:
contour = contours[np.argmax(cnt_area)] # use max area polygon
polygon = contour.reshape(-1, 2)
# pbox = cv2.boundingRect(polygon) # Min Max Rectangle
prbox = cv2.boxPoints(cv2.minAreaRect(polygon)) # Rotated Rectangle
# box_in_img = pbox
rbox_in_img = prbox
else: # empty mask
location = cxy_wh_2_rect(target_pos, target_sz)
rbox_in_img = np.array([[location[0], location[1]],
[location[0] + location[2], location[1]],
[location[0] + location[2], location[1] + location[3]],
[location[0], location[1] + location[3]]])
由结果更新状态。
target_pos[0] = max(0, min(state['im_w'], target_pos[0]))
target_pos[1] = max(0, min(state['im_h'], target_pos[1]))
target_sz[0] = max(10, min(state['im_w'], target_sz[0]))
target_sz[1] = max(10, min(state['im_h'], target_sz[1]))
state['target_pos'] = target_pos
state['target_sz'] = target_sz
state['score'] = score
state['mask'] = mask_in_img if mask_enable else []
state['ploygon'] = rbox_in_img if mask_enable else []
return state
SiamMask
SiamMask 是网络结构的抽象,主要定义模块。
def __init__(self, anchors=None, o_sz=127, g_sz=127):
super(SiamMask, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors # anchor_cfg
self.anchor_num = len(self.anchors["ratios"]) * len(self.anchors["scales"])
self.anchor = Anchors(anchors)
self.features = None
self.rpn_model = None
self.mask_model = None
self.o_sz = o_sz
self.g_sz = g_sz
self.all_anchors = None
set_all_anchors
set_all_anchors 函数在测试中并没有用到。
# cx,cy,w,h
if not self.anchor.generate_all_anchors(image_center, size):
return
all_anchors = self.anchor.all_anchors[1] # cx, cy, w, h
self.all_anchors = torch.from_numpy(all_anchors).float().cuda()
self.all_anchors = [self.all_anchors[i] for i in range(4)]
feature_extractor
def feature_extractor(self, x):
return self.features(x)
rpn
def rpn(self, template, search):
pred_cls, pred_loc = self.rpn_model(template, search)
return pred_cls, pred_loc
mask
def mask(self, template, search):
pred_mask = self.mask_model(template, search)
return pred_mask
template
def template(self, z):
self.zf = self.feature_extractor(z)
cls_kernel, loc_kernel = self.rpn_model.template(self.zf)
return cls_kernel, loc_kernel
track
def track(self, x, cls_kernel=None, loc_kernel=None, softmax=False):
xf = self.feature_extractor(x)
rpn_pred_cls, rpn_pred_loc = self.rpn_model.track(xf, cls_kernel, loc_kernel)
if softmax:
rpn_pred_cls = self.softmax(rpn_pred_cls)
return rpn_pred_cls, rpn_pred_loc
Anchors
object.__dict__ 是用于存储对象(可写)属性的字典或其他映射对象。
def __init__(self, cfg):
self.stride = 8
self.ratios = [0.33, 0.5, 1, 2, 3]
self.scales = [8]
self.round_dight = 0
self.image_center = 0
self.size = 0
self.__dict__.update(cfg)
self.anchor_num = len(self.scales) * len(self.ratios)
self.anchors = None # in single position (anchor_num*4)
self.all_anchors = None # in all position 2*(4*anchor_num*h*w)
self.generate_anchors()
generate_anchors
round_dight似乎是为了兼容 Python2和3的舍入。
基础锚点的中心为原点,mmdetection
的 AnchorGenerator 支持这一操作,而 maskrcnn-benchmark
中的 AnchorGenerator 不能。
为什么中间结果是整形而返回值却不是?这与 AnchorGenerator 正好相反。
self.anchors = np.zeros((self.anchor_num, 4), dtype=np.float32)
size = self.stride * self.stride
count = 0
for r in self.ratios:
if self.round_dight > 0:
ws = round(math.sqrt(size*1. / r), self.round_dight)
hs = round(ws * r, self.round_dight)
else:
ws = int(math.sqrt(size*1. / r))
hs = int(ws * r)
for s in self.scales:
w = ws * s
h = hs * s
self.anchors[count][:] = [-w*0.5, -h*0.5, w*0.5, h*0.5][:]
count += 1
generate_all_anchors
generate_all_anchors 同时生成了两种数据格式的 anchor。
如果仅调用一次,为何不在初始化函数中调用?
避免重复生成?
self.image_center是整张图吗?
if self.image_center == im_c and self.size == size:
return False
self.image_center = im_c
self.size = size
a0x表示 a n c h o r 0 \mathrm{anchor}_0 anchor0 的 xy 坐标,即 x 和 y 对称。
x1、y1、x2、y2以及cx、cy、w、h的形状为 [anchor_num, 1, 1]。
self.anchors形状为[A, 4],由于不加 padding 会使得anchor起始点不是图像边缘,generate_all_anchors 输入为中心点和空间尺寸。
corner2center
a0x = im_c - size // 2 * self.stride
ori = np.array([a0x] * 4, dtype=np.float32)
zero_anchors = self.anchors + ori
x1 = zero_anchors[:, 0]
y1 = zero_anchors[:, 1]
x2 = zero_anchors[:, 2]
y2 = zero_anchors[:, 3]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(lambda x: x.reshape(self.anchor_num, 1, 1), [x1, y1, x2, y2])
cx, cy, w, h = corner2center([x1, y1, x2, y2])
disp_x是[1, 1, size],disp_y是[1, size, 1],两个相加会怎样?
cx为[anchor_num, 1, size],cy为[anchor_num, size,1]。
zero让其变为[anchor_num, size,1]。
利用 numpy 运算来 broadcast。
disp_x = np.arange(0, size).reshape(1, 1, -1) * self.stride
disp_y = np.arange(0, size).reshape(1, -1, 1) * self.stride
cx = cx + disp_x
cy = cy + disp_y
# broadcast
zero = np.zeros((self.anchor_num, size, size), dtype=np.float32)
cx, cy, w, h = map(lambda x: x + zero, [cx, cy, w, h])
x1, y1, x2, y2 = center2corner([cx, cy, w, h])
self.all_anchors = np.stack([x1, y1, x2, y2]), np.stack([cx, cy, w, h])
return True
Custom
Custom 是实际网络的载体。增加了 track_mask、track_refine、track_refine 和 refine 函数用于处理 mask。
def __init__(self, pretrain=False, **kwargs):
super(Custom, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.features = ResDown(pretrain=pretrain)
self.rpn_model = UP(anchor_num=self.anchor_num, feature_in=256, feature_out=256)
self.mask_model = MaskCorr()
self.refine_model = Refine()
def refine(self, f, pos=None):
return self.refine_model(f, pos)
def template(self, template):
self.zf = self.features(template)
def track(self, search):
search = self.features(search)
rpn_pred_cls, rpn_pred_loc = self.rpn(self.zf, search)
return rpn_pred_cls, rpn_pred_loc
def track_mask(self, search):
self.feature, self.search = self.features.forward_all(search)
rpn_pred_cls, rpn_pred_loc = self.rpn(self.zf, self.search)
self.corr_feature = self.mask_model.mask.forward_corr(self.zf, self.search)
pred_mask = self.mask_model.mask.head(self.corr_feature)
return rpn_pred_cls, rpn_pred_loc, pred_mask
def track_refine(self, pos):
pred_mask = self.refine_model(self.feature, self.corr_feature, pos=pos)
return pred_mask
MaskCorr
MaskCorr 并未从 Mask 中受益,而是直接使用了 DepthCorr。
注意这里 Mask 分支输出通道数巨大。
def __init__(self, oSz=63):
super(MaskCorr, self).__init__()
self.oSz = oSz
self.mask = DepthCorr(256, 256, self.oSz**2)
def forward(self, z, x):
return self.mask(z, x)
DepthCorr
DepthCorr 运行需要两个输入。
def __init__(self, in_channels, hidden, out_channels, kernel_size=3):
super(DepthCorr, self).__init__()
# adjust layer for asymmetrical features
self.conv_kernel = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, hidden, kernel_size=kernel_size, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.conv_search = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, hidden, kernel_size=kernel_size, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(hidden, hidden, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(hidden, out_channels, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward_corr(self, kernel, input):
kernel = self.conv_kernel(kernel)
input = self.conv_search(input)
feature = conv2d_dw_group(input, kernel)
return feature
def forward(self, kernel, search):
feature = self.forward_corr(kernel, search)
out = self.head(feature)
return out
conv2d_dw_group
只在 DepthCorr 中调用,为什么不整合到函数中?conv2d_dw_group 中变换x和kernel的维度。
batch, channel = kernel.shape[:2]
x = x.view(1, batch*channel, x.size(2), x.size(3)) # 1 * (b*c) * k * k
kernel = kernel.view(batch*channel, 1, kernel.size(2), kernel.size(3)) # (b*c) * 1 * H * W
out = F.conv2d(x, kernel, groups=batch*channel)
out = out.view(batch, channel, out.size(2), out.size(3))
return out
Refine
掩模细化模块。
 论文图9. 使用堆叠细化模块生成掩模的示意图。
论文图9. 使用堆叠细化模块生成掩模的示意图。
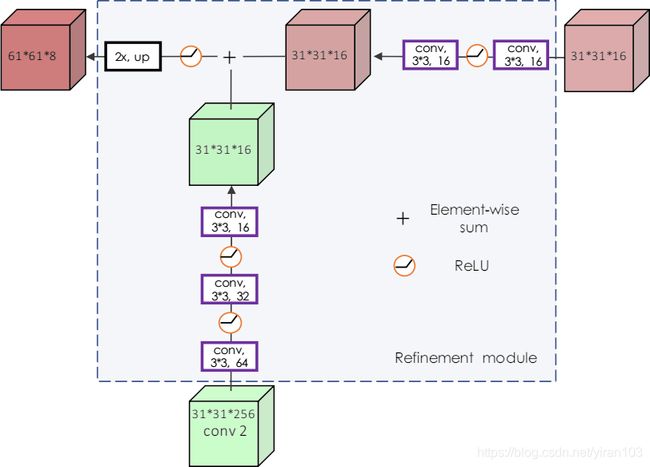
图7. 细化模块 U 3 U_3 U3 的示例。
self.v2、self.v1、self.v0为垂直分支(vertical),压缩通道;self.h2、self.h1、self.h0作用于水平分支(horizontal),消化融合结果。
模型实现与图中略有不同。
torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d 在由多个输入平面组成的输入图像上应用2D 转置卷积运算符。该模块可以看作 Conv2d 相对于其输入的梯度。它也被称为分数步长卷积或反卷积(尽管它不是实际的去卷积操作)。
def __init__(self):
"""
Mask refinement module
Please refer SiamMask (Appendix A)
https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05050
"""
super(Refine, self).__init__()
self.v0 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(64, 16, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(16, 4, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU())
self.v1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 16, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU())
self.v2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU())
self.h2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU())
self.h1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(16, 16, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(16, 16, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU())
self.h0 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(4, 4, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(4, 4, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU())
self.deconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 32, 15, 15)
self.post0 = nn.Conv2d(32, 16, 3, padding=1)
self.post1 = nn.Conv2d(16, 4, 3, padding=1)
self.post2 = nn.Conv2d(4, 1, 3, padding=1)
torch.nn.functional.pad 对于参数pad,要填充的维度数满足 ⌊ len(pad) 2 ⌋ \left\lfloor\frac{\text{len(pad)}}{2}\right\rfloor ⌊2len(pad)⌋ 并且填充维度设置从最后一个维度依次向前。例如,要填充输入张量的最后一个维度,则pad具有形式(padLeft, padRight);填充输入张量的最后2个维度使用(padLeft, padRight, padTop, padBottom);要填充最后3个维度,请使用(padLeft, padRight, padTop, padBottom, padFront, padBack)。
f为 ResNet 的特征图元组。
f[0]形状为[1, 64, 125, 125],
f[1]形状为[1, 256, 63, 63],
f[2]形状为[1, 512, 31, 31],
f[3]形状为[1, 1024, 31, 31]。
p0``p1``p2表示补0填充后,取出目标位置的特征图。
p3为相关特征图上的特征向量。
令人困惑的是p0、p1和p2中,目标特征块位于左上角而不是居中。
def forward(self, f, corr_feature, pos=None):
p0 = torch.nn.functional.pad(f[0], [16,16,16,16])[:, :, 4*pos[0]:4*pos[0]+61, 4*pos[1]:4*pos[1]+61]
p1 = torch.nn.functional.pad(f[1], [8,8,8,8])[:, :, 2*pos[0]:2*pos[0]+31, 2*pos[1]:2*pos[1]+31]
p2 = torch.nn.functional.pad(f[2], [4,4,4,4])[:, :, pos[0]:pos[0]+15, pos[1]:pos[1]+15]
p3 = corr_feature[:, :, pos[0], pos[1]].view(-1, 256, 1, 1)
out = self.deconv(p3)
out = self.post0(F.upsample(self.h2(out) + self.v2(p2), size=(31, 31)))
out = self.post1(F.upsample(self.h1(out) + self.v1(p1), size=(61, 61)))
out = self.post2(F.upsample(self.h0(out) + self.v0(p0), size=(127, 127)))
out = out.view(-1, 127*127)
return out
```## [ResDownS](https://github.com/foolwood/SiamMask/blob/master/experiments/siammask/custom.py#L17)
[ResDownS](https://github.com/foolwood/SiamMask/blob/master/experiments/siammask/custom.py#L17) 模块中,判断特征图尺寸,如果是 exemplar 则进行中心截取。
```python
def __init__(self, inplane, outplane):
super(ResDownS, self).__init__()
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inplane, outplane, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(outplane))
def forward(self, x):
x = self.downsample(x)
if x.size(3) < 20:
l, r = 4, -4
x = x[:, :, l:r, l:r]
return x
ResDown
ResDown 得到下采样之后的 resnet50 特征。
def __init__(self, pretrain=False):
super(ResDown, self).__init__()
self.features = resnet50(layer3=True, layer4=False)
if pretrain:
load_pretrain(self.features, 'resnet.model')
self.downsample = ResDownS(1024, 256)
def forward(self, x):
output = self.features(x)
p3 = self.downsample(output[-1])
return p3
def forward_all(self, x):
output = self.features(x)
p3 = self.downsample(output[-1])
return output, p3
get_dataset_zoo
检查data文件夹下的数据,文件夹命名需要与--dataset参数一致。
root = realpath(join(dirname(__file__), '../data'))
zoos = listdir(root)
def valid(x):
y = join(root, x)
if not isdir(y): return False
return exists(join(y, 'list.txt')) \
or exists(join(y, 'train', 'meta.json'))\
or exists(join(y, 'ImageSets', '2016', 'val.txt'))
zoos = list(filter(valid, zoos))
return zoos
总结
以上分析了 SiamMask 的大体结构。可以看出,数据增广、锚框管理以及损失函数的缺失导致无法组织训练。项目缺失的版图可以参照检测框架进行补充。这里,open-mmlab/mmdetection 比 facebookresearch/maskrcnn-benchmark 更为适宜。facebookresearch/maskrcnn-benchmark 虽然组织清晰,但仅有 Resize 和 RandomHorizontalFlip 变换。而 open-mmlab/mmdetection 的 ExtraAugmentation 提供:
- PhotoMetricDistortion
- Expand
- RandomCrop
并且,AnchorGenerator 支持设置锚点中心,与 SiamMask 兼容。
参考资料:
- 什么情况下应该设置 cudnn.benchmark = True?
- StrangerZhang/ pysot-toolkit
- noagarcia/visdom-tutorial
- fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
- Download jq
- Shell scripting: -z and -n options with if
- 7.3. Other Comparison Operators
- 4.12.3. Command Line Arguments
- Minimum-Area Rectangle Containing a Set of Points
- minimum-area-bounding-rectangle/python/min_bounding_rect.py
- minAreaRect()
- Finding minimum-area-rectangle for given points?
- How to resume interrupted download automatically in curl?
- What is an upright rectangle?
- What is numpy method int0?
