Python计算机视觉——图像搜索
文章目录
- 第七章——图像搜索
-
- 一、前期准备知识
-
-
- 1.基于内容的图像检索
- 2.视觉单词
-
- 二、图像搜索
-
-
- 流程1
- 流程2
- 流程3
-
- 三、使用几何特性对结果排序
第七章——图像搜索
主要内容:利用文本挖掘技术对基于图像视觉内容进行图像搜索
本章提出利用视觉单词的基本思想,解释完整的安装细节,在一个实例数据集上进行测试。
一、前期准备知识
1.基于内容的图像检索
在大型的图像数据库上,CBIR(Content-Based Image Retrieval,基于内容的图像检索)技术用于检索在视觉上具相似性的图像。返回的图像可以是颜色相似、纹理相似、图像中的物体或场景相似。
但在数据库很大的情况下,这样的查询方案会耗费过多的时间,因此引入文本挖掘技术到CBIR中处理问题,使得能够在数百万图像中搜索具有相似性内容的图像。
矢量空间模型是一个用于表示和搜索文本文档的模型。
2.视觉单词
视觉单词的定义在本章会经常用到,对于理解下文来说比较关键,因此在此重点讲解一下。
什么是视觉单词:
是图像中的基本单元,它基于子块提取、基于特征点提取和基于对象提取。视觉单词的生成基于图像视觉特征进行(基于子块的视觉单词提取也最终落实到视觉特征上)
如何得到视觉单词:
假定有N个图像,从每幅图像中检测得到一系列特征(如SIFT特征),可将这些SIFT特征看成图像中的单词。然后我们找到一些方法来寻找这些单词的代表(一般采用聚类算法),这些代表就构成了从N幅图像中提取的视觉单词。
如何使用视觉单词来表达图像:
每幅图像可以用一个无序的“视觉词袋”或称为“视觉单词表”来进行表达。
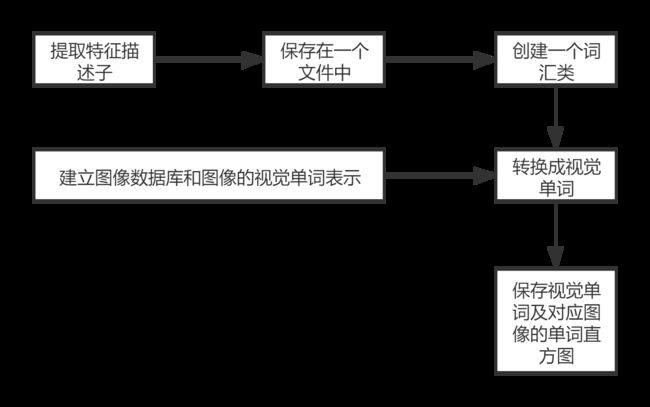
二、图像搜索
流程1
- 提取特征描述子
本章采用的是SIFT特征描述子,运行下面的代码,得到每幅图像提取出的描述子,并将每幅图像的描述子保存在一个文件中。
import sift
from imtools import get_imlist
imlist = get_imlist('picsa')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
featlist = [ imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
for i in range(nbr_images):
sift.process_image(imlist[i],featlist[i])
- 创建一个词汇类
创建名为vocabulary.py的文件,该代码创建一个词汇类,以及在训练图像数据集上训练出一个词汇的方法。
from numpy import *
from scipy.cluster.vq import *
import sift
class Vocabulary(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
self.voc = []
self.idf = []
self.trainingdata = []
self.nbr_words = 0
def train(self,featurefiles,k=100,subsampling=10):
""" Train a vocabulary from features in files listed
in featurefiles using k-means with k number of words.
Subsampling of training data can be used for speedup. """
nbr_images = len(featurefiles)
# read the features from file
descr = []
descr.append(sift.read_features_from_file(featurefiles[0])[1])
descriptors = descr[0] #stack all features for k-means
for i in arange(1,nbr_images):
descr.append(sift.read_features_from_file(featurefiles[i])[1])
descriptors = vstack((descriptors,descr[i]))
# k-means: last number determines number of runs
self.voc,distortion = kmeans(descriptors[::subsampling,:],k,1)
self.nbr_words = self.voc.shape[0]
# go through all training images and project on vocabulary
imwords = zeros((nbr_images,self.nbr_words))
for i in range( nbr_images ):
imwords[i] = self.project(descr[i])
nbr_occurences = sum( (imwords > 0)*1 ,axis=0)
self.idf = log( (1.0*nbr_images) / (1.0*nbr_occurences+1) )
self.trainingdata = featurefiles
def project(self,descriptors):
""" Project descriptors on the vocabulary
to create a histogram of words. """
# histogram of image words
imhist = zeros((self.nbr_words))
words,distance = vq(descriptors,self.voc)
for w in words:
imhist[w] += 1
return imhist
def get_words(self,descriptors):
""" Convert descriptors to words. """
return vq(descriptors,self.voc)[0]
- 保存视觉单词
import pickle
import vocabulary
imlist = get_imlist('picsa')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
featlist = [ imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images) ]
#生成词汇
voc = vocabulary.Vocabulary('ukbenchtest')
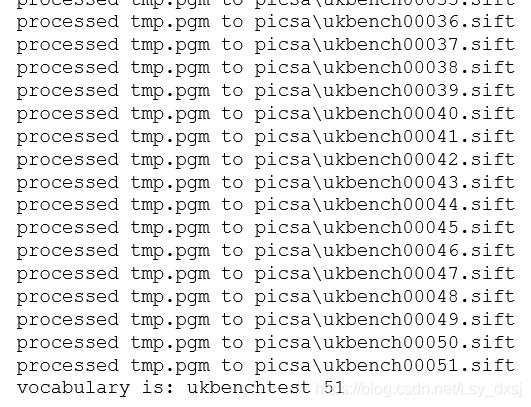
voc.train(featlist, 51, 4)
#保存词汇
with open('vocabulary.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(voc, f)
print('vocabulary is:', voc.name, voc.nbr_words)
流程2
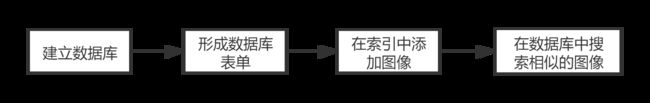
- 建立数据库
这里,我们使用的是SQLite作为数据库。
在开始之前,我们需要创建表、索引和索引器Indexer类,以便将图像数据写入数据库。
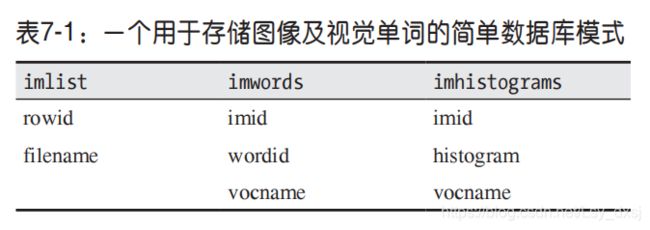
我们仅需一个包含三个表单的简单数据库模式。表单imlist包含所有要索引的图像文件名;imwords包含了一个那些单词的单词索引、用到了哪个词汇、以及单词出现在哪些图像中;imhistograms包含了全部每幅图像的单词直方图。
如下表所示:
创建名为imagesearch.py的文件,添加下面的代码:
class Indexer(object):
def __init__(self,db,voc):
""" Initialize with the name of the database
and a vocabulary object. """
self.con = sqlite.connect(db)
self.voc = voc
def __del__(self):
self.con.close()
def db_commit(self):
self.con.commit()
def create_tables(self):
""" Create the database tables. """
self.con.execute('create table imlist(filename)')
self.con.execute('create table imwords(imid,wordid,vocname)')
self.con.execute('create table imhistograms(imid,histogram,vocname)')
self.con.execute('create index im_idx on imlist(filename)')
self.con.execute('create index wordid_idx on imwords(wordid)')
self.con.execute('create index imid_idx on imwords(imid)')
self.con.execute('create index imidhist_idx on imhistograms(imid)')
self.db_commit()
- 添加图像
有了数据库表单,我们便可以在索引中添加图像。
在Indexer类中添加add_to_index()方法,将此方法添加到imagesearch.py中
def add_to_index(self,imname,descr):
""" Take an image with feature descriptors,
project on vocabulary and add to database. """
if self.is_indexed(imname): return
print('indexing', imname)
# get the imid
imid = self.get_id(imname)
# get the words
imwords = self.voc.project(descr)
nbr_words = imwords.shape[0]
# link each word to image
for i in range(nbr_words):
word = imwords[i]
# wordid is the word number itself
self.con.execute("insert into imwords(imid,wordid,vocname) values (?,?,?)", (imid,word,self.voc.name))
# store word histogram for image
# use pickle to encode NumPy arrays as strings
self.con.execute("insert into imhistograms(imid,histogram,vocname) values (?,?,?)", (imid,pickle.dumps(imwords),self.voc.name))
再使用两个辅助函数::is_indxed() 用来检查图像是否已经被索引,get_id() 则对一幅图像
文件名给定 id 号。将下面的代码添加进imagesearch.py
def get_id(self,imname):
""" Get an entry id and add if not present. """
cur = self.con.execute(
"select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname)
res=cur.fetchone()
if res==None:
cur = self.con.execute(
"insert into imlist(filename) values ('%s')" % imname)
return cur.lastrowid
else:
return res[0]
def is_indexed(self,imname):
""" Returns True if imname has been indexed. """
im = self.con.execute("select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname).fetchone()
return im != None
下面的示例代码会遍历整个 ukbench 数据库中的样本图像,并将其加入我们的索引,这里,假设列表 imlist 和 featlist 分别包含之前图像文件名及图像描述子,vocabulary.pkl 包含已经训练好的词汇
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
import imagesearch
import sift
from sqlite3 import dbapi2 as sqlite
from imtools import get_imlist
#获取图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('picsa')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
# load vocabulary
#载入词汇
with open('picsa.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)
#创建索引
indx = imagesearch.Indexer('testImaAdd.db',voc)
indx.create_tables()
# go through all images, project features on vocabulary and insert
#遍历所有的图像,并将它们的特征投影到词汇上
for i in range(nbr_images)[:500]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
indx.add_to_index(imlist[i],descr)
# commit to database
#提交到数据库
indx.db_commit()
con = sqlite.connect('testImaAdd.db')
print(con.execute('select count (filename) from imlist').fetchone())
print(con.execute('select * from imlist').fetchone())
运行结果如下:

如果在最后一行用 fetchall() 来代替 fetchone(),会得到一个包含所有文件名的
长列表

- 在数据库中搜索图像
建立好图像的索引,我们就可以在数据库中搜索相似的图像了。这里用的是BoW(词袋模型)来表示整个图像。
从一个(很大的训练图像)集提取特征描述子,利用一些聚类算法可以构建出视觉单词,它只是在给定特征描述子空间中的一组向量集,在采用K-means进行聚类时得到的视觉单词是聚类质心。用视觉单词直方图来表示图像,则该模型便称为BOW模型。
为实现搜索,我们在imagesearch.py中添加Searcher类
class Searcher(object):
def __init__(self,db,voc):
""" Initialize with the name of the database. """
self.con = sqlite.connect(db)
self.voc = voc
def __del__(self):
self.con.close()
一个图像的数据库很大,逐一比较整个数据库中的所有直方图往往是不行的,我们需要找到一个大小合理的候选集,单词索引的作用便在于此:我们可以利用单词索引获得候选集,然后只需在候选集上进行逐一比较。
流程3
- 获得候选图像
利用建立起来的索引找到包含特定单词的所有图像。在Searcher类中加入 candidates_from_word() 方法,给出包含特定单词的所有图像 id 号
def candidates_from_word(self,imword):
""" Get list of images containing imword. """
im_ids = self.con.execute(
"select distinct imid from imwords where wordid=%d" % imword).fetchall()
return [i[0] for i in im_ids]
在Searcher类中加入candidates_from_histogram方法,获得包含多个单词的候选图像,对每一个图像id 出现的次数进行跟踪,显示有多少单词与单词直方图中的单词匹配
def candidates_from_histogram(self,imwords):
""" Get list of images with similar words. """
# get the word ids
words = imwords.nonzero()[0]
# find candidates
candidates = []
for word in words:
c = self.candidates_from_word(word)
candidates+=c
# take all unique words and reverse sort on occurrence
tmp = [(w,candidates.count(w)) for w in set(candidates)]
tmp.sort(cmp=lambda x,y:cmp(x[1],y[1]))
tmp.reverse()
# return sorted list, best matches first
return [w[0] for w in tmp]
最后结果返回一个包含图像 id 的列表,排在列表最前面的是最好的匹配图像
比如,下例打印了从索引中查找出的前 10 个图像 id
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import imagesearch
import operator
src = imagesearch.Searcher('test.db', voc)
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[0])
iw = voc.project(descr)
print('ask using a histogram...')
print(src.candidates_from_histogram(iw)[:10])
- 用一幅图像进行查询
利用一幅图像进行查询时,没有必要进行完全的搜索,可直接比较单词直方图。
将下面的方法添加到 Searcher 类中
def get_imhistogram(self,imname):
""" Return the word histogram for an image. """
im_id = self.con.execute(
"select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname).fetchone()
s = self.con.execute(
"select histogram from imhistograms where rowid='%d'" % im_id).fetchone()
# use pickle to decode NumPy arrays from string
return pickle.loads(s[0])
合并查询方法:
def query(self, imname):
""" 查找所有与 imname 匹配的图像列表 . """
h = self.get_imhistogram(imname)
candidates = self.candidates_from_histogram(h)
matchscores = []
for imid in candidates:
# 获取名字
cand_name = self.con.execute(
"select filename from imlist where rowid=%d" % imid).fetchone()
cand_h = self.get_imhistogram(cand_name)
cand_dist = sqrt(sum(self.voc.idf * (h - cand_h) ** 2))
matchscores.append((cand_dist, imid))
# 返回排序后的距离及对应数据库 ids 列表
matchscores.sort()
return matchscores
query() 方法获取图像的文件名,对上一例子的图像进行查询,会再次打印前 10 个结果,包括候选图像与查询图像间的距离。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
src = imagesearch.Searcher('test.db', voc)
print('try a query...')
print(src.query(imlist[0])[:10])
运行结果如图:
![]()
这次结果比前面打印出来的 10 个结果要好很多。距离为 0 的图像对应查询图像本身。
- 确定对比基准并绘制结果
为评价搜索结果的好坏,可计算出前4个位置中搜索到相似图像数。
这里给出了计算分数的函数,将它添加到 imagesearch.py 中,你就可以开始优化查询了
def compute_ukbench_score(src,imlist):
""" Returns the average number of correct
images on the top four results of queries. """
nbr_images = len(imlist)
pos = zeros((nbr_images,4))
# get first four results for each image
for i in range(nbr_images):
pos[i] = [w[1]-1 for w in src.query(imlist[i])[:4]]
# compute score and return average
score = array([ (pos[i]//4)==(i//4) for i in range(nbr_images)])*1.0
return sum(score) / (nbr_images)
# import PIL and pylab for plotting
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
下面是用于显示实际搜索结果的函数,添加该函数到 imagesearch.py 中
def plot_results(src,res):
""" Show images in result list 'res'. """
figure()
nbr_results = len(res)
for i in range(nbr_results):
imname = src.get_filename(res[i])
subplot(1,nbr_results,i+1)
imshow(array(Image.open(imname)))
axis('off')
show()
例如,
nbr_results = 6
res = [w[1] for w in src.query(imlist[0])[:nbr_results]]
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res)
运行结果如图:

左一为拿出的一幅图,右方五幅图为查询到的与左一相似的图,左二最为相似。
三、使用几何特性对结果排序
利用一些考虑到特征几何关系的准则重排搜索到的靠前结果,可以提高准确率。最常用的方法是在查询图像与靠前图像的特征位置间拟合单应性。
下面是一个载入所有模型文件并用单应性对靠前的图像进行重排的完整例子:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
import sift
import imagesearch
import homography
from imtools import get_imlist
from sqlite3 import dbapi2 as sqlite
# load image list and vocabulary
#载入图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('picsa')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#载入特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
#载入词汇
with open('vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)
src = imagesearch.Searcher('testImaAdd.db',voc)
# index of query image and number of results to return
#查询图像索引和查询返回的图像数
q_ind = 16
nbr_results = 10
# regular query
# 常规查询(按欧式距离对结果排序)
res_reg = [w[1] for w in src.query(imlist[q_ind])[:nbr_results]]
print('top matches (regular):', res_reg)
# load image features for query image
#载入查询图像特征
q_locs,q_descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[q_ind])
fp = homography.make_homog(q_locs[:,:2].T)
# RANSAC model for homography fitting
#用单应性进行拟合建立RANSAC模型
model = homography.RansacModel()
rank = {}
# load image features for result
#载入候选图像的特征
for ndx in res_reg[1:]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[ndx]) # because 'ndx' is a rowid of the DB that starts at 1
# get matches
matches = sift.match(q_descr,descr)
ind = matches.nonzero()[0]
ind2 = matches[ind]
tp = homography.make_homog(locs[:,:2].T)
# compute homography, count inliers. if not enough matches return empty list
try:
H,inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp[:,ind],tp[:,ind2],model,match_theshold=4)
except:
inliers = []
# store inlier count
rank[ndx] = len(inliers)
# sort dictionary to get the most inliers first
sorted_rank = sorted(rank.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True)
res_geom = [res_reg[0]]+[s[0] for s in sorted_rank]
print ('top matches (homography):', res_geom)
# 显示查询结果
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_reg[:8]) #常规查询
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_geom[:8]) #重排后的结果