卷积核的grad为none_pytorch入门与实践(1):张量的基本操作和自动微分requires_grad=True...
PyTorch是一个基于Python的库,提供了一个具有灵活易用的深度学习框架,是近年来最受欢迎的深度学习框架之一。
如果你是新新新手,可以先学习以下教程: 深度学习之PyTorch实战-基础学习及搭建环境 PyTorch中文文档
改编自:
(1) DEEP LEARNING WITH PYTORCH: A 60 MINUTE BLITZ
(2) https://www.kesci.com/home/project/5e0038642823a10036ae9ebf/code
1 初识PyTorch
1.1 张量
1.导入pytorch包
import torch2.创建一个未初始化的5x3张量
x = torch.empty(5, 3)
print(x)
tensor([[2.7517e+12, 7.5338e+28, 3.0313e+32],
[6.3828e+28, 1.4603e-19, 1.0899e+27],
[6.8943e+34, 1.1835e+22, 7.0976e+22],
[1.8515e+28, 4.1988e+07, 3.0357e+32],
[2.7224e+20, 7.7782e+31, 4.7429e+30]])3.创建一个随机初始化的5x3张量
x = torch.rand(5, 3)
print(x)
tensor([[0.2218, 0.1979, 0.9491],
[0.2082, 0.6139, 0.1096],
[0.1491, 0.5660, 0.7435],
[0.8009, 0.0788, 0.0223],
[0.4252, 0.2422, 0.8202]])4.创建一个5x3的0张量,类型为long
x = torch.zeros(5, 3, dtype=torch.long)
print(x)
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])5.直接从数组创建张量
x = torch.tensor([5.5, 3])
print(x)
tensor([5.5000, 3.0000])6.创建一个5x3的单位张量,类型为double
x = torch.ones(5, 3, dtype=torch.double)
print(x)
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)7.从已有的张量创建相同维度的新张量,并且重新定义类型为float
x = torch.randn_like(x, dtype=torch.float)
print(x)
tensor([[ 0.0385, 0.2725, 0.7144],
[ 0.1436, 0.0642, 0.4125],
[ 0.2571, 2.0826, -1.0106],
[-0.4239, 0.6424, 1.3656],
[-0.4444, 0.5675, 1.3937]])8.打印一个张量的维度
print(x.size())
torch.Size([5, 3])9.将两个张量相加
y = torch.rand(5, 3)
print(x + y)
# 方法二
# print(torch.add(x, y))
# 方法三
#result = torch.empty(5, 3)
#torch.add(x, y, out=result)
#print(result)
# 方法四
#y.add_(x)
#print(y)
tensor([[ 0.5639, 0.3429, 1.2488],
[ 0.1815, 0.8415, 1.1878],
[ 0.9620, 2.9639, -0.8427],
[ 0.2482, 0.8666, 1.7800],
[-0.1678, 1.1261, 1.5676]])10.打印张量的第一列
print(x[:, 0]) #第一行
print(x[0]) #第一列
tensor([ 0.0385, 0.1436, 0.2571, -0.4239, -0.4444])
tensor([0.0385, 0.2725, 0.7144])11.将一个4x4的张量resize成一个一维张量
x = torch.randn(4, 4)
y = x.view(16)
print(x.size(),y.size())
torch.Size([4, 4]) torch.Size([16])12.将一个4x4的张量,resize成一个2x8的张量
y = x.view(2, 8)
print(x.size(),y.size())
# 方法二
z = x.view(-1, 8) # 确定一个维度,-1的维度会被自动计算
print(x.size(),z.size())
torch.Size([4, 4]) torch.Size([2, 8])
torch.Size([4, 4]) torch.Size([2, 8])13.从张量中取出数字
x = torch.randn(1)
print(x)
print(x.item())
tensor([-1.2852])
-1.2852163314819336
x = torch.randn(2,2)
print(x)
print(x[1,1].item())
tensor([[-0.3501, 1.0590],
[-1.0007, -0.4674]])
-0.467426478862762451.2 Numpy的操作
14.将张量装换成numpy数组
a = torch.ones(5)
print(a)
b = a.numpy()
print(b)
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]15.将张量+1,并观察上题中numpy数组的变化
a.add_(1)
print(a)
print(b)
tensor([2., 2., 2., 2., 2.])
[2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]16.从numpy数组创建张量
import numpy as np
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
print(a)
print(b)
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], dtype=torch.float64)17.将numpy数组+1并观察上题中张量的变化
np.add(a, 1, out=a)
print(a)
print(b)
[2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
tensor([2., 2., 2., 2., 2.], dtype=torch.float64)2 自动微分
2.1 张量的自动微分
18.新建一个张量,并设置requires_grad=True
x = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
print(x)
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)19.对张量进行任意操作(y = x + 2)
y = x + 2
print(y)
print(y.grad_fn) # y就多了一个AddBackward的对象
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]], grad_fn=)
20.再对y进行任意操作
z = y * y * 3
out = z.mean()
print(z) # z多了MulBackward的对象
print(out) # out多了MeanBackward的对象
tensor([[27., 27.],
[27., 27.]], grad_fn=)
tensor(27., grad_fn=) 2.2 梯度
21.对out进行反向传播
out.backward()22.打印梯度d(out)/dx
print(x.grad) #out=0.25*Σ3(x+2)^2
# d(out)/dx = 1/4 * 6x = 1.5x
tensor([[4.5000, 4.5000],
[4.5000, 4.5000]])23.创建一个结果为矢量的计算过程(y=x*2^n)
x = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
print(x)
y = x * 2
while y.data.norm() < 1000:
y = y * 2
print(y)
tensor([-0.1457, 0.0342, 0.1276], requires_grad=True)
tensor([-1193.1697, 279.8315, 1045.1823], grad_fn=) 24.计算v = [0.1, 1.0, 0.0001]处的梯度
v = torch.tensor([0.1, 1.0, 0.0001], dtype=torch.float)
y.backward(v)
print(x.grad)
tensor([8.1920e+02, 8.1920e+03, 8.1920e-01])25.关闭梯度的功能
print(x.requires_grad)
print((x ** 2).requires_grad)
with torch.no_grad():
print((x ** 2).requires_grad)
# 方法二
# print(x.requires_grad)
# y = x.detach()
# print(y.requires_grad)
# print(x.eq(y).all())
True
True
False3 神经网络
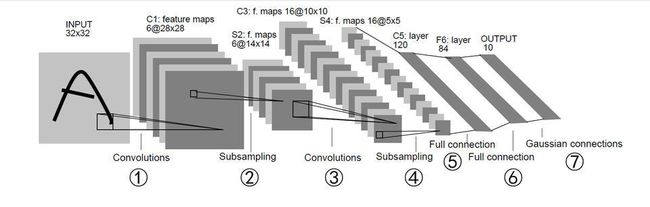
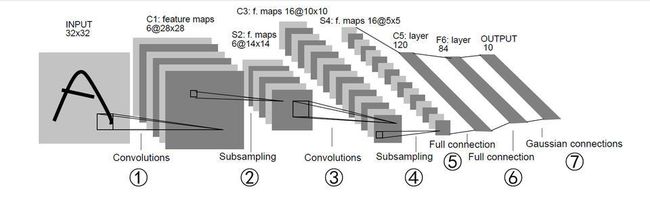
这部分会实现LeNet5,结构如下所示
3.1 定义网络
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 26.定义①的卷积层,输入为32x32的图像,卷积核大小5x5卷积核种类6
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
# 27.定义③的卷积层,输入为前一层6个特征,卷积核大小5x5,卷积核种类16
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
# 28.定义⑤的全链接层,输入为16*5*5,输出为120
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) # 6*6 from image dimension
# 29.定义⑥的全连接层,输入为120,输出为84
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
# 30.定义⑥的全连接层,输入为84,输出为10
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# 31.完成input-S2,先卷积+relu,再2x2下采样
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
# 32.完成S2-S4,先卷积+relu,再2x2下采样
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2) #卷积核方形时,可以只写一个维度
# 33.将特征向量扁平成行向量
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)
# 34.使用fc1+relu
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
# 35.使用fc2+relu
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
# 36.使用fc3
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
print(net)
Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)37.打印网络的参数
params = list(net.parameters())
# print(params)
print(len(params))
1038.打印某一层参数的形状
print(params[0].size())
torch.Size([6, 3, 5, 5])39.随机输入一个向量,查看前向传播输出
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)
print(input.size()) # 1个样本,3个channel,32*32像素
print(input)
out = net(input)
print(out)
torch.Size([1, 3, 32, 32])
tensor([[[[ 0.8842, 0.3144, -0.3450, ..., 1.3449, 0.5608, 0.3913],
[ 1.2463, -0.6526, -0.8858, ..., 1.8576, 0.1731, -1.8414],
[ 0.6541, -1.7835, 1.1173, ..., 0.9162, 0.0133, -1.2699],
...,
[ 0.2942, -1.3088, 1.2589, ..., -0.3612, -0.2821, 0.3796],
[-1.2562, 0.4472, -0.0288, ..., 0.7728, 0.4552, -1.1600],
[-1.3940, -0.1773, 0.2355, ..., 0.0686, 0.1527, 0.7244]],
[[-0.9507, 1.3473, 0.1791, ..., -0.8668, -0.1624, -1.0063],
[ 2.0376, 0.0706, -0.4181, ..., -0.7650, -0.9501, 0.8084],
[-0.2065, -0.5103, -1.1074, ..., 0.8636, -0.8002, -0.5690],
...,
[-0.4108, 0.5790, -1.2921, ..., 0.4494, 0.3363, 0.6388],
[-0.7036, -1.3791, -1.6519, ..., 0.7853, -0.1587, -0.6029],
[-0.7042, -0.2481, -0.5580, ..., -0.9274, -0.8770, 0.5443]],
[[-1.0507, -1.0034, -0.9321, ..., 0.7069, 0.8155, -1.2291],
[-0.4410, -0.9667, 0.3475, ..., -0.7563, 2.0873, -0.9078],
[-0.2733, -0.2245, 1.7173, ..., -0.4200, -1.6980, 0.7572],
...,
[ 0.9761, 0.7852, 0.1797, ..., 0.5471, 1.1544, -1.7472],
[-0.2204, -0.9797, -0.3549, ..., -0.8765, 0.2938, 0.5266],
[-1.7714, 0.1623, -0.7405, ..., -1.4199, 0.1131, 0.4714]]]])
tensor([[ 0.0688, 0.0990, 0.0778, 0.0592, 0.0277, -0.0268, -0.0284, -0.0938,
-0.1056, 0.0487]], grad_fn=) 40.将梯度清零
net.zero_grad()41.随机一个梯度进行反向传播
print(torch.randn(1, 10))
out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10))
tensor([[-0.8285, 0.2922, 0.5672, -0.1644, -2.0075, 0.0337, 2.2223, -0.3571,
1.1908, 0.8642]])3.2 损失函数
42.用自带的MSELoss()定义损失函数
criterion = nn.MSELoss()43.随机一个真值,并用随机的输入计算损失
target = torch.randn(10) # 随机真值
print(target)
target = target.view(1, -1) # 变成行向量
print(target)
output = net(input) # 用随机输入计算输出
print(output)
loss = criterion(output, target) # 计算损失
print(loss)
tensor([-0.4188, 0.1543, 0.8085, -1.9596, 0.5578, -0.2232, 0.4089, 2.4674,
-0.1676, -0.9115])
tensor([[-0.4188, 0.1543, 0.8085, -1.9596, 0.5578, -0.2232, 0.4089, 2.4674,
-0.1676, -0.9115]])
tensor([[ 0.0688, 0.0990, 0.0778, 0.0592, 0.0277, -0.0268, -0.0284, -0.0938,
-0.1056, 0.0487]], grad_fn=)
tensor(1.2847, grad_fn=) 44.将梯度初始化,计算上一步中loss的反向传播
net.zero_grad()
print('conv1.bias.grad before backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
conv1.bias.grad before backward
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])45.计算43中loss的反向传播
loss.backward()
print('conv1.bias.grad after backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
conv1.bias.grad after backward
tensor([ 0.0101, 0.0003, -0.0068, -0.0084, 0.0030, 0.0060])3.3 更新权重
46.定义SGD优化器算法,学习率设置为0.01
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)46.使用优化器更新网络的权重
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = net(input)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
# 更新权重
optimizer.step()