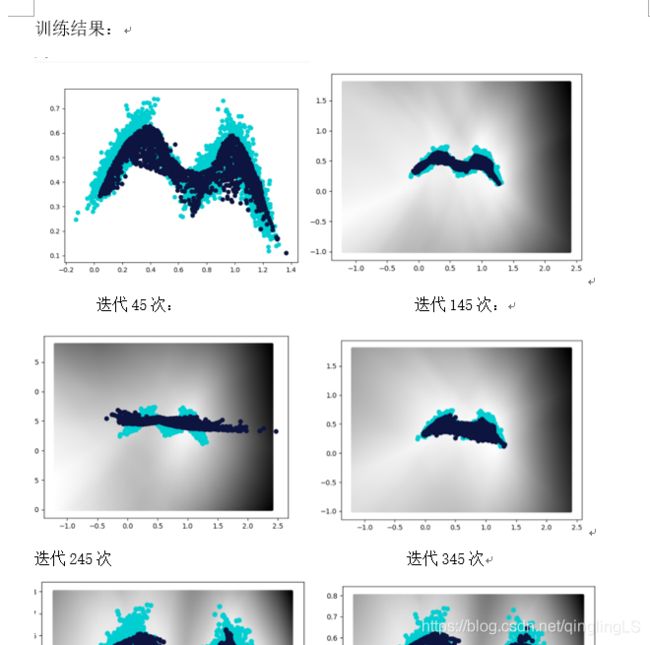
【模式识别与深度学习】用gan,wgan,wgan-gp来拟合指定形状的高斯分布:pytorch对抗网络
基于PyTorch实现生成对抗网络
拟合给定分布
要求可视化训练过程
实验报告
对比GAN、WGAN、WGAN-GP(稳定性、性能)
对比不同优化器的影响
注:代码需要一个叫points.mat的文件,point.mat里存储了原始图像,也就是上面兰色的M形状的图案。
需要跑的话在下面的网址进行下载:
https://download.csdn.net/download/qinglingls/11243079
实验报告:
https://download.csdn.net/download/qinglingls/11243082
代码:
gan.py
#coding=utf-8
import torch.autograd
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.utils import save_image
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np #二维数组
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib
from PIL import Image
import os
torch.cuda=True
batch_size=2048 #batch大小
num_epoch=10000 # 迭代次数
z_dimension=2 #噪声维度
matplotlib.use("TkAgg")
'''
载入训练数据
'''
data = sio.loadmat('points.mat');
xx_train=np.array(data['xx'])
plt.figure(1)
plt.scatter(xx_train[:,0],xx_train[:,1])
#plt.show()
'''
定义迭代的batch大小
'''
def iterate_minibatch(x, batch_size, shuffle=True):
indices = np.arange(x.shape[0])
if shuffle:
np.random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, x.shape[0], batch_size):
yield x[indices[i:i + batch_size], :]
'''
for x_batch in iterate_minibatch(xx_train, batch_size=batch_size):
print(x_batch.shape)
'''
#定义判别器 #####Discriminator######使用多层网络来作为判别器
#将图片28x28展开成784,然后通过多层感知器,中间经过斜率设置为0.2的LeakyReLU激活函数,
# 最后接sigmoid激活函数得到一个0到1之间的概率进行二分类。
class discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(discriminator,self).__init__()
self.dis=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2,50),#输入特征数为2,输出为10
#nn.ReLU(True), # relu激活
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),#进行非线性映射
nn.Linear(50,50),#进行一个线性映射
#nn.ReLU(True), # relu激活
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Linear(50,1),
#nn.Sigmoid()#也是一个激活函数,二分类问题中,
# sigmoid可以班实数映射到【0,1】,作为概率值,
# 多分类用softmax函数
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x=self.dis(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x
####### 定义生成器 Generator #####
#输入一个2维的0~1之间的高斯分布,然后通过第一层线性变换将其映射到10维,
# 然后通过LeakyReLU激活函数,接着进行一个线性变换,再经过一个LeakyReLU激活函数,
# 然后经过线性变换将其变成784维,最后经过Tanh激活函数是希望生成的假的图片数据分布
# 能够在-1~1之间。
class generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(generator,self).__init__()
self.gen=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2,50),#用线性变换将输入映射到10维
nn.ReLU(True),#relu激活
nn.Linear(50,2),#线性变换
#nn.ReLU(True),#relu激活
#nn.Linear(10,2),#线性变换
#nn.Tanh()#Tanh激活使得生成数据分布在【-1,1】之间
)
def forward(self, x):
x=self.gen(x)
return x
#创建对象
D=discriminator()
G=generator()
if torch.cuda:
D=D.cuda()
G=G.cuda()
#########判别器训练train#####################
#分为两部分:1、真的图像判别为真;2、假的图像判别为假
#此过程中,生成器参数不断更新
#首先需要定义loss的度量方式 (二分类的交叉熵)
#其次定义 优化函数,优化函数的学习率为0.0003
criterion = nn.BCELoss() #是单目标二分类交叉熵函数
#d_optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
#g_optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
#d_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
#g_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
g_optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(G.parameters(), lr=0.0005,alpha=0.9)
d_optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(D.parameters(), lr=0.0005,alpha=0.9)
iterator=0
###########################进入训练##判别器的判断过程#####################
for epoch in range(num_epoch): #进行多个epoch的训练
x = np.linspace(-1.2, 2.4, 200)
y = np.linspace(-1, 1.8, 200)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
m, n = X.shape
point = []
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
point.append([X[i][j], Y[i][j]])
point = np.array(point)
iterator=0
for x_batch in iterate_minibatch(xx_train, batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True):
iterator=iterator+1
#print(x_batch.shape)
#print(iterator)
# =============================训练判别器==================
x_batch=torch.from_numpy(x_batch).float()#batch_size个数据,每个数据二维
real_point = Variable(x_batch).cuda() # 将tensor变成Variable放入计算图中
real_label = Variable(torch.ones(batch_size)).cuda() # 定义真实的点点label为1
fake_label = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size)).cuda() # 定义假的点点的label为0
# 计算真实点点的损失
real_out = D(real_point) # 将真实点点放入判别器中
d_loss_real = criterion(real_out, real_label) # 得到点点图片的loss
#print("d_loss_real: %s",d_loss_real)
real_scores = real_out # 得到真实点点的判别值,输出的值越接近1越好
#print("real_scores: %s",real_scores)
# 计算假的图片的损失
z = Variable(torch.randn(batch_size, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
fake_point = G(z) # 随机噪声放入生成网络中,生成一个假的点点
fake_out = D(fake_point) # 判别器判断假的点点
d_loss_fake = criterion(fake_out, fake_label) # 得到假的点点的loss
#print("d_loss_fake: %s",d_loss_fake)
fake_scores = fake_out # 得到假点点的判别值,对于判别器来说,假点点的损失越接近0越好
#print("fake_scores: %s",fake_scores)
#损失函数和优化
d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake # 损失包括判真损失和判假损失
d_optimizer.zero_grad() # 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
d_loss.backward() # 将误差反向传播
d_optimizer.step() # 更新参数
# ==================训练生成器============================
################################生成网络的训练###############################
# 原理:目的是希望生成的假的图片被判别器判断为真的图片,
# 在此过程中,将判别器固定,将假的图片传入判别器的结果与真实的label对应,
# 反向传播更新的参数是生成网络里面的参数,
# 这样可以通过更新生成网络里面的参数,来训练网络,使得生成的图片让判别器以为是真的
# 这样就达到了对抗的目的
# 计算假的图片的损失
# generate noise z 生成噪声z
z_batch = Variable(torch.randn(batch_size, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
fake_point = G(z_batch) # 随机噪声输入到生成器中,得到一副假的点点
output = D(fake_point) # 经过判别器得到的结果
g_loss = criterion(output, real_label) # 得到的假的点点与真实的点点的label的loss
# bp and optimize
g_optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度归0
g_loss.backward() # 进行反向传播
g_optimizer.step() # .step()一般用在反向传播后面,用于更新生成网络的参数
# 打印中间的损失
print('Epoch[{}/{}],d_loss:{:.6f},g_loss:{:.6f} '
'D real: {:.6f},D fake: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, num_epoch, d_loss.data.item(), g_loss.data.item(),
real_scores.data.mean(), fake_scores.data.mean() # 打印的是真实点点的损失均值
))
fake_images = fake_point.cpu().data
point_data = point.astype(np.float32)
point_data = torch.from_numpy(point_data)
point_data = point_data.cuda()
decision = D(point_data)
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(point[:, 0], point[:, 1], c=decision.data.cpu().numpy()[:, 0], marker='.',cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(xx_train[:, 0], xx_train[:, 1], c='#00CED1')
plt.scatter(fake_images[:, 0], fake_images[:, 1], c='#0C143F')
print(fake_images.shape)
print(xx_train.shape)
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.01)
'''
if epoch == 0:
real_images = to_img(real_point.cpu().data)
save_image(real_images, './img/real_images.png')
fake_images = to_img(real_point.cpu().data)
save_image(fake_images, './img/fake_images-{}.png'.format(epoch + 1))
'''
# 保存模型
torch.save(G.state_dict(), './generator.pth')
torch.save(D.state_dict(), './discriminator.pth')
wgan
在gan的基础上进行修改:
- 去除sigmoid
- 不使用具有动量的优化方法,比如使用Adam,转而使用诸如RMSProp,SGD等方法,使用RMSProp,因为该方法可以处理梯度不稳定的情况。
- 需要对discriminator的权重做修整限制以确保lipschitz连续约束,代码示例如下
for p in netD.parameters():
p.data.clamp_(clamp_lower, clamp_upper)
这里的clamp_lower和clamp_upper是文章中的约束范围,这里的取值是经验参数,有人推荐使用-0.01和0.01 - 将BCEloss 改为非log的loss,按照文章的记载,通常会使用直接同1和-1做比较,代码示例如下
one=t.FloatTensor([1])
mone=-1*one
…
output=netd(input)
output.backward(one)
output2=netd(fake_pic)
output2.backward(mone)
wgan.py
#coding=utf-8
import torch.autograd
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.utils import save_image
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np #二维数组
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torchvision.utils import make_grid
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib
import os
torch.cuda=True
batch_size=2048 #batch大小
num_epoch=10000 # 迭代次数
z_dimension=2 #噪声维度
matplotlib.use("TkAgg")
'''
载入训练数据
'''
data = sio.loadmat('points.mat');
xx_train=np.array(data['xx'])
plt.figure(1)
plt.scatter(xx_train[:,0],xx_train[:,1])
#plt.show()
'''
定义迭代的batch大小
'''
def iterate_minibatch(x, batch_size, shuffle=True):
indices = np.arange(x.shape[0])
if shuffle:
np.random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, x.shape[0], batch_size):
yield x[indices[i:i + batch_size], :]
'''
for x_batch in iterate_minibatch(xx_train, batch_size=batch_size):
print(x_batch.shape)
'''
'''
生成噪声
'''
#定义判别器 #####Discriminator######使用多层网络来作为判别器
#将图片28x28展开成784,然后通过多层感知器,中间经过斜率设置为0.2的LeakyReLU激活函数,
# 最后接sigmoid激活函数得到一个0到1之间的概率进行二分类。
class discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(discriminator,self).__init__()
self.dis=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2,50),#输入特征数为2,输出为10
#nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),#进行非线性映射
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(50,50),#进行一个线性映射
#nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(50,1),
#nn.Sigmoid()#也是一个激活函数,二分类问题中,
# sigmoid可以班实数映射到【0,1】,作为概率值,
# 多分类用softmax函数
)
#self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x=self.dis(x)
# x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x
####### 定义生成器 Generator #####
#输入一个2维的0~1之间的高斯分布,然后通过第一层线性变换将其映射到10维,
# 然后通过LeakyReLU激活函数,接着进行一个线性变换,再经过一个LeakyReLU激活函数,
# 然后经过线性变换将其变成784维,最后经过Tanh激活函数是希望生成的假的图片数据分布
# 能够在-1~1之间。
class generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(generator,self).__init__()
self.gen=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2,50),#用线性变换将输入映射到10维
nn.ReLU(True),#relu激活
nn.Linear(50,2),#线性变换
#nn.ReLU(True),#relu激活
#nn.Linear(10,2),#线性变换
#nn.Tanh()#Tanh激活使得生成数据分布在【-1,1】之间
)
def forward(self, x):
x=self.gen(x)
return x
#创建对象
D=discriminator()
G=generator()
if torch.cuda:
D=D.cuda()
G=G.cuda()
#########判别器训练train#####################
#分为两部分:1、真的图像判别为真;2、假的图像判别为假
#此过程中,生成器参数不断更新
#首先需要定义loss的度量方式 (二分类的交叉熵)
#其次定义 优化函数,优化函数的学习率为0.0003
#criterion = nn.BCELoss() #是单目标二分类交叉熵函数
#d_optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
#g_optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
#d_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
#g_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
g_optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(G.parameters(), lr= 0.001,alpha=0.9)
d_optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(D.parameters(), lr= 0.001,alpha=0.9)
iterator=0
one=torch.FloatTensor(batch_size,1).zero_()+1
#print(one),print(one.shape)
minus_one=-1*one
#print(minus_one),print(minus_one.shape)
###########################进入训练##判别器的判断过程#####################
for epoch in range(num_epoch): #进行多个epoch的训练
# iterator=0
x = np.linspace(-1.2, 2.4, 200)
y = np.linspace(-1, 1.8, 200)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
m, n = X.shape
point = []
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
point.append([X[i][j], Y[i][j]])
point = np.array(point)
for x_batch in iterate_minibatch(xx_train, batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True):
iterator=iterator+1
#print(x_batch.shape)
#print(iterator)
# modification: clip param for discriminator
for parm in D.parameters():
parm.data.clamp_(-0.4, 0.4)
# 学到后面,如果不发生变化了,就把上面数改大一些。
# =============================训练判别器==================
D.zero_grad()
# train netd with real img
x_batch=torch.from_numpy(x_batch).float()#batch_size个数据,每个数据二维
real_point = Variable(x_batch).cuda() # 将tensor变成Variable放入计算图中
#real_label = Variable(torch.ones(batch_size)).cuda() # 定义真实的点点label为1
#fake_label = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size)).cuda() # 定义假的点点的label为0
## train netd with real img
# 计算真实点点的损失
real_out = D(real_point) # 将真实点点放入判别器中
real_out.backward(one.cuda())
#d_loss_real=real_out
#d_loss_real = criterion(real_out, real_label) # 得到点点图片的loss
#print("d_loss_real: %s",d_loss_real)
#real_scores = real_out # 得到真实点点的判别值,输出的值越接近1越好
#print("real_scores: %s",real_scores)
## train netd with fake img
# 计算假的图片的损失
## train netd with fake img
#z = Variable(torch.randn(batch_size, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
z_batch = Variable(torch.randn(batch_size, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
fake_point = G(z_batch).detach() # 随机噪声放入生成网络中,生成一个假的点点
fake_out = D(fake_point) # 判别器判断假的点点
fake_out.backward(minus_one.cuda())
#d_loss_fake=fake_out
#d_loss_fake = criterion(fake_out, fake_label) # 得到假的点点的loss
#print("d_loss_fake: %s",d_loss_fake)
#fake_scores = fake_out # 得到假点点的判别值,对于判别器来说,假点点的损失越接近0越好
#print("fake_scores: %s",fake_scores)
#损失函数和优化
#d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake # 损失包括判真损失和判假损失
#d_optimizer.zero_grad() # 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
#d_loss.backward() # 将误差反向传播
d_optimizer.step() # 更新参数
# ==================训练生成器============================
################################生成网络的训练###############################
# 原理:目的是希望生成的假的图片被判别器判断为真的图片,
# 在此过程中,将判别器固定,将假的图片传入判别器的结果与真实的label对应,
# 反向传播更新的参数是生成网络里面的参数,
# 这样可以通过更新生成网络里面的参数,来训练网络,使得生成的图片让判别器以为是真的
# 这样就达到了对抗的目的
# 计算假的图片的损失
# train netd more: because the better netd is,
# the better netg will be
if (iterator + 1) % 1 == 0:
# generate noise z 生成噪声z
G.zero_grad()
z_batch = Variable(torch.randn(batch_size, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
fake_point = G(z_batch) # 随机噪声输入到生成器中,得到一副假的点点
real_out = D(fake_point) # 经过判别器得到的结果
real_out.backward(one.cuda())
#g_loss = real_out
# g_loss = criterion(output, real_label) # 得到的假的点点与真实的点点的label的loss
# bp and optimize
#g_optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度归0
# g_loss.backward() # 进行反向传播
g_optimizer.step() # .step()一般用在反向传播后面,用于更新生成网络的参数
#fake_u=G(z_batch)
#points=make_grid(fake_u.data*0.5+0.5).cpu()#chw
#plt.imshow(points.permute(1, 2, 0).numpy()) # HWC
#plt.show()
print(epoch)
#print(num_epoch)
print(real_out.mean())
#print(d_loss.shape)
print(fake_out.mean())
#print(g_loss.shape)
#print(real_scores.mean())
#print(real_scores.shape)
#print(fake_scores.mean())
#print(fake_scores.shape)
# 打印中间的损失
#print('Epoch[{}/{}],d_loss:{:.6s},g_loss:{:.6s} '
# 'D real: {:.6s},D fake: {:.6s}'.format(
# epoch, num_epoch, d_loss.data.mean(), g_loss.data.mean(),
# real_scores.data, fake_scores.data.mean() # 打印的是真实点点的损失均值
# ))
fake_images = fake_point.cpu().data
point_data = point.astype(np.float32)
point_data = torch.from_numpy(point_data)
point_data = point_data.cuda()
decision = D(point_data)
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(point[:, 0], point[:, 1], c=decision.data.cpu().numpy()[:, 0], marker='.', cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(xx_train[:, 0], xx_train[:, 1], c='#00CED1')
plt.scatter(fake_images[:, 0], fake_images[:, 1], c='#0C143F')
#print(fake_images.shape)
#print(xx_train.shape)
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.01)
'''
if epoch == 0:
real_images = to_img(real_point.cpu().data)
save_image(real_images, './img/real_images.png')
fake_images = to_img(real_point.cpu().data)
save_image(fake_images, './img/fake_images-{}.png'.format(epoch + 1))
'''
# 保存模型
torch.save(G.state_dict(), './generator.pth')
torch.save(D.state_dict(), './discriminator.pth')
Wgan-gp
相对于WGAN的情况WGAN-GP主要是将原有的discriminator 的权重clipping修改为gradient penalty:

然后训练过程改一改,就成了。
wgan-gp
#coding=utf-8
import torch.autograd
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.utils import save_image
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np #二维数组
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.autograd as autograd
from torchvision.utils import make_grid
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib
import os
torch.cuda=True
BATCH_SIZE=2048 #batch大小
ITERS=10000 # 迭代次数
z_dimension=2 #噪声维度
LAMBDA = 10 # Gradient penalty lambda hyperparameter
matplotlib.use("TkAgg")
'''
载入训练数据
'''
data = sio.loadmat('points.mat');
xx_train=np.array(data['xx'])
plt.figure(1)
plt.scatter(xx_train[:,0],xx_train[:,1])
#plt.show()
'''
定义迭代的batch大小
'''
def iterate_minibatch(x, BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True):
indices = np.arange(x.shape[0])
if shuffle:
np.random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, x.shape[0], BATCH_SIZE):
yield x[indices[i:i + BATCH_SIZE], :]
'''
for x_batch in iterate_minibatch(xx_train, BATCH_SIZE=BATCH_SIZE):
print(x_batch.shape)
'''
def calc_gradient_penalty(netD, real_data, fake_data):
#print real_data.size()
alpha = torch.rand(BATCH_SIZE, 1)
alpha = alpha.expand(real_data.size())
alpha = alpha.cuda(0)
interpolates = alpha * real_data + ((1 - alpha) * fake_data)
interpolates = interpolates.cuda(0)
interpolates = autograd.Variable(interpolates, requires_grad=True)
disc_interpolates = netD(interpolates)
gradients = autograd.grad(outputs=disc_interpolates, inputs=interpolates,
grad_outputs=torch.ones(disc_interpolates.size()).cuda(0),
create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)[0]
gradient_penalty = ((gradients.norm(2, dim=1) - 1) ** 2).mean() * LAMBDA
return gradient_penalty
#定义判别器 #####Discriminator######使用多层网络来作为判别器
#将图片28x28展开成784,然后通过多层感知器,中间经过斜率设置为0.2的LeakyReLU激活函数,
# 最后接sigmoid激活函数得到一个0到1之间的概率进行二分类。
class discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(discriminator,self).__init__()
self.dis=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2,50),#输入特征数为2,输出为10
#nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),#进行非线性映射
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(50,50),#进行一个线性映射
#nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(50,1),
#nn.Sigmoid()#也是一个激活函数,二分类问题中,
# sigmoid可以班实数映射到【0,1】,作为概率值,
# 多分类用softmax函数
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x=self.dis(x)
# x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x
####### 定义生成器 Generator #####
#输入一个2维的0~1之间的高斯分布,然后通过第一层线性变换将其映射到10维,
# 然后通过LeakyReLU激活函数,接着进行一个线性变换,再经过一个LeakyReLU激活函数,
# 然后经过线性变换将其变成784维,最后经过Tanh激活函数是希望生成的假的图片数据分布
# 能够在-1~1之间。
class generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(generator,self).__init__()
self.gen=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2,50),#用线性变换将输入映射到10维
nn.ReLU(True),#relu激活
nn.Linear(50,2),#线性变换
#nn.ReLU(True),#relu激活
#nn.Linear(10,2),#线性变换
#nn.Tanh()#Tanh激活使得生成数据分布在【-1,1】之间
)
def forward(self, x):
x=self.gen(x)
return x
#创建对象
D=discriminator()
G=generator()
if torch.cuda:
D=D.cuda()
G=G.cuda()
#########判别器训练train#####################
#分为两部分:1、真的图像判别为真;2、假的图像判别为假
#此过程中,生成器参数不断更新
#首先需要定义loss的度量方式 (二分类的交叉熵)
#其次定义 优化函数,优化函数的学习率为0.0003
#criterion = nn.BCELoss() #是单目标二分类交叉熵函数
#d_optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
#g_optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(),lr=0.0001)
#d_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
#g_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
g_optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(G.parameters(), lr= 0.001,alpha=0.9)
d_optimizer = torch.optim.RMSprop(D.parameters(), lr= 0.002,alpha=0.9)
iterator=0
one=torch.FloatTensor(BATCH_SIZE,1).zero_()+1
#print(one),print(one.shape)
minus_one=-1*one
#print(minus_one),print(minus_one.shape)
###########################进入训练##判别器的判断过程#####################
for epoch in range(ITERS): #进行多个epoch的训练
# iterator=0
x = np.linspace(-1.2, 2.4, 200)
y = np.linspace(-1, 1.8, 200)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
m, n = X.shape
point = []
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
point.append([X[i][j], Y[i][j]])
point = np.array(point)
for p in D.parameters(): # reset requires_grad
p.requires_grad = True # they are set to False below in netG update
for x_batch in iterate_minibatch(xx_train, BATCH_SIZE=BATCH_SIZE,shuffle=True):
iterator=iterator+1
#print(x_batch.shape)
#print(iterator)
# modification: clip param for discriminator
#for parm in D.parameters():
# parm.data.clamp_(-0.4, 0.4)
# 学到后面,如果不发生变化了,就把上面数改大一些。
# =============================训练判别器==================
D.zero_grad()
# train netd with real img
x_batch=torch.from_numpy(x_batch).float()#BATCH_SIZE个数据,每个数据二维
real_point = Variable(x_batch).cuda() # 将tensor变成Variable放入计算图中
#real_label = Variable(torch.ones(BATCH_SIZE)).cuda() # 定义真实的点点label为1
#fake_label = Variable(torch.zeros(BATCH_SIZE)).cuda() # 定义假的点点的label为0
## train netd with real img
# 计算真实点点的损失
real_out = D(real_point) # 将真实点点放入判别器中
real_out=real_out.mean()
real_out.backward(minus_one.cuda())
#d_loss_real=real_out
#d_loss_real = criterion(real_out, real_label) # 得到点点图片的loss
#print("d_loss_real: %s",d_loss_real)
#real_scores = real_out # 得到真实点点的判别值,输出的值越接近1越好
#print("real_scores: %s",real_scores)
## train netd with fake img
# 计算假的图片的损失
## train netd with fake img
#z = Variable(torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
z_batch = Variable(torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
fake_point = autograd.Variable(G(z_batch).data) # 随机噪声放入生成网络中,生成一个假的点点
#fake_point = G(z_batch).detach() # 随机噪声放入生成网络中,生成一个假的点点
inputv = fake_point
fake_out = D(fake_point) # 判别器判断假的点点
fake_out =fake_out.mean() # 判别器判断假的点点
fake_out.backward(one.cuda())
# train with gradient penalty
gradient_penalty = calc_gradient_penalty(D, real_point.data, fake_point.data)
gradient_penalty.backward()
#d_loss_fake=fake_out
#d_loss_fake = criterion(fake_out, fake_label) # 得到假的点点的loss
#print("d_loss_fake: %s",d_loss_fake)
#fake_scores = fake_out # 得到假点点的判别值,对于判别器来说,假点点的损失越接近0越好
#print("fake_scores: %s",fake_scores)
#损失函数和优化
#d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake # 损失包括判真损失和判假损失
#d_optimizer.zero_grad() # 在反向传播之前,先将梯度归0
#d_loss.backward() # 将误差反向传播
D_cost = fake_out - real_out + gradient_penalty
Wasserstein_D = real_out - fake_out
d_optimizer.step() # 更新参数
# ==================训练生成器============================
################################生成网络的训练###############################
# 原理:目的是希望生成的假的图片被判别器判断为真的图片,
# 在此过程中,将判别器固定,将假的图片传入判别器的结果与真实的label对应,
# 反向传播更新的参数是生成网络里面的参数,
# 这样可以通过更新生成网络里面的参数,来训练网络,使得生成的图片让判别器以为是真的
# 这样就达到了对抗的目的
# 计算假的图片的损失
# train netd more: because the better netd is,
# the better netg will be
#if (iterator + 1) % 1 == 0:
for p in D.parameters():
p.requires_grad = False # to avoid computation
D.zero_grad()
G.zero_grad()
# generate noise z 生成噪声z
z_batch = Variable(torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, z_dimension)).cuda() # 随机生成一些噪声
fake_point = G(z_batch) # 随机噪声输入到生成器中,得到一副假的点点
Generator=D(fake_point)
Generator = Generator.mean()
Generator.backward(minus_one.cuda())
Generator_cost = -Generator
#real_out = D(fake_point) # 经过判别器得到的结果
#real_out.backward(one.cuda())
# g_loss = real_out
# g_loss = criterion(output, real_label) # 得到的假的点点与真实的点点的label的loss
# bp and optimize
# g_optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度归0
# g_loss.backward() # 进行反向传播
g_optimizer.step() # .step()一般用在反向传播后面,用于更新生成网络的参数
# Write logs and save samples
#lib.plot.plot('', D_cost.cpu().data.numpy())
#plot('', Generator_cost.cpu().data.numpy())
#lib.plot.plot('', Wasserstein_D.cpu().data.numpy())
print(Generator_cost)
print(D_cost)
print(Wasserstein_D)
#fake_u=G(z_batch)
#points=make_grid(fake_u.data*0.5+0.5).cpu()#chw
#plt.imshow(points.permute(1, 2, 0).numpy()) # HWC
#plt.show()
print(epoch)
#print(ITERS)
print(real_out.mean())
#print(d_loss.shape)
print(fake_out.mean())
#print(g_loss.shape)
#print(real_scores.mean())
#print(real_scores.shape)
#print(fake_scores.mean())
#print(fake_scores.shape)
# 打印中间的损失
#print('Epoch[{}/{}],d_loss:{:.6s},g_loss:{:.6s} '
# 'D real: {:.6s},D fake: {:.6s}'.format(
# epoch, ITERS, d_loss.data.mean(), g_loss.data.mean(),
# real_scores.data, fake_scores.data.mean() # 打印的是真实点点的损失均值
# ))
fake_images = fake_point.cpu().data
point_data = point.astype(np.float32)
point_data = torch.from_numpy(point_data)
point_data = point_data.cuda()
decision = D(point_data)
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(point[:, 0], point[:, 1], c=decision.data.cpu().numpy()[:, 0], marker='.', cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(xx_train[:, 0], xx_train[:, 1], c='#00CED1')
plt.scatter(fake_images[:, 0], fake_images[:, 1], c='#0C143F')
#print(fake_images.shape)
#print(xx_train.shape)
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.01)
'''
if epoch == 0:
real_images = to_img(real_point.cpu().data)
save_image(real_images, './img/real_images.png')
fake_images = to_img(real_point.cpu().data)
save_image(fake_images, './img/fake_images-{}.png'.format(epoch + 1))
'''
# 保存模型
torch.save(G.state_dict(), './generator.pth')
torch.save(D.state_dict(), './discriminator.pth')