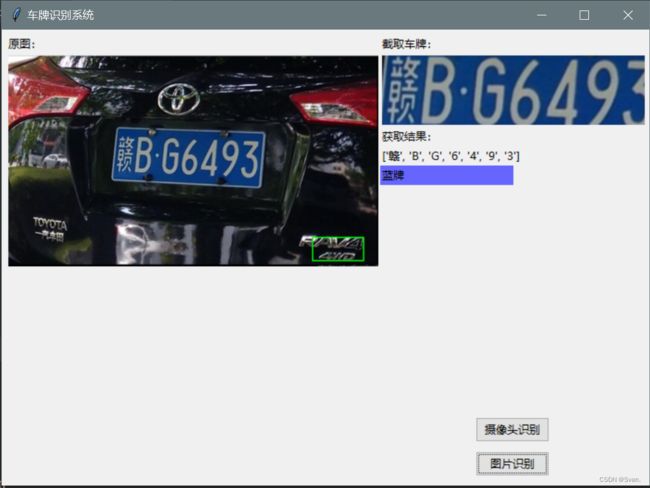
基于opencv的车牌识别系统(UI界面采用tkinter设计)
基于opencv的车牌识别系统(UI界面采用tkinter设计)
本系统采用python语言搭配opencv进行开发,在传统的车牌识别项目上进行改进,开发独特的GUI界面,方便使用者的使用。
需要源码的朋友点赞、关注我、再私信我获取源码,如果未能及时回复可以留下邮箱耐心等待奥
项目结构
项目结构很简单主要由以下三种文件构成:
- predict.py
- surface.py
- svmchinese.dat(用于存放训练好的模型)
其余文件还包括用于训练和测试的图片数据集,这里就不一一列举了
项目实现的流程
利用tkinter设计UI界面包括主窗口、按钮(button)、摄像头界面,识别结果的可视化等控件。
class Surface(ttk.Frame):
pic_path = ""
viewhigh = 400 #摄像头
viewwide = 400
update_time = 0
thread = None
thread_run = False
camera = None
color_transform = {"green":("绿牌","#55FF55"), "yello":("黄牌","#FFFF00"), "blue":("蓝牌","#6666FF")}
def __init__(self, win):
ttk.Frame.__init__(self, win)
frame_left = ttk.Frame(self)
frame_right1 = ttk.Frame(self)
frame_right2 = ttk.Frame(self)
win.title("车牌识别系统")
win.geometry('700x500')
self.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=tk.YES, padx="5", pady="5")
frame_left.pack(side=LEFT,expand=1,fill=BOTH)
frame_right1.pack(side=TOP,expand=1,fill=tk.Y)
frame_right2.pack(side=RIGHT,expand=0.5)
ttk.Label(frame_left, text='原图:').pack(anchor="nw")
ttk.Label(frame_right1, text='截取车牌:').grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=tk.W)
from_pic_ctl = ttk.Button(frame_right2, text="图片识别", width=10, command=self.from_pic)
from_vedio_ctl = ttk.Button(frame_right2, text="摄像头识别", width=10, command=self.from_vedio)
self.image_ctl = ttk.Label(frame_left)
self.image_ctl.pack(anchor="nw")
self.roi_ctl = ttk.Label(frame_right1)
self.roi_ctl.grid(column=0, row=1, sticky=tk.W)
ttk.Label(frame_right1, text='获取结果:').grid(column=0, row=2, sticky=tk.W)
self.r_ctl = ttk.Label(frame_right1, text="")
self.r_ctl.grid(column=0, row=3, sticky=tk.W)
self.color_ctl = ttk.Label(frame_right1, text="", width="20")
self.color_ctl.grid(column=0, row=4, sticky=tk.W)
from_vedio_ctl.pack(anchor="se", pady="5")
from_pic_ctl.pack(anchor="se", pady="5")
self.predictor = predict.CardPredictor()
self.predictor.train_svm()
打开识别图片的按钮点击事件的设计
def get_imgtk(self, img_bgr):
img = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
im = Image.fromarray(img)
imgtk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=im)
wide = imgtk.width()
high = imgtk.height()
if wide > self.viewwide or high > self.viewhigh:
wide_factor = self.viewwide / wide
high_factor = self.viewhigh / high
factor = min(wide_factor, high_factor)
wide = int(wide * factor)
if wide <= 0 : wide = 1
high = int(high * factor)
if high <= 0 : high = 1
im=im.resize((wide, high), Image.ANTIALIAS)
imgtk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=im)
return imgtk
打开摄像头识别按钮点击事件的设计
def from_vedio(self):
if self.thread_run:
return
if self.camera is None:
self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not self.camera.isOpened():
mBox.showwarning('警告', '摄像头打开失败!')
self.camera = None
return
self.thread = threading.Thread(target=self.vedio_thread, args=(self,))
self.thread.setDaemon(True)
self.thread.start()
self.thread_run = True
打开摄像头或者图片识别,按识别的方式采用不同方法对捕捉到的画面结果进行识别:
def from_pic(self):
self.thread_run = False
self.pic_path = askopenfilename(title="选择识别图片", filetypes=[("jpg图片", "*.jpg")])
if self.pic_path:
img_bgr = predict.imreadex(self.pic_path)
self.imgtk = self.get_imgtk(img_bgr)
self.image_ctl.configure(image=self.imgtk)
resize_rates = (1, 0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.4)
for resize_rate in resize_rates:
print("resize_rate:", resize_rate)
r, roi, color = self.predictor.predict(img_bgr, resize_rate)
if r:
break
self.show_roi(r, roi, color)
@staticmethod
def vedio_thread(self):
self.thread_run = True
predict_time = time.time()
while self.thread_run:
_, img_bgr = self.camera.read()
self.imgtk = self.get_imgtk(img_bgr)
self.image_ctl.configure(image=self.imgtk)
if time.time() - predict_time > 2:
r, roi, color = self.predictor.predict(img_bgr)
self.show_roi(r, roi, color)
predict_time = time.time()
print("run end")
最后设计关闭窗口的事件:
def close_window():
print("destroy")
if surface.thread_run :
surface.thread_run = False
surface.thread.join(2.0)
win.destroy()
预测模型的设计
预测模型设计思路为:
1、训练设计所需图片数据的尺寸,并读取图片数据;
2、根据设定的阈值和图片直方图,找出波峰,用于分隔字符;
3、根据找出的波峰,分隔图片,从而得到逐个字符图片;
4、将来自opencv的sample,用于svm训练;
5、训练svm、字符识别;
6、高斯去噪、去掉图像中不会是车牌的区域、找到图像边缘、使用开运算和闭运算让图像边缘成为一个整体;
7、查找图像边缘整体形成的矩形区域,可能有很多,车牌就在其中一个矩形区域中、矩形区域可能是倾斜的矩形,需要矫正,以便使用颜色定位、识别到的字符、定位的车牌图像、车牌颜色;
class CardPredictor:
def __init__(self):
#车牌识别的部分参数保存在js中,便于根据图片分辨率做调整
f = open('config.js')
j = json.load(f) #读取文件
for c in j["config"]:
if c["open"]:
self.cfg = c.copy()
break
else:
raise RuntimeError('没有设置有效配置参数')
def __del__(self):
self.save_traindata()
def train_svm(self):
self.model = SVM(C=1, gamma=0.5) #识别英文字母和数字,c表示容忍度,c越高,说明越不能容忍出现误差
self.modelchinese = SVM(C=1, gamma=0.5) #识别中文
if os.path.exists("svm.dat"):
self.model.load("svm.dat")
else:
chars_train = []
chars_label = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk("train\\chars2"):
if len(os.path.basename(root)) > 1:
continue
root_int = ord(os.path.basename(root))
for filename in files:
filepath = os.path.join(root,filename)
digit_img = cv2.imread(filepath)
digit_img = cv2.cvtColor(digit_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
chars_train.append(digit_img)
chars_label.append(root_int)
chars_train = list(map(deskew, chars_train))
chars_train = preprocess_hog(chars_train)
#chars_train = chars_train.reshape(-1, 20, 20).astype(np.float32)
chars_label = np.array(chars_label)
self.model.train(chars_train, chars_label)
if os.path.exists("svmchinese.dat"):
self.modelchinese.load("svmchinese.dat")
else:
chars_train = []
chars_label = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk("train\\charsChinese"):
if not os.path.basename(root).startswith("zh_"):
continue
pinyin = os.path.basename(root)
index = provinces.index(pinyin) + PROVINCE_START + 1 #1是拼音对应的汉字
for filename in files:
filepath = os.path.join(root,filename)
digit_img = cv2.imread(filepath)
digit_img = cv2.cvtColor(digit_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
chars_train.append(digit_img)
#chars_label.append(1)
chars_label.append(index)
chars_train = list(map(deskew, chars_train))
chars_train = preprocess_hog(chars_train)
#chars_train = chars_train.reshape(-1, 20, 20).astype(np.float32)
chars_label = np.array(chars_label)
print(chars_train.shape)
self.modelchinese.train(chars_train, chars_label)
def save_traindata(self):
if not os.path.exists("svm.dat"):
self.model.save("svm.dat")
if not os.path.exists("svmchinese.dat"):
self.modelchinese.save("svmchinese.dat")
def accurate_place(self, card_img_hsv, limit1, limit2, color):
row_num, col_num = card_img_hsv.shape[:2]
xl = col_num
xr = 0
yh = 0
yl = row_num
#col_num_limit = self.cfg["col_num_limit"]
row_num_limit = self.cfg["row_num_limit"]
col_num_limit = col_num * 0.8 if color != "green" else col_num * 0.5#绿色有渐变
for i in range(row_num):
count = 0
for j in range(col_num):
H = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 0)
S = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 1)
V = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 2)
if limit1 < H <= limit2 and 34 < S and 46 < V:
count += 1
if count > col_num_limit:
if yl > i:
yl = i
if yh < i:
yh = i
for j in range(col_num):
count = 0
for i in range(row_num):
H = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 0)
S = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 1)
V = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 2)
if limit1 < H <= limit2 and 34 < S and 46 < V:
count += 1
if count > row_num - row_num_limit:
if xl > j:
xl = j
if xr < j:
xr = j
return xl, xr, yh, yl
def predict(self, car_pic, resize_rate=1):
if type(car_pic) == type(""):
img = imreadex(car_pic)
else:
img = car_pic
pic_hight, pic_width = img.shape[:2]
if pic_width > MAX_WIDTH:
pic_rate = MAX_WIDTH / pic_width
img = cv2.resize(img, (MAX_WIDTH, int(pic_hight*pic_rate)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
if resize_rate != 1:
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(pic_width*resize_rate), int(pic_hight*resize_rate)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
pic_hight, pic_width = img.shape[:2]
print("h,w:", pic_hight, pic_width)
blur = self.cfg["blur"]
#高斯去噪
if blur > 0:
img = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (blur, blur), 0)#图片分辨率调整
oldimg = img
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#equ = cv2.equalizeHist(img)
#img = np.hstack((img, equ))
#去掉图像中不会是车牌的区域
kernel = np.ones((20, 20), np.uint8)
img_opening = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
img_opening = cv2.addWeighted(img, 1, img_opening, -1, 0);
#找到图像边缘
ret, img_thresh = cv2.threshold(img_opening, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
img_edge = cv2.Canny(img_thresh, 100, 200)
#使用开运算和闭运算让图像边缘成为一个整体
kernel = np.ones((self.cfg["morphologyr"], self.cfg["morphologyc"]), np.uint8)
img_edge1 = cv2.morphologyEx(img_edge, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
img_edge2 = cv2.morphologyEx(img_edge1, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
#查找图像边缘整体形成的矩形区域,可能有很多,车牌就在其中一个矩形区域中
try:
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img_edge2, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
except ValueError:
image, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img_edge2, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours = [cnt for cnt in contours if cv2.contourArea(cnt) > Min_Area]
print('len(contours)', len(contours))
#一一排除不是车牌的矩形区域
car_contours = []
for cnt in contours:
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
area_width, area_height = rect[1]
if area_width < area_height:
area_width, area_height = area_height, area_width
wh_ratio = area_width / area_height
#print(wh_ratio)
#要求矩形区域长宽比在2到5.5之间,2到5.5是车牌的长宽比,其余的矩形排除
if wh_ratio > 2 and wh_ratio < 5.5:
car_contours.append(rect)
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
#oldimg = cv2.drawContours(oldimg, [box], 0, (0, 0, 255), 2)
#cv2.imshow("edge4", oldimg)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
print(len(car_contours))
print("精确定位")
card_imgs = []
#矩形区域可能是倾斜的矩形,需要矫正,以便使用颜色定位
for rect in car_contours:
if rect[2] > -1 and rect[2] < 1:#创造角度,使得左、高、右、低拿到正确的值
angle = 1
else:
angle = rect[2]
rect = (rect[0], (rect[1][0]+5, rect[1][1]+5), angle)#扩大范围,避免车牌边缘被排除
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
heigth_point = right_point = [0, 0]
left_point = low_point = [pic_width, pic_hight]
for point in box:
if left_point[0] > point[0]:
left_point = point
if low_point[1] > point[1]:
low_point = point
if heigth_point[1] < point[1]:
heigth_point = point
if right_point[0] < point[0]:
right_point = point
if left_point[1] <= right_point[1]:#正角度
new_right_point = [right_point[0], heigth_point[1]]
pts2 = np.float32([left_point, heigth_point, new_right_point])#字符只是高度需要改变
pts1 = np.float32([left_point, heigth_point, right_point])
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1, pts2)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(oldimg, M, (pic_width, pic_hight))
point_limit(new_right_point)
point_limit(heigth_point)
point_limit(left_point)
card_img = dst[int(left_point[1]):int(heigth_point[1]), int(left_point[0]):int(new_right_point[0])]
card_imgs.append(card_img)
#cv2.imshow("card", card_img)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
elif left_point[1] > right_point[1]:#负角度
new_left_point = [left_point[0], heigth_point[1]]
pts2 = np.float32([new_left_point, heigth_point, right_point])#字符只是高度需要改变
pts1 = np.float32([left_point, heigth_point, right_point])
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1, pts2)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(oldimg, M, (pic_width, pic_hight))
point_limit(right_point)
point_limit(heigth_point)
point_limit(new_left_point)
card_img = dst[int(right_point[1]):int(heigth_point[1]), int(new_left_point[0]):int(right_point[0])]
card_imgs.append(card_img)
#cv2.imshow("card", card_img)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
创作不易,走过路过不要错过,点个赞再走吧,需要源码的朋友可以点赞关注我,再私信我获取源码!!!!